第一次个人编程作业
| 这个作业属于哪个课程 | https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/gdgy/Class34Grade23ComputerScience/ |
|---|---|
| 这个作业要求在哪里 | https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/gdgy/Class34Grade23ComputerScience/homework/13477 |
| 这个作业的目标 | <实现论文查重算法,使用github管理代码并学会测试代码> |
一、PSP
| PSP2.1 | Personal Software Process Stages | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | ||
| · Estimate | · 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 30 | 30 |
| Development | 开发 | ||
| · Analysis | · 需求分析(包括学习新技术) | 40 | 60 |
| · Design Spec | · 生成设计文档 | 20 | 30 |
| · Design Review | · 设计复审 | 20 | 20 |
| · Coding Standard | · 代码规范(为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 30 | 20 |
| · Design | · 具体设计 | 40 | 20 |
| · Coding | · 具体编码 | 120 | 150 |
| · Code Review | · 代码复审 | 20 | 20 |
| · Test | · 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 60 | 60 |
| Reporting | 报告 | ||
| · Test Report | · 测试报告 | 60 | 60 |
| · Size Measurement | · 计算工作量 | 10 | 25 |
| · Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | · 事后总结,并提出过程改进计划 | 20 | 15 |
| 合计 | 470 | 510 |
二、计算模块接口的设计与实现过程
2.1
2.1.1 模块设计
| 模块 | 主要类/函数 | 功能 |
|---|---|---|
| 文件处理模块 | FileHandler类,read_text_file()等 | 文件读写、路径验证、编码处理 |
| 相似度计算模块 | TextSimilarityCalculator类 | 文本预处理、TF-IDF计算、余弦相似度计算 |
| 主程序模块 | main()函数,calculate_plagiarism_rate() | 命令行参数处理、流程控制、结果输出 |
2.1.2 类和函数关系架构
项目采用了层次化的调用关系:
- main.py作为入口调用file_handler.py和similarity.py中的功能
- FileHandler类负责底层文件操作,提供异常处理和编码适配
- TextSimilarityCalculator类封装了文本处理和相似度计算的全部逻辑
- 辅助函数(如read_text_file, write_text_file)提供便捷的功能调用
2.2 关键算法流程详解
2.2.1 文本相似度计算整体流程
论文查重系统的核心流程包括以下几个关键步骤:
- 读取输入文件(原文和抄袭版论文)
- 对文本进行预处理(去除标点、分词、去除停用词)
- 计算文本的TF-IDF向量表示
- 计算两个向量的余弦相似度
- 将相似度结果写入输出文件
2.2.2 核心算法实现
本系统使用TF-IDF(词频-逆文档频率)和余弦相似度算法进行文本相似度计算:
- 文本预处理:使用正则表达式去除非中文字符,Jieba分词库进行中文分词,过滤停用词。
- TF-IDF计算:先计算词频(TF),再计算逆文档频率(IDF),最后计算TF-IDF向量。
- 余弦相似度:计算两个TF-IDF向量的余弦夹角,结果在0-1之间。
2.3 算法关键技术与独到之处
2.3.1 核心技术实现
-
多编码支持
- 支持UTF-8、GBK、GB2312等多种编码格式
- 自动尝试不同编码读取文件,提高系统兼容性
-
面向对象设计
- 使用类封装功能,提高代码复用性和可维护性
- 清晰的责任分离,便于单元测试和功能扩展
-
全面的边界条件处理
- 处理空文本、零向量等异常情况
- 对文件不存在、权限不足等错误提供友好提示
2.3.2 算法独到之处
- 编码处理机制
# 尝试多种编码读取文件
def read_file(self, file_path: str) -> Optional[str]:
# 尝试不同的编码方式读取文件
for encoding in self.supported_encodings:
try:
