tolua源码之小白剖析(四)
前面分析完了C#是怎么访问到lua层变量的,那我们这里就研究下lua是怎么访问到C#对象的,这也是比较重要的,因为我们在写业务逻辑的时候,大部分时间都是用lua访问C#层对象,用C#层访问lua变量还是比较少见的,以官方demo为例,08_AccessingArray:
using UnityEngine;
using LuaInterface;
public class AccessingArray : MonoBehaviour
{
private string script =
@"
function TestArray(array)
local len = array.Length
for i = 0, len - 1 do
print('Array: '..tostring(array[i]))
end
local iter = array:GetEnumerator()
while iter:MoveNext() do
print('iter: '..iter.Current)
end
local t = array:ToTable()
for i = 1, #t do
print('table: '.. tostring(t[i]))
end
local pos = array:BinarySearch(3)
print('array BinarySearch: pos: '..pos..' value: '..array[pos])
pos = array:IndexOf(4)
print('array indexof bbb pos is: '..pos)
return 1, '123', true
end
";
LuaState lua = null;
LuaFunction func = null;
string tips = null;
void Start()
{
new LuaResLoader();
lua = new LuaState();
lua.Start();
lua.DoString(script, "AccessingArray.cs");
tips = "";
int[] array = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
func = lua.GetFunction("TestArray");
func.BeginPCall();
func.Push(array);
func.PCall();
double arg1 = func.CheckNumber();
string arg2 = func.CheckString();
bool arg3 = func.CheckBoolean();
Debugger.Log("return is {0} {1} {2}", arg1, arg2, arg3);
func.EndPCall();
//调用通用函数需要转换一下类型,避免可变参数拆成多个参数传递
object[] objs = func.LazyCall((object)array);
if (objs != null)
{
Debugger.Log("return is {0} {1} {2}", objs[0], objs[1], objs[2]);
}
lua.CheckTop();
}
}
这个例子里面,lua会接收来自C#的对象,并调用它的方法(GetEnumerator,MoveNext,ToTable),以及通过下标索引进行访问。不知道大家还记不记得在第二节我们分析LuaState初始化流程时候,tolua注册了一些基础类,其中就包含我们这个例子用到的System.Array:
void OpenBaseLibs()
{
BeginModule(null);
BeginModule("System");
System_ArrayWrap.Register(this);
EndModule();//end System
EndModule(); //end global
ArrayMetatable = metaMap[typeof(System.Array)];
}
那么我们就再来重复温习一遍这个流程吧。
BeginModule(null);
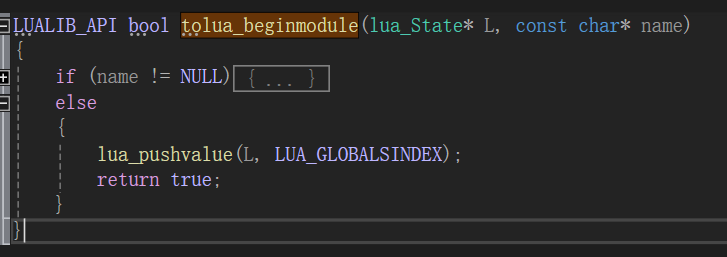
在lua栈中插入全局表,此时Lua栈状态:
BeginModule("System");
会进入到这个函数,我们来逐步分析:
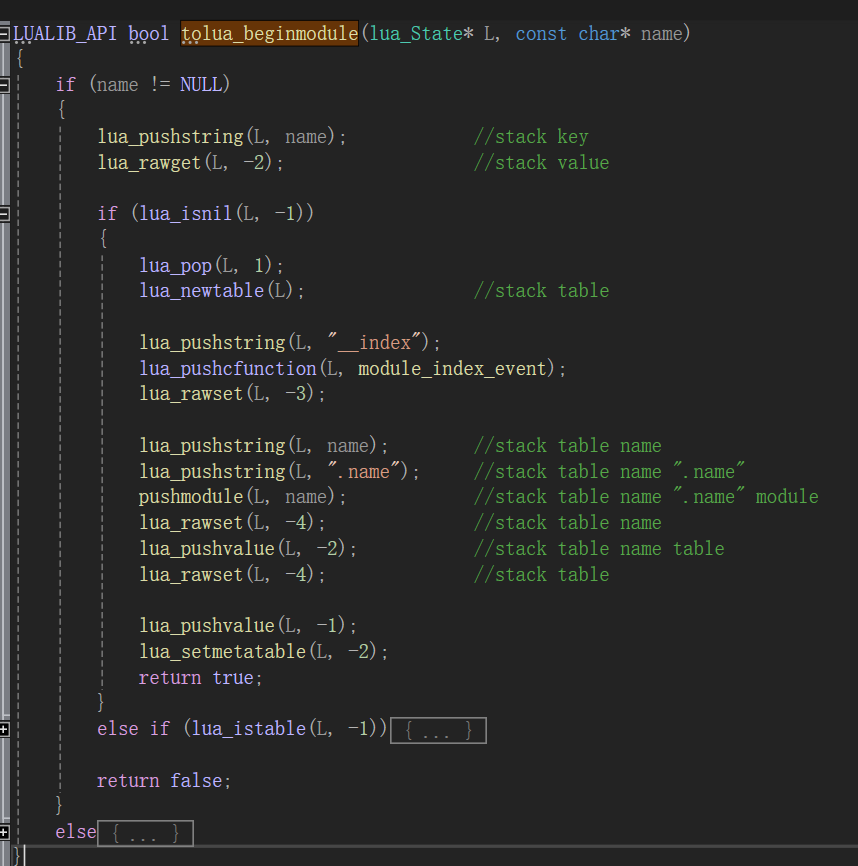
