JAVA-继承
继承的概念
公共类(Public)下的继承
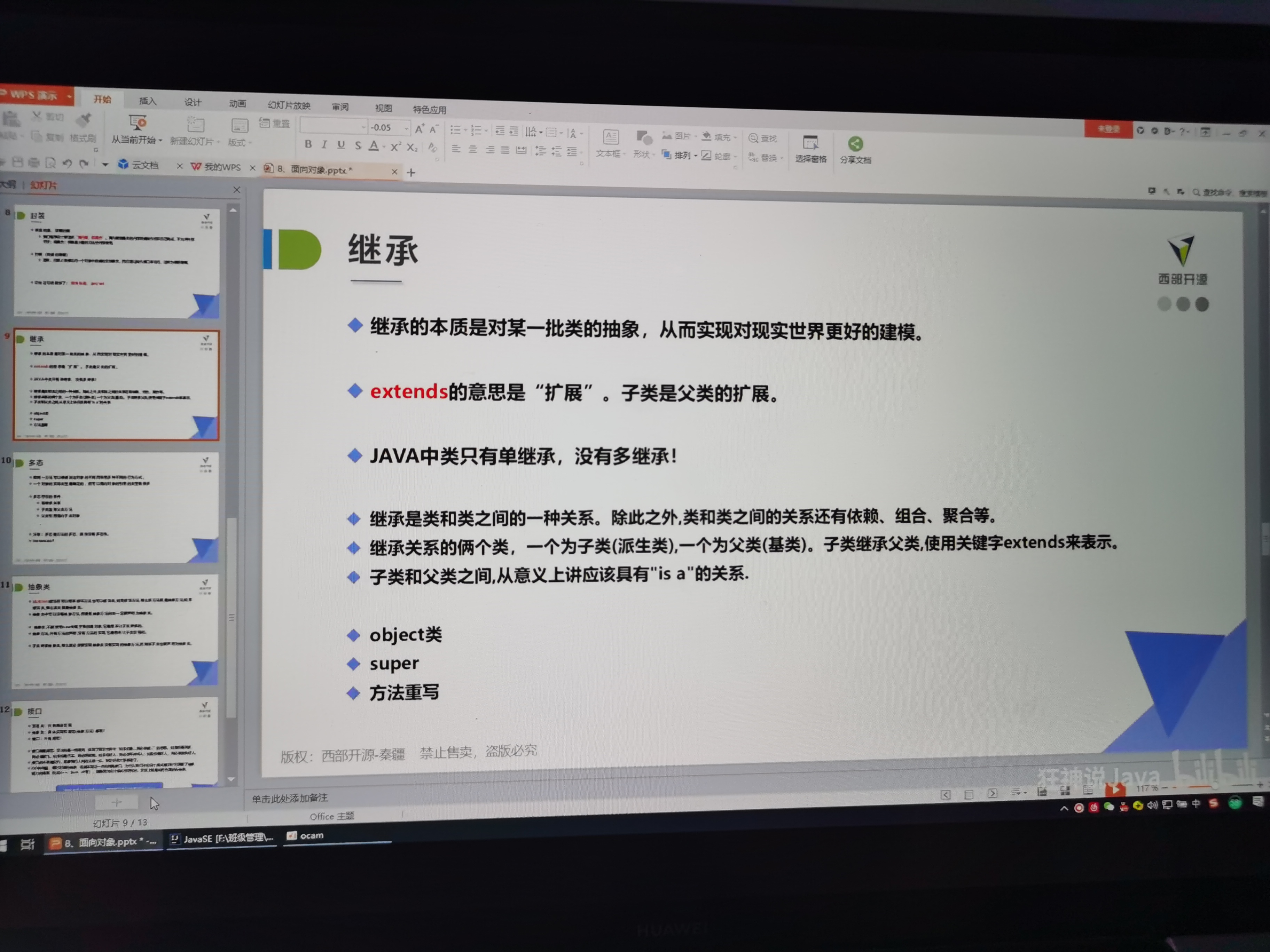
package oop.继承;
import oop.Student;
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
student student = new student();
student.test("陈丹宇");
}
}
package oop.继承;
//JAVA中,所有的类,都默认直接或者间接继承object
//person 人 : 父类
public class person {
public String name = "chendanyu";
public void print(){
System.out.println("Person");
}
}
package oop.继承;
//学生 is 人: 派生类,子类
//子类继承了父类,就会拥有父类的全部方法
public class student extends person{
public String name = "qq";
public void print(){
System.out.println("Student");
}
public void test(String name){
System.out.println(name);//陈丹宇
System.out.println(this.name);//qq
System.out.println(super.name);//chendanyu
}
}
super与this的使用区别
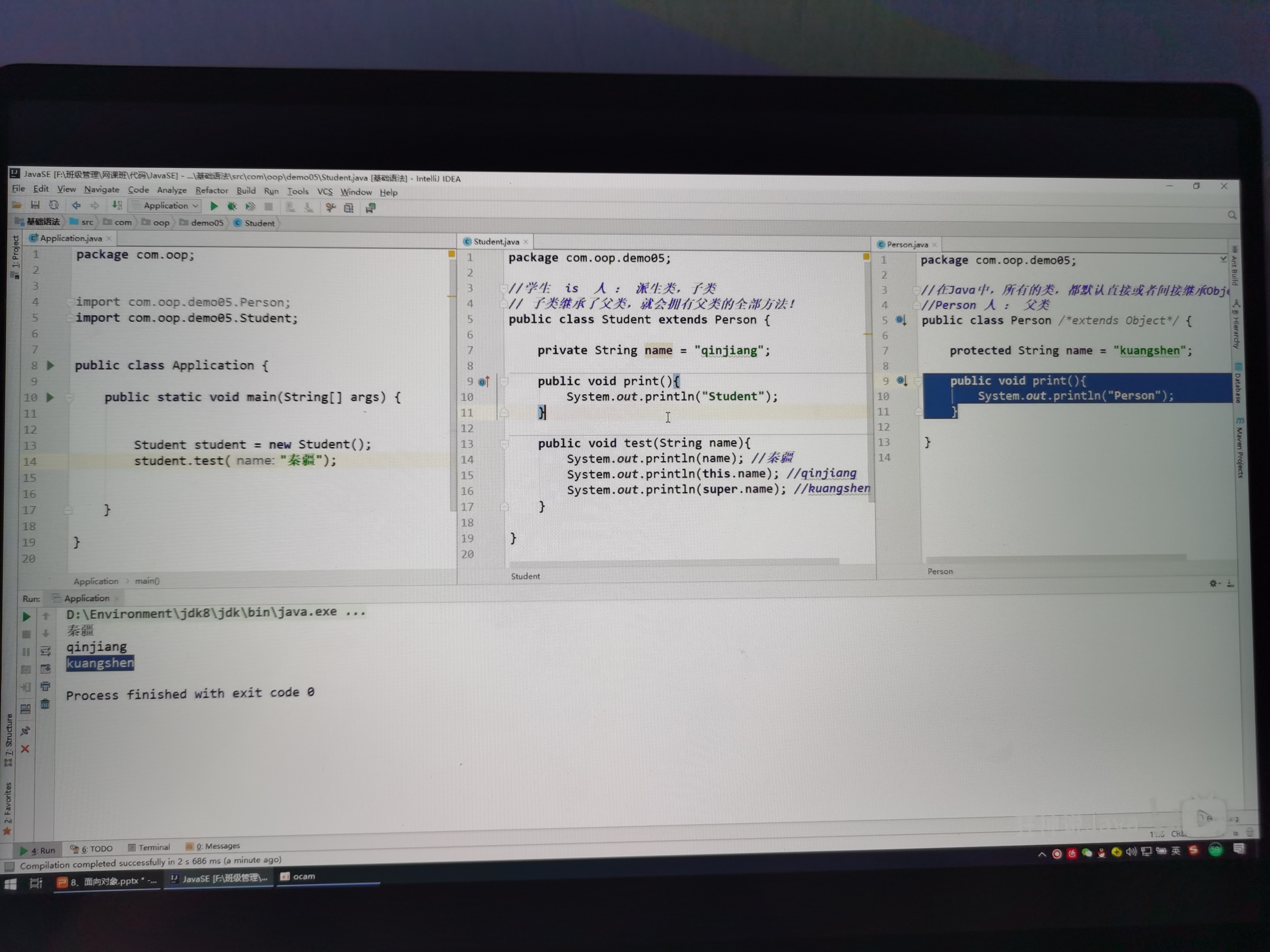
package oop.继承;
import oop.Student;
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
student student = new student();
student.test("陈丹宇");
student.test1();
}
}
package oop.继承;