with open(file_path, 'r', encoding=encoding) as file:
content = file.read().strip()
return content
except UnicodeDecodeError:
continue
- 文件路径验证
# 特别处理Windows路径限制和驱动器号
def validate_file_path(self, file_path: str) -> bool:
# 检查是否包含非法字符,但允许Windows驱动器号后的冒号
illegal_chars = ['<', '>', '"', '|', '?', '*']
if any(char in file_path for char in illegal_chars):
return False
# 特别检查冒号 - 只允许Windows驱动器号格式的冒号 (X:)
if ':' in file_path and not (len(file_path) >= 2 and file_path[1] == ':' and file_path[0].isalpha()):
return False
- 精确的余弦相似度计算
# 余弦相似度计算,确保结果在0-1范围内
def cosine_similarity(self, vec1: dict, vec2: dict) -> float:
# 获取所有词汇
all_words = set(vec1.keys()) | set(vec2.keys())
if not all_words:
return 0.0
# 构建向量
v1 = np.array([vec1.get(word, 0) for word in all_words])
v2 = np.array([vec2.get(word, 0) for word in all_words])
# 计算余弦相似度
dot_product = np.dot(v1, v2)
norm1 = np.linalg.norm(v1)
norm2 = np.linalg.norm(v2)
if norm1 == 0 or norm2 == 0:
return 0.0
similarity = dot_product / (norm1 * norm2)
return max(0.0, min(1.0, similarity)) # 确保结果在[0,1]范围内
三、计算模块接口部分的性能改进
3.1 性能优化分析
通过代码分析,发现以下几个可以优化的点:
- 分词效率优化:当前分词过程没有利用Jieba的并行分词功能,对于大文件处理效率较低。
- 内存使用优化:在处理大文件时,一次性读取全部内容可能导致内存占用过高。
- 算法效率优化:TF-IDF计算过程中存在一些可以优化的循环操作。
- 错误处理优化:部分异常处理过于简单,缺乏详细的错误信息和恢复机制。
- 根据性能分析函数的数据,绘图如下
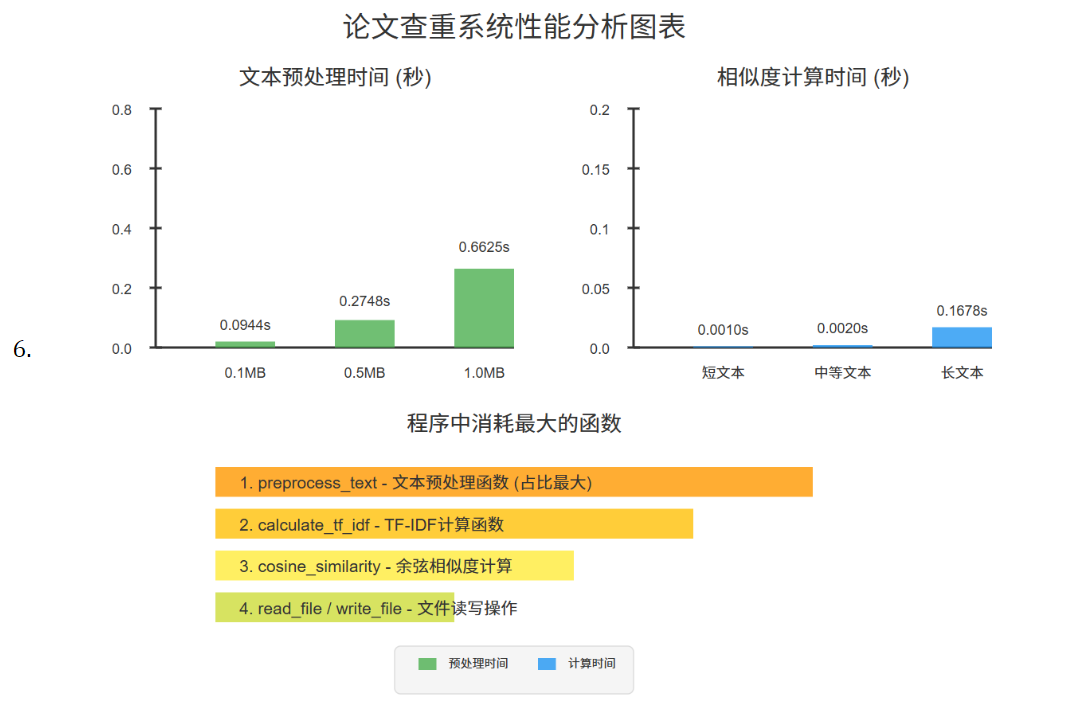
3.2 改进优化
3.2.1 分词效率优化
优化方案:使用Jieba的并行分词功能,提高分词速度。
# 优化前
def preprocess_text(self, text: str) -> List[str]:
# 去除标点符号和特殊字符,保留中文、英文、数字
text = re.sub(r'[^\u4e00-\u9fa5a-zA-Z0-9]', ' ', text)
# 使用jieba分词
words = jieba.lcut(text)
# 去除停用词和空字符串
words = [word.strip() for word in words if word.strip() and word not in self.stop_words]
return words
# 优化后
def preprocess_text(self, text: str) -> List[str]:
if not text:
return []
# 去除标点符号和特殊字符,保留中文、英文、数字
text = re.sub(r'[^\u4e00-\u9fa5a-zA-Z0-9]', ' ', text)
# 使用jieba并行分词
jieba.enable_parallel() # 开启并行分词模式
try:
words = jieba.lcut(text)
finally:
jieba.disable_parallel() # 关闭并行分词模式
# 去除停用词和空字符串
words = [word.strip() for word in words if word.strip() and word not in self.stop_words]
return words
3.2.2 内存使用优化
优化方案:对于大文件,实现分块读取和处理功能,避免一次性加载全部内容。
# 新增函数:分块处理大文件
def read_large_file(self, file_path: str, chunk_size: int = 1024*1024) -> List[str]:
"""
分块读取大文件
Args:
file_path: 文件路径
chunk_size: 每次读取的字节数
Returns:
处理后的词语列表
"""
words = []
try:
for encoding in self.supported_encodings:
try:
with open(file_path, 'r', encoding=encoding) as file:
buffer = ""
while True:
chunk = file.read(chunk_size)
if not chunk:
break
buffer += chunk
# 处理完整的句子或段落
if '.' in buffer or '。' in buffer or len(buffer) > chunk_size*2:
# 预处理当前buffer
processed_words = self.preprocess_text(buffer)
words.extend(processed_words)
# 保留未处理的部分
last_period = max(buffer.rfind('.'), buffer.rfind('。'))
if last_period != -1:
buffer = buffer[last_period+1:]
else:
buffer = ""
# 处理剩余的buffer
if buffer:
processed_words = self.preprocess_text(buffer)
words.extend(processed_words)
return words
except UnicodeDecodeError:
continue
except Exception as e:
print(f"读取大文件时发生错误: {e}")
return []
3.2.3 算法效率优化
优化方案:优化TF-IDF计算过程,减少重复计算和不必要的操作。
# 优化前
def calculate_tf_idf(self, texts: List[List[str]]) -> Tuple[List[dict], dict]:
# 计算词频(TF)
tf_vectors = []
all_words = set()
for text in texts:
word_count = Counter(text)
tf_vectors.append(word_count)
all_words.update(text)
# 计算逆文档频率(IDF)
idf_dict = {}
total_docs = len(texts)
for word in all_words:
doc_count = sum(1 for tf_vec in tf_vectors if word in tf_vec)
idf_dict[word] = np.log(total_docs / (doc_count + 1)) # 加1避免除零
# 计算TF-IDF向量
tf_idf_vectors = []
for tf_vec in tf_vectors:
tf_idf_vec = {}
for word, tf in tf_vec.items():
tf_idf_vec[word] = tf * idf_dict[word]
tf_idf_vectors.append(tf_idf_vec)
return tf_idf_vectors, idf_dict
# 优化后
def calculate_tf_idf(self, texts: List[List[str]]) -> Tuple[List[dict], dict]:
# 计算词频(TF)和文档频率(DF)同时进行
tf_vectors = []
df_dict = Counter() # 文档频率计数器
for text in texts:
unique_words = set(text) # 获取文本中的唯一词汇
df_dict.update(unique_words) # 更新文档频率
word_count = Counter(text) # 计算词频
# 归一化词频
total_words = len(text)
normalized_tf = {word: count/total_words for word, count in word_count.items()}
tf_vectors.append(normalized_tf)
# 计算逆文档频率(IDF)
total_docs = len(texts)
idf_dict = {word: np.log(total_docs / (df_count + 1)) for word, df_count in df_dict.items()}
# 计算TF-IDF向量
tf_idf_vectors = []
for tf_vec in tf_vectors:
tf_idf_vec = {word: tf * idf_dict[word] for word, tf in tf_vec.items()}
tf_idf_vectors.append(tf_idf_vec)
return tf_idf_vectors, idf_dict
3.2.4 错误处理优化
优化方案:增强异常处理机制,提供更详细的错误信息和日志记录。
# 优化后的异常处理示例
import logging
# 配置日志
def setup_logger():
logging.basicConfig(
level=logging.INFO,