lua_pushstring(L, name); //stack key
lua_rawget(L, -2); //stack value
这里解释下-2的概念:-2表示从栈顶往下数第2个索引,此时"System"是第一个索引,"_G"是第二个索引,那这个方法表示,以"System"为key,读取_G中对应key的值,并最终把返回值留在栈顶。
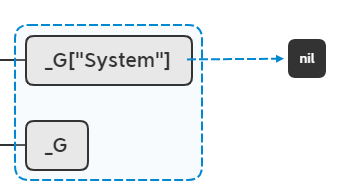
lua_pop(L, 1);
lua_newtable(L); //stack table
lua_pop表示从栈顶弹出n个元素,这里弹出1个,把nil弹出:
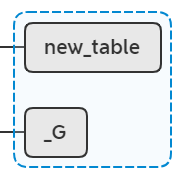
lua_pushstring(L, "__index");
lua_pushcfunction(L, module_index_event);
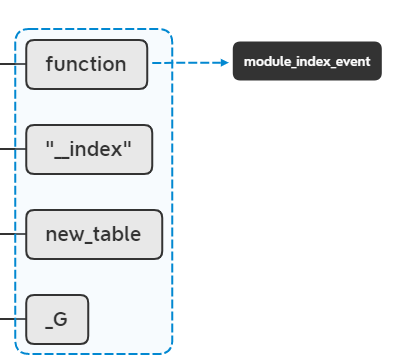
lua_rawset(L, -3);
此时,会依次从lua栈中弹出值和键,并把他们赋值给new_table。相当于执行 new_table["__index"] = function。至于module_index_event是什么,后面再解释。
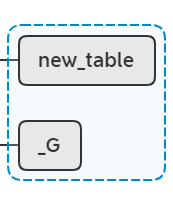
lua_pushstring(L, name); //stack table name
lua_pushstring(L, ".name"); //stack table name ".name"
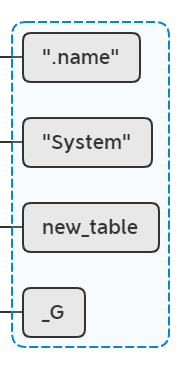
pushmodule(L, name); //stack table name ".name" module
这个函数使用了一个buffer来缓存当前注册过程中已经注册过的namespace,这样就能够通过拼接得到当前namespace的完整名称。但这里System已经是完整名称了,所以push进lua栈的还是System:
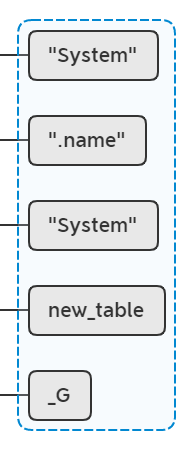
lua_rawset(L, -4); //stack table name
相当于执行 new_table[".name"] = "System",此时lua栈:
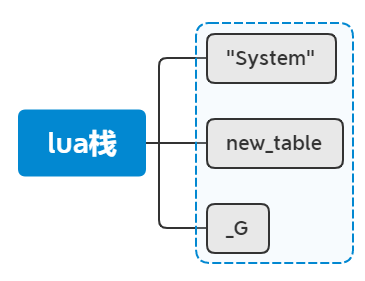
lua_pushvalue(L, -2); //stack table name table
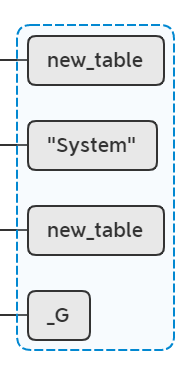
lua_rawset(L, -4); //stack table
相当于执行,_G["System"] = new_table:
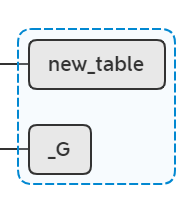
lua_pushvalue(L, -1);
lua_setmetatable(L, -2);
相当于执行setmetatable(new_table, new_table),此时堆栈:
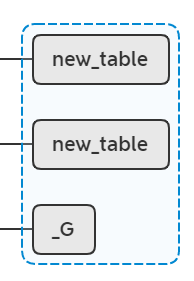
做个总结,目前为止做了哪些事情:
- 新建_G.System表
- _G.System[__index] = module_index_event
- _G.System[.name] = "System"
- setmatatable(_G.System, _G.System)
然后我们再来看看System_ArrayWrap绑定了什么(我这里只截取我们等会分析要用到的方法):
首先是BeginClass:
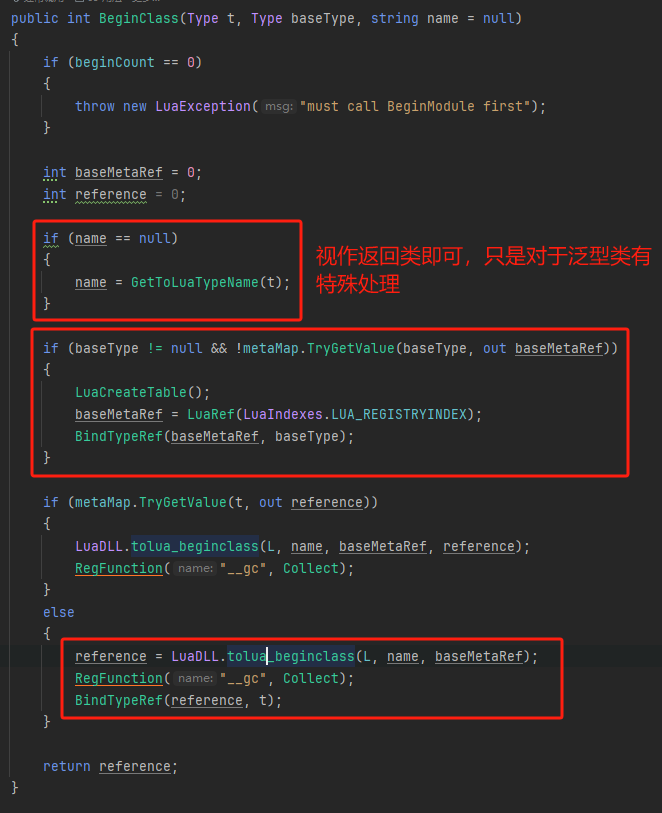
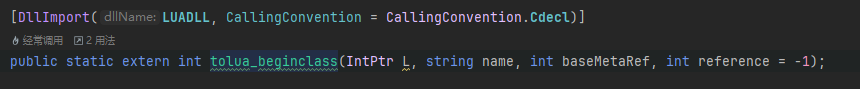
首先会判断是否有提前绑定好基类,System.Array的基类是System.Object,这个已经是提前绑定好了的。然后我们这个类型也没有生成过,自然会走我最下面表红框的区域,然后我们看看tolua_beginclass做了什么:
static void _addtoloaded(lua_State* L)
{
lua_getref(L, LUA_RIDX_LOADED);
_pushfullname(L, -3);
lua_pushvalue(L, -3);
lua_rawset(L, -3);
lua_pop(L, 1);
}
LUALIB_API int tolua_beginclass(lua_State* L, const char* name, int baseType, int ref)
