收获:第"四"题用到了HashSet,来实现"用户已经报名,不能重复报名"的操作
第一题目:
//购书系统_P70
class Book {
private int book_id;
private String bookName;
private int price;
private int repertory;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Book{" +
"book_id=" + book_id +
", bookName='" + bookName + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
", repertory=" + repertory +
'}';
}
public int getBook_id() {
return book_id;
}
public void setBook_id(int book_id) {
this.book_id = book_id;
}
public String getBookName() {
return bookName;
}
public void setBookName(String bookName) {
this.bookName = bookName;
}
public int getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(int price) {
this.price = price;
}
public int getRepertory() {
return repertory;
}
public void setRepertory(int repertory) {
this.repertory = repertory;
}
public Book(int book_id, String bookName, int price, int repertory) {
this.book_id = book_id;
this.bookName = bookName;
this.price = price;
this.repertory = repertory;
}
}
class BuyBook {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
Book book[] = new Book[3];
book[0] = new Book(1, "Java", 58, 100);
book[1] = new Book(2, "HTML", 38, 100);
book[2] = new Book(3, "Go", 48, 100);
System.out.println("请输入id来购买书本:");
for (Book b : book) {
System.out.println(Arrays.asList(b));
}
boolean flag = true;
while (flag) {
int id = scanner.nextInt();
switch (id) {
case 1:
System.out.println("你选择购买的是:" + book[0]);
System.out.println("请输入你要购买" + book[0].getBookName() + "的数量:");
int number = scanner.nextInt();
int repertory = book[0].getRepertory();
book[0].setRepertory(repertory - number);
if (book[0].getRepertory() < 0) {
System.out.println("没货了");
flag = false;
break;
}
System.out.println("你需要支付:" + book[0].getPrice() * number + "元");
System.out.println("你还需要购买吗?退出'Y',继续购买'N' ");
String choose = scanner.next();
if (choose.equals("N")) {
System.out.println("继续购买,继续输入id进行购买...");
continue;
} else if (choose.equals("N")) {
System.out.println("谢谢惠顾,退出购买...");
flag = false;
break;
} else {
System.out.println("由于你随便输入,系统判定你退出购买,多读书...");
flag = false;
break;
}
case 2:
System.out.println("你选择购买的是:" + book[1]);
System.out.println("请输入你要购买" + book[1].getBookName() + "的数量:");
int number1 = scanner.nextInt();
int repertory1 = book[0].getRepertory();
book[1].setRepertory(repertory1 - number1);
if (book[1].getRepertory() < 0) {
System.out.println("没货了");
flag = false;
break;
}
System.out.println("你需要支付:" + book[1].getPrice() * number1 + "元");
System.out.println("你还需要购买吗?退出'Y',继续购买'N' ");
