动态规划
通过组合子问题来解决问题,各个子问题不独立,子问题包含公共子问题,每个子问题求解一次将结果保存在表中
1:描述最优解结构
2:定义递归的最优解
3:自底向上求解最优解的值
4:根据每步的计算结果构造最优解
适用动态规划的两个基本要素:
1:最优子结构:当问题最优解中包含子问题的最优解
2:重叠子问题
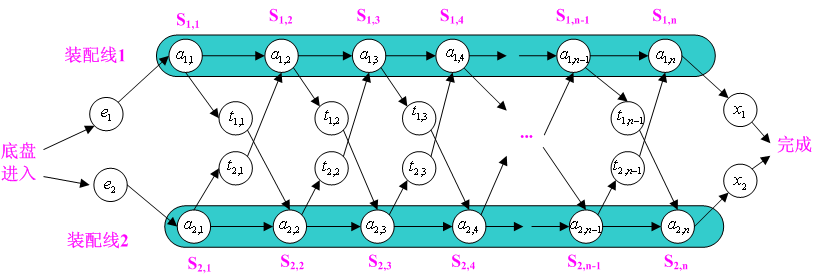
我们令fi[j]为底盘到Si,j的最优解i=0,1 j=1....n
问题最优解:f* = min(f1[n]+x1,f2[n]+x2)
f1[j] = min(f1[j-1]+a1,j-1,f2[j-1]+t2,j-1+a2,j-1) 2<=j<=n
f1[1] = e1 + a11
f2[j] = min(f2[j-1]+a2,j-1,f1[j-1]+t1,j-1+a1,j-1) 2<=j<=n
f2[1] = e2 + a21
其中f1[j-1]、f2[j-1]为最优解,包含最优子结构
包含重叠子问题:比如f1[n]和f2[n]都会对f1[n-1]和f2[n-1]求解符合动态规划的两个基本要素。
a = [[7,9,3,4,8,4],[8,5,6,4,5,7]] t = [[2,3,1,3,4],[2,1,2,2,1]] e = [2,4] x = [3,2] f1 = [] f2 = [] def Fastest_way(a,t,e,x,n): f1.append(a[0][0]+e[0]) f2.append(a[1][0]+e[1]) for index in range(1,n): temp1 = f1[index-1] + a[0][index] temp2 = f2[index-1] + t[1][index-1] + a[0][index] if temp1 < temp2: f1.append(temp1) else: f1.append(temp2) temp1 = f2[index-1] + a[1][index] temp2 = f1[index-1] + t[0][index-1] + a[1][index] if temp1 < temp2: f2.append(temp1) else: f2.append(temp2) return min(f1[n-1]+x[0],f2[n-1]+x[1]) print (Fastest_way(a,t,e,x,len(a[0]))) for i in f1: print(i) for i in f2: print(i)
http://www.cnblogs.com/Anker/archive/2013/03/09/2951785.html


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号