{
int reference = ref;
lua_pushstring(L, name);
lua_newtable(L);
_addtoloaded(L);
if (ref == LUA_REFNIL)
{
lua_newtable(L);
lua_pushvalue(L, -1);
reference = luaL_ref(L, LUA_REGISTRYINDEX);
}
else
{
lua_getref(L, reference);
}
if (baseType != 0)
{
lua_getref(L, baseType);
lua_setmetatable(L, -2);
}
lua_pushlightuserdata(L, &tag);
lua_pushnumber(L, 1);
lua_rawset(L, -3);
lua_pushstring(L, ".name");
_pushfullname(L, -4);
lua_rawset(L, -3);
lua_pushstring(L, ".ref");
lua_pushinteger(L, reference);
lua_rawset(L, -3);
lua_pushstring(L, "__call");
lua_pushcfunction(L, class_new_event);
lua_rawset(L, -3);
tolua_setindex(L);
tolua_setnewindex(L);
return reference;
}
我们同样一步步分析,此时我们的lua栈是这样的:
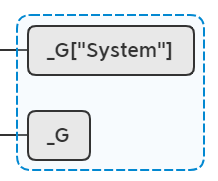
int reference = ref;
lua_pushstring(L, name);
lua_newtable(L);
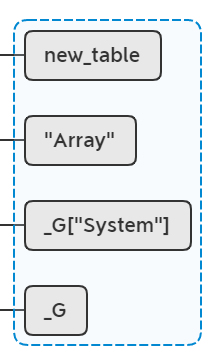
lua_getref(L, LUA_RIDX_LOADED);
_pushfullname(L, -3);
lua_pushvalue(L, -3);
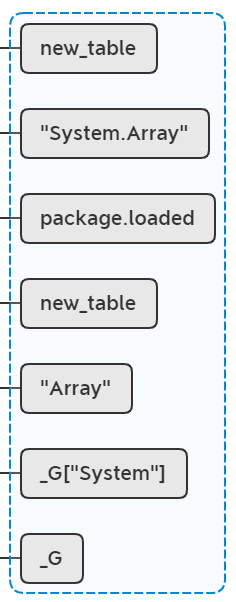
lua_rawset(L, -3);
相当于执行package.loaded["System.Array"] = new_table
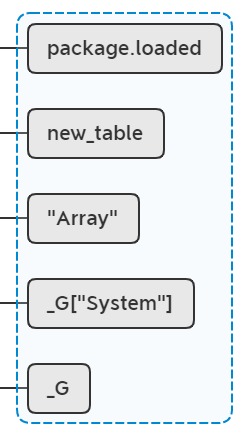
lua_pop(L, 1);
弹出栈顶:
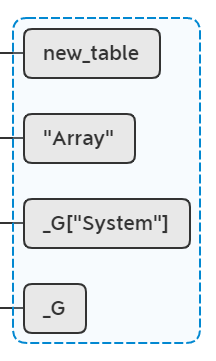
lua_newtable(L);
lua_pushvalue(L, -1);
reference = luaL_ref(L, LUA_REGISTRYINDEX);
新增一个表,并将表再压入栈一次,并根据新压入栈顶的new_table_2生成一个reference值:
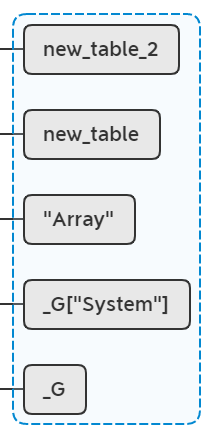
if (baseType != 0)
{
lua_getref(L, baseType);
lua_setmetatable(L, -2);
}
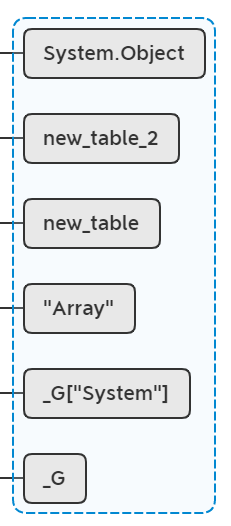
再执行setmetatable(new_table_2, System.Object)
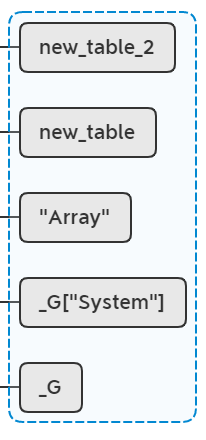
lua_pushlightuserdata(L, &tag);
lua_pushnumber(L, 1);
lua_rawset(L, -3);
相当于执行new_table_2[&tag] = 1
lua_pushstring(L, ".name");
_pushfullname(L, -4);
lua_rawset(L, -3);
相当于执行new_table_2[.name] = "System.Array"
lua_pushstring(L, ".ref");
lua_pushinteger(L, reference);
lua_rawset(L, -3);
相当于执行new_table_2[.ref] = reference
lua_pushstring(L, "__call");
lua_pushcfunction(L, class_new_event);
lua_rawset(L, -3);
相当于执行new_table_2[__call] = class_new_event,这样我们能在lua层实例化C#对象。