String choose1 = scanner.next();
if (choose1.equals("N")) {
System.out.println("继续购买,继续输入id进行购买...");
continue;
} else if (choose1.equals("N")) {
System.out.println("谢谢惠顾,退出购买...");
} else {
System.out.println("由于你随便输入,系统判定你退出购买,多读书...");
}
case 3:
System.out.println("你选择购买的是:" + book[2]);
System.out.println("请输入你要购买" + book[2].getBookName() + "的数量:");
int number2 = scanner.nextInt();
int repertory2 = book[2].getRepertory();
book[2].setRepertory(repertory2 - number2);
if (book[2].getRepertory() < 0) {
System.out.println("没货了");
flag = false;
break;
}
System.out.println("你需要支付:" + book[1].getPrice() * number2 + "元");
System.out.println("你还需要购买吗?退出'Y',继续购买'N' ");
String choose2 = scanner.next();
if (choose2.equals("N")) {
System.out.println("继续购买,继续输入id进行购买...");
continue;
} else if (choose2.equals("N")) {
System.out.println("谢谢惠顾,退出购买...");
} else {
System.out.println("由于你随便输入,系统判定你退出购买,多读书...");
}
default:
System.out.println("对不起,没有这个书本,请到其他店看看...");
flag = false;
break;
}
}
System.out.println("库存信息:");
for (Book b : book) {
System.out.println(Arrays.asList(b));
}
}
}
第二道题
//银行存取卡_P73
class Bank {
private String account;
private String password;
private int money = 500;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Bank{" +
"account='" + account + '\'' +
", password='" + password + '\'' +
", money=" + money +
'}';
}
public int getMoney() {
return money;
}
public void setMoney(int money) {
this.money = money;
}
public String getAccount() {
return account;
}
public void setAccount(String account) {
this.account = account;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
}
class TestRegister {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int testVerificationCode = 0;
Random random = new Random();
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
Bank register = new Bank();
boolean flag = true;
while (flag) {
System.out.println("请输入序号");
System.out.println("1-登陆系统");
System.out.println("2-注册系统");
System.out.println("3-查看账号、密码、存款");
System.out.println("4-退出系统");
int i = scanner.nextInt();
switch (i) {
case 1:
System.out.println("登入你的账号");
String account = scanner.next();
System.out.println("输入你的密码");
String password = scanner.next();
if (account.equals(register.getAccount()) && password.equals(register.getPassword())) {
System.out.println("为了你的账号安全,请再输入一次密码");
String password2 = scanner.next();
if (password.equals(password2)) {
System.out.println("密码验证成功");
System.out.println();
int number1 = random.nextInt(8) + 1;
int number2 = random.nextInt(8) + 1;
