一、"REST"的快速开发:
解释: "快速开发"和"入门案例"的区别:(省略了很多重复的代码)
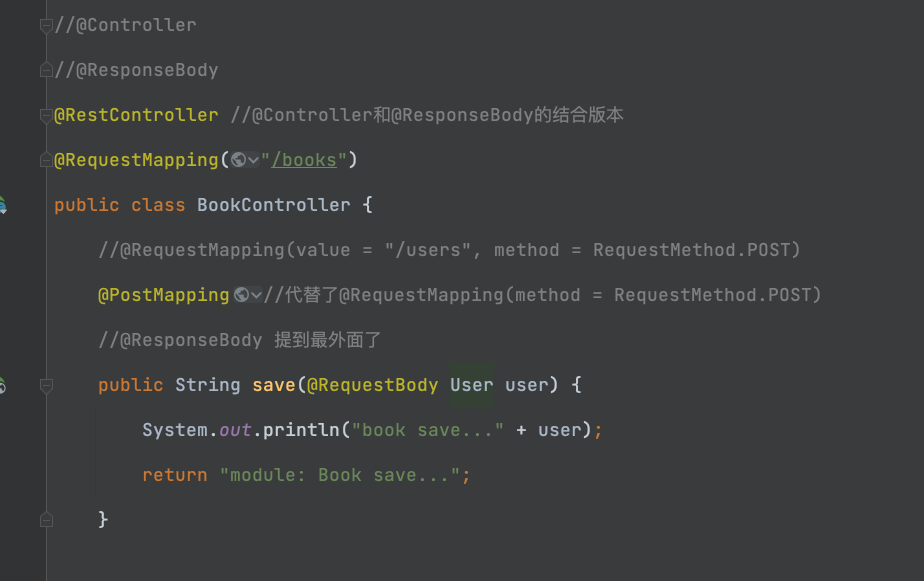
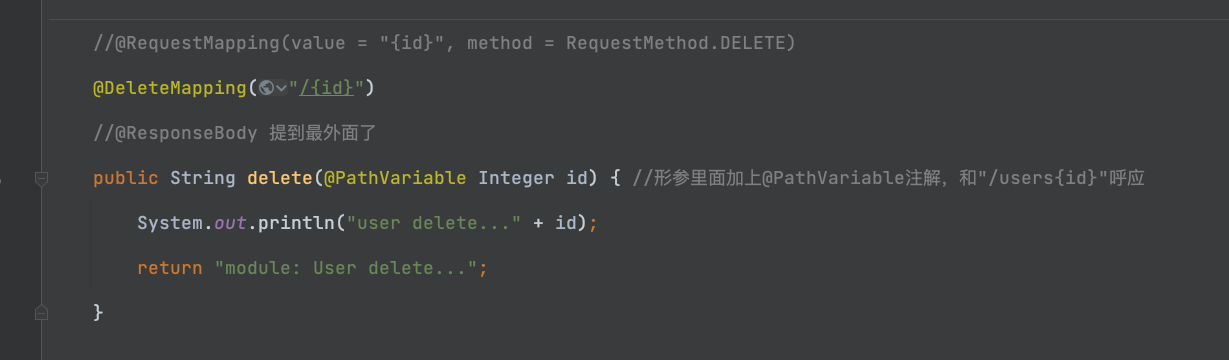
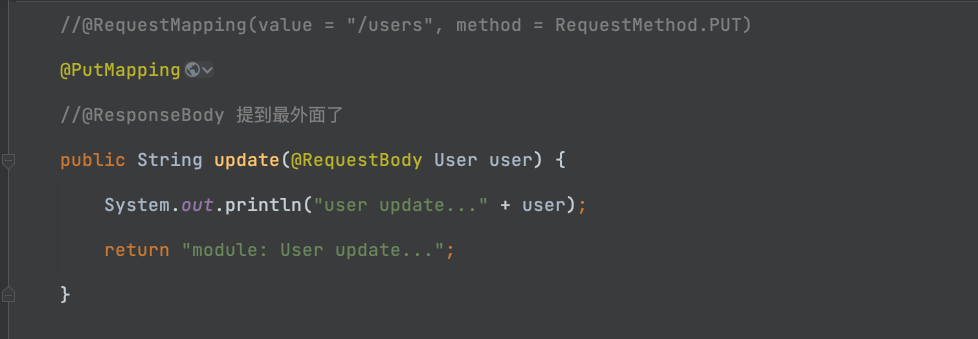
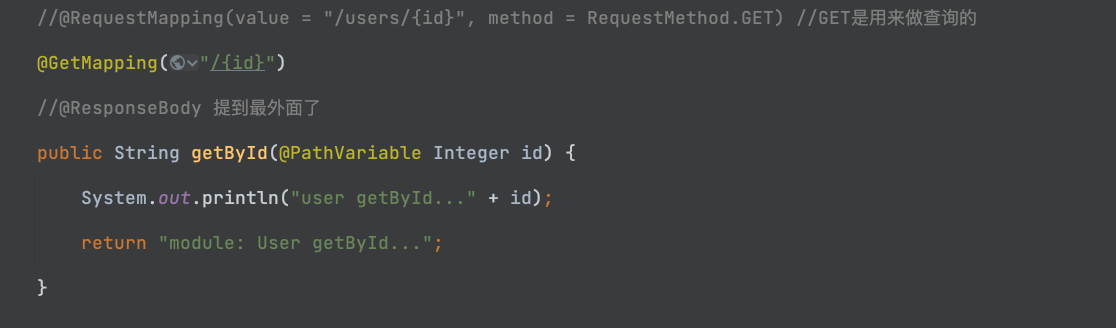
1.1-给大家看一下区别:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
二、详细解析:
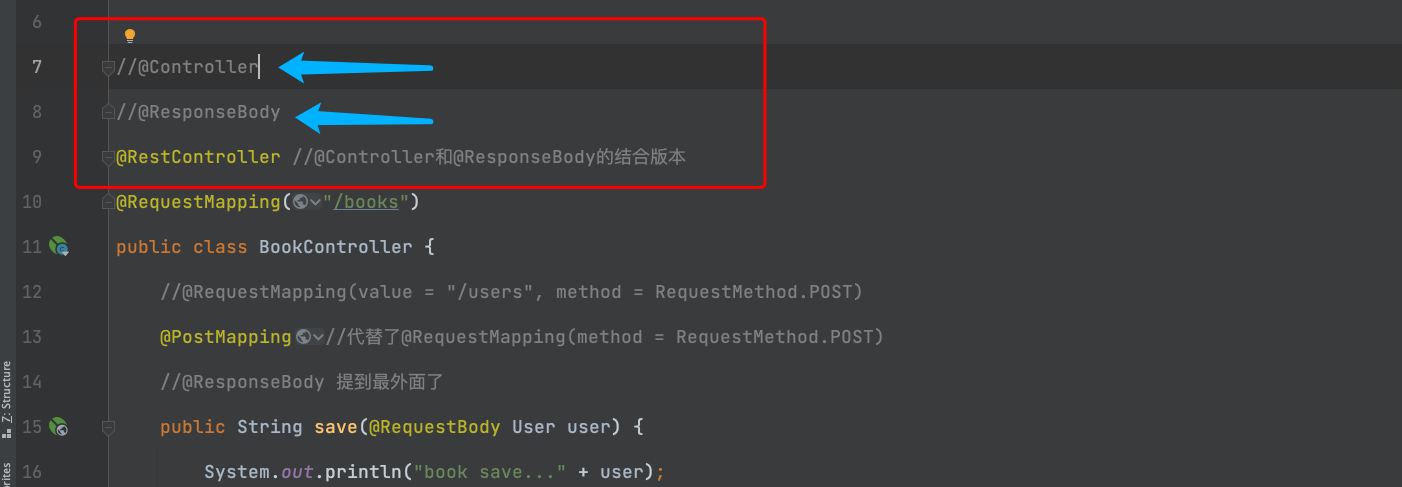
2.1-"@ResponseBody "的简化
解析:因为每个代码块都有这个注解,我们干脆直接把它放到外面去。
2.2-"@Controller"的简化
解析:因为"@ResponseBody "来到外面,可以和"@Controller"集合,所以"@Controller"这个注解可以不用写了。把他们合并成"@RestController"
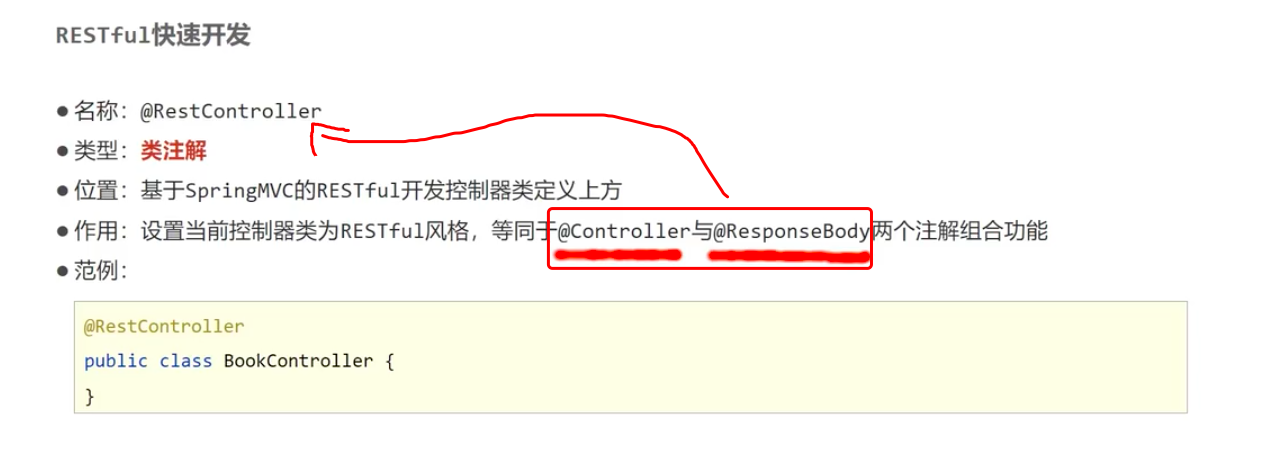
2.3-"@RestController"的出现:
解析: 他是由"@ResponseBody"注解和"@Controller"注解的结合。
![]()
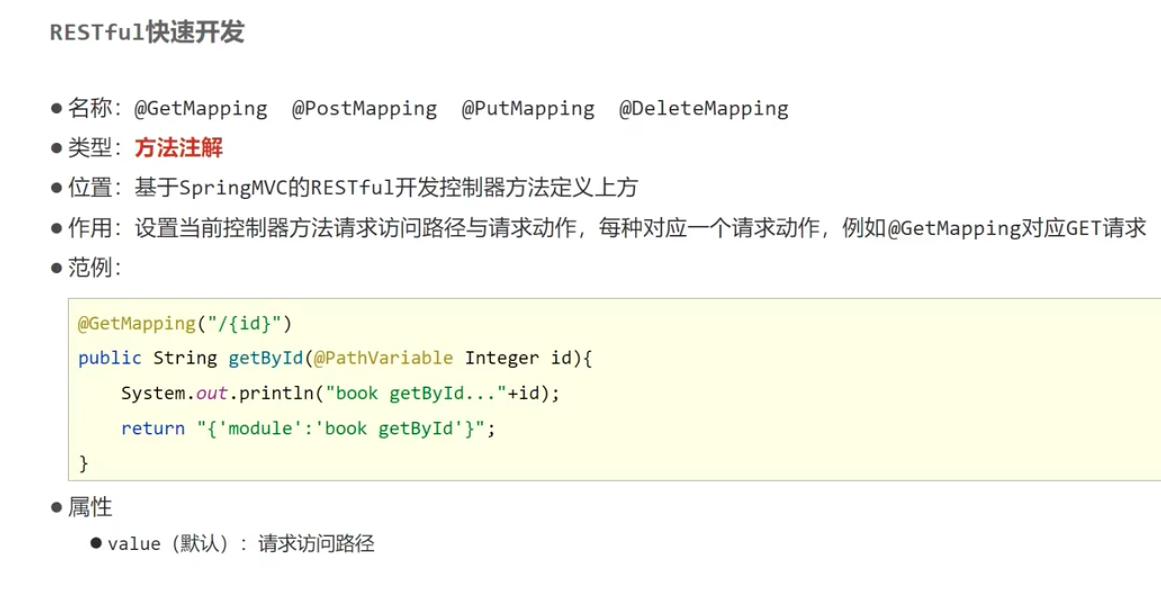
2.4-"XXX","Mapping"的简化
@RequestMapping(value = "/users", method = RequestMethod.POST)
@RequestMapping(value = "{id}", method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
@RequestMapping(value = "/users", method = RequestMethod.PUT)
@RequestMapping(value = "/users/{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
