java----反射
《为什么要反射》

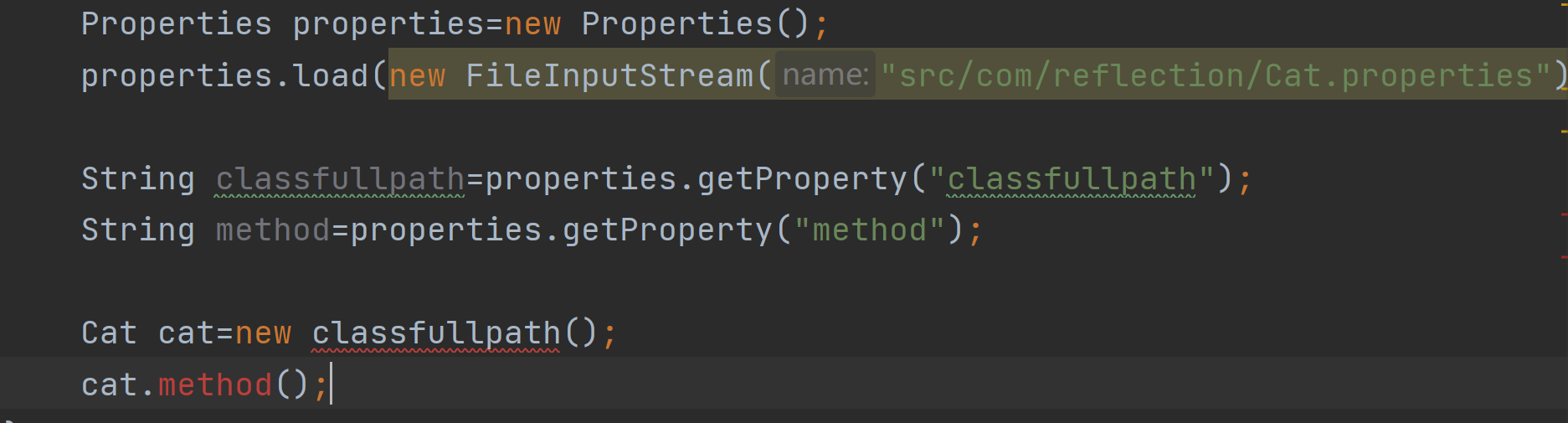
明显是不能的:
虽然我们可以通过properties来获取到String形态下的classfullpath和method是什么,但是如果直接new 和 使用绝对会如下一样报错

《反射机制与原理》

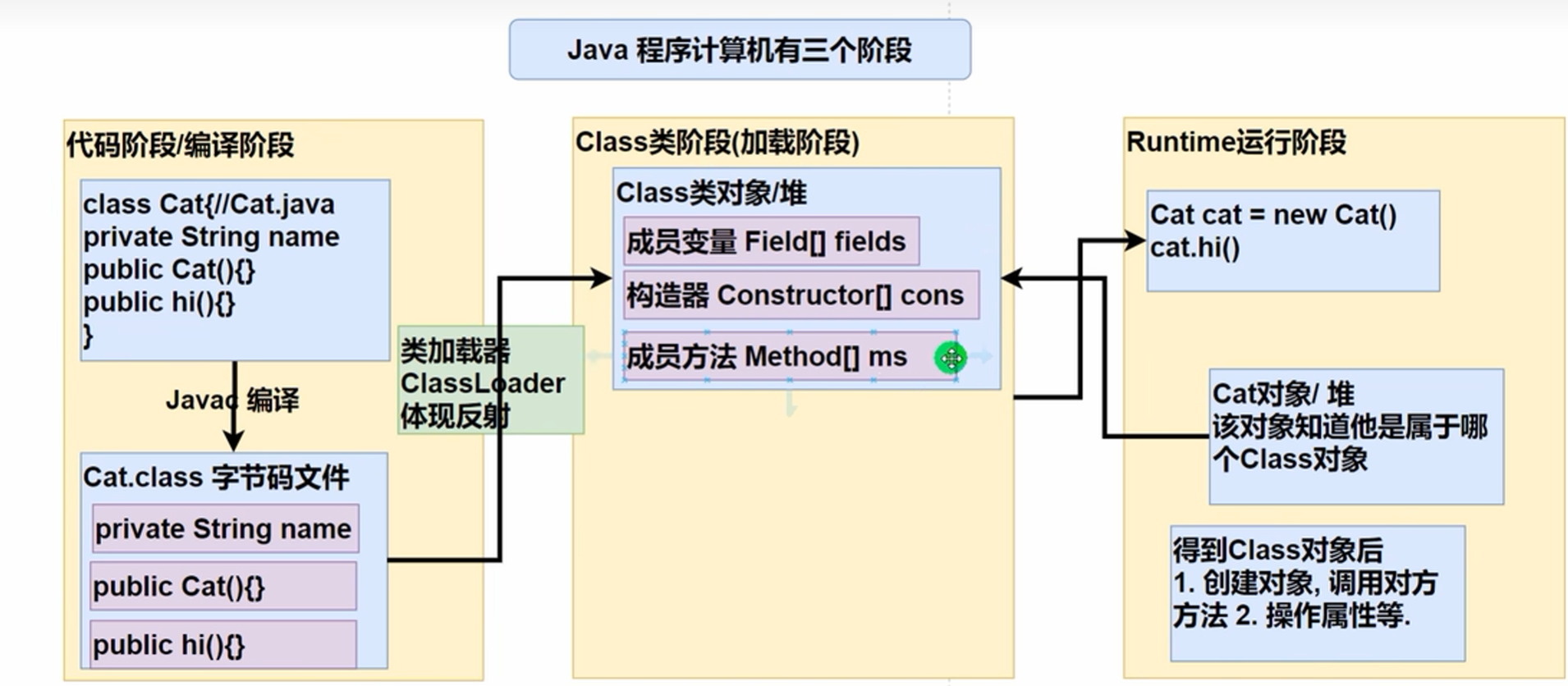
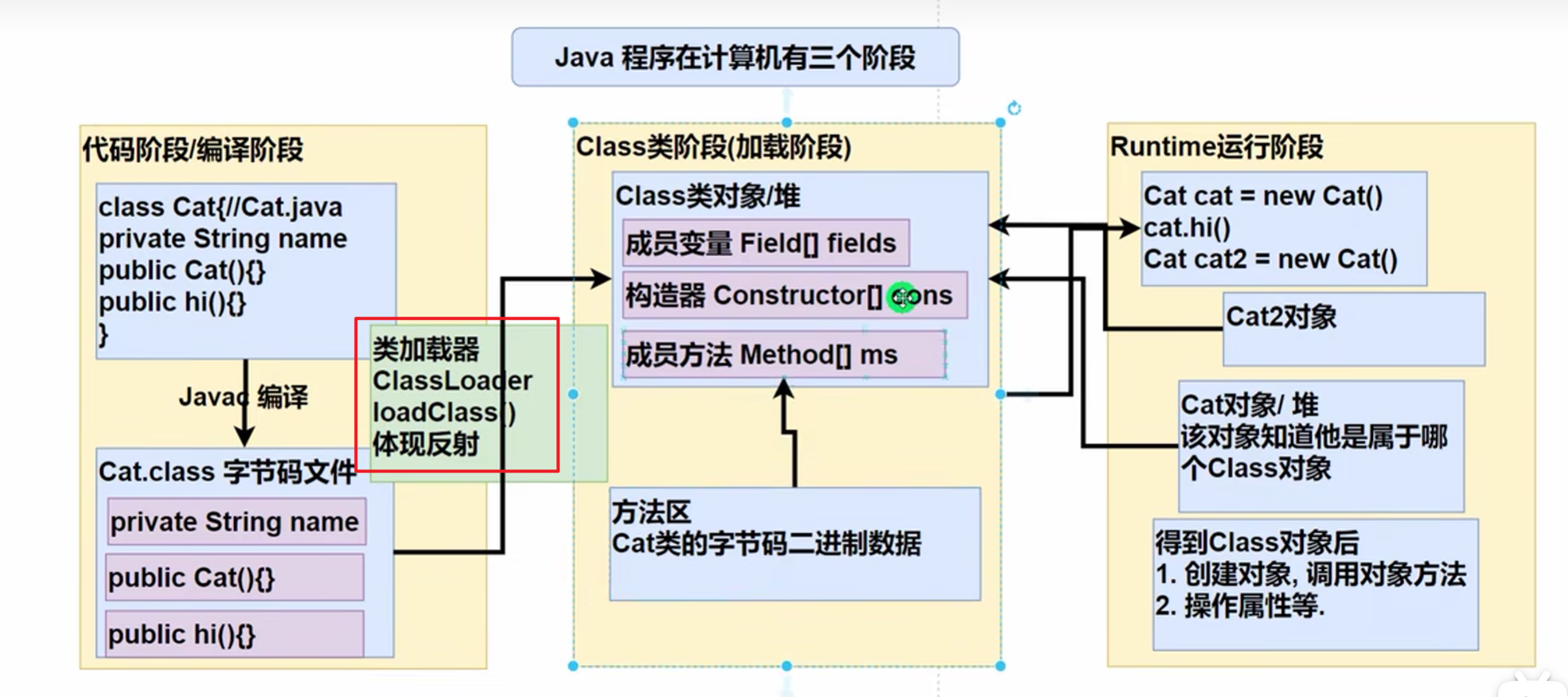
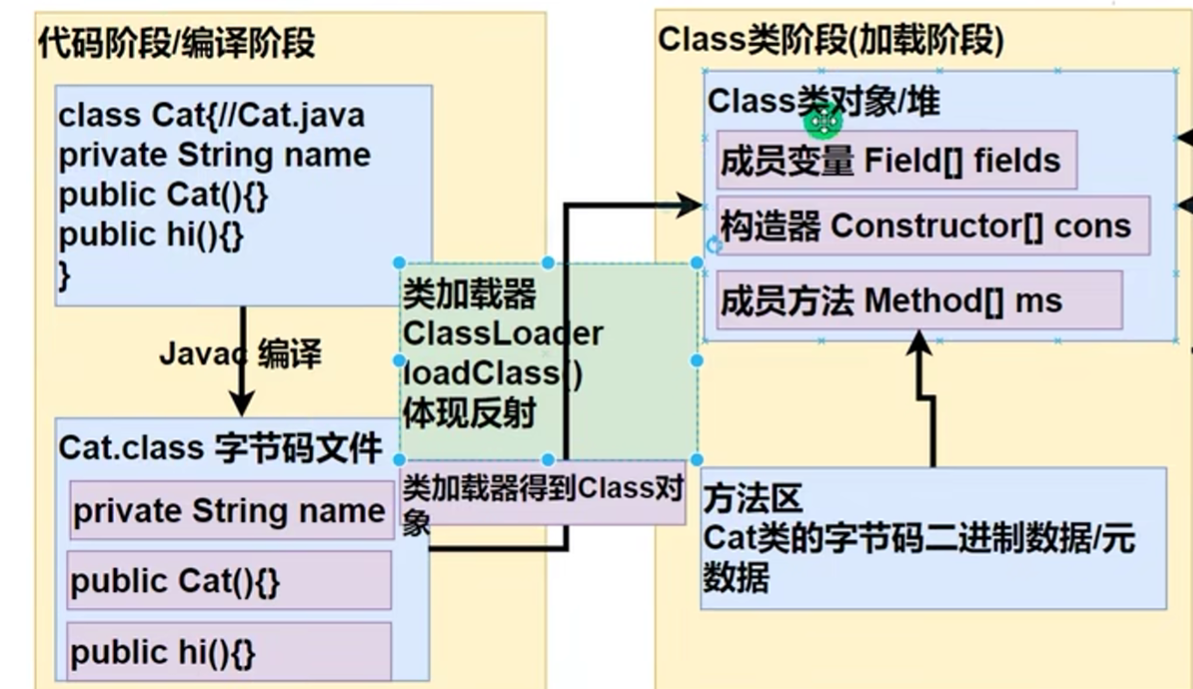
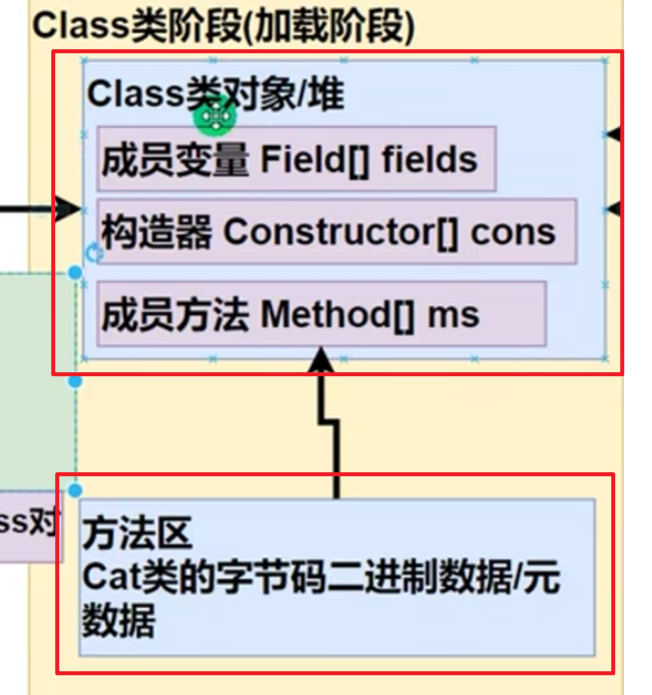
class类型对象在讲static时说过,其中堆中,而且在new(实例化)对象之前就产生了