tolua_setindex(L);
LUALIB_API void tolua_setindex(lua_State* L)
{
lua_pushstring(L, "__index");
lua_pushcfunction(L, class_index_event);
lua_rawset(L, -3);
}
相当于执行new_table_2["__index"] = class_index_event
tolua_setnewindex(L);
LUALIB_API void tolua_setnewindex(lua_State* L)
{
lua_pushstring(L, "__newindex");
lua_pushcfunction(L, class_newindex_event);
lua_rawset(L, -3);
}
相当于执行new_table_2["__newindex"] = class_newindex_event
至此,BeginClass结束,我们来总结下BeginClass做了什么:
- 在package.loaded中保存System.Array表
- 新增一个表(new_table_2),作为System.Array的元表(在BeginClass中没实现这个,在EndClass中实现的)
- 根据new_table_2生成一个全局唯一的reference,返回给C#层
- 设置new_table_2的元表为System.Object
- 执行new_table_2[&tag] = 1,new_table_2[.name] = "System.Array",new_table_2[.ref] = reference,new_table_2[__call] = class_new_event,new_table_2["__index"] = class_index_event,new_table_2["__index"] = class_index_event
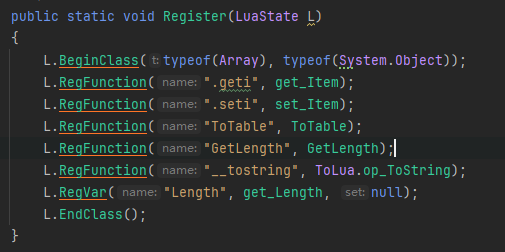
然后我们分析下L.RegFunction("GetLength", GetLength);是怎么注册进Lua层的:
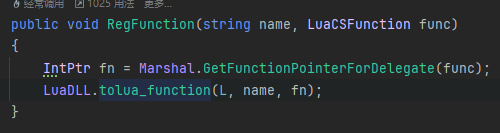
首先,是获取注册方法的指针,然后调用tolua_function进行绑定
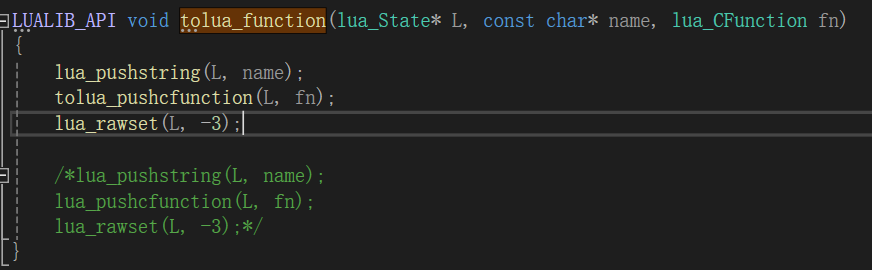
这个过程很简单,就是相当于执行了new_table_2["GetLength"] = GetLength()
然后,我们再看看属性/字段的注册:L.RegVar("Length", get_Length, null);
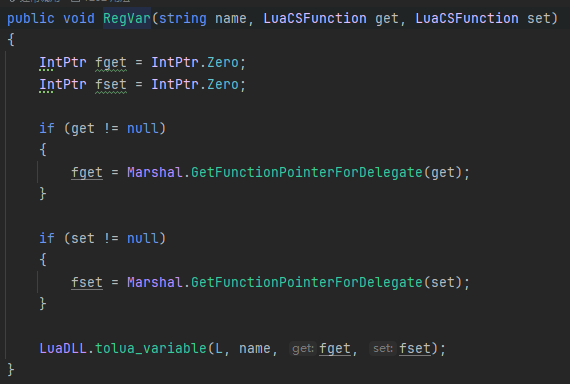
属性/字段都会生成一个get方法,set方法,然后我们获取这2个方法的指针,调用tolua_variable进行绑定。
LUALIB_API void tolua_variable(lua_State* L, const char* name, lua_CFunction get, lua_CFunction set)
{
lua_pushlightuserdata(L, &gettag);
lua_rawget(L, -2);
if (!lua_istable(L, -1))
{
/* create .get table, leaving it at the top */
lua_pop(L, 1);
lua_newtable(L);
lua_pushlightuserdata(L, &gettag);
lua_pushvalue(L, -2);
lua_rawset(L, -4);
}
lua_pushstring(L, name);
//lua_pushcfunction(L, get);
tolua_pushcfunction(L, get);
lua_rawset(L, -3); /* store variable */
lua_pop(L, 1); /* pop .get table */
/* set func */
if (set != NULL)
{
lua_pushlightuserdata(L, &settag);
lua_rawget(L, -2);
if (!lua_istable(L, -1))
{
/* create .set table, leaving it at the top */
lua_pop(L, 1);
lua_newtable(L);