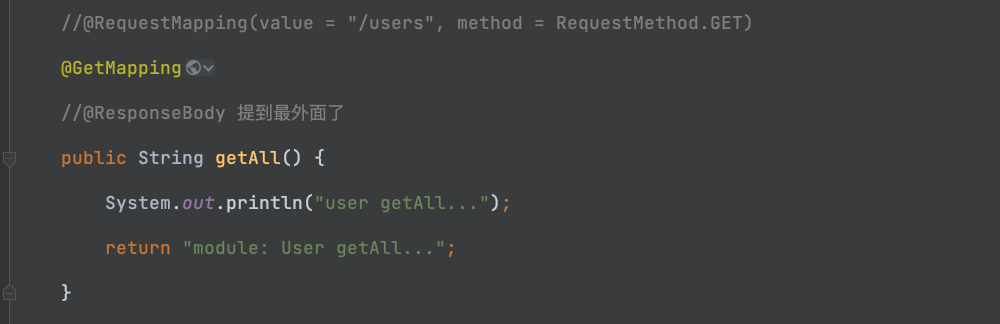
@RequestMapping(value = "/users", method = RequestMethod.GET)
解析:"value = "/users" ----> value这个部分,用提到外面的"@RequestMapping("/books")",来简化了
2.4.1- 对2.4进行继续简化
剩下:
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST)
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.PUT)
@RequestMapping( method = RequestMethod.GET)
@RequestMapping( method = RequestMethod.GET)
解析:这部分统一用:
@PostMapping
@DeleteMapping("/{id}")
@PutMapping
@GetMapping("/{id}")
@GetMapping
三、来对比一下"简化前"和"简化后的代码块"
简化前(没删除之前):
//@Controller
//@ResponseBody
@RestController //@Controller和@ResponseBody的结合版本
@RequestMapping("/books")
public class BookController {
//@RequestMapping(value = "/users", method = RequestMethod.POST)
@PostMapping//代替了@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST)
//@ResponseBody 提到最外面了
public String save(@RequestBody User user) {
System.out.println("book save..." + user);
return "module: Book save...";
}