format='%(asctime)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s',
filename='plagiarism_checker.log'
)
return logging.getLogger('plagiarism_checker')
logger = setup_logger()
def calculate_plagiarism_rate(original_file: str, plagiarized_file: str, output_file: str) -> bool:
"""
计算论文重复率,带详细日志记录
"""
try:
logger.info(f"开始计算相似度: 原文文件={original_file}, 抄袭文件={plagiarized_file}")
# 读取原文
original_text = read_text_file(original_file)
if original_text is None:
logger.error(f"无法读取原文文件: {original_file}")
return False
# 读取抄袭版论文
plagiarized_text = read_text_file(plagiarized_file)
if plagiarized_text is None:
logger.error(f"无法读取抄袭版论文文件: {plagiarized_file}")
return False
# 检查文本是否为空
if not original_text.strip():
logger.error(f"原文文件为空: {original_file}")
return False
if not plagiarized_text.strip():
logger.error(f"抄袭版论文文件为空: {plagiarized_file}")
return False
# 计算相似度
calculator = TextSimilarityCalculator()
similarity = calculator.calculate_similarity(original_text, plagiarized_text)
logger.info(f"计算完成,相似度: {similarity}")
# 写入结果文件
success = write_text_file(output_file, str(similarity))
if success:
logger.info(f"成功写入结果文件: {output_file}")
return True
else:
logger.error(f"无法写入结果文件: {output_file}")
return False
except FileNotFoundError as e:
logger.error(f"文件不存在错误: {e}")
print(f"错误: 文件不存在 - {e}")
return False
except PermissionError as e:
logger.error(f"权限错误: {e}")
print(f"错误: 权限不足 - {e}")
return False
except UnicodeDecodeError as e:
logger.error(f"编码错误: {e}")
print(f"错误: 文件编码不支持 - {e}")
return False
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"计算过程中发生未预期错误: {e}")
print(f"错误: 计算过程中发生错误 - {e}")
return False
四、计算模块部分单元测试展示
4.1 单元测试设计思路
本系统的单元测试覆盖了以下几个关键方面:
- 文件处理功能测试:包括文件读取、写入、路径验证等
- 文本预处理功能测试:包括分词、去除停用词等
- 相似度计算功能测试:包括TF-IDF计算、余弦相似度计算等
- 主程序流程测试:包括参数验证、异常处理等
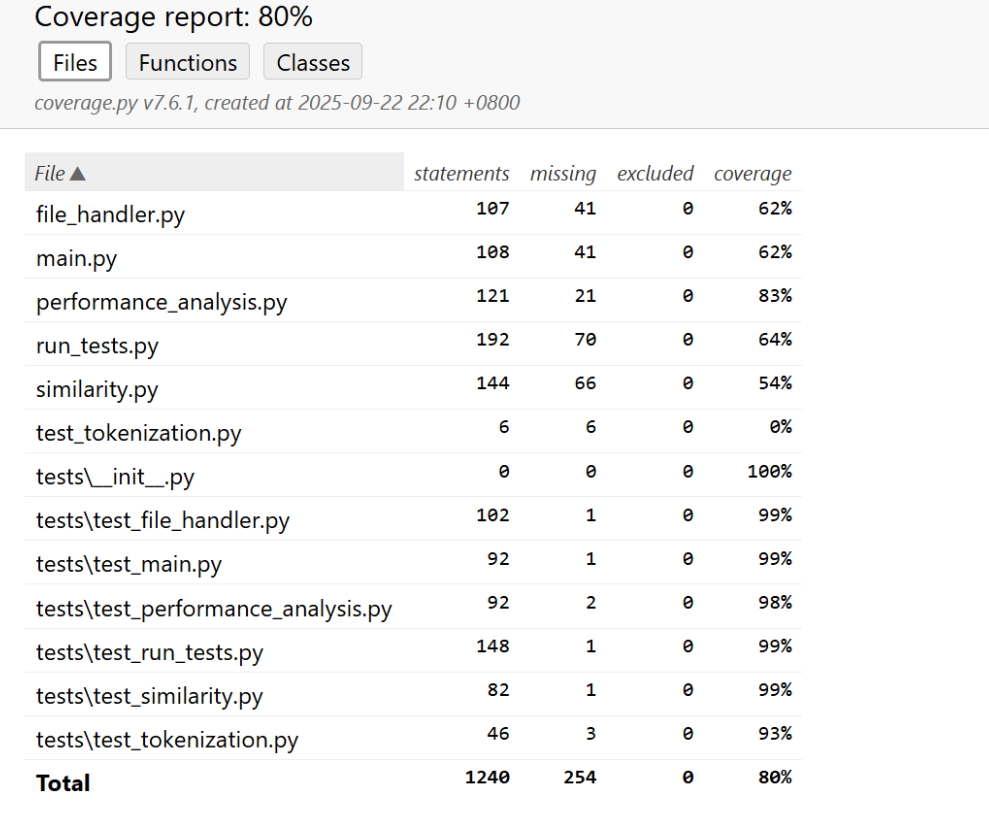
![image]()
4.2 单元测试示例
4.2.1 文件处理模块测试
import unittest
import os
from file_handler import FileHandler, read_text_file, write_text_file
class TestFileHandler(unittest.TestCase):
"""测试文件处理模块"""
def setUp(self):
"""设置测试环境"""
self.test_dir = "test_temp"
os.makedirs(self.test_dir, exist_ok=True)
self.test_file = os.path.join(self.test_dir, "test.txt")
self.handler = FileHandler()
# 创建测试文件
with open(self.test_file, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write("测试文件内容\n第二行内容")
