Lucene全文检索学习笔记
编辑日志:
2020/11/11
初步编写完,发布随笔
2020/11/18
添加内容:
Lucene同一个文档中,不同field使用不同分词器的实现方式。
正文:
Lucene是什么东西?
抄百度百科上的说法:
Lucene是apache软件基金会4 jakarta项目组的一个子项目,是一个开放源代码的全文检索引擎工具包,但它不是一个完整的全文检索引擎,而是一个全文检索引擎的架构,提供了完整的查询引擎和索引引擎,部分文本分析引擎(英文与德文两种西方语言)。
Lucene的目的是为软件开发人员提供一个简单易用的工具包,以方便的在目标系统中实现全文检索的功能,或者是以此为基础建立起完整的全文检索引擎。Lucene是一套用于全文检索和搜寻的开源程式库,由Apache软件基金会支持和提供。
Lucene提供了一个简单却强大的应用程式接口,能够做全文索引和搜寻。在Java开发环境里Lucene是一个成熟的免费开源工具。
就其本身而言,Lucene是当前以及最近几年最受欢迎的免费Java信息检索程序库。人们经常提到信息检索程序库,虽然与搜索引擎有关,但不应该将信息检索程序库与搜索引擎相混淆。
基于上面的说明,我总结一下:
- Lucene的功能是做全文检索 。
- Lucene是一个工具包,一个架构,并不是一个完整个检索引擎。
- Lucene提供了简单易用的API接口,可以做全文检索和搜寻
- Lucene是信息检索程序库(用于检索自己内部的信息),并不是搜索引擎(像百度一样可以检索外部信息)
前面一直都有提到全文检索,那什么是“全文检索”呢?
上一段百度百科的说法:
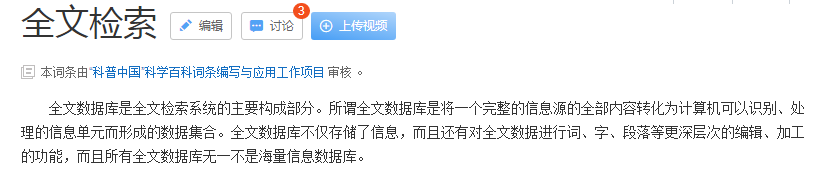
就我个人的理解,全文检索就是对整段的信息内容进行检索。
像我们MySQL数据库,假如你有个字段content,我们在这个content里面使用like '%hello world%',进行查询,这其实也算全文检索,因为你需要匹配整个这个字段的全部内容。
再举个栗子。你大学思修考试开卷考,题目是问你怎么看待:“不要把友情当爱情”,那你是不是要结合课本找关键点,那你就要整本书都翻一遍才能找到相关的内容,对吧,这其实就是全文检索。
全文检索的实现方式有很多种,例如最笨的,一个字一个字慢慢找,找完全部总能发现有没有(每次都一样慢)。也有对信息内容进行索引,弄成像字典一样,在进行查找(建字典时慢,查询时快)
MySQL数据库里面其实也有一个FullText类型的索引,这就是一个全文检索索引。
没了解过的可以参考下这两篇文章
https://www.cnblogs.com/shen-qian/p/11883442.html
http://xiaorui.cc/archives/2754
回到我们的主题Lucene,为什么MySQL都已经提供了一个全文检索,我们还有另外找一个Lucene呢?
当然是因为性能,一旦数据量大了,MySQL的FullText性能便会显著下降。所以我们才要找别的替换。
我这里不做各种全文检索工具的对比,我直接就讲Lucene了,因为我在用这个。
Lucene
首先说下Lucene的索引创建流程和查询流程:
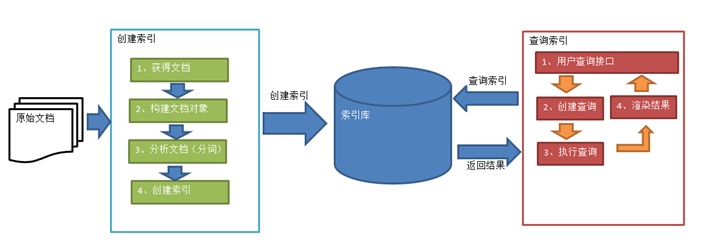
创建索引:
- 获取我们自己的信息内容,不管是MySQL中的,还是文件系统的,还是用户输入的
- 构建一个文档对象,指定哪些是要存的,哪些是要索引的,字段名字是啥............
