python的文件操作学习
创建一个包含文件各行内容的列表:
首先是要用 with open ("filename", ''r'') as file: 来打开;
然后我们可以定义一个列表,如lines=[],以lines=filename.readlines(),来读取:

注意以上几个点:
os是系统内置函数:os.path.exists(filename)是用来验证是否有filename这个文件夹的;
求数组的长度,大小是用 len (array);
eval()函数方法:
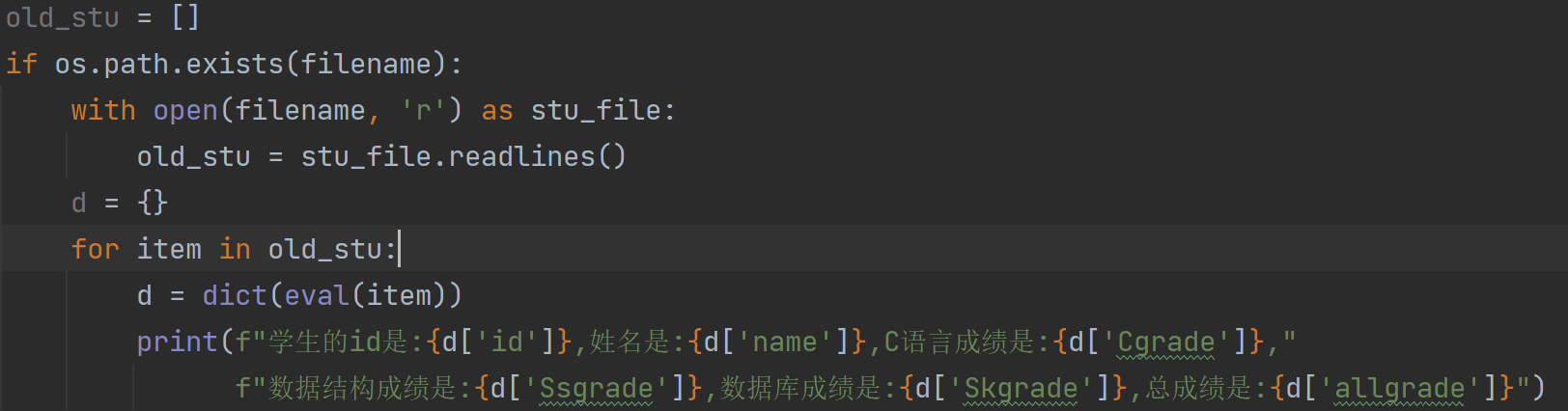
dict()是强制转化为字典的方法,eval的方法是:
1.eval函数与list,str,dict,tuple之间的转化
# 字符串转换成列表
a = "[[1,2], [3,4], [5,6], [7,8]]"
print(type(a))
b = eval(a)
print(b,type(b))
<class 'str'>
[[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6], [7, 8]] <class 'list'>
>>>
# 字符串转换成字典
a = "{1: 4, 2: 5}"
print(type(a))
b = eval(a)
print(type(b))
print(b)
<class 'str'>
<class 'dict'>
{1: 4, 2: 5}
>>>
# 字符串转换成元组
a = "([1,2], [3,4], [5,6])"
print(type(a))
b=eval(a)
print(type(b))
print(b)
<class 'str'>
<class 'tuple'>
([1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6])
>>>
这里字符串的转化应该可以简单的理解为eval()函数解析掉""(双引号),然后读取里面的数据类型(这是小道办法,比较好记)

我这里文件中的数据都是这样的,通过readlines()读过来的都是字符串;其实这里不要dict()都可以。
写入
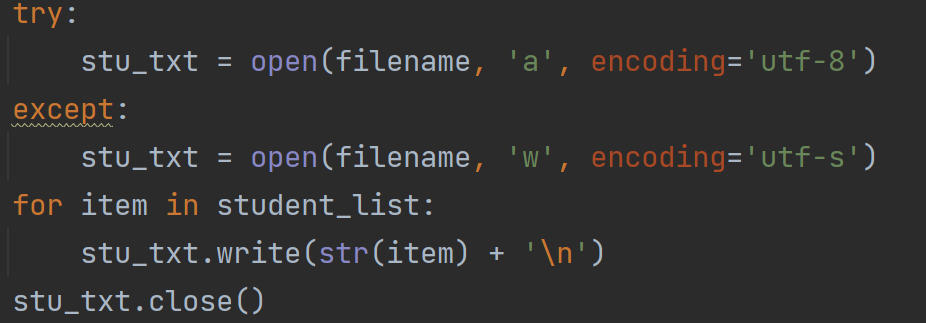
当我不想刷新掉文件里面的原来内容时,且只想加入内容可以用 open (filename, 'a');
当数据想一行一行往文件中写时,可以+"\n",正如我上面所写


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号