//@RequestMapping(value = "{id}", method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
@DeleteMapping("/{id}")
//@ResponseBody 提到最外面了
public String delete(@PathVariable Integer id) { //形参里面加上@PathVariable注解,和"/users{id}"呼应
System.out.println("Bookdelete..." + id);
return "module: Book delete...";
}
//@RequestMapping(value = "/Book", method = RequestMethod.PUT)
@PutMapping
//@ResponseBody 提到最外面了
public String update(@RequestBody User user) {
System.out.println("Book update..." + user);
return "module: Book update...";
}
//@RequestMapping(value = "/users/{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET) //GET是用来做查询的
@GetMapping("/{id}")
//@ResponseBody 提到最外面了
public String getById(@PathVariable Integer id) {
System.out.println("Book getById..." + id);
return "module: Bookr getById...";
}
//@RequestMapping(value = "/users", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@GetMapping
//@ResponseBody 提到最外面了
public String getAll() {
System.out.println("Book getAll...");
return "module: Book getAll...";
}
}
简化后:(已经删除)
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/books")
public class BookController {
@PostMapping
public String save(@RequestBody User user) {
System.out.println("book save..." + user);
return "module: Book save...";
}
@DeleteMapping("/{id}")
public String delete(@PathVariable Integer id) {
System.out.println("Book delete..." + id);
return "module: Book delete...";
}
@PutMapping
public String update(@RequestBody User user) {
System.out.println("Book update..." + user);
return "module: Book update...";
}
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public String getById(@PathVariable Integer id) {
System.out.println("Book getById..." + id);
return "module: Book getById...";
}
@GetMapping
public String getAll() {
System.out.println("Book getAll...");
return "module: Book getAll...";
}
}
四、总结:
4.1:
![]()
4.2:
![]()
4.3:小结:
![]()



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号