- 分析信息内容,如果需要分词,就按照指定的分词规则进行分词
- 创建索引,保存文档对象
查询:
- 输入查询条件
- 构建查询
- 解析查询条件,如果需要分词,就按照指定的分词规则进行分词
- 执行查询
- 根据文档id获取文档对象
- 渲染结果
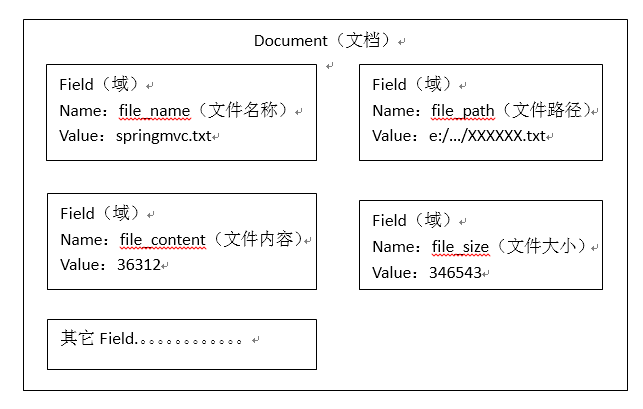
文档对象是什么呢?
mysql里面有数据库、表、列、行,Lucene里面没有这么多,只有document、field
document就等于行,一个document文档 相当于 一行记录
field就等于列,但是又和列不太一样,field字段必须有,才能往里面加数据,但是field字段不限制数据类型,也不限制长度,甚至你也可以没有,或者一个document里面有两个相同的field字段
分析文档:(假设有段内容:Lucene is a Java full-text search engine)
- 提取单词,按空格分隔提取单词:Lucene、is、a、Java、full-text、search、engine
- 转小写:lucene、is、a、java、full-text、search、engine
- 去标点、去停用词、去分割线:lucene、java、full、text、search、engine
- 最后剩余的就是一个语汇单元,也就是词
最后分析出的每一个词都和field域结果,就成了term,例如上面一句话就分析出6个trem。Term的格式是(field:value)
content:lucene
content:java
content:full
content:text
content:search
content:engine
Lucene使用的是倒排索引结构,正常我们是现根据文本内容去查关键词,但是现在变成了先把文本内容进行分析分词,对文本内容中的词建立索引,然后拿关键词去查索引,最后根据索引值去找文本内容,这就变成了倒排索引结构。
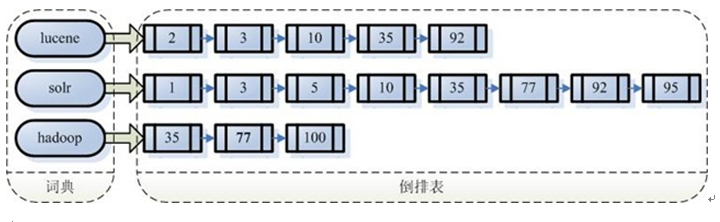
插入文档时,便会将文档进行分析分词,并将词进行创建索引,组成词典,每个词后面会跟着一些出现过的这个词的文档ID(每个文档都会有的一个默认自增的唯一id),同时将文档存起来
查询时根据查询条件,去查询索引,找到对应的词,或取文档ID,并根据文档ID去获取对应的文档内容。
Lucene只提供一系列的jar给我们使用
可以自己去官网进行下载 https://lucene.apache.org/
我是用maven的,所以我不去官网下
<!-- lucene核心依赖包 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.lucene</groupId>
<artifactId>lucene-core</artifactId>
<version>${lucene.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- lucene通用分词依赖包 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.lucene</groupId>
<artifactId>lucene-analyzers-common</artifactId>
<version>${lucene.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- lucene查询解析器依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.lucene</groupId>
<artifactId>lucene-queryparser</artifactId>
<version>${lucene.version}</version>
</dependency>
版本你们自己选,我用的不是最新的
<properties>
<lucene.version>8.0.0</lucene.version>
</properties>
建个maven项目,随便找个类,写个测试方法
/** * 添加索引文档: * 第一步:创建一个indexwriter对象。 * 1)指定索引库的存放位置Directory对象 * 2)指定一个分析器,对文档内容进行分析。 * 第二步:创建document对象。 * 第三步:创建field对象,将field添加到document对象中。 * 第四步:使用indexwriter对象将document对象写入索引库,此过程进行索引创建。并将索引和document对象写入索引库。 * 第五步:关闭IndexWriter对象。 * */ @Test public void addIndex() throws IOException { // 1)指定索引库的存放位置Directory对象 Directory directory = FSDirectory.open(new File("D:\\workspace\\java_web\\solr-demo\\luceneDir\\luceneData").toPath()); // 2)指定一个分词器,对文档内容进行分析。 IndexWriterConfig indexWriterConfig = new IndexWriterConfig(new IKAnalyzer()); // 第一步:创建一个indexwriter对象。 IndexWriter indexWriter = new IndexWriter(directory,indexWriterConfig); File fileDir = new File("D:\\workspace\\java_web\\solr-demo\\luceneDir"); for (File file : fileDir.listFiles()) { if (file.isDirectory()) { continue; } // 第二步:创建document对象。 