Java基础知识_LinkedHashMap
一、LinkedHashMap剖析
LinkedHashMap数据结构图
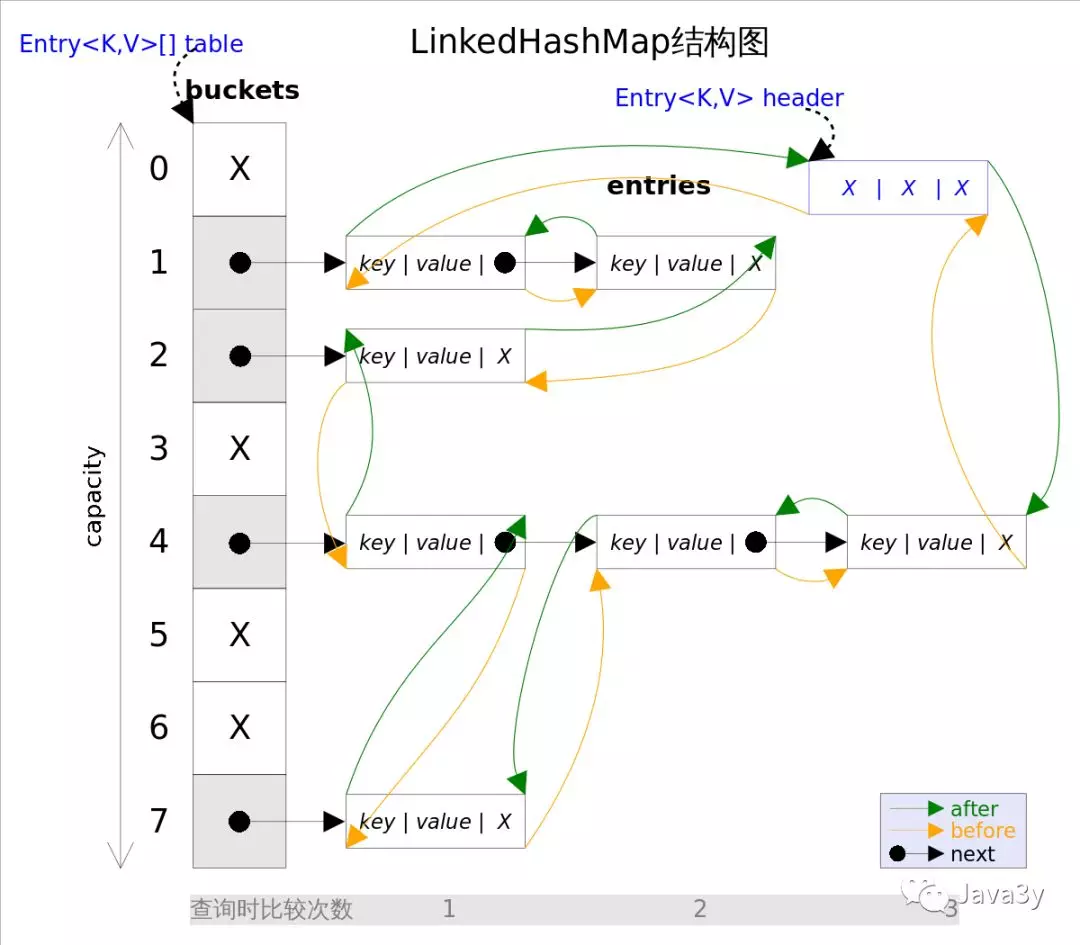
归纳总结出LinkedHashMap几点
底层是散列表和双向链表
允许为null,不同步
插入顺序是有序的(底层链表致使有序)
装载因子和初始容量对LinkedHashMap影响很大
同时也给我带了几个疑问
access-ordered和insertion-ordered具体的使用和意思
为什么说初始容量对遍历没有影响
1.1 LinkedHashMap的域
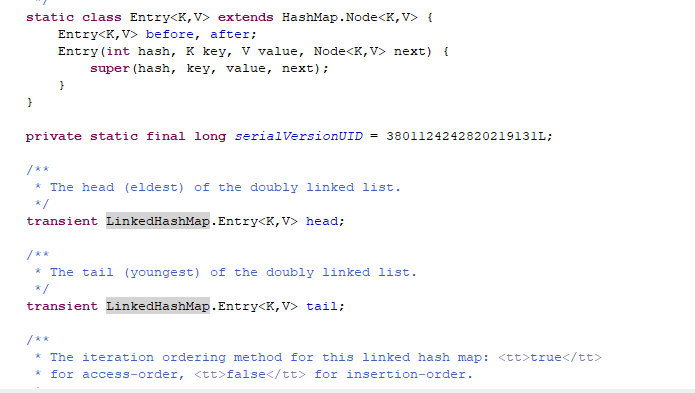
继承HashMap的Node节点,它是双向链表,包含前置指针和后置指针
1.2 LinkedHashMap重写的方法
下面举例两个比较重要的
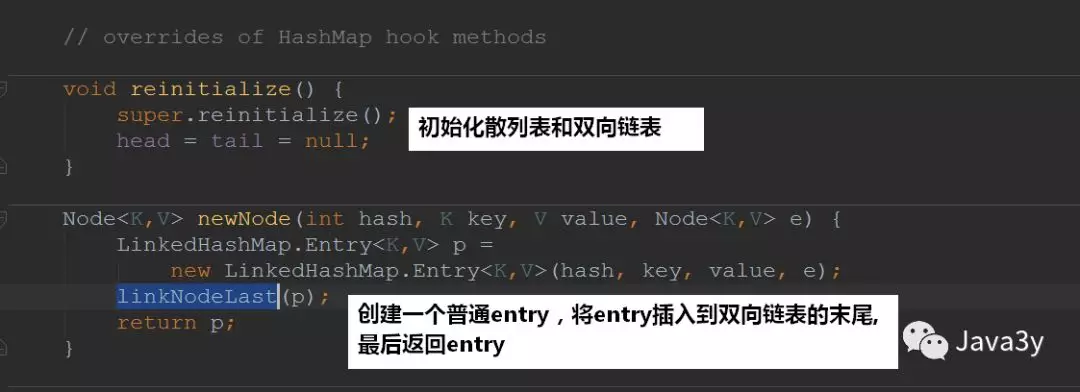
这就印证了我们的LinkedHashMap的底层确实是散列表和双向链表
在构建新节点的时候,构建的是LinkedHashMap.Entry不再是Node
1.3 构造方法
可以发现LinkedHashMap有5个构造方法。
下面我们来看看构造方法的定义是怎么样的:
1 public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) { 2 super(initialCapacity, loadFactor); 3 accessOrder = false; 4 } 5 6 /** 7 * Constructs an empty insertion-ordered <tt>LinkedHashMap</tt> instance 8 * with the specified initial capacity and a default load factor (0.75). 9 * 10 * @param initialCapacity the initial capacity 11 * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is negative 12 */ 13 public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity) { 14 super(initialCapacity); 15 accessOrder = false; 16 } 17 18 /** 19 * Constructs an empty insertion-ordered <tt>LinkedHashMap</tt> instance 20 * with the default initial capacity (16) and load factor (0.75). 