lua_pushlightuserdata(L, &settag);
lua_pushvalue(L, -2);
lua_rawset(L, -4);
}
lua_pushstring(L, name);
//lua_pushcfunction(L, set);
tolua_pushcfunction(L, set);
lua_rawset(L, -3); /* store variable */
lua_pop(L, 1); /* pop .set table */
}
}
这个就比较复杂了,我们也逐行分析一下:
lua_pushlightuserdata(L, &gettag);
lua_rawget(L, -2);
获取new_table_2[&gettag]值,这个因为首次创建必然为nil
if (!lua_istable(L, -1))
{
/* create .get table, leaving it at the top */
lua_pop(L, 1);
......
}
弹出nil
if (!lua_istable(L, -1))
{
......
lua_newtable(L);
lua_pushlightuserdata(L, &gettag);
lua_pushvalue(L, -2);
lua_rawset(L, -4);
}
新建一个表new_table_3,然后执行new_table_2[&gettag] = new_table_3,此时lua栈:
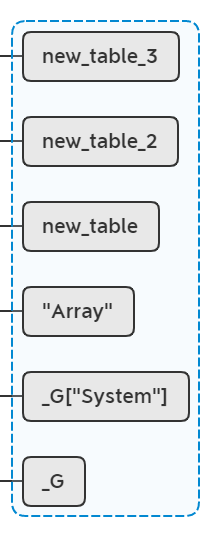
lua_pushstring(L, name);
//lua_pushcfunction(L, get);
tolua_pushcfunction(L, get);
lua_rawset(L, -3); /* store variable */
相当于执行new_table_3["length"] = get()
lua_pop(L, 1); /* pop .get table */
弹出new_table_3,此时lua栈恢复:
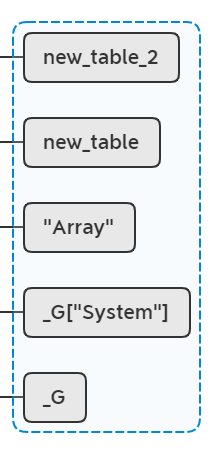
if (set != NULL)
{
lua_pushlightuserdata(L, &settag);
lua_rawget(L, -2);
if (!lua_istable(L, -1))
{
/* create .set table, leaving it at the top */
lua_pop(L, 1);
lua_newtable(L);
lua_pushlightuserdata(L, &settag);
lua_pushvalue(L, -2);
lua_rawset(L, -4);
}
lua_pushstring(L, name);
//lua_pushcfunction(L, set);
tolua_pushcfunction(L, set);
lua_rawset(L, -3); /* store variable */
lua_pop(L, 1); /* pop .set table */
}
set方法与get方法类似,不做分析,做个总结:
- 注册C#层方法,会先获取该方法的指针,然后以元表["方法名"] = 方法指针;的方式进行存入
- 注册C#层属性和字段,在Wrap文件中,会分别输出它们的get方法和set方法,同样会获得它们的指针。然后判断元表[&gettag]表,元表[&settag]表是否存在,不存在就创建一下,然后将get和set方法分别存入,例如length属性就按照元表[&gettag][length] = get()进行存储。
注册完毕,执行EndClass
LUALIB_API void tolua_endclass(lua_State* L)
{
lua_setmetatable(L, -2);
lua_rawset(L, -3);
}
相当于执行setmetatable(new_table, new_table_2),_G["System"]["Array"] = new_table,此时lua栈恢复:
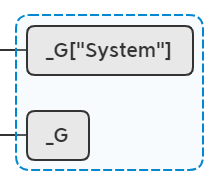
所有类都注册完毕,,执行EndModule
LUALIB_API void tolua_endmodule(lua_State* L)
{
lua_pop(L, 1);
int len = (int)sb.len;
while (len-- >= 0)
{
if (sb.buffer[len] == '.')