int number3 = random.nextInt(8) + 1;
int number4 = random.nextInt(8) + 1;
testVerificationCode = number1 + number2 + number3 + number4;
System.out.println();
System.out.println("请输入验证码...");
System.out.println("验证码 :请输出" + number1 + " + " + number2 + " + " + number3 + " + " + number4 + "等于多少");
int verificationCode = scanner.nextInt();
if (verificationCode == testVerificationCode) {
System.out.println("登入成功...");
System.out.println();
System.out.println("存钱输入'C' // 取钱输入'Q' // 退出'随便'输入 ");
String choose = scanner.next();
if (choose.equals("Q")) {
System.out.println("尊贵的客人,你的取多少钱?");
int money = scanner.nextInt();
int money1 = register.getMoney();
if (register.getMoney() < money) {
System.out.println("对不起,你的卡没有这么多钱...");
continue;
} else {
register.setMoney(money1 - money);
System.out.println("你已经取出:" + money + "元");
continue;
}
} else if (choose.equals("C")) {
System.out.println("尊贵的客人,你的存多少钱?");
int money_c = scanner.nextInt();
int money1 = register.getMoney();
register.setMoney(money1 + money_c);
System.out.println("你已经存出:" + money_c + "元");
continue;
} else {
System.out.println("由于你随便输入,系统自动判定你退出...");
break;
}
} else {
System.out.println("你的密码输入错误,请重新登录...");
continue;
}
} else {
System.out.println("你的密码输入错误,系统判断你非法登入,已退出程序,请重新登录...");
break;
}
} else {
System.out.println("登录失败");
System.out.println("因为你登录失败,系统判定你为非法登入,请重修启动系统");
flag = false;
break;
}
case 2:
System.out.println("注册你的账号");
String setAccount = scanner.next();
register.setAccount(setAccount);
System.out.println("注册你的密码");
String setPassword = scanner.next();
register.setPassword(setPassword);
System.out.println("------------------------");
continue;
case 3:
System.out.println("你的账号: " + register.getAccount());
System.out.println("你的密码:" + register.getPassword());
System.out.println("你的存款:" + register.getMoney());
System.out.println("------------------------");
continue;
case 4:
System.out.println("你还需要操作吗?需要输入'Y',不需要输入'N'");
String next4 = scanner.next();
if (next4.equals("Y")) {
continue;
} else if (next4.equals("N")) {
flag = false;
break;
} else {
System.out.println("因为你不按规定输入,系统默认你不再继续操作");
flag = false;
break;
}
default: {
System.out.println("电脑卡顿...");
flag = false;
break;
}
}
}
}
}
第三道题:
//查看手机配置和功能_P73
class MobilePhoneConfiguration {
private String phoneMobile;
private String phoneType;
private String phoneOperatingSystem;
private int phonePrice;
private int phoneInternal;
private PhoneFunction phoneFunction;
public MobilePhoneConfiguration(String phoneMobile,
String phoneType, String phoneOperatingSystem,