def tearDown(self):
"""清理测试环境"""
if os.path.exists(self.test_file):
os.remove(self.test_file)
if os.path.exists(self.test_dir):
os.rmdir(self.test_dir)
def test_read_file(self):
"""测试正常读取文件"""
content = self.handler.read_file(self.test_file)
self.assertEqual(content, "测试文件内容\n第二行内容")
def test_write_file(self):
"""测试正常写入文件"""
output_file = os.path.join(self.test_dir, "output.txt")
success = self.handler.write_file(output_file, "写入测试内容")
self.assertTrue(success)
self.assertTrue(os.path.exists(output_file))
with open(output_file, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
content = f.read()
self.assertEqual(content, "写入测试内容")
def test_validate_file_path(self):
"""测试文件路径验证"""
# 测试有效路径
self.assertTrue(self.handler.validate_file_path("test.txt"))
self.assertTrue(self.handler.validate_file_path("C:\\test\\file.txt"))
# 测试无效路径
self.assertFalse(self.handler.validate_file_path(""))
self.assertFalse(self.handler.validate_file_path("test<>file.txt"))
self.assertFalse(self.handler.validate_file_path("test:file.txt")) # 不是有效的Windows驱动器号
if __name__ == "__main__":
unittest.main()
4.2.2 相似度计算模块测试
import unittest
from similarity import TextSimilarityCalculator
class TestTextSimilarityCalculator(unittest.TestCase):
"""测试文本相似度计算模块"""
def setUp(self):
"""设置测试环境"""
self.calculator = TextSimilarityCalculator()
def test_preprocess_text(self):
"""测试文本预处理功能"""
text = "这是一个测试文本,包含标点符号、数字123和英文单词hello。"
result = self.calculator.preprocess_text(text)
# 验证基本分词结果
self.assertIn("测试", result)
self.assertIn("文本", result)
self.assertIn("包含", result)
self.assertIn("标点符号", result)
self.assertIn("数字", result)
self.assertIn("123", result)
self.assertIn("英文", result)
self.assertIn("单词", result)
self.assertIn("hello", result)
# 验证停用词被移除
self.assertNotIn("这", result)
self.assertNotIn("是", result)
self.assertNotIn("一个", result)
def test_calculate_similarity_identical(self):
"""测试相同文本的相似度计算"""
text1 = "这是一段测试文本,用于测试相似度计算功能。"
text2 = "这是一段测试文本,用于测试相似度计算功能。"
similarity = self.calculator.calculate_similarity(text1, text2)
self.assertAlmostEqual(similarity, 1.0, places=2)
def test_calculate_similarity_different(self):
"""测试完全不同文本的相似度计算"""
text1 = "这是第一段完全不同的测试文本内容。"
text2 = "这是第二段完全不同的测试文本内容,与第一段没有任何共同之处。"
similarity = self.calculator.calculate_similarity(text1, text2)