Document document = new Document(); //文件名 String fileName = file.getName(); //文件内容 String fileContent = FileUtils.readFileToString(file, Charset.forName("utf-8")); //文件路径 String filePath = file.getPath(); //文件的大小 long fileSize = FileUtils.sizeOf(file); //文件父目录路径 String parentPath = file.getParent(); // 第三步:创建field对象,将field添加到document对象中。 // TextField,会分词、索引,可选存储 // StringField,不分词、不索引,会存储 // StringField,不分词、索引,可选存储 Field fileNameField = new TextField("file_name",fileName, Field.Store.YES); Field fileContentField = new TextField("file_content",fileContent, Field.Store.YES); Field parentPathField = new StringField("parent_path",parentPath, Field.Store.YES); Field filePathField = new StoredField("file_path",filePath); Field fileSizeField = new StoredField("file_size",fileSize); // 将field添加到document对象中。 document.add(fileNameField); document.add(fileContentField); document.add(parentPathField); document.add(filePathField); document.add(fileSizeField); // 第四步:使用indexwriter对象将document对象写入索引库,此过程进行索引创建。并将索引和document对象写入索引库。 indexWriter.addDocument(document); } indexWriter.commit(); // 第五步:关闭IndexWriter对象。 indexWriter.close(); }
我自己随便复制了些文件作为数据保存到Lucene中
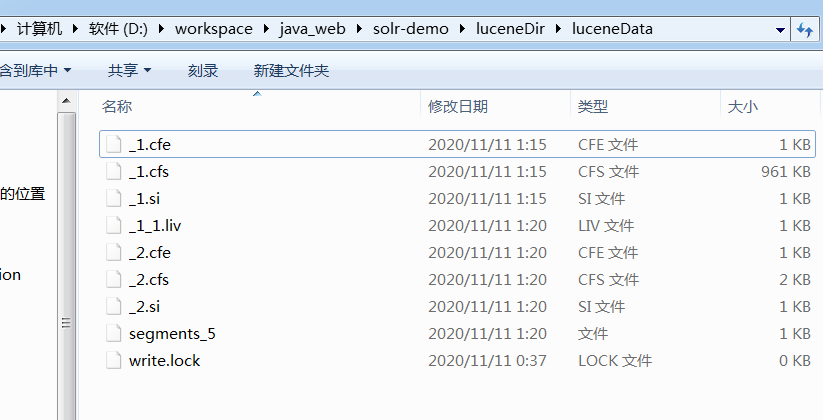
执行测试你会得到这么一堆东西,都是二进制的
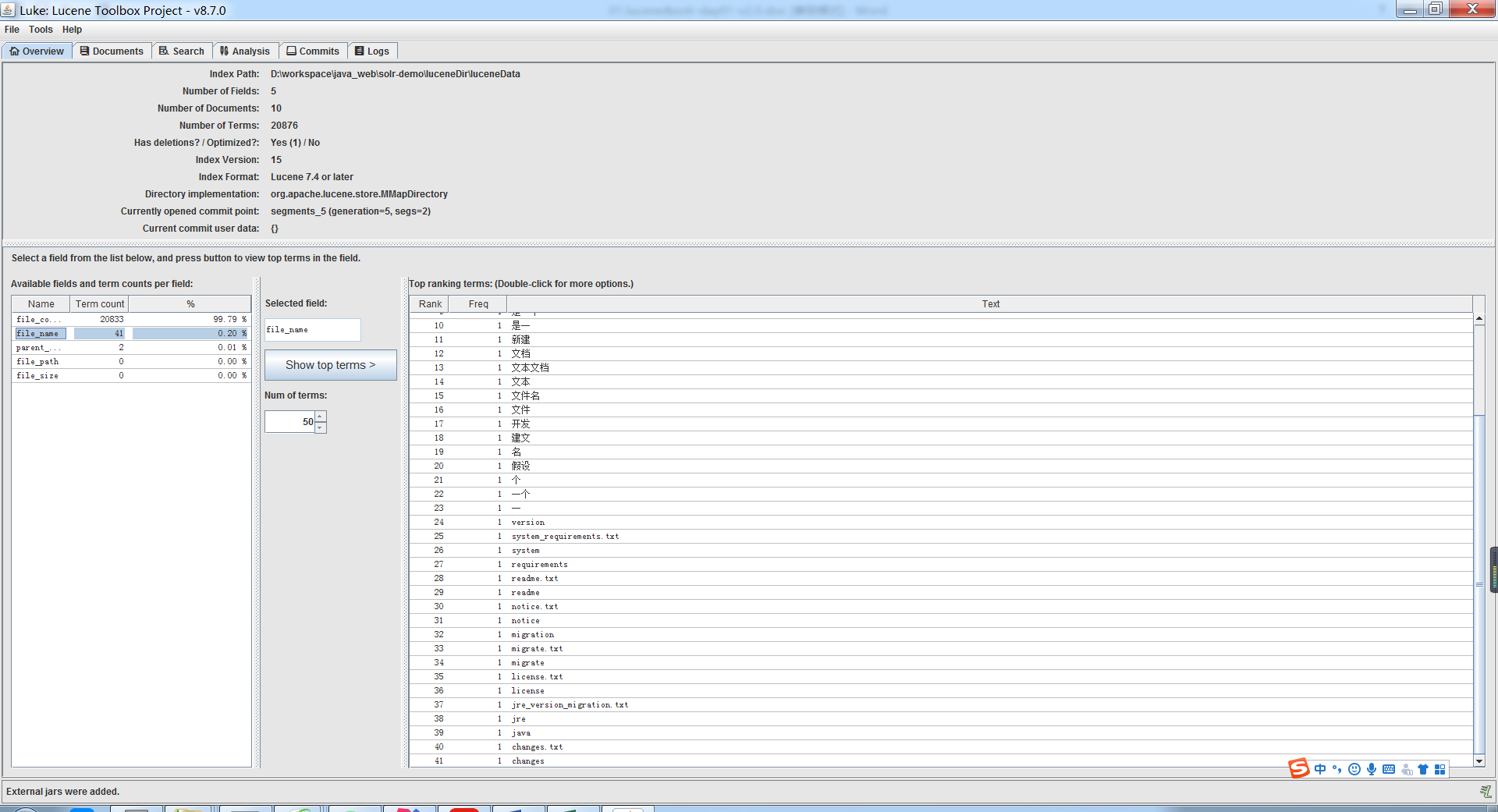
目前我只找到Luke这个工具可以看这些索引文件,可以自行下载,但是要注意Luke和Lucene的版本,不然是读不了的。
github的: https://github.com/DmitryKey/luke/releases
码云的: https://gitee.com/mirrors/luke?utm_source=alading&utm_campaign=repo
当然你从官网上下载的Lucene里面也有Luke这个工具,还是版本对的上的那种
分词器:
Lucene将文本内容分析,要做的就是分词,Lucene自己支持英文和德文,但是其他语言分词就不是很好,需要自己扩展
我们官网下载的压缩包里面就有很多扩展分词器的jar包
自己挑几个导入项目就好
这个测试方法可以让你看下分词效果
@Test public void testAnalyzer() throws Exception { //创建一个标准分析器对象 Analyzer analyzer = new StandardAnalyzer(); //获得tokenStream对象 //第一个参数:域名,可以随便给一个 //第二个参数:要分析的文本内容 TokenStream tokenStream = analyzer.tokenStream("test", " 最新版在https://code.google.com/p/ik-analyzer/上,支持Lucene 4.10从2006年12月推出1.0版开始"); //添加一个引用,可以获得每个关键词 CharTermAttribute charTermAttribute = tokenStream.addAttribute(CharTermAttribute.class); //添加一个偏移量的引用,记录了关键词的开始位置以及结束位置 OffsetAttribute offsetAttribute = tokenStream.addAttribute(OffsetAttribute.class); //将指针调整到列表的头部 tokenStream.reset(); //遍历关键词列表,通过incrementToken方法判断列表是否结束 while(tokenStream.incrementToken()) { //关键词的起始位置 System.out.println("start->" + offsetAttribute.startOffset()); //取关键词 System.err.println(charTermAttribute); //结束位置 System.out.println("end->" + offsetAttribute.endOffset()); } tokenStream.close(); }
中文分词器:IKAnalyzer ,这是比较好的一款分词器,可以支持自己扩展词汇和停用词
https://github.com/magese/ik-analyzer-solr
自己下载完后跟踪说明配置下就行
