哈希表数据结构总结
前言
一直在使用C#的Dictionary和HashSet,但对于它们的理解一直都比较的浅显,没有深入的去学习了解,趁现在难得空闲,抓紧补充下这个方面的知识,以助于能在工作上更好的优化自己的代码。
Hash可以为我们做什么?
了解一个东西,最好的方法是从它能为我们做什么来入手。假如一家百货超市内有A,B,C1,C2,D...多个商品,它们分门别类的存储在货架上,我们可以用一个数组来表示,例如商品[1]=A,商品[2]=B,商品[3]=C1等等,数组索引表示货架索引,值表示商品。但当商品数量多起来,当我们想要搜索D商品在哪个货架索引时,我们就需要遍历整个数组进行查找,这种时候这个查询方法效率很低,所以我们不得思考其他办法了。
Hash算法因此应运而生,我们可以通过键值对的方式,对商品进行存储,例如,商品[A]=1,商品[B]=2,商品[C1]=3,商品[C2]=4,这样就大大加快了我们的查询效率。对于数组而言,我们可以通过索引找到内存地址,就能找到对应的值。但对于Hash表而言,它的键可以是整数,或者是字符串,或者一个实例对象。但是这个键并不会直接对应相应的内存地址,这个键只是方便我们进行索引,要想找到这个内存地址,我们还需要对键进行运算,运算后得到的数字才可以找到对应的内存地址。
给这个键运算的过程就是哈希函数了。
Hash函数
Hash函数有很多种算法,最简单的就是【除留余数法】,即hash_key = key % p(假设数组长度为m,p<=m),例如上面商品的例子,假设A对象的内存地址是1,B对象的内存地址是8,我们哈希表长度是5,那么A对象的哈希值=1%5=1,B对象的哈希值=8%5=3。
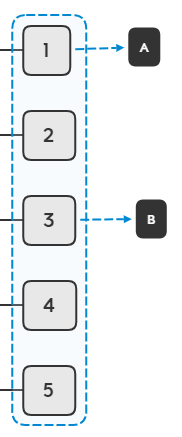
Hash函数有以下特征:
- 相同的key进行Hash计算,得到的结果一定是同一Hash地址。
- 不同的key进行Hash计算,得到的结果也可能是同一Hash地址,这种现象称为Hash冲突。
例如C1的内存地址是2,C2的内存地址是7,它俩计算得到的Hash值都是2,那么这种时候,我们该怎么办呢?
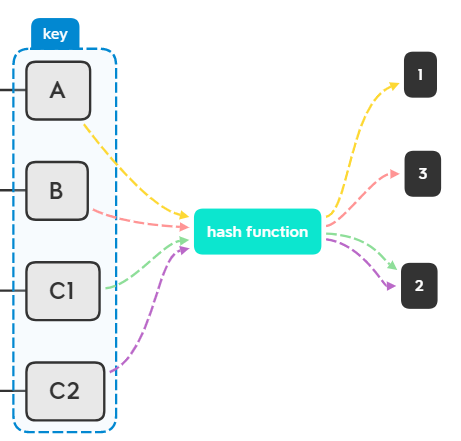
哈希冲突
如上面所言,冲突是可能会存在的,所以我们就需要引入其他方法来解决冲突,常见的方法有2种,一种是开放寻址法,一种叫做封闭寻址法。
开放寻址法
开放寻址法(Open Addressing)是哈希表中解决键冲突的一种策略,其核心思想是所有元素直接存储在哈希表数组内,当发生冲突时,通过特定的探测序列寻找下一个可用槽位,而非借助链表等外部数据结构。
核心原理:
- 当插入或查找元素时,若哈希函数计算的位置已被占用(即冲突),则按照“探测序列”寻找下一个空槽。
- 负载因子(已存储元素数/哈希表总槽位数)需要控制在0.7以下,过高会导致冲突概率激增,效率下降。
常见的探测方法:
- 线性探测:
- 规则:若位置 H 冲突,依次尝试 H+1,H+2,H+3...
- 优点:连续内存访问,对缓存友好
- 限制:易导致聚集,即连续占用的槽位形成长簇,增加查找时间
- 二次探测:
- 规则:若位置 H 冲突,依次尝试 H + 1², H + 2², H + 3²...