在javac编译过后通过类加载器ClassLoader生成Class类,完成后可得到Cat对象
在Class类中,原来的
成员变量被封装到了Field数组中,变成了Field类
构造器封装到了Constructor数组中,变成了Constructor类
成员方法封装到了Method数组中,变成了Method类

《反射主要类》

知道这些后可以解决上面的问题了:

注意一下:获取成员变量只有在变量时公开的情况下才能够获取到

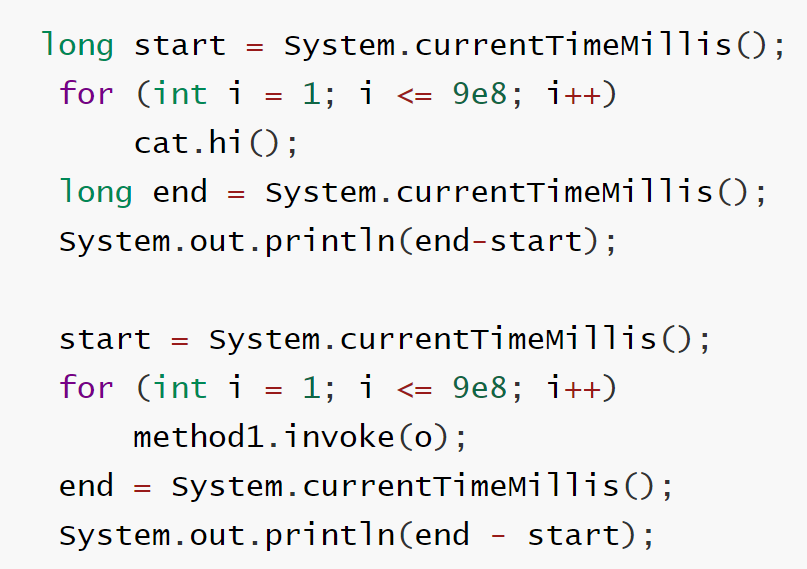
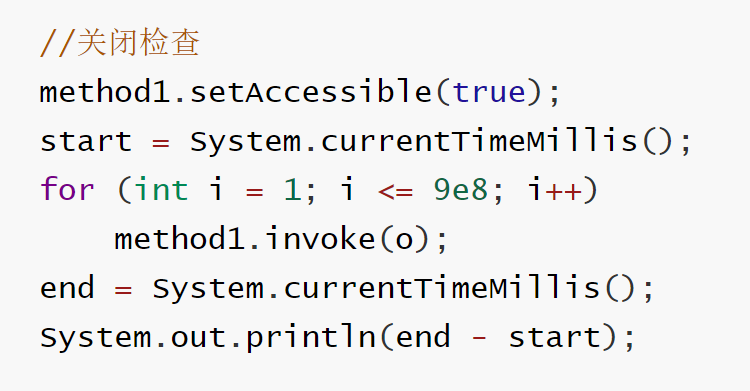
《反射调用优化》




《关于Class类》
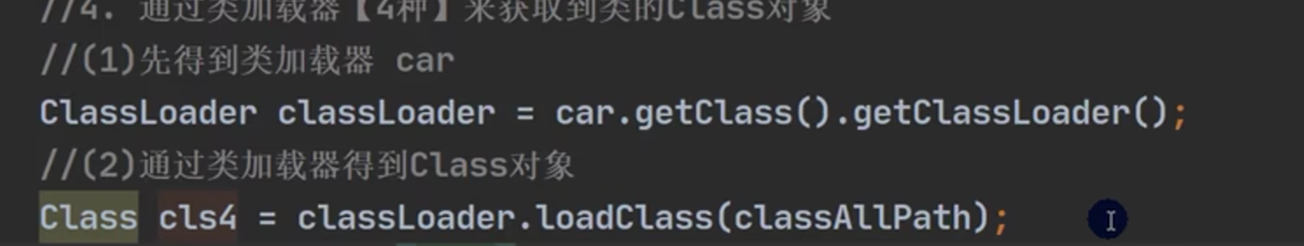
1.

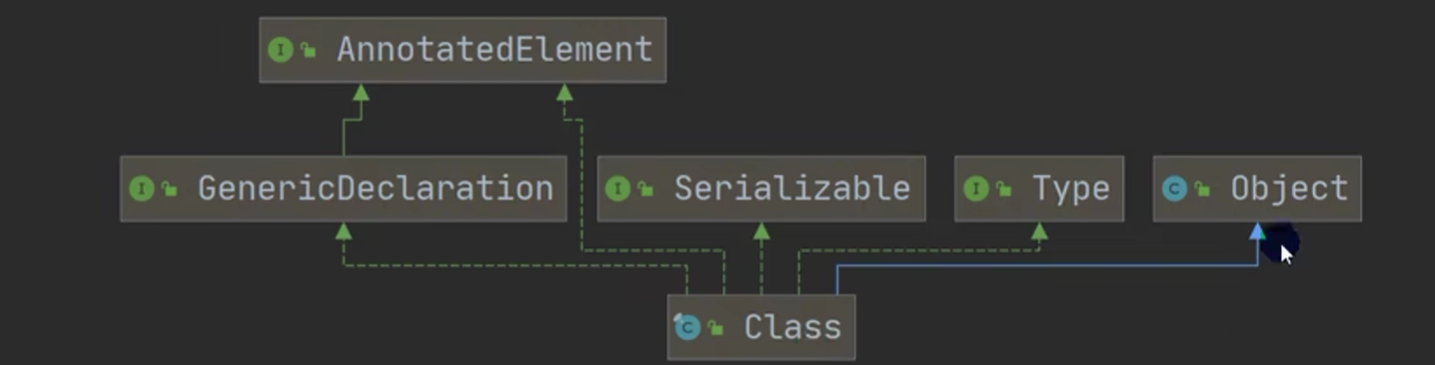
2.