int phonePrice, int phoneInternal,
PhoneFunction phoneFunction) {
this.phoneMobile = phoneMobile;
this.phoneType = phoneType;
this.phoneOperatingSystem = phoneOperatingSystem;
this.phonePrice = phonePrice;
this.phoneInternal = phoneInternal;
this.phoneFunction = phoneFunction;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "MobilePhoneConfiguration{" +
"phoneMobile='" + phoneMobile + '\'' +
", phoneType='" + phoneType + '\'' +
", phoneOperatingSystem='" + phoneOperatingSystem + '\'' +
", phonePrice=" + phonePrice +
", phoneInternal=" + phoneInternal +
", phoneFunction=" + phoneFunction +
'}';
}
public String getPhoneMobile() {
return phoneMobile;
}
public void setPhoneMobile(String phoneMobile) {
this.phoneMobile = phoneMobile;
}
public String getPhoneType() {
return phoneType;
}
public void setPhoneType(String phoneType) {
this.phoneType = phoneType;
}
public String getPhoneOperatingSystem() {
return phoneOperatingSystem;
}
public void setPhoneOperatingSystem(String phoneOperatingSystem) {
this.phoneOperatingSystem = phoneOperatingSystem;
}
public int getPhonePrice() {
return phonePrice;
}
public void setPhonePrice(int phonePrice) {
this.phonePrice = phonePrice;
}
public int getPhoneInternal() {
return phoneInternal;
}
public void setPhoneInternal(int phoneInternal) {
this.phoneInternal = phoneInternal;
}
public PhoneFunction getPhoneFunction() {
return phoneFunction;
}
public void setPhoneFunction(PhoneFunction phoneFunction) {
this.phoneFunction = phoneFunction;
}
}
class PhoneFunction {
private String phoneCall;
private String phoneGame;
private String phoneMusic;
public PhoneFunction(String phoneCall, String phoneGame, String phoneMusic) {
this.phoneCall = phoneCall;
this.phoneGame = phoneGame;
this.phoneMusic = phoneMusic;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "PhoneFunction{" +
"phoneCall='" + phoneCall + '\'' +
", phoneGame='" + phoneGame + '\'' +
", phoneMusic='" + phoneMusic + '\'' +
'}';
}
public String getPhoneCall() {
return phoneCall;
}
public void setPhoneCall(String phoneCall) {
this.phoneCall = phoneCall;
}
public String getPhoneGame() {
return phoneGame;
}
public void setPhoneGame(String phoneGame) {
this.phoneGame = phoneGame;
}
public String getPhoneMusic() {
return phoneMusic;
}
public void setPhoneMusic(String phoneMusic) {
this.phoneMusic = phoneMusic;
}
}
class TestMobilePhoneConfiguration {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MobilePhoneConfiguration mobilePhoneConfiguration[] = new MobilePhoneConfiguration[3];