//学生 is 人: 派生类,子类
//子类继承了父类,就会拥有父类的全部方法
public class student extends person{
public String name = "qq";
public void print(){
System.out.println("Student");
}
public void test(String name){
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(this.name);
System.out.println(super.name);
}
public void test1(){
print();//student
this.print();//student
super.print();//person
}
}
package oop.继承;
//JAVA中,所有的类,都默认直接或者间接继承object
//person 人 : 父类
public class person {
public void say(){
System.out.println("学生说了一句话");
}
public String name = "chendanyu";
public void print(){
System.out.println("Person");
}
}
方法重写
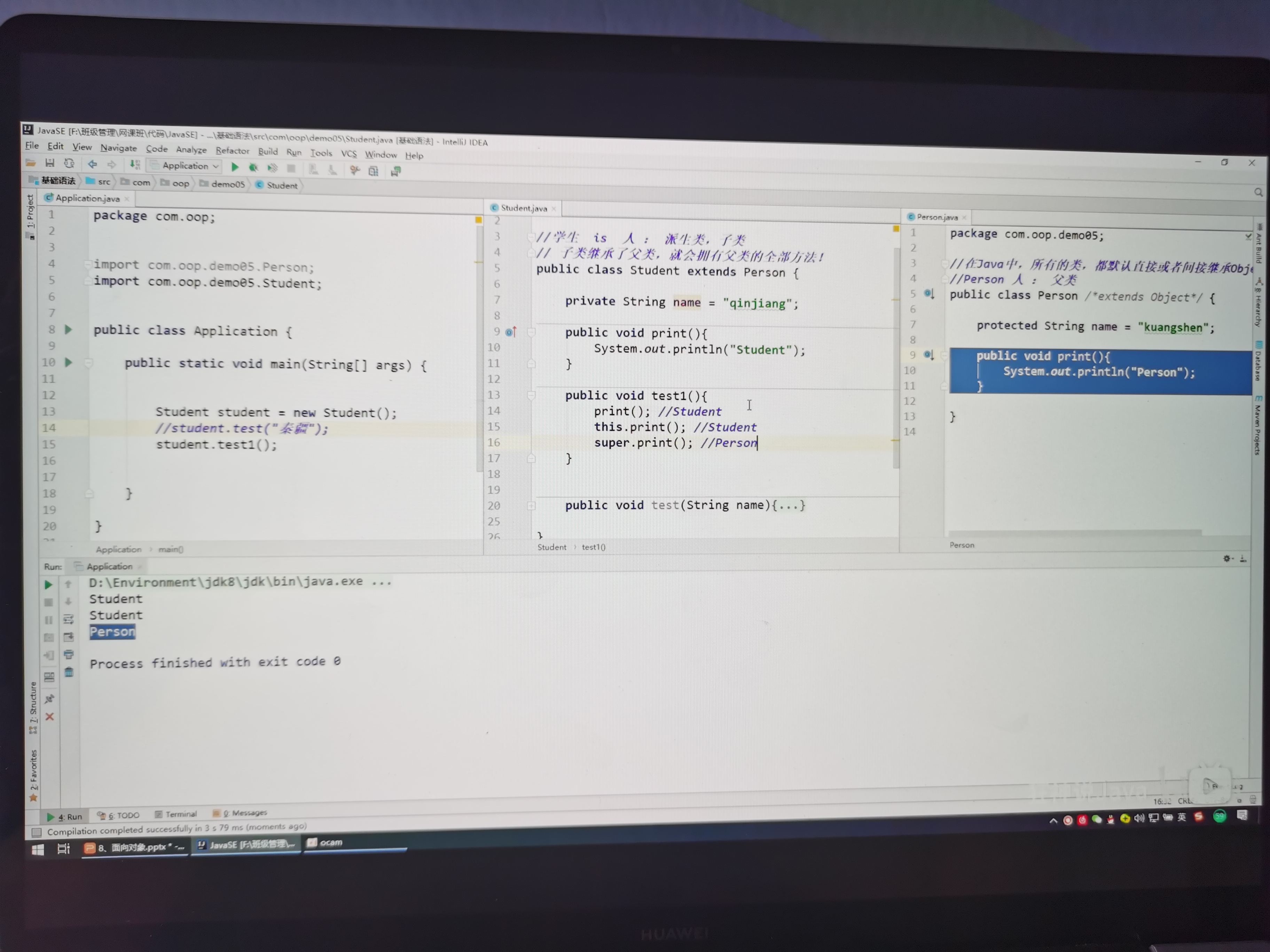
package oop.方法重写;
import oop.方法重写.A;
import oop.方法重写.B;
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
A a = new A();
a.test();
//父类的应用指向了子类
B b = new A();//子类重写了父类的方法
b.test();
}
}
package oop.方法重写;
public class A extends B{
//子类继承父类方法重写的快捷键
//Ctrl + Ins
//Override 重写的意思