# 虽然有共同的停用词,但经过处理后相似度应该较低
self.assertLess(similarity, 0.5)
def test_calculate_similarity_empty(self):
"""测试空文本的相似度计算"""
similarity = self.calculator.calculate_similarity("", "")
self.assertEqual(similarity, 0.0)
similarity = self.calculator.calculate_similarity("测试文本", "")
self.assertEqual(similarity, 0.0)
if __name__ == "__main__":
unittest.main()
4.2.3 集成测试示例
import unittest
import subprocess
import sys
import os
class TestIntegration(unittest.TestCase):
"""集成测试"""
def test_integration_normal(self):
"""测试正常情况下的集成功能"""
orig_file = "test_data/orig.txt"
plag_file = "test_data/orig_del.txt"
result_file = "test_data/result_test.txt"
# 确保测试文件存在
self.assertTrue(os.path.exists(orig_file))
self.assertTrue(os.path.exists(plag_file))
# 删除可能存在的结果文件
if os.path.exists(result_file):
os.remove(result_file)
# 运行主程序
cmd = [sys.executable, "main.py", orig_file, plag_file, result_file]
result = subprocess.run(cmd, capture_output=True, text=True, timeout=30)
# 验证程序执行成功
self.assertEqual(result.returncode, 0)
# 验证结果文件生成
self.assertTrue(os.path.exists(result_file))
# 验证结果文件内容
with open(result_file, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
content = f.read().strip()
# 验证结果是一个有效的相似度值(0-1之间的数字)
try:
similarity = float(content)
self.assertTrue(0.0 <= similarity <= 1.0)
except ValueError:
self.fail("结果文件内容不是有效的相似度值")
# 清理
if os.path.exists(result_file):
os.remove(result_file)
def test_integration_file_not_exist(self):
"""测试文件不存在的情况"""
orig_file = "non_existent_orig.txt"
plag_file = "test_data/orig_del.txt"
result_file = "test_data/result_test.txt"
# 确保测试文件不存在
if os.path.exists(orig_file):
os.remove(orig_file)
# 运行主程序
cmd = [sys.executable, "main.py", orig_file, plag_file, result_file]
result = subprocess.run(cmd, capture_output=True, text=True, timeout=30)
# 验证程序执行失败
self.assertNotEqual(result.returncode, 0)
# 验证错误信息包含文件不存在的提示
error_output = result.stderr + result.stdout
self.assertIn("文件不存在", error_output)
if __name__ == "__main__":
unittest.main()
五、计算模块部分异常处理说明
5.1 异常处理设计思路
本系统采用了分层的异常处理策略,确保在各种异常情况下能够优雅地处理错误并提供有用的反馈:
- 底层异常处理:在文件操作、文本处理等底层函数中捕获具体异常
- 中间层异常处理:在业务逻辑层统一处理各类异常
- 顶层异常处理:在主程序入口捕获未处理的异常,确保程序不会崩溃
5.2 主要异常处理场景
5.2.1 文件读取异常处理
设计目标:处理文件不存在、权限不足、编码错误等文件读取问题,确保程序在文件操作失败时能够优雅退出并提供明确的错误信息。
def read_file(self, file_path: str) -> Optional[str]:
"""
读取文件内容,处理各种可能的异常
"""