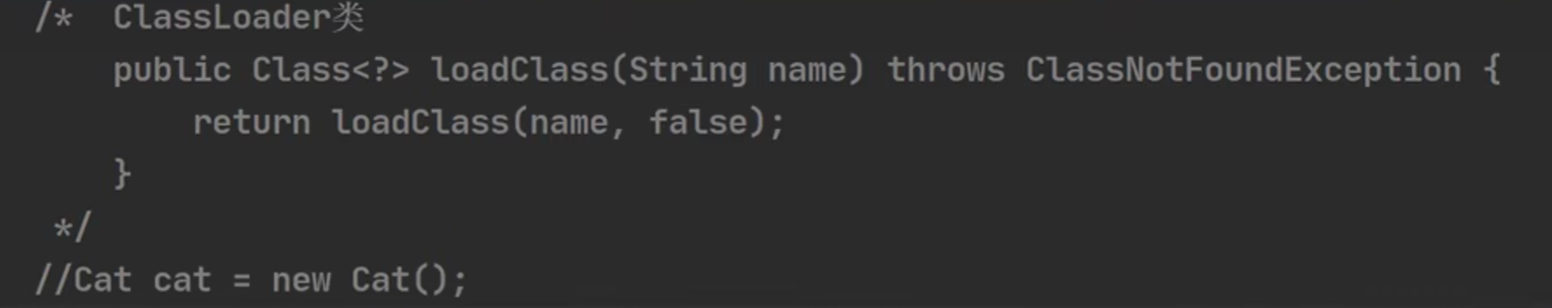
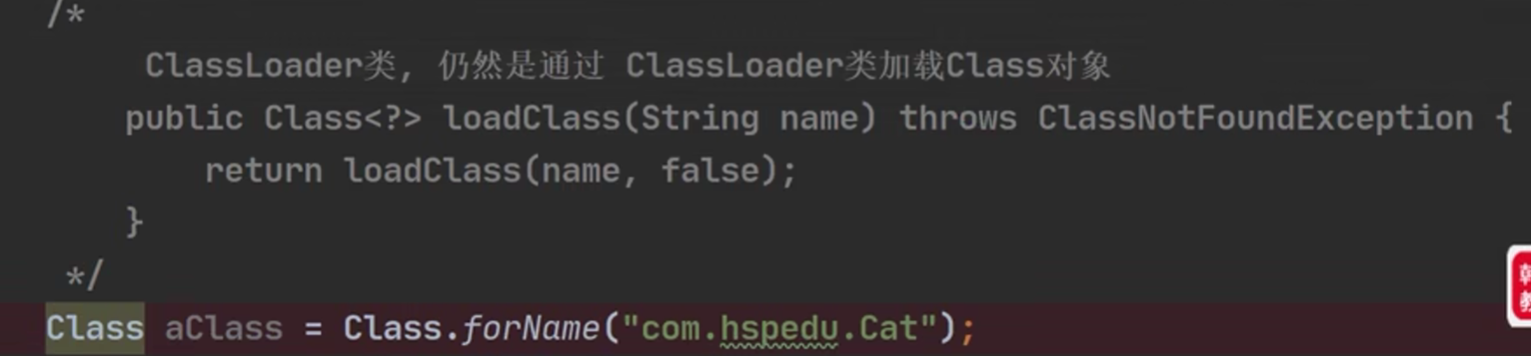
系统通过loadClass方法来创建Class类对象

在当 new 这个对象 或者 用反射 Class cls= Class.forName(classFullPath);
都会引起系统调用loadClass方法创建Class类对象
普通的new:
用反射:
3.