下面是我的文件放置,你们可自行配置
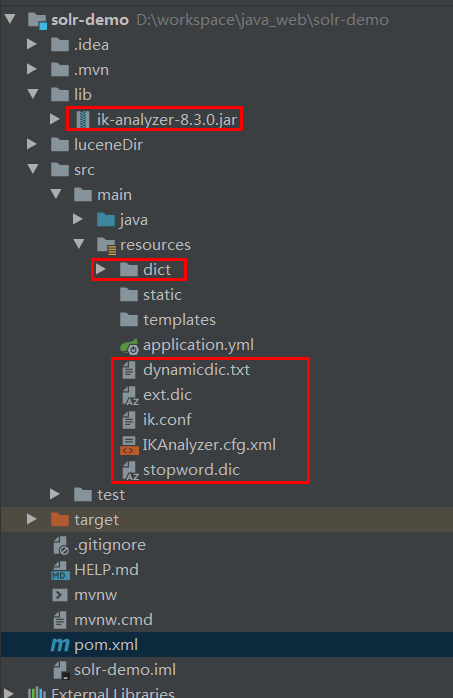
然后创建 IKAnalyzer 重新执行方法就好了
Analyzer analyzer = new IKAnalyzer();
编程代码:
下面增删改查的代码都齐了,基本的就这些,其他扩展的自己找资料吧
import org.apache.commons.io.FileUtils; import org.apache.lucene.analysis.Analyzer; import org.apache.lucene.analysis.TokenStream; import org.apache.lucene.analysis.tokenattributes.CharTermAttribute; import org.apache.lucene.analysis.tokenattributes.OffsetAttribute; import org.apache.lucene.document.*; import org.apache.lucene.index.*; import org.apache.lucene.queryparser.classic.ParseException; import org.apache.lucene.search.*; import org.apache.lucene.store.Directory; import org.apache.lucene.store.FSDirectory; import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; import org.wltea.analyzer.lucene.IKAnalyzer; import java.io.File; import java.io.IOException; import java.nio.charset.Charset; /** * lucene的基本使用 * */ public class LuceneDemoTest { /** * 查看分词器效果 * */ @Test public void testAnalyzer() throws Exception { //创建一个标准分析器对象 // Analyzer analyzer = new StandardAnalyzer(); Analyzer analyzer = new IKAnalyzer(); //获得tokenStream对象 //第一个参数:域名,可以随便给一个 //第二个参数:要分析的文本内容 TokenStream tokenStream = analyzer.tokenStream("test", " 最新版在https://code.google.com/p/ik-analyzer/上,支持Lucene 4.10从2006年12月推出1.0版开始"); //添加一个引用,可以获得每个关键词 CharTermAttribute charTermAttribute = tokenStream.addAttribute(CharTermAttribute.class); //添加一个偏移量的引用,记录了关键词的开始位置以及结束位置 OffsetAttribute offsetAttribute = tokenStream.addAttribute(OffsetAttribute.class); //将指针调整到列表的头部 tokenStream.reset(); //遍历关键词列表,通过incrementToken方法判断列表是否结束 while(tokenStream.incrementToken()) { //关键词的起始位置 System.out.println("start->" + offsetAttribute.startOffset()); //取关键词 System.out.println(charTermAttribute); //结束位置 System.out.println("end->" + offsetAttribute.endOffset()); } tokenStream.close(); } /** * 添加索引文档: * 第一步:创建一个indexwriter对象。 * 1)指定索引库的存放位置Directory对象 * 2)指定一个分析器,对文档内容进行分析。 * 第二步:创建document对象。 * 第三步:创建field对象,将field添加到document对象中。 * 第四步:使用indexwriter对象将document对象写入索引库,此过程进行索引创建。并将索引和document对象写入索引库。 * 第五步:关闭IndexWriter对象。 * */ @Test public void addIndex() throws IOException { // 1)指定索引库的存放位置Directory对象 Directory directory = FSDirectory.open(new File("D:\\workspace\\java_web\\solr-demo\\luceneDir\\luceneData").toPath()); // 2)指定一个分词器,对文档内容进行分析。 IndexWriterConfig indexWriterConfig = new IndexWriterConfig(new IKAnalyzer()); // 第一步:创建一个indexwriter对象。 IndexWriter indexWriter = new IndexWriter(directory,indexWriterConfig); File fileDir = new File("D:\\workspace\\java_web\\solr-demo\\luceneDir"); for (File file : fileDir.listFiles()) { if (file.isDirectory()) { continue; } // 第二步:创建document对象。 