JAVA-面向对象
面向对象(oo)
面向对象编程(oop)
面向对象的本质--> 以类的方式组织代码,以对象组织(封装)数据
三大特性:封装、继承、多态
使用Split Right分页面编辑-->点文件右键
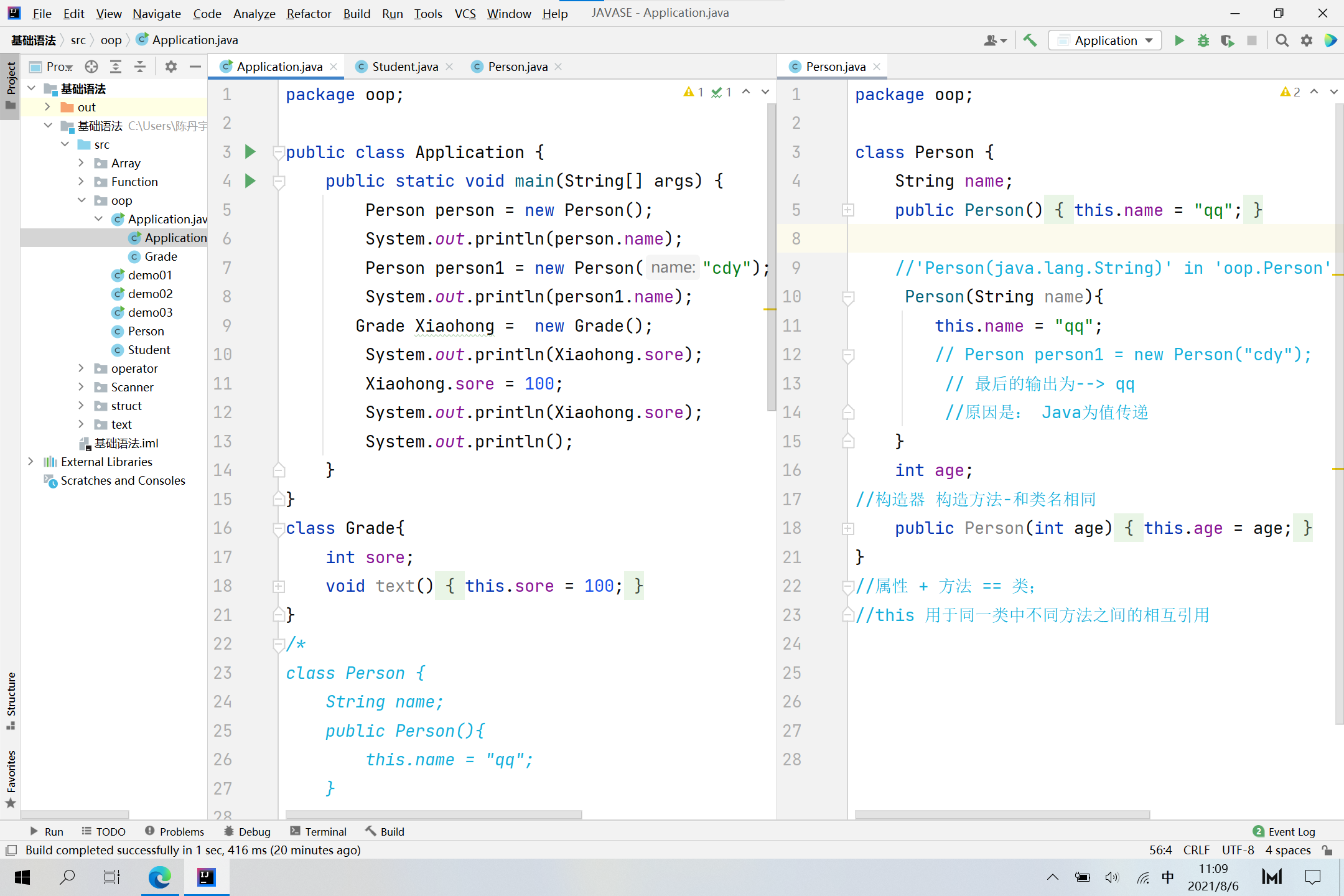
package oop;
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person person = new Person();
System.out.println(person.name);
Person person1 = new Person("cdy");
System.out.println(person1.name);
Grade Xiaohong = new Grade();
System.out.println(Xiaohong.sore);
Xiaohong.sore = 100;
System.out.println(Xiaohong.sore);