{
sb.len = len;
return;
}
}
sb.len = 0;
}
弹出栈顶,恢复buffer缓存,此时lua栈:
然后再执行一次执行EndModule,弹出_G,至此,C#注册进lua层分析完毕。
接下来,我们来分析第二个关键点,C#层的array对象是怎么注册进行lua层的。
func.Push(array);
public void Push(Array array)
{
luaState.Push(array);
++argCount;
}
public void Push(Array array)
{
if (array == null)
{
LuaPushNil();
}
else
{
PushUserData(array, ArrayMetatable);
}
}
void PushUserData(object o, int reference)
{
int index;
if (translator.Getudata(o, out index))
{
if (LuaDLL.tolua_pushudata(L, index))
{
return;
}
translator.Destroyudata(index);
}
index = translator.AddObject(o);
LuaDLL.tolua_pushnewudata(L, reference, index);
}
之前漏说一点,BeginClass不是会返回一个reference值,这个值会以LuaState.metaMap[System.Array] = reference的方式进行保存,这个ArrayMetatable就是LuaState.metaMap[System.Array]。解释清楚这一点后,我们直接来看最后一个函数,PushUserData。
index = translator.AddObject(o);
LuaDLL.tolua_pushnewudata(L, reference, index);
public int AddObject(object obj)
{
int index = objects.Add(obj);
if (!TypeChecker.IsValueType(obj.GetType()))
{
objectsBackMap[obj] = index;
}
return index;
}
首先会给这个obj对象新增一个index值,如果该obj对象不属于值类型,会在objectsBackMap缓存起来,然后调用该tolua_pushnewudata方法,传入System.Array的reference值,和给这个对象刚刚创建好的index索引,我们来看C层代码:
LUALIB_API void tolua_pushnewudata(lua_State* L, int metaRef, int index)
{
lua_getref(L, LUA_RIDX_UBOX);
tolua_newudata(L, index);
lua_getref(L, metaRef);
lua_setmetatable(L, -2);
lua_pushvalue(L, -1);
lua_rawseti(L, -3, index);
lua_remove(L, -2);
}
- 这里lua新建立了一个userData,并给该userData索引赋值为index
- 取出System.Array表,将System.Array设置为userData元表
- LUA_RIDX_UBOX[index] = userData
- 移除LUA_RIDX_UBOX出栈,此时栈中保留刚刚建立好的userData
经过这一个步骤,C#层的array就被压入栈中了。此时lua栈:
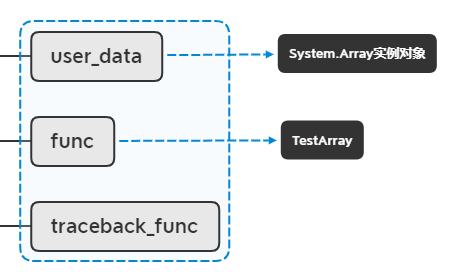
func.PCall();
然后执行lua方法,
local len = array.Length
不知道兄弟们还记不记得我们之前建立的元表中__index的元方法,当我们在userData找不到Length时,自然就去元表的__index方法中寻找了:
static int class_index_event(lua_State* L)
{
int t = lua_type(L, 1);
if (t == LUA_TUSERDATA)
{
lua_getfenv(L, 1);
if (!lua_rawequal(L, -1, TOLUA_NOPEER)) // stack: t k env
{
while (lua_istable(L, -1)) // stack: t k v mt
{
lua_pushvalue(L, 2);
lua_rawget(L, -2);
if (!lua_isnil(L, -1))
{
return 1;
}
lua_pop(L, 1);
lua_pushlightuserdata(L, &gettag);
lua_rawget(L, -2); //stack: obj key env tget
if (lua_istable(L, -1))
{
lua_pushvalue(L, 2); //stack: obj key env tget key
lua_rawget(L, -2); //stack: obj key env tget func
if (lua_isfunction(L, -1))
{
lua_pushvalue(L, 1);
lua_call(L, 1, 1);
return 1;
}
lua_pop(L, 1);
}
lua_pop(L, 1);
if (lua_getmetatable(L, -1) == 0) // stack: t k v mt mt
{
lua_pushnil(L);