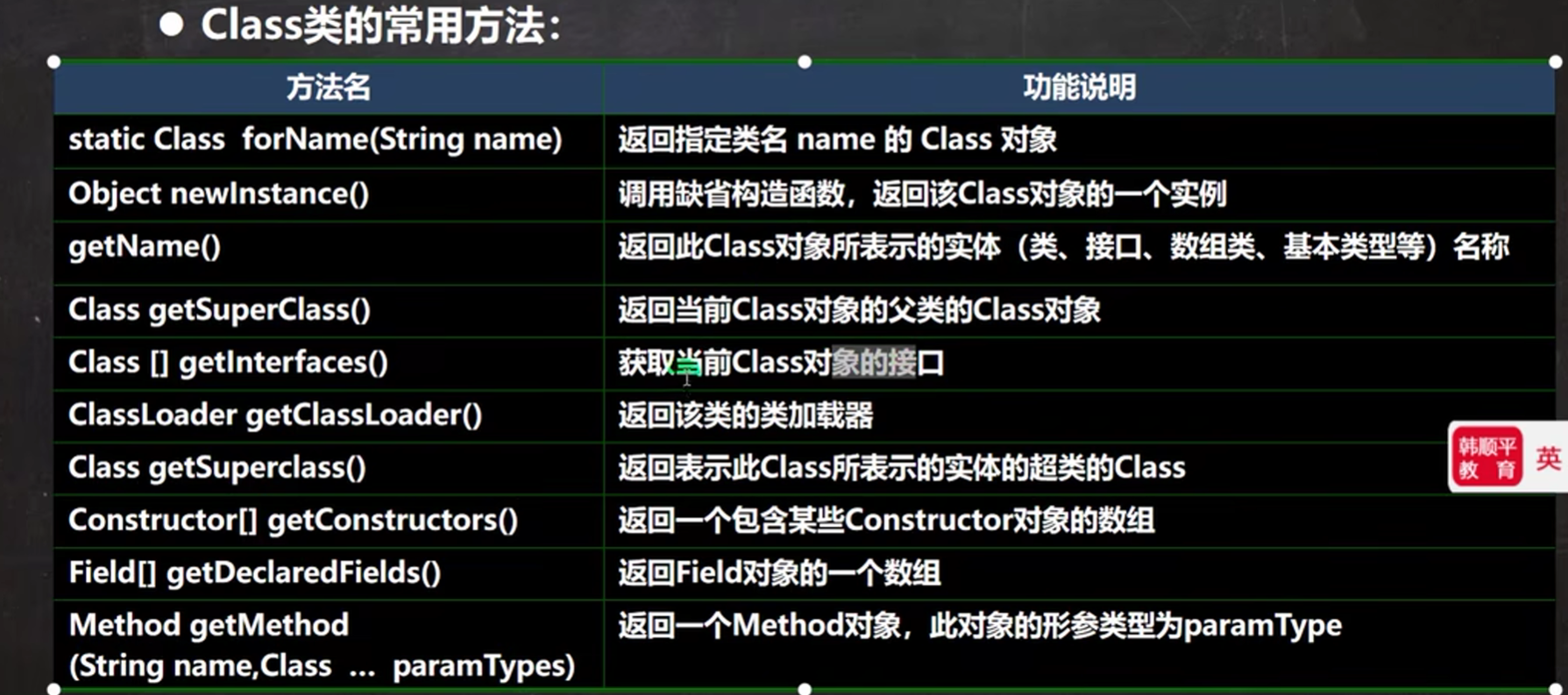

《Class类常用方法》
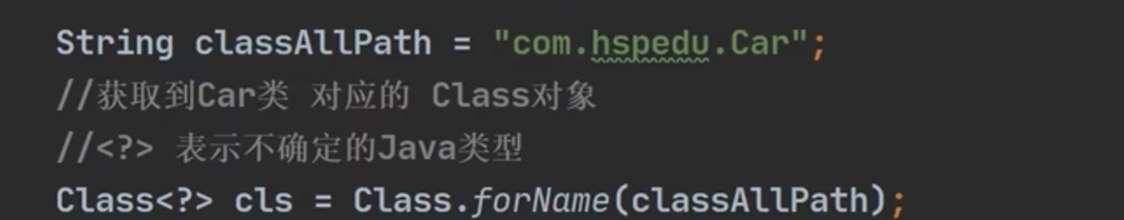

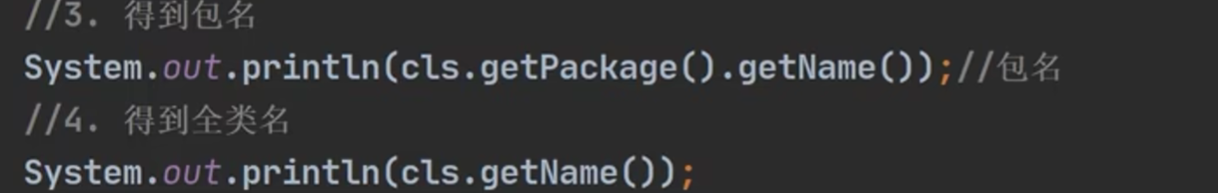
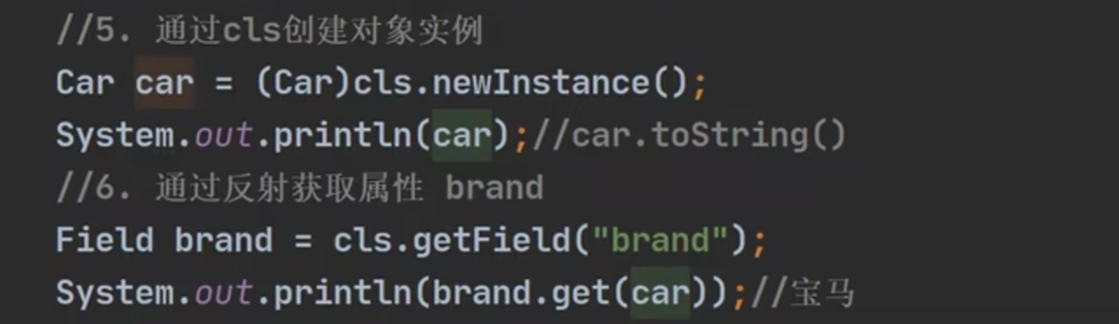
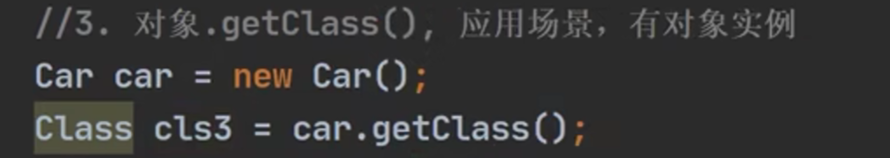
《获取Class类对象的方式》



《有Class类的类型》

《静态加载和动态加载》

对1的解释:
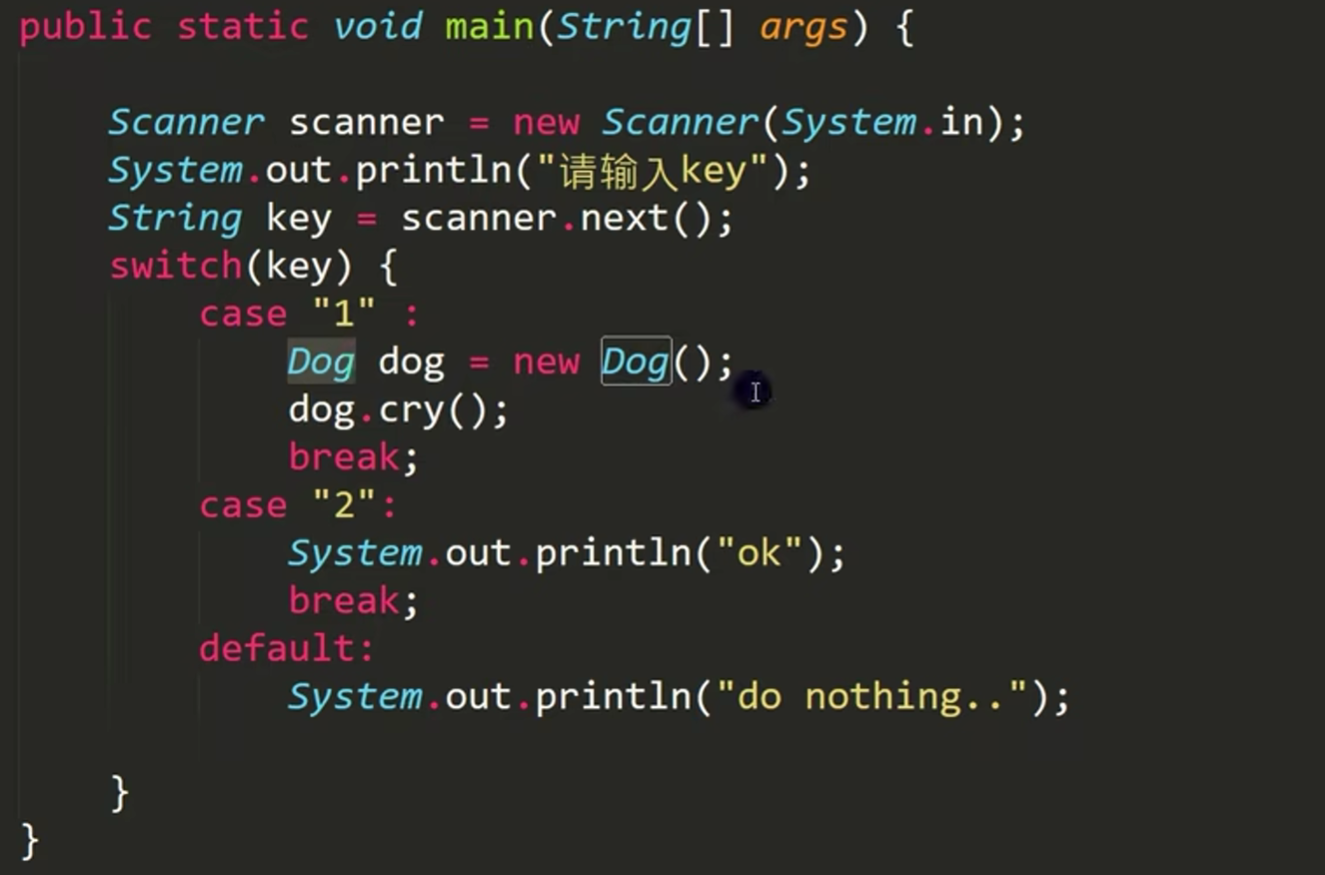
假如我有如上代码,而且我没有写(或引入)Dog包:毫无疑问会报错,编译不会通过,这个用new的为静态加载:

但是如果我有如下代码:
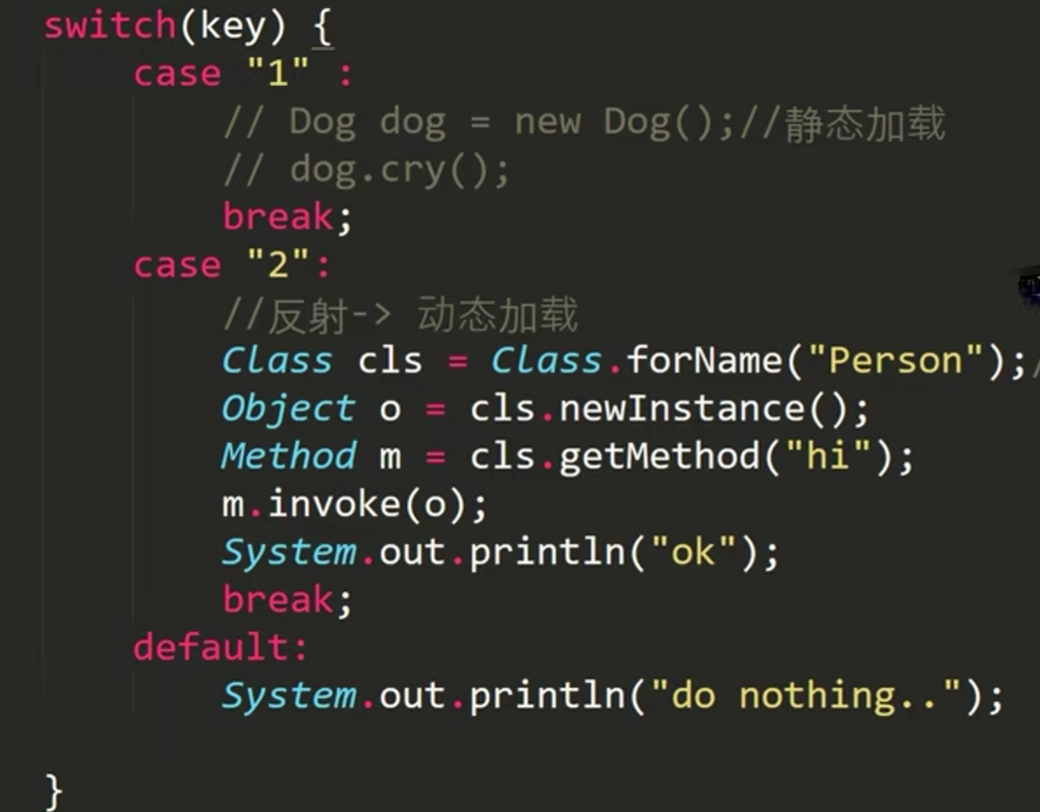
我用反射动态加载,则编译不会报错,只有在我输入2,进入到case "2"运行了加载类的语句时才会报错
1,2,3都是静态加载,4是动态加载