mobilePhoneConfiguration[0] = new MobilePhoneConfiguration("XiaoMi",
"Utral",
"安卓系统",
4000,
128,
new PhoneFunction("打电话", "打游戏", "听音乐"));
mobilePhoneConfiguration[1] = new MobilePhoneConfiguration("HuaWei",
"Utral",
"鸿蒙系统",
8000,
256,
new PhoneFunction("打电话", "打游戏", "听音乐"));
mobilePhoneConfiguration[2] = new MobilePhoneConfiguration("Apple",
"IOS系统",
"苹果",
5000,
256,
new PhoneFunction("打电话", "打游戏", "听音乐"));
System.out.println("手机配置:");
for (MobilePhoneConfiguration m : mobilePhoneConfiguration) {
System.out.println(Arrays.asList(m));
}
}
}
第四道题
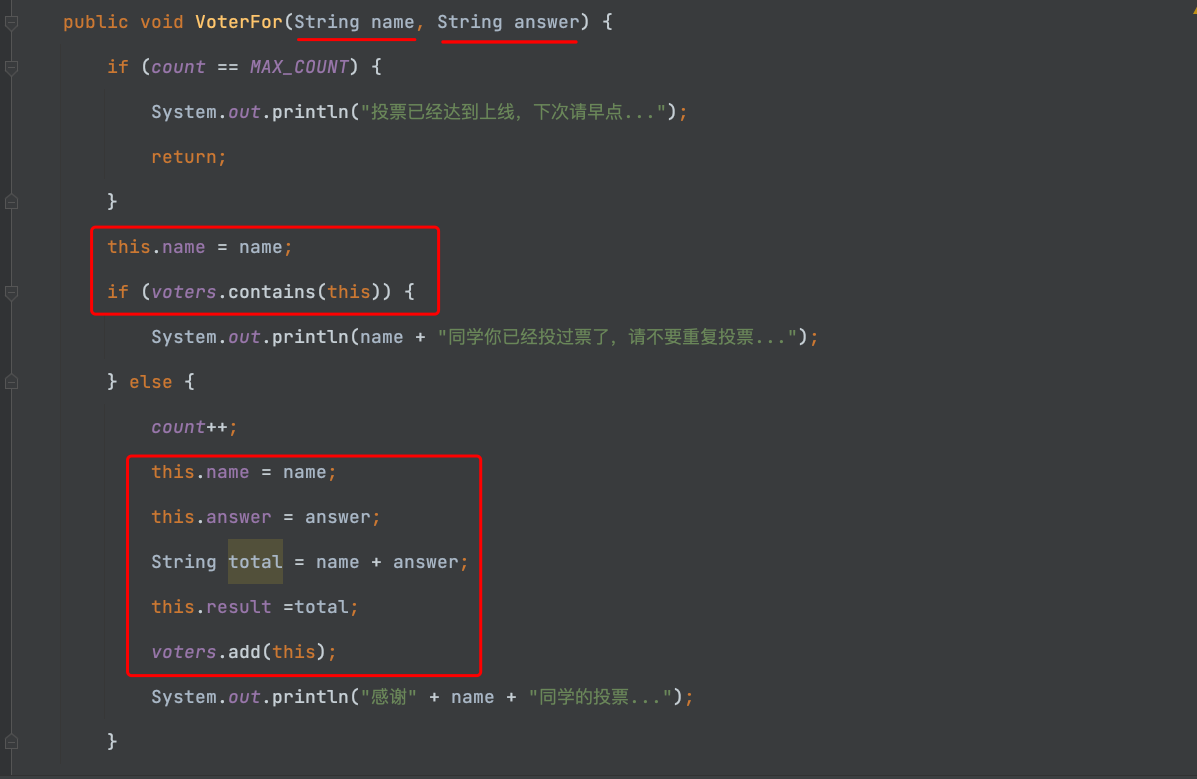
//学生投票系统_P80页
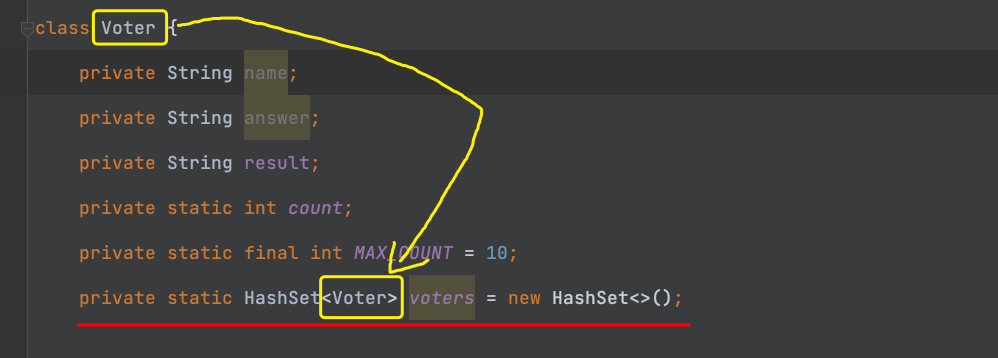
class Voter {
private String name;
private String answer;
private String result;
private static int count;
private static final int MAX_COUNT = 10;
private static HashSet<Voter> voters = new HashSet<>();
public void VoterFor(String name, String answer) {
if (count == MAX_COUNT) {
System.out.println("投票已经达到上线,下次请早点...");
return;
}
this.name = name;
if (voters.contains(this)) {
System.out.println(name + "同学你已经投过票了,请不要重复投票...");
} else {
count++;
this.name = name;
this.answer = answer;
String total = name + answer;
this.result =total;
voters.add(this);
System.out.println("感谢" + name + "同学的投票...");
}
}
//打印投票信息
public void printResult() {
System.out.println("参与投票数量:" + count + "个");
System.out.println("参与投票的结果如下");
for (Voter voter : voters) {
System.out.println(voter.result);
System.out.println("//---------------------------------");
}
}
}
class VoterTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Voter voter1 = new Voter();
Voter voter2 = new Voter();
Voter voter3 = new Voter();
voter1.VoterFor("tom", "不同意");
voter1.VoterFor("tom", "不同意");
voter2.VoterFor("LILI", "一般同意");
voter3.VoterFor("YAYA", "同意");
voter3.printResult();
}
}
附加:对第"四"题的解析:
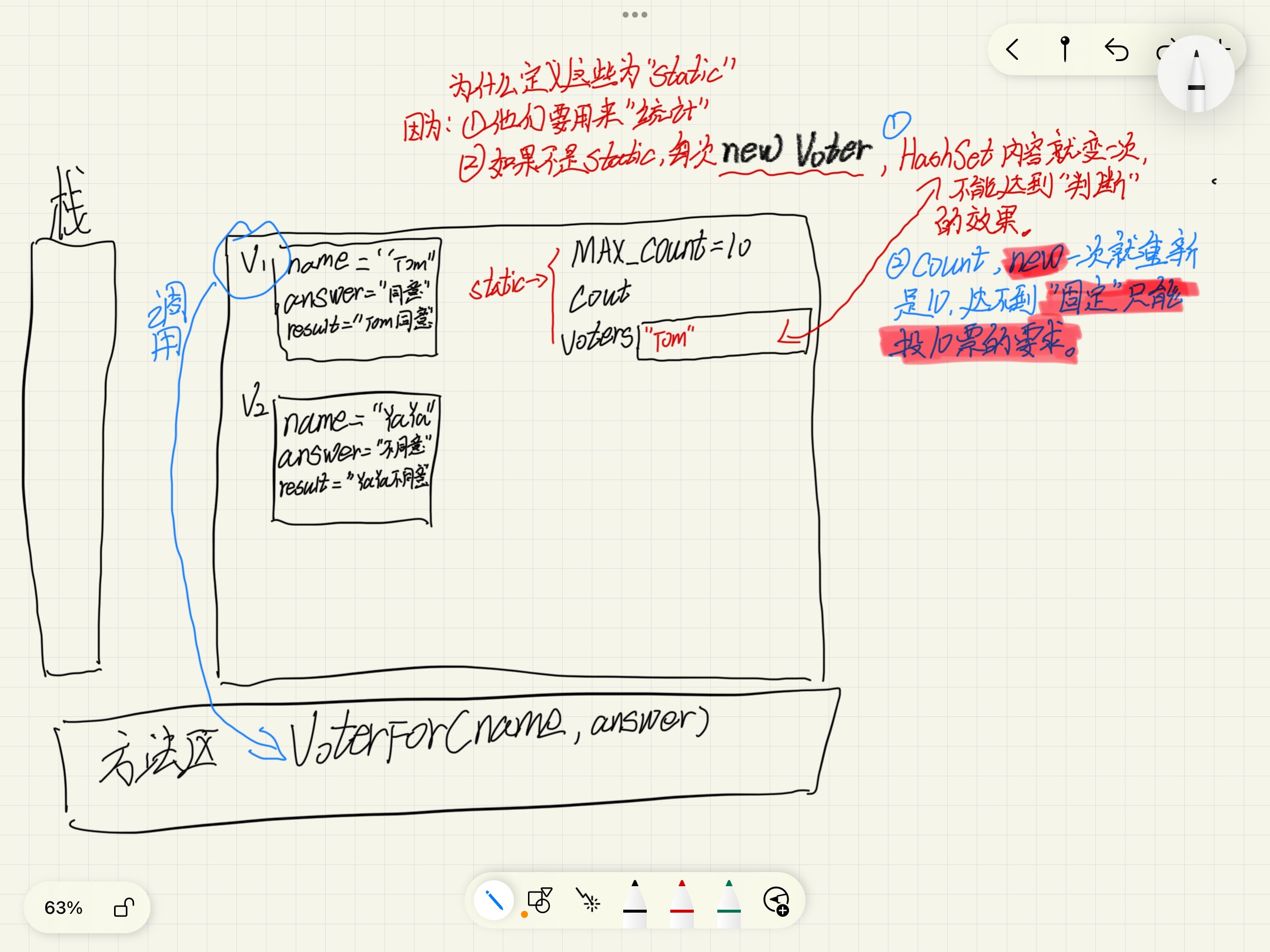
1-目的:
把用户名都放到HashSet里面,在投票前,对HashSet进行判段,如果已经存在这个用户了,就提示"已经投过了"
2-对VoterFor方法的剖析
![]()
voters.contains(this)方法,是HashSet的方法,他不能传入"String"。但是可以传入"HashSet"定义过的Class的成员变量。
问:什么是["HashSet"定义过的Class的成员变量]
答1:"HashSet"定义过的Class(而且这个Class是Voter)
private static HashSet< Voter > voters = new HashSet<>();
答2:那么Voter这个类的"成员变量"就可以放到"HashSet的方法中"
小结:
![]()
1-所以:Voter的成员变量,"name"、"answer"、"result" 可以放到"HashSet的方法中"。
2-比如这道题的:voters.contains(this)和voters.add(this);
3-当然是要成员变量的格式当然是:"用this关键字"
this.name = name;
this.answer = answer;
String total = name + answer;
this.result =total;
voters.add(this);
总结:
![]()



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号