- 优点:减少聚集现象
- 限制:需哈希表大小为质数且满足 4k+3 形式,否则可能无法遍历所有槽位。
- 双重哈希:
- 规则:使用第二个哈希函数 H2(key) 计算步长,探测序列为 H + i*H2(key)(i 为尝试次数)。
- 优点:不同键的探测步长不同,冲突率最低。
- 限制:需确保 H2(key) 与表大小互质,例如表大小为质数,H2 返回 1 ≤ H2 < size。
基本数据结构
private enum EntryState { Empty, Occupied, Deleted }
private class Entry
{
public TKey key { get; set; }
public TVal val { get; set; }
public EntryState state { get; set; }
}
private Entry[] buckets; // 哈希表
private double count; // occupied槽数量
private readonly double loadFactorThreshold = 0.7f; // 负载因子
// 初始化
public HashTable(int initialCapacity = 16)
{
this.buckets = new Entry[initialCapacity];
}
// 哈希函数
private int GetHashIndex(TKey key, int capacity = -1)
{
if (capacity == -1)
{
capacity = buckets.Length;
}
int hash = key.GetHashCode();
// hash值可能为负,这样保证一定为整数
return (hash % capacity + capacity) % capacity;
}
插入
- 按探测序列找到空槽或标记为“已删除”的槽位后插入。
- 若表接近满载,需扩容;会新建更大的哈希表(通常双倍大小),重新插入所有元素。
// 插入
public void Insert(TKey key, TVal value)
{
if(key == null)
{
return;
}
// 检查插入后数量是否达到负载因子阙值,达到了话要扩容
if (count / buckets.Length >= loadFactorThreshold)
{
Resize();
}
int index = GetHashIndex(key);
int originalIndex = index;
do
{
if (buckets[index] == null)
{
buckets[index] = new Entry();
}
var entry = buckets[index];
if(entry.state == EntryState.Empty || entry.state == EntryState.Deleted)
{
// 空槽直接开插
entry.key = key;
entry.val = value;
entry.state = EntryState.Occupied;
count++;
return;
}
else if(entry.state == EntryState.Occupied && entry.key.Equals(key))
{
entry.val = value;
return;
}
// 线性探测
index = (index + 1) % buckets.Length;
} while (index != originalIndex);
}
// 扩容哈希表
private void Resize()
{
int newCapacity = buckets.Length * 2;
var newBuckets = new Entry[newCapacity];
// 重新插入,容量变了肯定要重新插入,因为新容量计算的哈希值肯定跟旧容量不一样
foreach (var entry in buckets)
{
if (entry?.state == EntryState.Occupied)
{
// 根据线性探测法,一直找到newBuckets可以插入的索引
int index = GetHashIndex(entry.key, newCapacity);
while (newBuckets[index]?.state == EntryState.Occupied)
index = (index + 1) % newCapacity;
newBuckets[index] = new Entry
{
key = entry.key,
val = entry.val,
state = EntryState.Occupied
};
}
}
buckets = newBuckets;
}
查找
- 沿探测序列依次检查,直到找到目标键或者遇到空槽(说明键不存在)
// 查找
public bool TryGetValue(TKey key, out TVal val)
{
val = default;
if(key == null)
{
return false;
}
int index = GetHashIndex(key);
int originalIndex = index;
do
{
var entry = buckets[index];
// 查找断开了,表示没有该键
if(entry == null || entry.state == EntryState.Empty)
{
break;
}
// 找到了
if(entry.state == EntryState.Occupied && entry.key.Equals(key))
{
val = entry.val;
return true;
}
index = (index + 1) % buckets.Length;
} while (index != originalIndex);
return false;
}
删除
- 不能直接清空槽位,否则会破坏后续探测序列。
- 需使用特殊标记(如 DELETED)标识已删除位置,插入时可复用,查找时继续探测。
// 删除逻辑
public bool Delete(TKey key)
{
if(key == null)
{
return false;
}
int index = GetHashIndex(key);
int originalIndex = index;
do
{
var entry = buckets[index];
if(entry == null || entry.state == EntryState.Empty)
{
break;
}
if(entry.state == EntryState.Occupied && entry.key.Equals(key))
{
entry.state = EntryState.Deleted;
count--;
return true;
}
index = (index + 1) % buckets.Length;
} while (index != originalIndex);
return false;
}
全部代码
点击查看开放寻址法 哈希代码
class HashTable<TKey, TVal>
{
private enum EntryState { Empty, Occupied, Deleted }
private class Entry
{
public TKey key { get; set; }
public TVal val { get; set; }
public EntryState state { get; set; }
}
private Entry[] buckets; // 哈希表
private double count; // occupied槽数量