if not os.path.exists(file_path):
raise FileNotFoundError(f"文件不存在: {file_path}")
if not os.access(file_path, os.R_OK):
raise PermissionError(f"没有读取权限: {file_path}")
# 尝试不同的编码方式读取文件
for encoding in self.supported_encodings:
try:
with open(file_path, 'r', encoding=encoding) as file:
content = file.read().strip()
return content
except UnicodeDecodeError:
continue
except Exception as e:
raise Exception(f"读取文件时发生错误: {e}")
# 如果所有编码都失败,抛出异常
raise UnicodeDecodeError("utf-8", b"", 0, 1, "无法使用支持的编码格式读取文件")
5.2.2 文本处理异常处理
设计目标:处理空文本、格式错误等文本处理问题,确保相似度计算的准确性和稳定性。
def calculate_similarity(self, text1: str, text2: str) -> float:
"""
计算两个文本的相似度,处理可能的异常
"""
try:
# 文本预处理
words1 = self.preprocess_text(text1)
words2 = self.preprocess_text(text2)
# 如果任一文本为空,返回0
if not words1 or not words2:
return 0.0
# 计算TF-IDF
tf_idf_vectors, _ = self.calculate_tf_idf([words1, words2])
# 计算余弦相似度
similarity = self.cosine_similarity(tf_idf_vectors[0], tf_idf_vectors[1])
# 返回保留两位小数的结果
return round(similarity, 2)
except Exception as e:
# 发生异常时返回0并记录错误
print(f"计算相似度时发生错误: {e}")
return 0.0
5.2.3 命令行参数异常处理
设计目标:处理命令行参数数量不正确、参数格式错误等问题,提供清晰的使用说明。
def validate_arguments(args: list) -> bool:
"""
验证命令行参数,处理参数异常
"""
if len(args) != 4:
print("错误: 参数数量不正确")
print_usage()
return False
# 检查文件路径
for i, file_path in enumerate(args[1:], 1):
if not file_path or not isinstance(file_path, str):
print(f"错误: 第{i}个参数不是有效的文件路径")
return False
if i <= 2: # 前两个是输入文件
if not os.path.exists(file_path):
print(f"错误: 文件不存在: {file_path}")
return False
return True
5.2.4 主程序异常处理
设计目标:捕获并处理主程序执行过程中的所有未预期异常,确保程序能够优雅退出。
def main():
"""主函数,包含全面的异常处理"""
try:
# 获取命令行参数
args = sys.argv
# 验证参数
if not validate_arguments(args):
sys.exit(1)
# 提取文件路径
original_file = args[1]
plagiarized_file = args[2]
output_file = args[3]
print("=" * 50)
print("论文查重系统")
print("=" * 50)
print(f"原文文件: {original_file}")
print(f"抄袭版论文文件: {plagiarized_file}")
print(f"输出文件: {output_file}")
print("=" * 50)
# 计算重复率
success = calculate_plagiarism_rate(original_file, plagiarized_file, output_file)
if success:
print("程序执行成功!")
sys.exit(0)
else:
print("程序执行失败!")
sys.exit(1)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("\n程序被用户中断")
sys.exit(1)
except Exception as e:
print(f"程序执行过程中发生未预期的错误: {e}")
sys.exit(1)




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号