《类加载的过程》
也就是如上的过程:
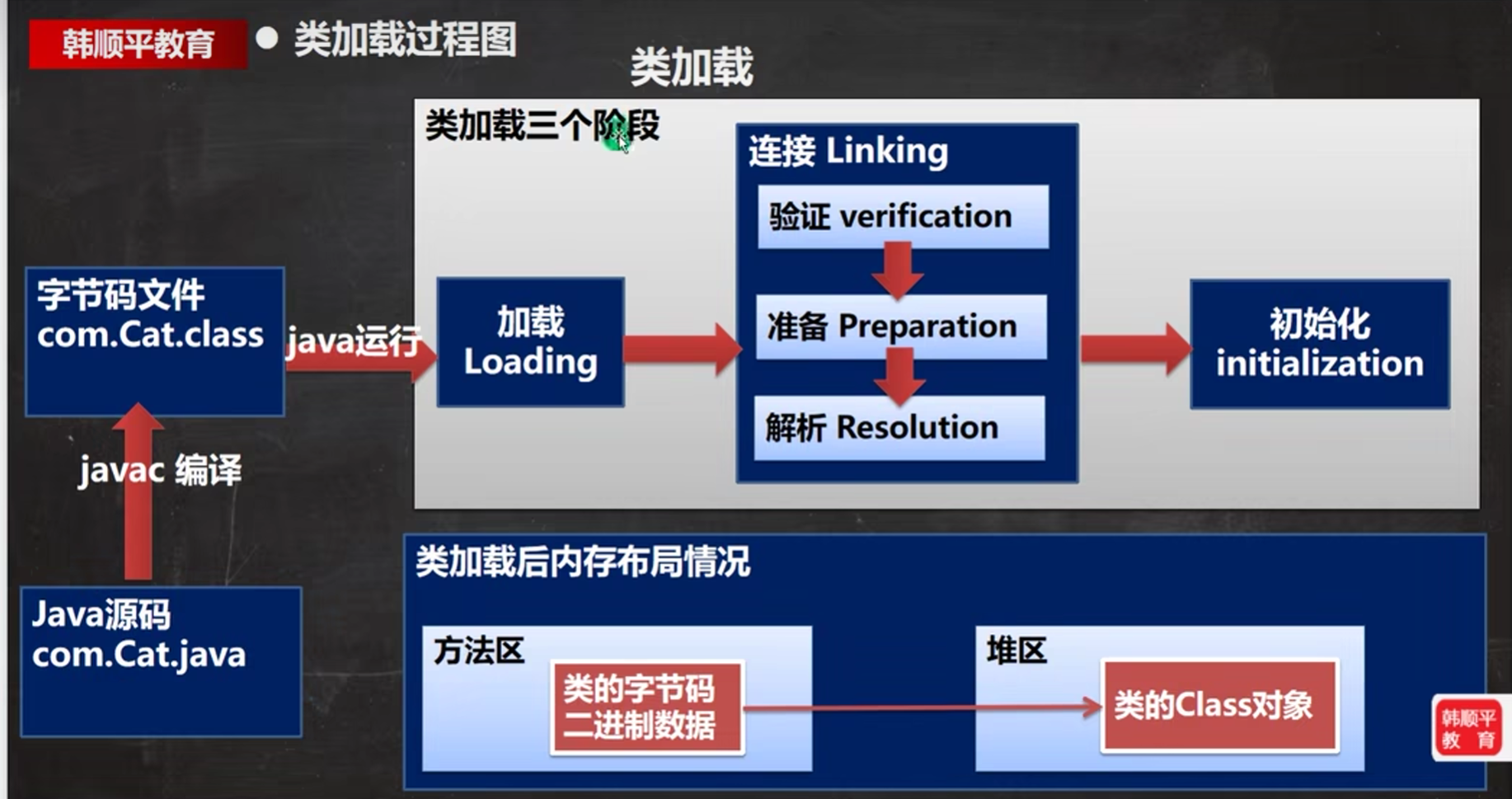
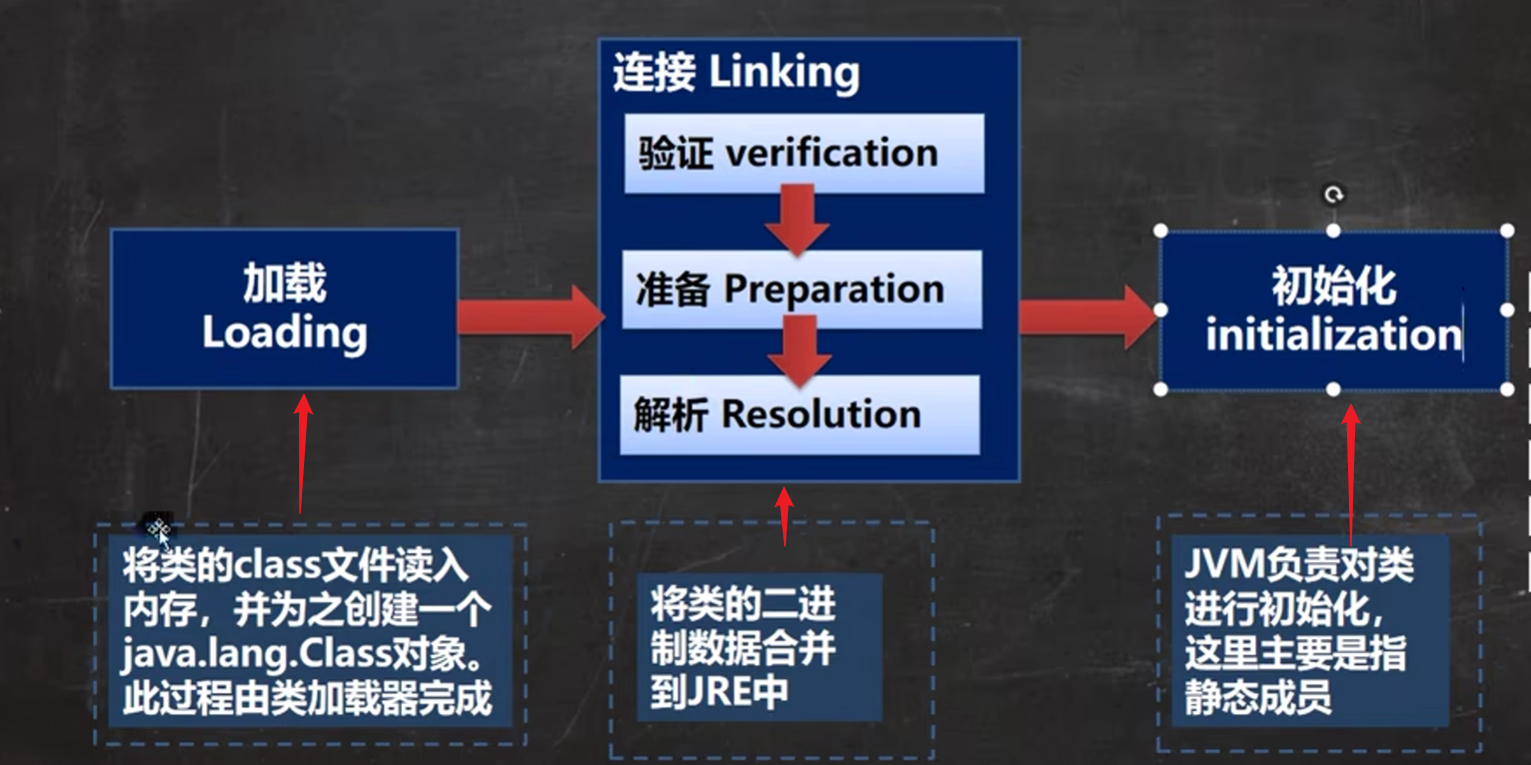
加载阶段:

也就是这个阶段了:
验证阶段:

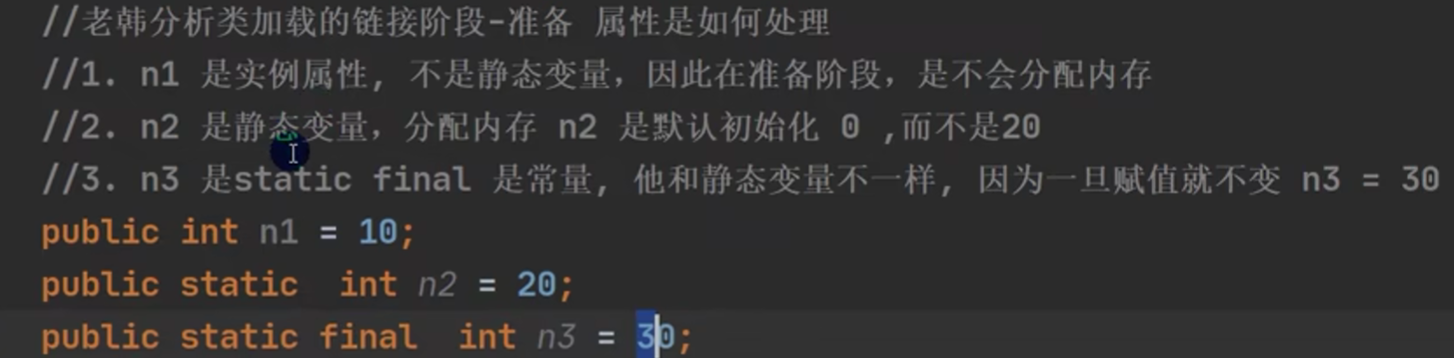
准备阶段:

解析阶段:

即将两个类之间虚拟的关系,在有了实际的内存地址后转化为了真正的实际关系
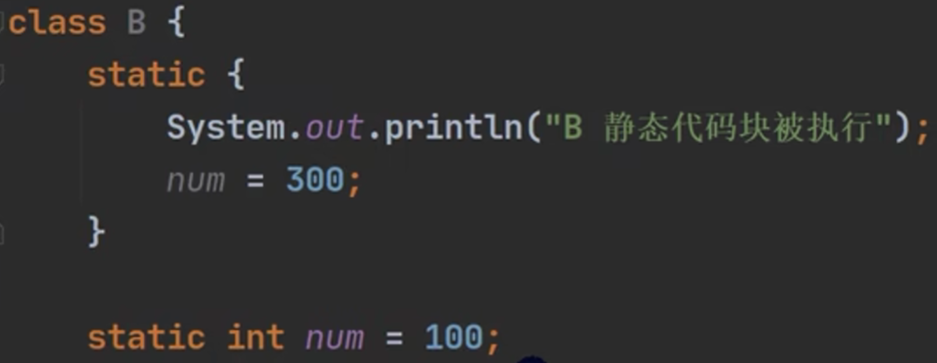
初始化阶段:

如:
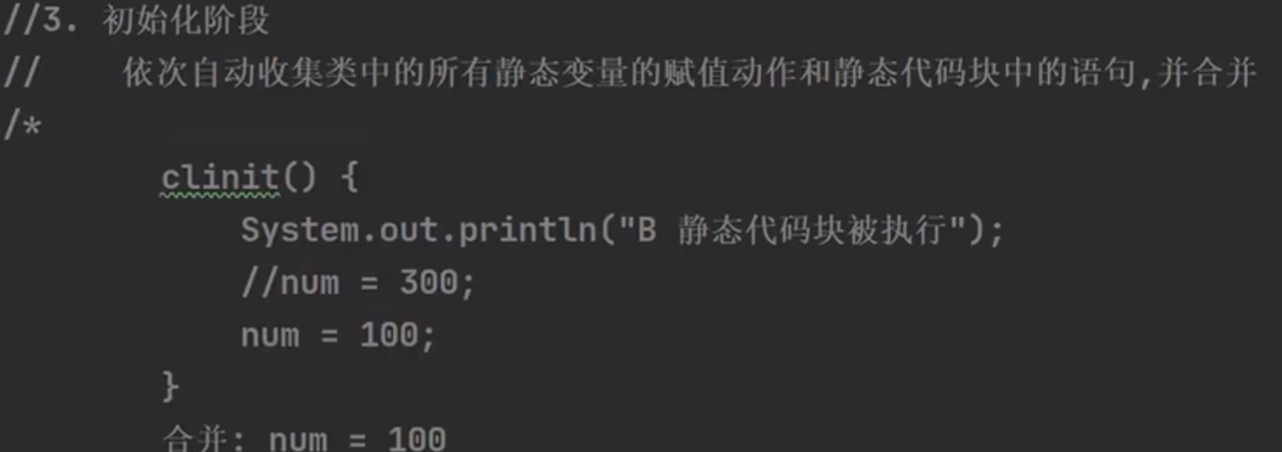
执行的顺序是:

正因为有上面的保证才有:

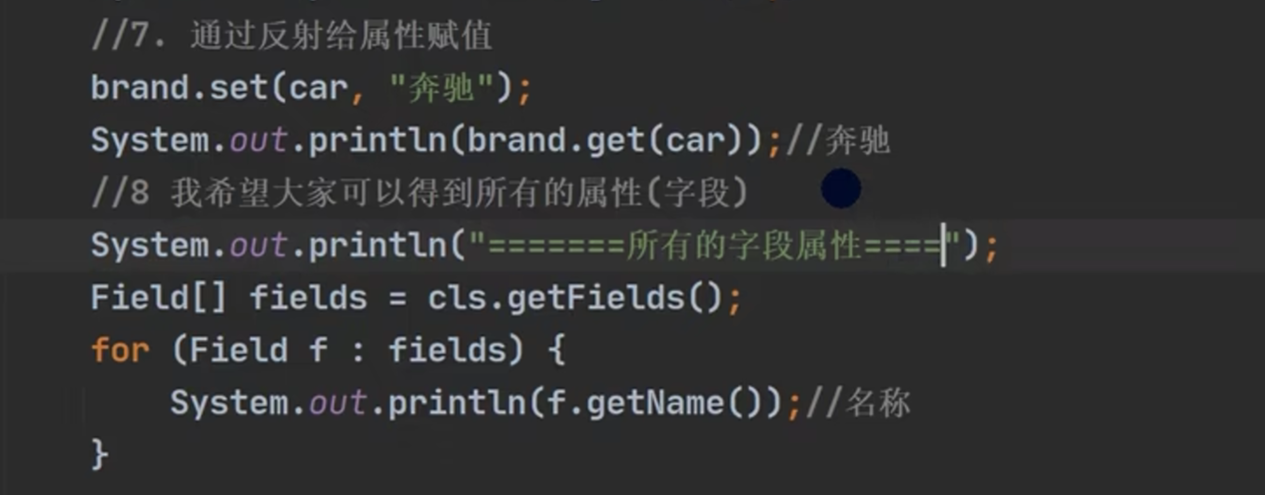
《调用API获取类结构信息》
《Class类》

注意像getFields,getDeclaredFields是以数组形式的,而且类为Field
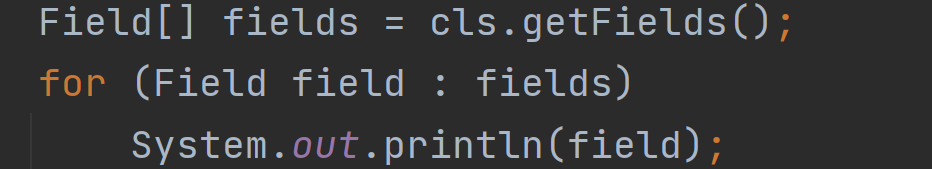
返回的样子
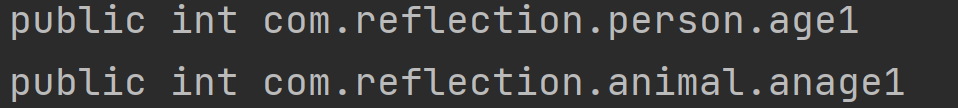
《Field类》
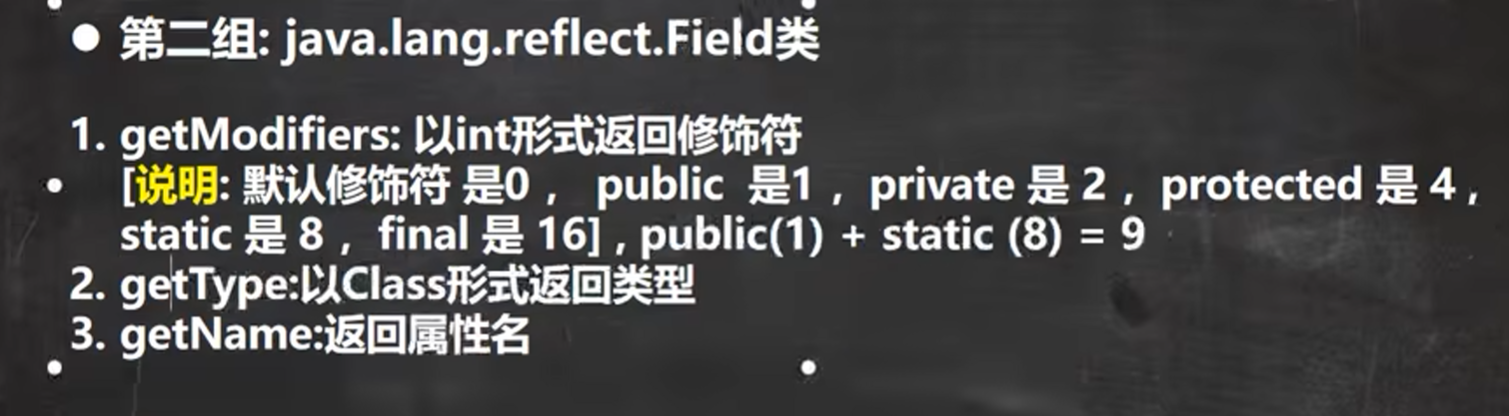
getType的返回值:
《Method类》

对于第四点的解释:
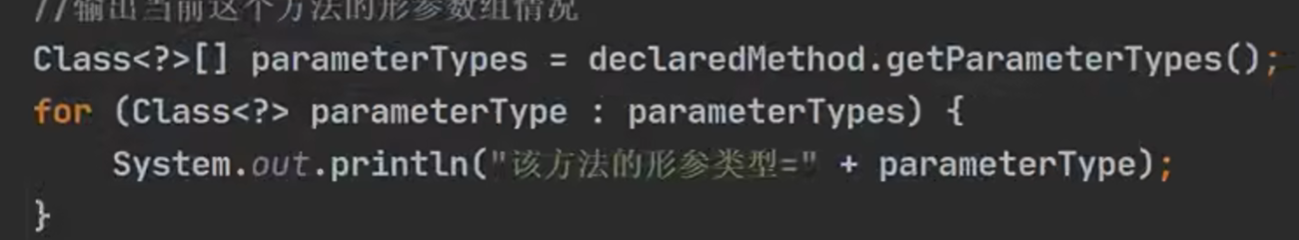
输出(如果无参,则不会有任何输出):
《Constructor类》

《通过反射创建对象实例》


这里说明一点:因为在指定了访问修饰符与参数的情况下,不可能出现相同构造器,因此上面的方法可以精确地拿出我们想要的构造器
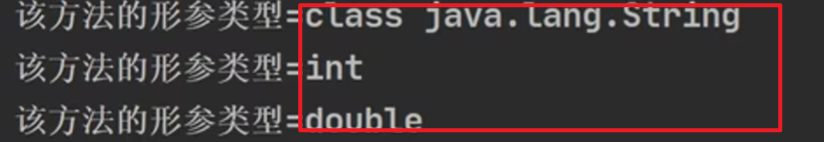
《通过反射访问类中的成员属性》