@Override//注解:有功能的注释
public void test() {
super.test();
}
/*
public void test(){
System.out.println("A-->test");
}
*/
}
package oop.方法重写;
public class B {
public void test(){
System.out.println("B-->test");
}
}
继承与重写的小结
继承
学生 is 人: 派生类,子类
子类继承了父类,就会拥有父类的全部方法
JAVA中,所有的类,都默认直接或者间接继承object
person 人 : 父类
父类中私有的东西(private)--子类中初始无法继承
父类对子类之间存在无参构造,在子类无参调用中会默认将父类的无参构造一起调用
super注意点:
1.super调用父类的构造方法,必须在构造方法发第一个;
2.super必须只能出现在子类的方法或者构造方法中
3.super和this不能同时调用方法
Vs this:
代表对象不同:
this:本身调用者这个对象
super:代表父类对象的应用
前提:
this:没有继承也可以使用
super:只能在继承条件下才可以使用
构造方法
this(); 本类的构造
super();父类的构造
重写
重写都是方法的重写,和属性无关
重写的快捷键 ctrl+o
静态的方法和非静态的方法区别很大
静态方法: 方法的调用只和左边,定义的右边未起作用
重写:需要有继承关系,子类重写父类的方法!
1,方法名必须相同
2,参数列表列表必须相同
3,修饰符:范围可以扩大但不能缩小: public>protected>default>private
4,抛出的异常:范围,可以被缩小,但不能扩大: ClassNotFoundException-->Exceptiion(大)
重写。子类的方法和父类必须一致,方法体不同
为什么要重写
1.父类的功能,子类不一定需要,或者不一定满足
2.重写的快捷键 ctrl+o, override




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号