21 */ 22 public LinkedHashMap() { 23 super(); 24 accessOrder = false; 25 } 26 27 /** 28 * Constructs an insertion-ordered <tt>LinkedHashMap</tt> instance with 29 * the same mappings as the specified map. The <tt>LinkedHashMap</tt> 30 * instance is created with a default load factor (0.75) and an initial 31 * capacity sufficient to hold the mappings in the specified map. 32 * 33 * @param m the map whose mappings are to be placed in this map 34 * @throws NullPointerException if the specified map is null 35 */ 36 public LinkedHashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) { 37 super(); 38 accessOrder = false; 39 putMapEntries(m, false); 40 } 41 42 /** 43 * Constructs an empty <tt>LinkedHashMap</tt> instance with the 44 * specified initial capacity, load factor and ordering mode. 45 * 46 * @param initialCapacity the initial capacity 47 * @param loadFactor the load factor 48 * @param accessOrder the ordering mode - <tt>true</tt> for 49 * access-order, <tt>false</tt> for insertion-order 50 * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is negative 51 * or the load factor is nonpositive 52 */ 53 public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity, 54 float loadFactor, 55 boolean accessOrder) { 56 super(initialCapacity, loadFactor); 57 this.accessOrder = accessOrder; 58 } 59 60 61 /** 62 * Returns <tt>true</tt> if this map maps one or more keys to the 63 * specified value. 