System.out.println();
}
}
class Grade{
int sore;
void text(){
this.sore = 100;
}
}
/*
class Person {
String name;
public Person(){
this.name = "qq";
}
//'Person(java.lang.String)' in 'oop.Person' cannot be applied to '()'
Person(String name){
this.name = "qq";
// Person person1 = new Person("cdy");
// 最后的输出为--> qq
//原因是: Java为值传递
}
int age;
//构造器 构造方法-和类名相同
public Person(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
//属性 + 方法 == 类;
//this 用于同一类中不同方法之间的相互引用
构造器
1,和类名相同的属性方法
2,没有返回值
3,快捷键 Alt + Ins
作用
1,new 的本质在调用函数
2,初始化对象的值
注意点
1,定义有参构造后,如果想使用无参构造,显示的定义一个无参构造
*/
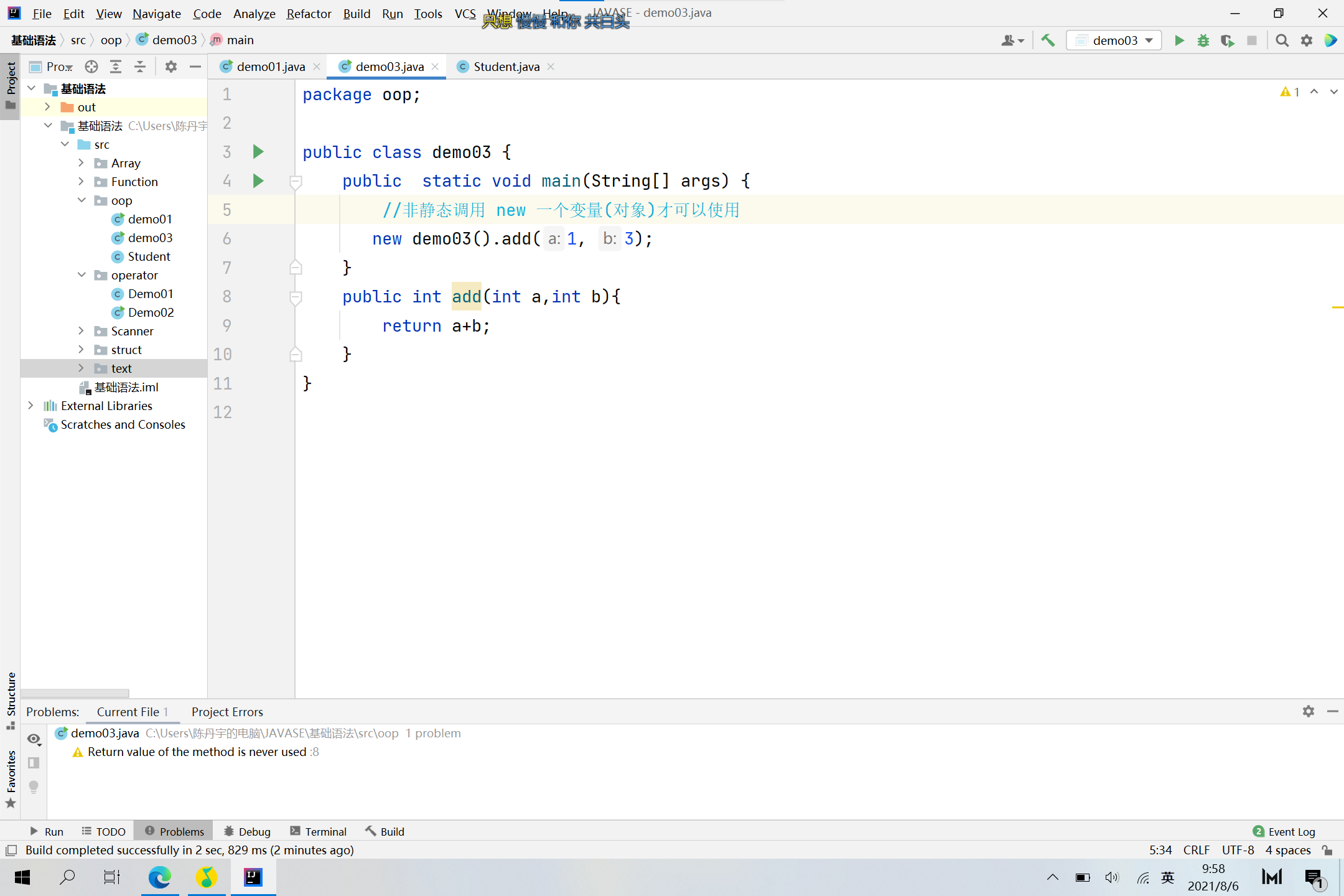
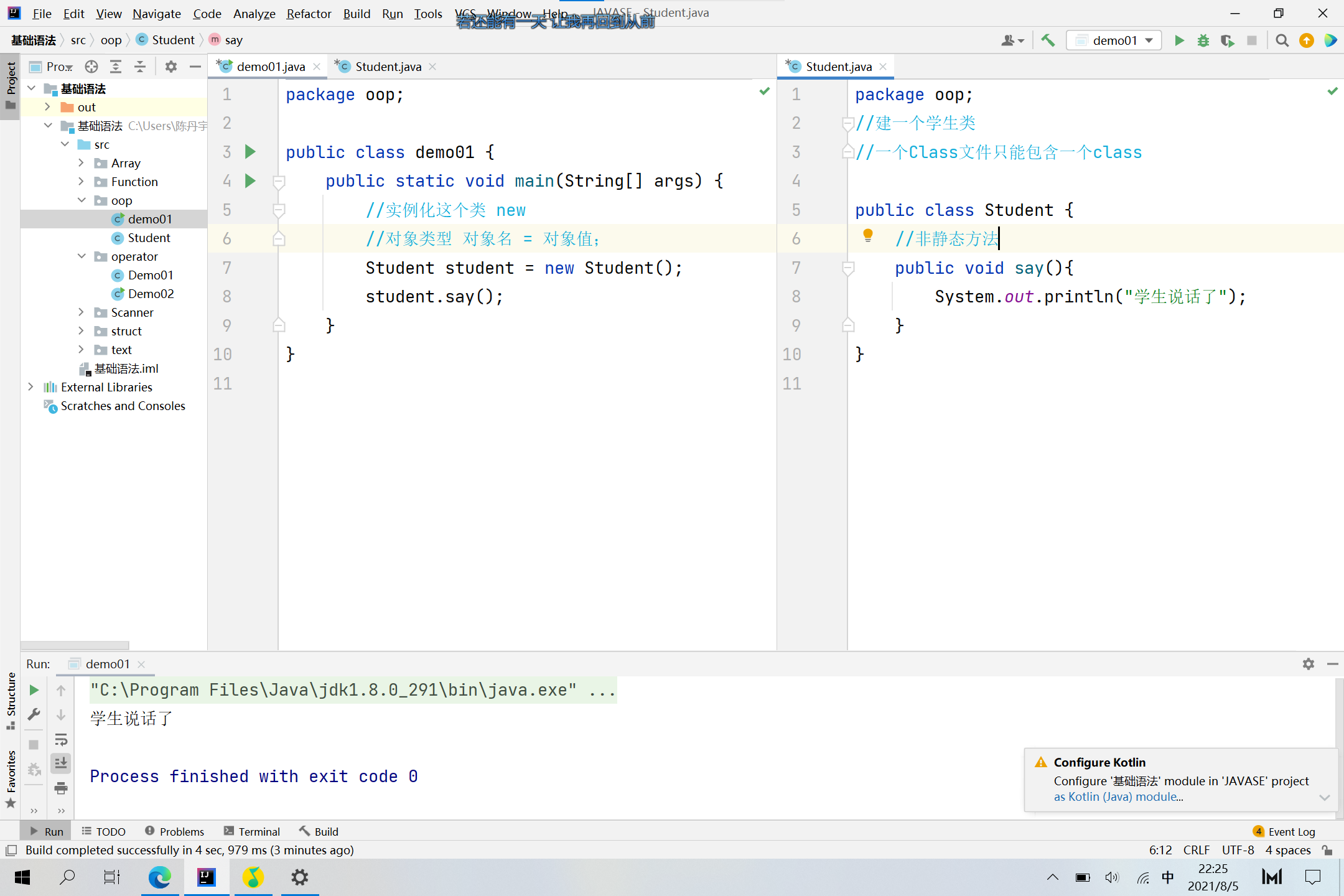
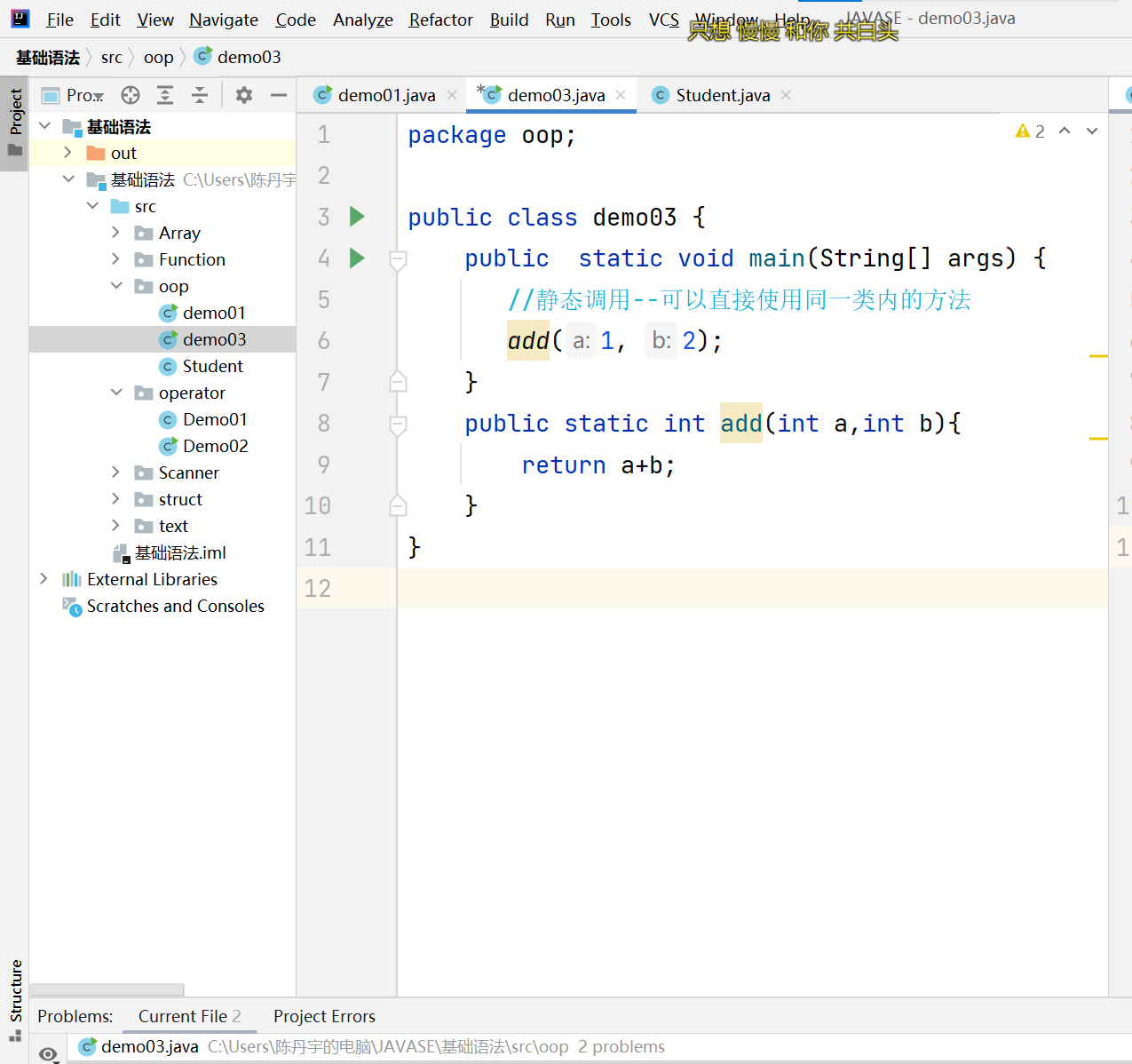
Private-对象
package oop;
public class Application1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println();
demo02 cdy = new demo02();
int a = demo02.sum(1, 2);
System.out.println(a); //a==3
System.out.println(cdy.Chinese);//输出为0.0
cdy.setMath(100) ;
System.out.println(cdy.getMath());//输出为100
}
}
//下文为源码的类库
/*
package oop;
public class demo02 {
private double Math;
public double Chinese;
public static double English;
public double getMath() {
return Math;
}
public void setMath(double math) {
Math = math;
}
public static int sum(int a,int b){
return a+b;
}
}
*/




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号