}
lua_remove(L, -2); // stack: t k v mt
}
};
lua_settop(L, 2);
lua_pushvalue(L, 1); // stack: obj key obj
while (lua_getmetatable(L, -1) != 0)
{
lua_remove(L, -2); // stack: obj key mt
if (lua_isnumber(L, 2)) // check if key is a numeric value
{
lua_pushstring(L, ".geti");
lua_rawget(L, -2); // stack: obj key mt func
if (lua_isfunction(L, -1))
{
lua_pushvalue(L, 1);
lua_pushvalue(L, 2);
lua_call(L, 2, 1);
return 1;
}
}
else
{
lua_pushvalue(L, 2); // stack: obj key mt key
lua_rawget(L, -2); // stack: obj key mt value
if (!lua_isnil(L, -1))
{
return 1;
}
lua_pop(L, 1);
lua_pushlightuserdata(L, &gettag);
lua_rawget(L, -2); //stack: obj key mt tget
if (lua_istable(L, -1))
{
lua_pushvalue(L, 2); //stack: obj key mt tget key
lua_rawget(L, -2); //stack: obj key mt tget value
if (lua_isfunction(L, -1))
{
lua_pushvalue(L, 1);
lua_call(L, 1, 1);
return 1;
}
}
}
lua_settop(L, 3);
}
lua_settop(L, 2);
int* udata = (int*)lua_touserdata(L, 1);
if (*udata == LUA_NULL_USERDATA)
{
return luaL_error(L, "attemp to index %s on a nil value", lua_tostring(L, 2));
}
if (toluaflags & FLAG_INDEX_ERROR)
{
return luaL_error(L, "field or property %s does not exist", lua_tostring(L, 2));
}
}
else if (t == LUA_TTABLE)
{
lua_pushvalue(L, 1); //stack: obj key obj
while (lua_getmetatable(L, -1) != 0) //stack: obj key obj mt
{
lua_remove(L, -2); // stack: obj key mt
lua_pushvalue(L, 2); // stack: obj key mt key
lua_rawget(L, -2); // stack: obj key mt value
if (!lua_isnil(L, -1))
{
if (lua_isfunction(L, -1)) //cache static function
{
lua_pushvalue(L, 2); // stack: obj key mt value key
lua_pushvalue(L, -2); // stack: obj key mt value key value
lua_rawset(L, 1);
}
return 1;
}
lua_pop(L, 1);
lua_pushlightuserdata(L, &gettag);
lua_rawget(L, -2); //stack: obj key mt tget
if (lua_istable(L, -1))
{
lua_pushvalue(L, 2); //stack: obj key mt tget key
lua_rawget(L, -2); //stack: obj key mt tget value
if (lua_isfunction(L, -1))
{
lua_pushvalue(L, 1);
lua_call(L, 1, 1);
return 1;
}
}
lua_settop(L, 3);
}
if (_preload(L))
{
return 1;
}
if (toluaflags & FLAG_INDEX_ERROR)
{
return luaL_error(L, "field or property %s does not exist", lua_tostring(L, 2));
}
}
lua_pushnil(L);
return 1;
}
很长,很复杂,我们一点点分析。此时堆栈情况:
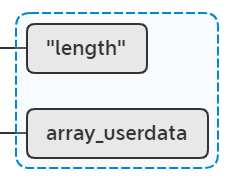
int t = lua_type(L, 1);
t必然是user_data,然后执行:
lua_getfenv(L, 1);
将array_userdata的环境表压入栈,此时lua栈环境:
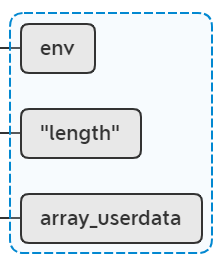
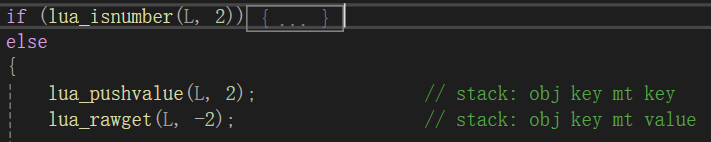
if (!lua_rawequal(L, -1, TOLUA_NOPEER))
这里返回false,不走这个判断。
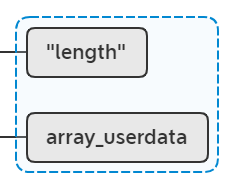