Document document = new Document(); //文件名 String fileName = file.getName(); //文件内容 String fileContent = FileUtils.readFileToString(file, Charset.forName("utf-8")); //文件路径 String filePath = file.getPath(); //文件的大小 long fileSize = FileUtils.sizeOf(file); //文件父目录路径 String parentPath = file.getParent(); // 第三步:创建field对象,将field添加到document对象中。 // TextField,会分词、索引,可选存储 // StringField,不分词、不索引,会存储 // StringField,不分词、索引,可选存储 Field fileNameField = new TextField("file_name",fileName, Field.Store.YES); Field fileContentField = new TextField("file_content",fileContent, Field.Store.YES); Field parentPathField = new StringField("parent_path",parentPath, Field.Store.YES); Field filePathField = new StoredField("file_path",filePath); Field fileSizeField = new StoredField("file_size",fileSize); // 将field添加到document对象中。 document.add(fileNameField); document.add(fileContentField); document.add(parentPathField); document.add(filePathField); document.add(fileSizeField); // 第四步:使用indexwriter对象将document对象写入索引库,此过程进行索引创建。并将索引和document对象写入索引库。 indexWriter.addDocument(document); } indexWriter.commit(); // 第五步:关闭IndexWriter对象。 indexWriter.close(); } /** * 删除索引文档: * 第一步:创建一个indexwriter对象。 * 1)指定索引库的存放位置Directory对象 * 2)指定一个分析器,对文档内容进行分析。 * 第二步:创建查询条件。 * 第三步:删除索引 * 第四步:关闭IndexWriter对象。 * */ @Test public void deleteIndex() throws IOException { // 1)指定索引库的存放位置Directory对象 Directory directory = FSDirectory.open(new File("D:\\workspace\\java_web\\solr-demo\\luceneDir\\luceneData").toPath()); // 2)指定一个分词器,对文档内容进行分析。 IndexWriterConfig indexWriterConfig = new IndexWriterConfig(new IKAnalyzer()); // 第一步:创建一个indexwriter对象。 IndexWriter indexWriter = new IndexWriter(directory,indexWriterConfig); // 删除 // indexWriter.deleteDocuments(new Term("file_name","知识")); indexWriter.deleteAll(); // 关闭 indexWriter.close(); } /** * 更新是默认先删除,再重新创建的,不能只改部分字段 * 更新索引文档: * 第一步:创建一个indexwriter对象。 * 1)指定索引库的存放位置Directory对象 * 2)指定一个分析器,对文档内容进行分析。 * 第二步:创建document对象。 * 第三步:创建field对象,将field添加到document对象中。 * 第四步:更新索引 * 第五步:关闭IndexWriter对象。 * */ @Test public void updateIndex() throws IOException{ // 1)指定索引库的存放位置Directory对象 Directory directory = FSDirectory.open(new File("D:\\workspace\\java_web\\solr-demo\\luceneDir\\luceneData").toPath()); // 2)指定一个分词器,对文档内容进行分析。 IndexWriterConfig indexWriterConfig = new IndexWriterConfig(new IKAnalyzer()); // 第一步:创建一个indexwriter对象。 IndexWriter indexWriter = new IndexWriter(directory,indexWriterConfig); // 第二步:创建document对象。 Document document = new Document(); //向document对象中添加域。 //不同的document可以有不同的域,同一个document可以有相同的域。 