64 * 65 * @param value value whose presence in this map is to be tested 66 * @return <tt>true</tt> if this map maps one or more keys to the 67 * specified value 68 */
从构造方法上我们可以知道的是:LinkedHashMap默认使用的是插入顺序
LinkedHashMap的put方法和HashMap是一样的。在创建节点的时候,调用的是LinkedHashMap重写的方法

1.5 get方法
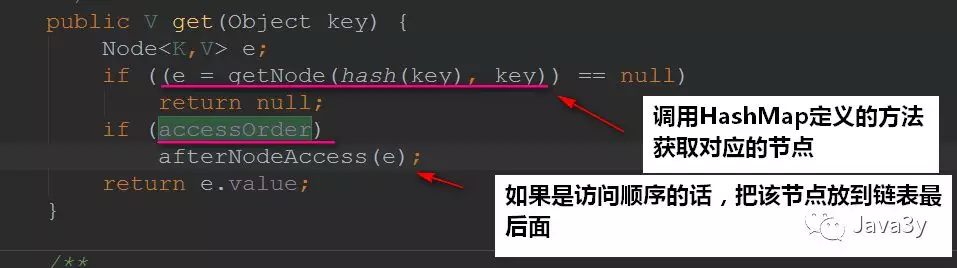
get方法也多了,判断是否为访问顺序
1.6 remove方法
对于remove方法,在linkedhashMap中也没有重写,它调用的还是父类的HashMap的remove方法,在LinkedHashMap中重写的是afterNodeRemoval(Node<K,V> e)这个方法
当然了,在remove的时候会涉及到上面重写的方法:
1.7 遍历的方法
Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet()是被重写的了
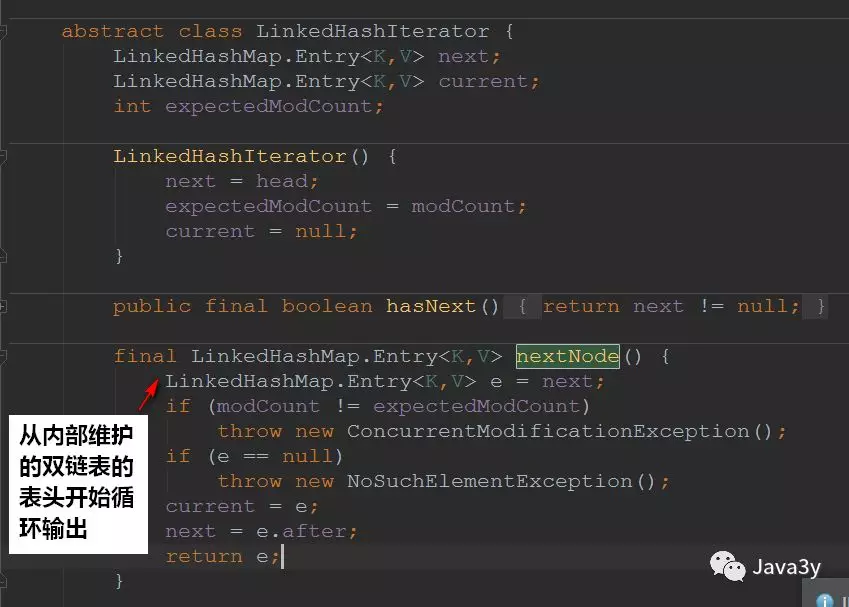
看到了这里,我们就知道为啥注释说:初始容量对遍历没有影响
因为它遍历的是LinkedHashMap内部维护的一个双向链表,而不是散列表(当然了,链表双向链表的元素都来源于散列表)
总结
LinkedHashMap比HashMap多了一个双向链表的维护,在数据结构而言它要复杂一些,阅读源码起来比较轻松一些,因为大多都由HashMap实现了..
1.HashMap对元素的遍历顺序跟Entry插入的顺序无关,而LinkedHashMap对元素的遍历顺序可以跟Entry<K,V>插入的顺序保持一致。
2.当LinkedHashMap处于Get获取顺序遍历模式下,当执行get() 操作时,会将对应的Entry<k,v>移到遍历的最后位置。
3.LinkedHashMap处于按插入顺序遍历的模式下,如果新插入的<key,value> 对应的key已经存在,对应的Entry在遍历顺序中的位置并不会改变。
4.除了遍历顺序外,其他特性HashMap和LinkedHashMap基本相同。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号