private readonly double loadFactorThreshold = 0.7f; // 负载因子
// 初始化
public HashTable(int initialCapacity = 16)
{
this.buckets = new Entry[initialCapacity];
}
// 哈希函数
private int GetHashIndex(TKey key, int capacity = -1)
{
if (capacity == -1)
{
capacity = buckets.Length;
}
int hash = key.GetHashCode();
// hash值可能为负,这样保证一定为整数
return (hash % capacity + capacity) % capacity;
}
// 插入
public void Insert(TKey key, TVal value)
{
if(key == null)
{
return;
}
// 检查插入后数量是否达到负载因子阙值,达到了话要扩容
if (count / buckets.Length >= loadFactorThreshold)
{
Resize();
}
int index = GetHashIndex(key);
int originalIndex = index;
do
{
if (buckets[index] == null)
{
buckets[index] = new Entry();
}
var entry = buckets[index];
if(entry.state == EntryState.Empty || entry.state == EntryState.Deleted)
{
// 空槽直接开插
entry.key = key;
entry.val = value;
entry.state = EntryState.Occupied;
count++;
return;
}
else if(entry.state == EntryState.Occupied && entry.key.Equals(key))
{
entry.val = value;
return;
}
// 线性探测
index = (index + 1) % buckets.Length;
} while (index != originalIndex);
}
// 扩容哈希表
private void Resize()
{
int newCapacity = buckets.Length * 2;
var newBuckets = new Entry[newCapacity];
// 重新插入,容量变了肯定要重新插入,因为新容量计算的哈希值肯定跟旧容量不一样
foreach (var entry in buckets)
{
if (entry?.state == EntryState.Occupied)
{
// 根据线性探测法,一直找到newBuckets可以插入的索引
int index = GetHashIndex(entry.key, newCapacity);
while (newBuckets[index]?.state == EntryState.Occupied)
index = (index + 1) % newCapacity;
newBuckets[index] = new Entry
{
key = entry.key,
val = entry.val,
state = EntryState.Occupied
};
}
}
buckets = newBuckets;
}
// 查找
public bool TryGetValue(TKey key, out TVal val)
{
val = default;
if(key == null)
{
return false;
}
int index = GetHashIndex(key);
int originalIndex = index;
do
{
var entry = buckets[index];
// 查找断开了,表示没有该键
if(entry == null || entry.state == EntryState.Empty)
{
break;
}
// 找到了
if(entry.state == EntryState.Occupied && entry.key.Equals(key))
{
val = entry.val;
return true;
}
index = (index + 1) % buckets.Length;
} while (index != originalIndex);
return false;
}
// 删除逻辑
public bool Delete(TKey key)
{
if(key == null)
{
return false;
}
int index = GetHashIndex(key);
int originalIndex = index;
do
{
var entry = buckets[index];
if(entry == null || entry.state == EntryState.Empty)
{
break;
}
if(entry.state == EntryState.Occupied && entry.key.Equals(key))
{
entry.state = EntryState.Deleted;
count--;
return true;
}
index = (index + 1) % buckets.Length;
} while (index != originalIndex);
return false;
}
}
封闭寻址法
哈希算法中的封闭寻址法(又称链地址法或闭合散列法)是一种解决哈希冲突的策略,其核心思想是通过辅助数据结构(如链表、树等)存储同一哈希槽位上的冲突元素。
核心原理:
- 当多个元素通过哈希函数映射到同一槽位时,封闭寻址法不会将新元素存储到其他槽位,而是将其添加到该槽位关联的链表中。例如,若槽位i已存在元素A,新元素B哈希到i时,会被追加到i对应的链表末尾。
- 通常采用链表作为辅助结构,但当链表过长时可能转为红黑树。
基本数据结构
private class Entry
{
public TKey key { get; set; }
public TVal val { get; set; }
public Entry(TKey key, TVal val)
{
key = key;
val = val;
}
}
private LinkedList<Entry>[] buckets;
private double count;
private readonly double loadFactorThreshold = 0.7f;
public HashTable(int initialCapacity = 16)
{
buckets = new LinkedList<Entry>[initialCapacity];
}
// 哈希函数
private int GetHashIndex(TKey key, int capacity = -1)
{
if (capacity == -1)
{
capacity = buckets.Length;
}
int hash = key.GetHashCode();
// hash值可能为负,这样保证一定为整数
return (hash % capacity + capacity) % capacity;
}
插入
// 插入
public void Insert(TKey key, TVal val)
{
// 超过负载因子,重新扩容
if(count / buckets.Length >= loadFactorThreshold)
{
Resize();
}
int index = GetHashIndex(key);