Field fileNameField = new TextField("file_name","假设这里是一个文件名", Field.Store.YES); Field fileNameField2 = new TextField("file_name","这里是一个相同的文件名", Field.Store.YES); Field fileContentField = new TextField("file_content","假设这里是一个文件内容", Field.Store.YES); Field parentPathField = new StringField("parent_path","父目录", Field.Store.YES); Field filePathField = new StoredField("file_path","文档目录"); Field fileSizeField = new StoredField("file_size",9L); // 将field添加到document对象中。 document.add(fileNameField); document.add(fileNameField2); document.add(fileContentField); document.add(parentPathField); document.add(filePathField); document.add(fileSizeField); indexWriter.updateDocument(new Term("file_name", "知识"), document); //关闭indexWriter indexWriter.close(); } /** * 查询索引文档 * 第一步:创建一个Directory对象,也就是索引库存放的位置。 * 第二步:创建一个indexReader对象,需要指定Directory对象。 * 第三步:创建一个IndexSearcher对象,需要指定IndexReader对象 * 第四步:创建一个TermQuery对象,指定查询的域和查询的关键词。 * 第五步:执行查询。 * 第六步:返回查询结果。遍历查询结果并输出。 * 第七步:关闭IndexReader对象 * * lucene查询语法: * 1、使用Term去查询,Term的格式为 field:value value将被视为一个整体,不分词。或者,field:"value" value将被视为词组,会被分词 * 2、使用Field去查询, field:value ,不会对查询词进行分词,如果不指定field,则直接查默认field * 3、通配符模糊查询, field:v?l* ,其中?匹配一个字符,*匹配多个字符,实例可以匹配value、vilu,但是要注意,通配符不能出现在第一个字符上 * 4、相似度查询, field:value~ 会查询出和value相似的内容,例如aalue、valua * 5、指定距离查询,field:"hello world"~10 对这两个单词进行分词,如果两个词的间距在10个字符以内,则算匹配 * 6、范围查询,field:[N TO M} [中括号表示包含,{大括号表示不包含, TO 关键字,必须大写,实例表示值在 N 到 M 之间,包含 N,不包含M * 7、权重优先级,field:"hello^4 world",搜索和排序时,优先考虑hello * 8、Term操作符组合多条件,AND、OR、NOT、+、- ,都必须多个term才能用,且都大写 * 8.1、AND : field1:hello AND field2:world 表示field1字段必须有hello,同时field2字段也必须有world * 8.2、OR : field1:hello OR field2:world 表示field1字段有hello,或者,field2字段有world * 8.3、NOT : field1:hello NOT field2:world 表示field1字段必须有hello,同时,field2字段必须不能有world,NOT不能单独用 * 8.4、+ : +field1:hello field2:world 表示field1:hello必须有满足,类似AND ,如果term前面不带+-,则是说明可满足可不满足 * 8.5、- : -field1:hello field2:world 表示field1:hello必须不能满足,类似NOT * 9、分组,(field1:hello AND field2:world) OR field3:hello ,多个term时可以进行组合 * 10、特殊字符 + - && || ! ( ) { } [ ] ^ " ~ * ? : \ ,如果查询文本总就有特殊字符,则需要用\进行转义。 * QueryParser.escape(q) 可转换q中含有查询关键字的字符!如:* ,? 等 * */ @Test public void searchIndex() throws IOException, ParseException { // 第一步:创建一个Directory对象,指定索引库存放的位置。 FSDirectory directory = FSDirectory.open(new File("D:\\workspace\\java_web\\solr-demo\\luceneDir\\luceneData").toPath()); // 第二步:创建一个indexReader对象,需要指定Directory对象,用于读取索引。 IndexReader indexReader = DirectoryReader.open(directory); // 第三步:创建一个IndexSearcher对象,需要指定IndexReader对象 IndexSearcher indexSearcher = new IndexSearcher(indexReader); // 第四步:创建一个TermQuery对象,指定查询的域和查询的关键词。 // 查询有两种主要方式,一是使用Query的子类,二是使用QueryParser解析查询表达式 // 使用MatchAllDocsQuery查询索引目录中的所有文档,等同于*:* // Query query = new MatchAllDocsQuery(); // TermQuery,通过指定域查询,TermQuery不使用分析器所以建议匹配不分词的Field域查询,比如订单号、分类ID号等。等同于 file_name:文件 // Query query = new TermQuery(new Term("file_name","文件")); // 数字的范围查询,等同于 file_size:[1 TO 200] // Query query = NumericDocValuesField.newSlowRangeQuery("file_size",1L,200L); // 解析查询表达式,可以使用分词器 // QueryParser queryParser = new QueryParser("name", new IKAnalyzer()); // Query query = queryParser.parse("file_name:文件"); //创建一个布尔查询对象,多条件查询 BooleanQuery query = new BooleanQuery.Builder() .setMinimumNumberShouldMatch(10) .add(new TermQuery(new Term("file_content","lucene")), BooleanClause.Occur.FILTER) .add(new TermQuery(new Term("file_name","readme")), BooleanClause.Occur.MUST) .build(); System.err.println("查询条件:" + query); // 第五步:执行查询。 // 第一个参数是查询对象,第二个参数是查询结果返回的最大值 TopDocs topDocs = indexSearcher.search(query, 200); System.err.println("总匹配记录数:" + topDocs.totalHits); System.out.println(""); // 第六步:返回查询结果。遍历查询结果并输出。 for (ScoreDoc scoreDoc : topDocs.scoreDocs) { int docId = scoreDoc.doc; Document document = indexSearcher.doc(docId); System.out.println("file_name ==> " + document.get("file_name")); System.out.println("file_content ==> " + document.get("file_content")); System.out.println("parent_path ==> " + document.get("parent_path")); System.out.println("file_path ==> " + document.get("file_path")); System.out.println("file_size ==> " + document.get("file_size")); System.out.println("匹配值:" + scoreDoc.score); System.out.println("--------------------------------"); } // 第七步:关闭IndexReader对象 indexReader.close(); } }
Lucene的查询语法:
lucene查询语法:
1、使用Term去查询,Term的格式为 field:value value将被视为一个整体,不分词。或者,field:"value" value将被视为词组,会被分词
2、使用Field去查询, field:value ,不会对查询词进行分词,如果不指定field,则直接查默认field
3、通配符模糊查询, field:v?l* ,其中?匹配一个字符,*匹配多个字符,实例可以匹配value、vilu,但是要注意,通配符不能出现在第一个字符上
4、相似度查询, field:value~ 会查询出和value相似的内容,例如aalue、valua
5、指定距离查询,field:"hello world"~10 对这两个单词进行分词,如果两个词的间距在10个字符以内,则算匹配
6、范围查询,field:[N TO M} [中括号表示包含,{大括号表示不包含, TO 关键字,必须大写,实例表示值在 N 到 M 之间,包含 N,不包含M
7、权重优先级,field:"hello^4 world",搜索和排序时,优先考虑hello
8、Term操作符组合多条件,AND、OR、NOT、+、- ,都必须多个term才能用,且都大写
8.1、AND : field1:hello AND field2:world 表示field1字段必须有hello,同时field2字段也必须有world
8.2、OR : field1:hello OR field2:world 表示field1字段有hello,或者,field2字段有world
8.3、NOT : field1:hello NOT field2:world 表示field1字段必须有hello,同时,field2字段必须不能有world,NOT不能单独用
8.4、+ : +field1:hello field2:world 表示field1:hello必须有满足,类似AND ,如果term前面不带+-,则是说明可满足可不满足
8.5、- : -field1:hello field2:world 表示field1:hello必须不能满足,类似NOT