这个与上面介绍的cls.getFields,cls.getDeclare不同的是,其是可以通过属性名精确拿到成员变量
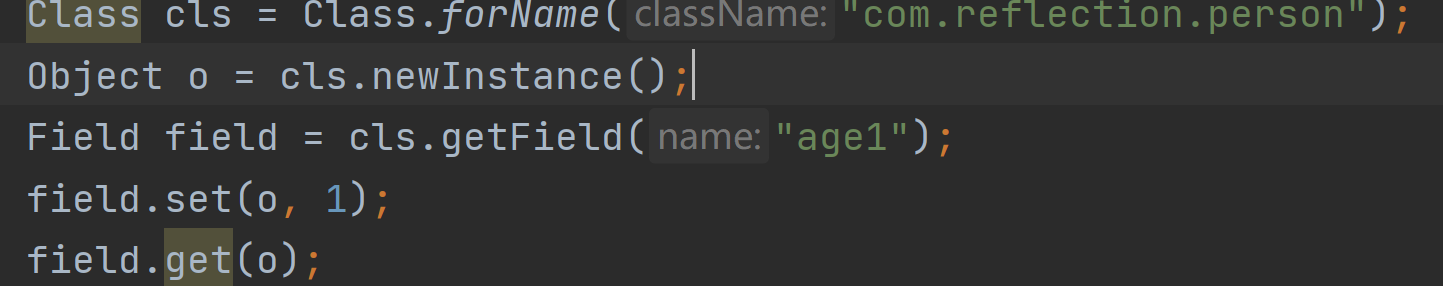
对于第四点的解释:static变量其与类有关,与对象无关
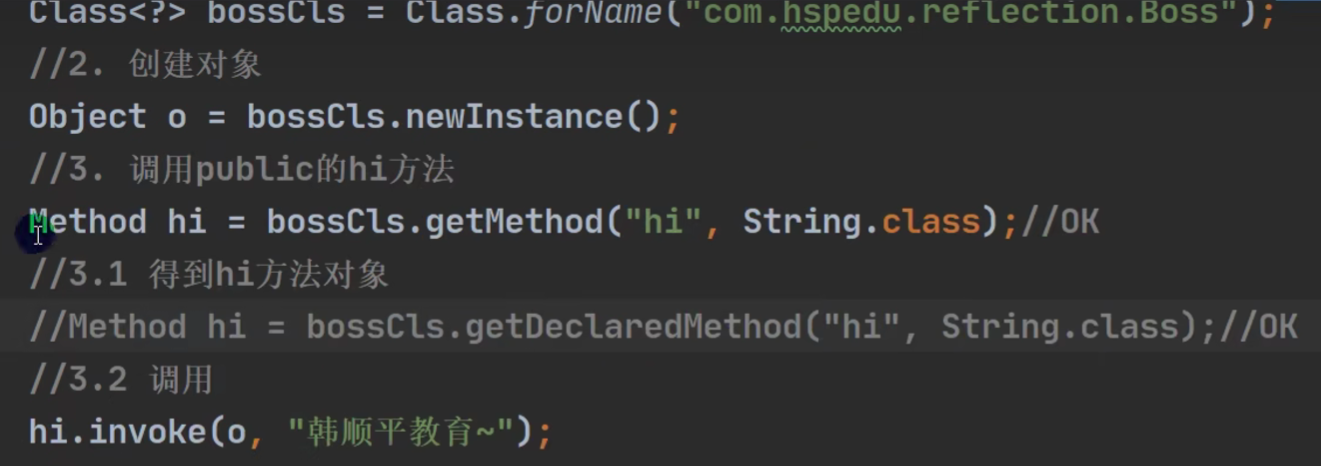
《通过反射调用类的成员方法》

《日后学习对反射的理解》
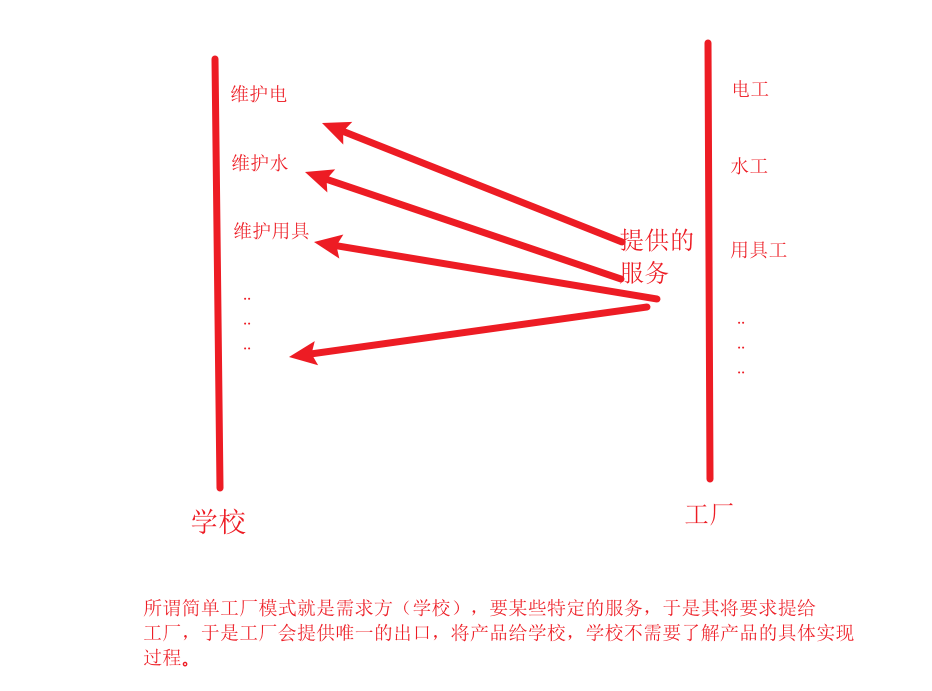
《简单工厂设计模式》
1 package com.cilinmengye.Reflect;
2
3 import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
4 import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
5
6 interface Operator {
7 double compute();
8 }
9
10 class Add implements Operator {
11 private double a, b;
12
13 public Add(double a, double b) {
14 this.a = a;
15 this.b = b;
16 }
17
18 public double compute() {
19 return a + b;
20 }
21 }
22
23 class Dec implements Operator {
24 private double a, b;
25
26 public Dec(double a, double b) {
27 this.a = a;
28 this.b = b;
29 }
30
31 public double compute() {
32 return a - b;
33 }
34 }
35
36 class Mul implements Operator {
37 private double a, b;
38
39 public Mul(double a, double b) {
40 this.a = a;
41 this.b = b;
42 }
43
44 public double compute() {
45 return a * b;
46 }
47 }
48
49 class Div implements Operator {
50 private double a, b;
51
52 public Div(double a, double b) {
53 this.a = a;
54 this.b = b;
55 }
56
57 public double compute() {
58 if (b == 0) {
59 System.out.println("除0错误");
60 return 0;
61 } else return a / b;
62 }
63 }
64
65 class OperatorFactory {
66 public static Operator creatOperator(String opName, double a, double b) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException {
67 Class c = Class.forName(opName);
68 Constructor con = c.getConstructor(double.class, double.class);
69 return (Operator) con.newInstance(a, b);
70 }
71 }
72
73
74 public class SimplyFactory {
75 public static void main(String []args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
76 Operator op=null;
//注意这里是全类名
77 op=OperatorFactory.creatOperator("com.cilinmengye.Reflect.Add",1,2);
//注意这里op.compute能够知道调用Add中的compute是因为java中的动态绑定机制
78 System.out.println(op.compute());
79 }
80 }
《用反射将类还原出来》