LinkedList<Entry> bucket = buckets[index];
if (bucket == null)
{
bucket = new LinkedList<Entry>();
}
foreach(var entry in bucket)
{
if(entry.key.Equals(key))
{
// 更新已存在的值
return;
}
}
bucket.AddLast(new Entry(key, val));
count++;
}
private void Resize()
{
int newCapacity = buckets.Length * 2;
var newBuckets = new LinkedList<Entry>[newCapacity];
foreach (var bucket in buckets)
{
if (bucket == null)
{
continue;
}
foreach (var entry in bucket)
{
int newIndex = GetHashIndex(entry.key, newCapacity);
if (newBuckets[newIndex] == null)
{
newBuckets[newIndex] = new LinkedList<Entry>();
}
newBuckets[newIndex].AddLast(entry);
}
}
buckets = newBuckets;
}
查找
// 查找
public bool TryGetValue(TKey key, out TVal val)
{
int index = GetHashIndex(key);
var bucket = buckets[index];
if(bucket != null)
{
foreach(var entry in bucket)
{
if(entry.key.Equals(key))
{
val = entry.val;
return true;
}
}
}
val = default;
return false;
}
删除
// 删除
public bool Delete(TKey key)
{
int index = GetHashIndex(key);
var bucket = buckets[index];
if(bucket != null)
{
var node = bucket.First;
while(node != null)
{
if(node.Value.key.Equals(key))
{
bucket.Remove(node);
count--;
return true;
}
node = node.Next;
}
}
return false;
}
完整代码
点击查看代码
class HashTable<TKey,TVal>
{
private class Entry
{
public TKey key { get; set; }
public TVal val { get; set; }
public Entry(TKey key, TVal val)
{
key = key;
val = val;
}
}
private LinkedList<Entry>[] buckets;
private double count;
private readonly double loadFactorThreshold = 0.7f;
public HashTable(int initialCapacity = 16)
{
buckets = new LinkedList<Entry>[initialCapacity];
}
// 哈希函数
private int GetHashIndex(TKey key, int capacity = -1)
{
if (capacity == -1)
{
capacity = buckets.Length;
}
int hash = key.GetHashCode();
// hash值可能为负,这样保证一定为整数
return (hash % capacity + capacity) % capacity;
}
// 插入
public void Insert(TKey key, TVal val)
{
// 超过负载因子,重新扩容
if(count / buckets.Length >= loadFactorThreshold)
{
Resize();
}
int index = GetHashIndex(key);
LinkedList<Entry> bucket = buckets[index];
if (bucket == null)
{
bucket = new LinkedList<Entry>();
}
foreach(var entry in bucket)
{
if(entry.key.Equals(key))
{
// 更新已存在的值
return;
}
}
bucket.AddLast(new Entry(key, val));
count++;
}
private void Resize()
{
int newCapacity = buckets.Length * 2;
var newBuckets = new LinkedList<Entry>[newCapacity];
foreach (var bucket in buckets)
{
if (bucket == null)
{
continue;
}
foreach (var entry in bucket)
{
int newIndex = GetHashIndex(entry.key, newCapacity);
if (newBuckets[newIndex] == null)
{
newBuckets[newIndex] = new LinkedList<Entry>();
}
newBuckets[newIndex].AddLast(entry);
}
}
buckets = newBuckets;
}
// 查找
public bool TryGetValue(TKey key, out TVal val)
{
int index = GetHashIndex(key);
var bucket = buckets[index];
if(bucket != null)
{
foreach(var entry in bucket)
{
if(entry.key.Equals(key))
{
val = entry.val;
return true;
}
}
}
val = default;
return false;
}
// 删除
public bool Delete(TKey key)
{
int index = GetHashIndex(key);
var bucket = buckets[index];
if(bucket != null)
{
var node = bucket.First;
while(node != null)
{
if(node.Value.key.Equals(key))
{
bucket.Remove(node);
count--;
return true;
}
node = node.Next;
}
}
return false;
}
}
总结
最后,做个总结,简单而言,Hash算法是一种数字摘要算法,可以看做是将无限长的字符转化为有限甚至固定长的数字。而这转化行为,有可能会产生相同的数字,也就是哈希冲突。为了解决哈希冲突,我们引入了2种解决方案,一种是开放寻址法,一种是封闭寻址法。
引用
[1] 哈希究竟代表什么?哈希表和哈希函数的核心原理
[2] C# 之Dictionary(字典)底层源码解析
[3] 【C++】关联式容器
[4] deepSeek



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号