9、分组,(field1:hello AND field2:world) OR field3:hello ,多个term时可以进行组合
10、特殊字符 + - && || ! ( ) { } [ ] ^ " ~ * ? : \ ,如果查询文本总就有特殊字符,则需要用\进行转义。
QueryParser.escape(q) 可转换q中含有查询关键字的字符!如:* ,? 等
完结。
下面是一个Lucene和solr的视频,可以看一下,个人觉得讲的比较好,
链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1Wcvu2y6BdRbhRT1YiI5XKw 提取码: tjvb
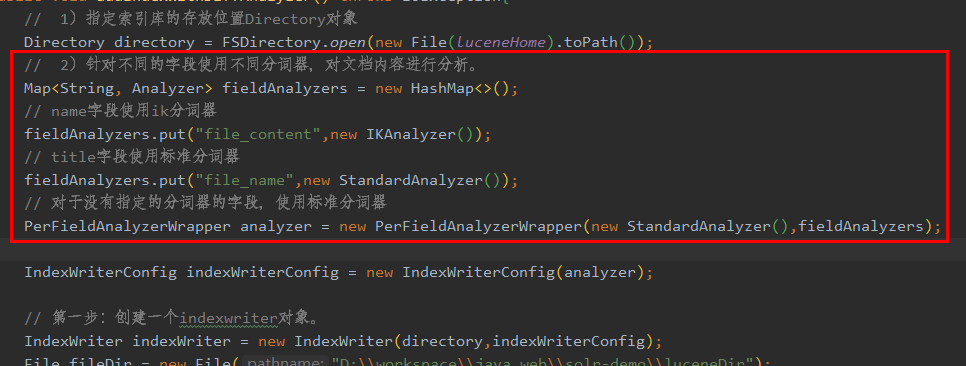
2020/11/18 新增内容:1、Lucene同一个文档中,不同field使用不同的分词器
主要代码:
![]()
完整代码:
/***
* 不同字段使用不同分词器
* */
@Test
public void addIndexWithDiffAnalyzer() throws IOException{
// 1)指定索引库的存放位置Directory对象
Directory directory = FSDirectory.open(new File(luceneHome).toPath());
// 2)针对不同的字段使用不同分词器,对文档内容进行分析。
Map<String, Analyzer> fieldAnalyzers = new HashMap<>();
// name字段使用ik分词器
fieldAnalyzers.put("file_content",new IKAnalyzer());
// title字段使用标准分词器
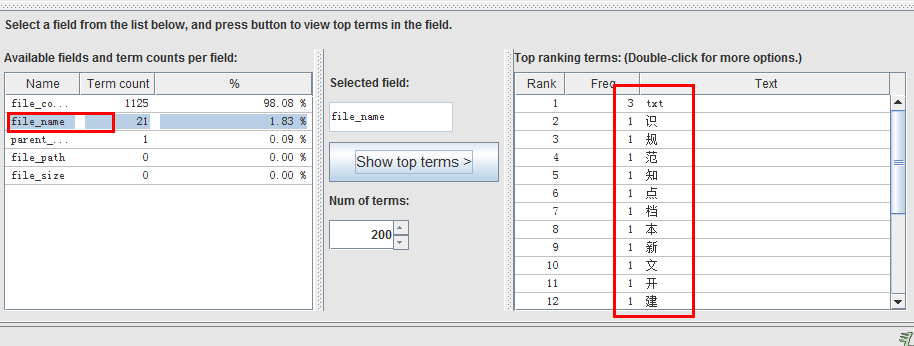
fieldAnalyzers.put("file_name",new StandardAnalyzer());
// 对于没有指定的分词器的字段,使用标准分词器
PerFieldAnalyzerWrapper analyzer = new PerFieldAnalyzerWrapper(new StandardAnalyzer(),fieldAnalyzers);
IndexWriterConfig indexWriterConfig = new IndexWriterConfig(analyzer);
// 第一步:创建一个indexwriter对象。
IndexWriter indexWriter = new IndexWriter(directory,indexWriterConfig);
File fileDir = new File("D:\\workspace\\java_web\\solr-demo\\luceneDir");
for (File file : fileDir.listFiles()) {
if (file.isDirectory()) {
continue;
}
// 第二步:创建document对象。
Document document = new Document();
//文件名
String fileName = file.getName();
//文件内容
String fileContent = FileUtils.readFileToString(file, Charset.forName("utf-8"));
//文件路径
String filePath = file.getPath();
//文件的大小
long fileSize = FileUtils.sizeOf(file);
//文件父目录路径
String parentPath = file.getParent();
// 第三步:创建field对象,将field添加到document对象中。
// TextField,会分词、索引,可选存储
// StringField,不分词、不索引,会存储
// StringField,不分词、索引,可选存储
Field fileNameField = new TextField("file_name",fileName, Field.Store.YES);
Field fileContentField = new TextField("file_content",fileContent, Field.Store.YES);
Field parentPathField = new StringField("parent_path",parentPath, Field.Store.YES);
Field filePathField = new StoredField("file_path",filePath);
Field fileSizeField = new StoredField("file_size",fileSize);
// 将field添加到document对象中。
document.add(fileNameField);
document.add(fileContentField);
document.add(parentPathField);
document.add(filePathField);
document.add(fileSizeField);
// 第四步:使用indexwriter对象将document对象写入索引库,此过程进行索引创建。并将索引和document对象写入索引库。
indexWriter.addDocument(document);
}
indexWriter.commit();
// 第五步:关闭IndexWriter对象。
indexWriter.close();
}
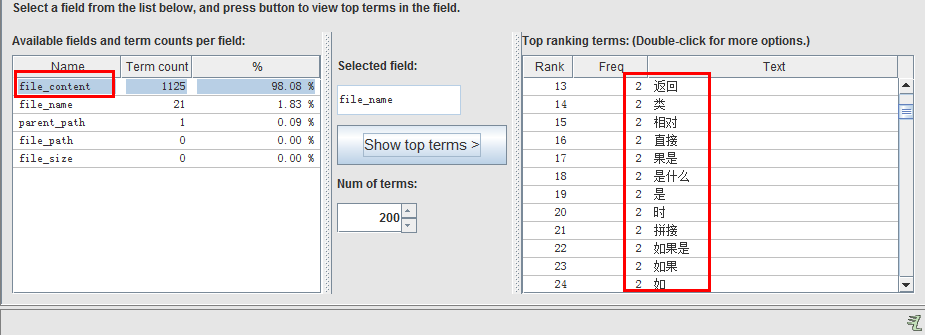
结果:
![]()





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号