lua_settop(L, 2);
强制从栈低开始到栈顶只保留3个元素,其他全部丢掉,就是只保留 array_userdata | "length",此时lua栈:
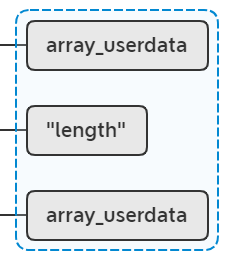
lua_pushvalue(L, 1); // stack: obj key obj
while (lua_getmetatable(L, -1) != 0)
取出array_userdata的元表:
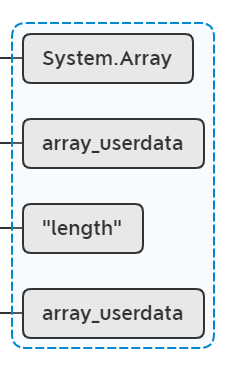
lua_remove(L, -2); // stack: obj key mt
移除从栈顶开始往下数第2个元素:
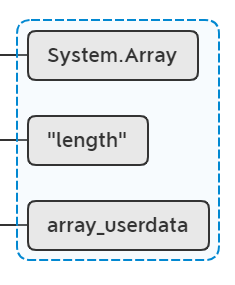
然后判断从栈低往上数第2个元素,也就是"length"是不是nbmber,这必然不是,走else以下语法。
lua_pushvalue(L, 2); // stack: obj key mt key
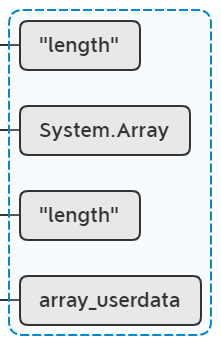
lua_rawget(L, -2); // stack: obj key mt value
相当于取值System.Array["length"],这必然为nil,因为length是属性,不直接存在System.Array表中。
if (!lua_isnil(L, -1))
{
return 1;
}
lua_pop(L, 1);
这里判断下栈顶是不是nil,不是nil则表示取到了,这里没有取得,执行lua_pop(L,1)方法,移除栈顶元素:
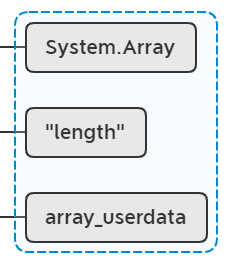
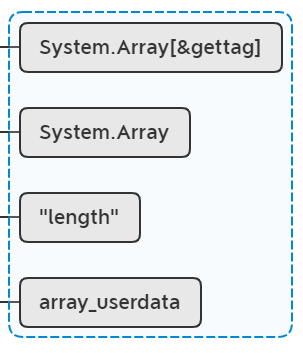
lua_pushlightuserdata(L, &gettag);
lua_rawget(L, -2); //stack: obj key mt tget
if (lua_istable(L, -1))
前面我们分析过了,System.Array[&gettag]是一个表来的,所以这里必然返回true。
lua_pushvalue(L, 2); //stack: obj key mt tget key
lua_rawget(L, -2); //stack: obj key mt tget value
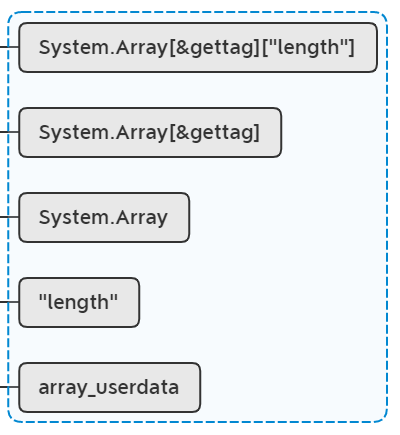
if (lua_isfunction(L, -1))
{
lua_pushvalue(L, 1);
lua_call(L, 1, 1);
return 1;
}
System.Array[&gettag]["length"]存储了get方法指针,此时再将array_userdata压入栈顶:
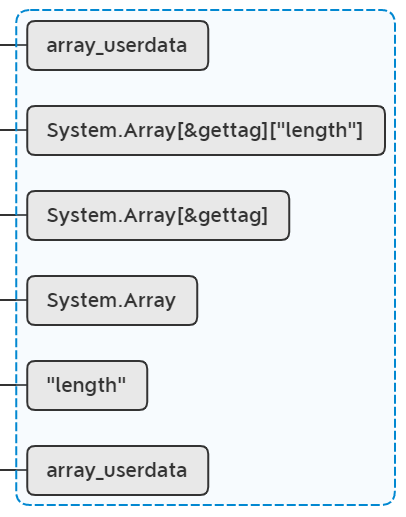
lua_call(L, 1, 1);
Lua函数调用遵循参数正序压栈规则,此处将对象自身(如 obj)作为第一个参数传递给函数,模拟 array_userdata:length() 的调用方式。然后这里就调用到了C#层的逻辑了,我们来看看C#层代码是怎么实现的。
[MonoPInvokeCallbackAttribute(typeof(LuaCSFunction))]
static int get_Length(IntPtr L)
{
try
{
Array obj = ToLua.ToObject(L, 1) as Array;
if (obj == null)
{
throw new LuaException("trying to index an invalid object reference");
}
LuaDLL.lua_pushinteger(L, obj.Length);
return 1;
}
catch (Exception e)
{
return LuaDLL.toluaL_exception(L, e);
}
}
首先看Array obj = ToLua.ToObject(L, 1) as Array;
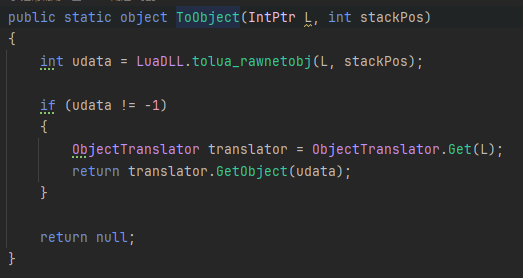
这里从取得栈低的reference值,还记得我们之前插入array元素到lua时,缓存了一个reference值嘛,此时我们根据这个值就能找到C#层中对应的对象。
LuaDLL.lua_pushinteger(L, obj.Length);
然后调用C#层接口,获得数组长度,并将长度值压入栈顶。至此分析结束。
然后这里做个总结,当在lua层调用C#接口时,
- 会去寻找lua层的C#对象(userdata)对应的元表
- 判断元表中是不是存在对应key的方法,如果不存在再判断下元表[&gettag]是否存在对应key的方法。
- 找到该方法后,这个方法是从c#层Wrap文件注册的,我们此时就执行到C#层注册的该方法。
- 然后这个方法有返回值,我们在C#层执行对应的Api接口,并将返回值插入lua栈中。
- 最后,lua层就能从栈顶获得返回值了。
看到这里,兄弟们不知道会不会有个疑问,这个东西,它性能消耗点在哪里?因为类型对象表都是提前注册好,而且也执行一次,这里的性能消耗点,相比于在C#层直接执行对应API,细看下来应该是多了这么几点:
- 寻找对应C#方法指针的过程
- 在C#层取得栈低元素的reference,然后在C#层找到该reference对应的C#对象
- 将API的返回值,插入到lua栈中。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号