1 package com.cilinmengye.Reflect;
2
3 import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
4 import java.lang.reflect.Field;
5 import java.lang.reflect.Method;
6 import java.lang.reflect.Modifier;
7
8 class Test {
9 private static final int c = 10;
10
11 public static void a() {
12 ;
13 }
14
15 public static void a1(int x, int y) {
16 ;
17 }
18
19 private int b1(double x, int y) {
20 return 0;
21 }
22
23 protected Test(int x, int y) {
24 ;
25 }
26
27 Test(int x) {
28 ;
29 }
30
31 class Text {
32 private int bb = 0;
33
34 private int Add() {
35 return 0;
36 }
37 }
38 }
39
40 public class ViewClass {
41 public static String getPackageStr(Class cls) {
42 Package p = cls.getPackage();
43 if (p == null) {
44 return "";
45 }
46 return "package " + p.getName();
47 }
48
49 public static String getModifyStr(int modifyInt) {
50 if (modifyInt == 0) return "";
51 return Modifier.toString(modifyInt);
52 }
53
54 public static String getClassStr(Class cls) {
55 int modifyInt = cls.getModifiers();
56 String type = Modifier.isInterface(modifyInt) ? "interface" : "class";
57 return getModifyStr(modifyInt) + " " + type + " " + cls.getSimpleName();
58 }
59
60 public static String getFieldStr(Class cls) {
61 Field[] fields = cls.getDeclaredFields();
62 StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder("\t");
63 for (Field f : fields) {
64 str.append(getModifyStr(f.getModifiers())).
65 append(" ").append(f.getType().getName()).append(" ").append(f.getName()).append(";\n");
66 }
67 return str.toString();
68 }
69
70 public static String getParamStr(Class[] classes) {
71 StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder();
72 for (Class cls : classes) {
73 str.append(cls.getSimpleName()).append(",");
74 }
75 String ans = str.toString();
76 if (ans.length() == 0) return "";
77 else return ans.substring(0, ans.length() - 1);
78 }
79
80 public static String getConstructorStr(Class cls) {
81 Constructor[] constructors = cls.getDeclaredConstructors();
82 StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder("\t");
83 for (Constructor c : constructors) {
84 str.append(getModifyStr(c.getModifiers())).append(" ").append(cls.getSimpleName()).
85 append(" (").append(getParamStr(c.getParameterTypes())).append(");").append("\n").append("\t");
86 }
87 return str.toString();
88 }
89
90 public static String getMethodStr(Class cls) {
91 Method[] methods = cls.getDeclaredMethods();
92 StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder("\t");
93 for (Method method : methods) {
94 str.append(getModifyStr(method.getModifiers())).append(" ").
95 append(method.getReturnType()).append(" ").append(method.getName()).append("(").
96 append(getParamStr(method.getParameterTypes())).append(");\n\t");
97 }
98 return str.toString();
99 }
100
101 public static String view(String className) throws ClassNotFoundException {
102 Class cls = Class.forName(className);
103 StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder(getPackageStr(cls) + "\n"
104 + getClassStr(cls) + "{\n"
105 + getFieldStr(cls) + "\n"
106 + getConstructorStr(cls) + "\n"
107 + getMethodStr(cls) + "\n");
108 Class[] classes = cls.getDeclaredClasses();
109 for (Class c : classes) {
110 str.append(view(c.getName()));
111 }
112 str.append("}\n");
113 return str.toString();
114 }
115 }
116
117 class App {
118 public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
119 String str = ViewClass.view("com.cilinmengye.Reflect.Test");
120 System.out.println(str);
121 }
122 }
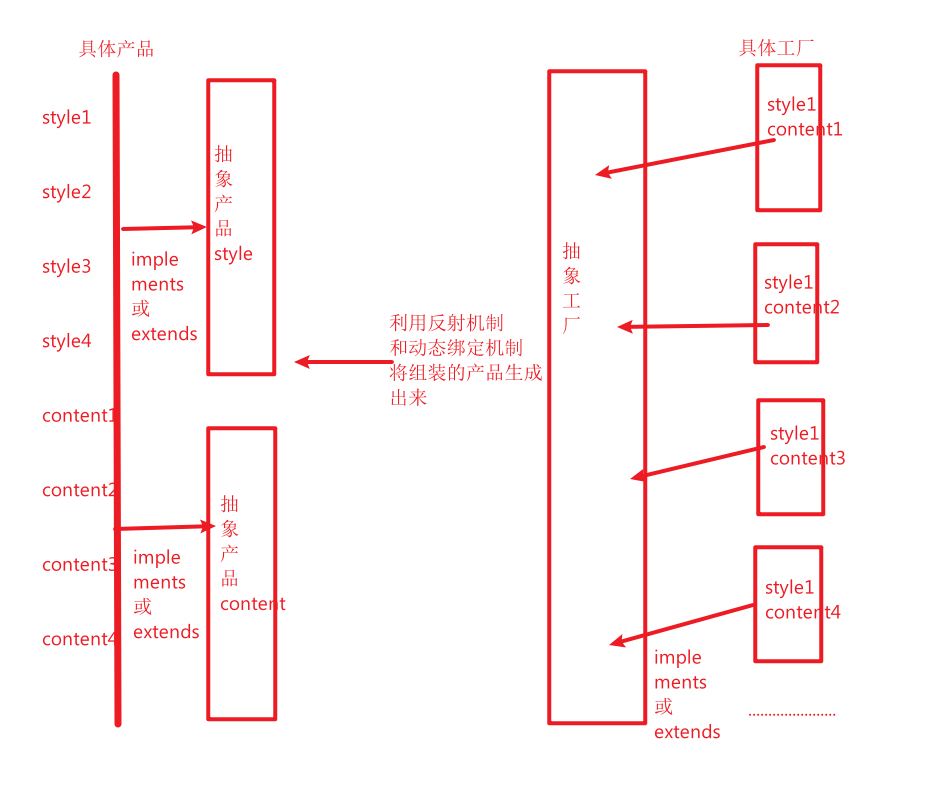
《抽象工厂模式》
抽象工厂模式只是在简单工厂模式上需要产品的组装而已,具体框架思路如下:
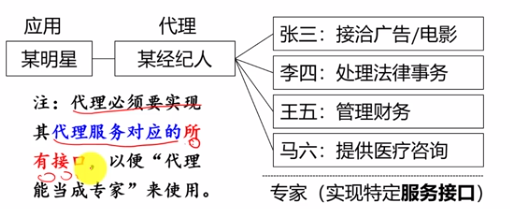
《代理模式》

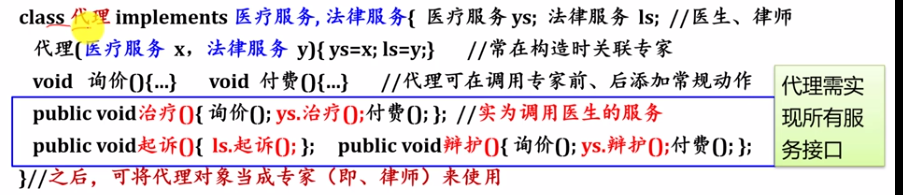
《静态代理》
专家:

代理:
代理实现了专家的接口,即要实现其方法,这样可以在代理类中调用与专家同名的方法,所以可以将代理当专家来用,
同时靠这个能够知道在代理类中的那个方法中调用哪一个专家的真正方法
《动态代理》
好博客连接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_46494427/article/details/124173617
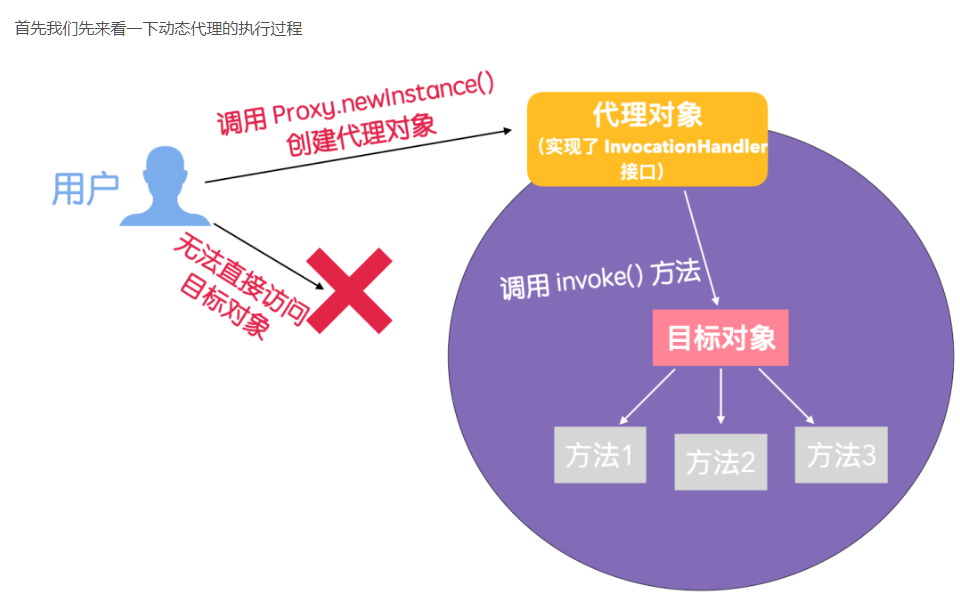
动态代理与静态代理相比,其可以实现一个统一的框架处理模式,面对大量需要代理的类其可以统一处理
1. 
这个dl是我们上面实现的框架:代理
2.
 这个S是专家
这个S是专家
1 package com.cilinmengye.Reflect;
2
3 import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
4 import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
5 import java.lang.reflect.Method;
6 import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
7
8 interface Doctor {
9 void care();
10 }
11
12 interface Teacher {
13 void talk();
14
15 void think();
16 }
17
18 class Doctor1 implements Doctor {
19 public void care() {
20 System.out.println("治疗!");
21 }
22 }
23
24 class Teacher1 implements Teacher {
25
26 @Override
27 public void talk() {
28 System.out.println("教授!");
29 }
30
31 @Override
32 public void think() {
33 System.out.println("思考!");
34 }
35 }
36
37 class Agent implements InvocationHandler {
38 private Object expert;
39
40 public void setExpert(Object expert) {
41 this.expert = expert;
42 }
43
44 private void do1() {
45 System.out.println("小动作开始!");
46 }
47
48 private void do2() {
49 System.out.println("小动作结束!");
50 }
51
52 public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
53 do1();
54 Object result = method.invoke(expert, args);
55 do2();
56 return result;
57 }
58 }
59
60 public class Oagent {
61 public static void main(String[] args) {
62 Agent a1 = new Agent(), a2 = new Agent();
63 Doctor1 doctor1 = new Doctor1();
64 Teacher1 teacher1 = new Teacher1();
65 a1.setExpert(doctor1);
66 a2.setExpert(teacher1);
67 Doctor e1 = (Doctor) Proxy.newProxyInstance(Doctor.class.getClassLoader()
68 , doctor1.getClass().getInterfaces(), a1);
69 e1.care();
70 Teacher e2 = (Teacher) Proxy.newProxyInstance(Teacher.class.getClassLoader()
71 , teacher1.getClass().getInterfaces(), a2);
72 e2.talk();
73 }
74 }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号