1.IO概念
Java IO也称为IO流,它的核心就是对文件的操作和对字节、字符类型的输入和输出流。IO是指对数据流的输入和输出,主要分为两大类:字节流和字符流。
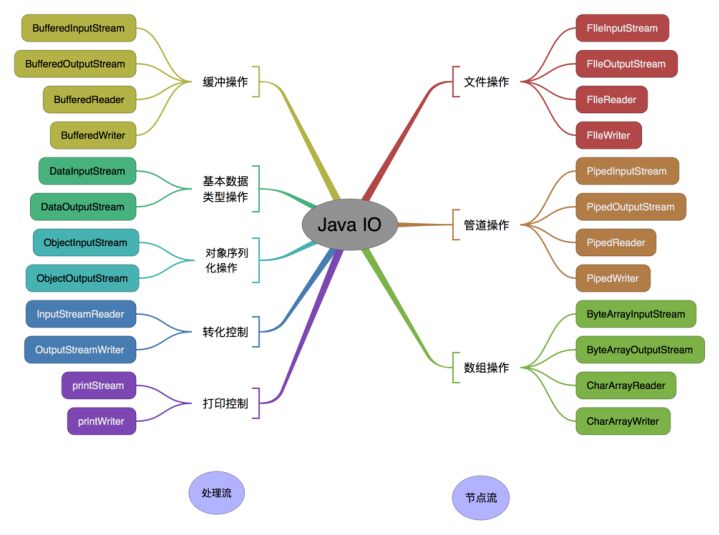
2.IO的分类图
3.IO类的继承关系
4.File类
1.概念
文件和目录路径名操作的类。
2.构造方法
- File(File parent, String child),
参数1 > parent 是File 类型的 文件路径
参数2 > child 是文件(包括文字名字和扩展名) - File(String pathname)
参数 > pathname 通过字符串地址的方式直接构造文件 - File(String parent,String child)
参数1 > parent 字符串的路径名
参数2 > child 是文件(包括文字名字和扩展名)
3.示例
3种构造方法创建文件。
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Io_Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
第二种 构造方法
参数 pathname 是过字符串地址的方式直接构造文件
*/
//File fileUrl =new File("E:\\java练习");
//File file=new File(fileUrl,"createFile_Demo.txt");
/*
第二种 构造方法
参数 pathname 是过字符串地址的方式直接构造文件
*/
//File file=new File("E:\\java练习\\createFile_Demo.txt");
/*
第三种 构造方法
参数1 > parent 字符串的路径名
参数2 > child 是文件(包括文字名字和扩展名)
*/
File file=new File("E:\\java练习","createFile_Demo.txt");
try {
// 判断文件是否存在
if(file.isFile()){
file.delete();
file.createNewFile();
}else {
// 创建文件
file.createNewFile();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(file);
}
}
5.IO的基本流
1.字节流
1.FileOutputStream 字节输出流
1.概念
已字节的方式 通过程序将文件写入到硬盘中。
2.构造方法
- FileOutputStream(File file) 通过File类指定要操作的文件。
- FileOutputStream(String str) 通过字符串地址的方式指定要操作的文件。
3.重载方法
1.write(); 按单个字节输出。
2.write(byte[] b) 按字节数组输出 。
3.write(| byte[] b, int off, int len) 按字节数组 并指数组中开始和结束的长度 输出。
4.示例
3种write的写入方法
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
public class Io_Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
//--------------------- 创建文件-------------------------------
/*
第二种 构造方法
参数 pathname 是过字符串地址的方式直接构造文件
*/
File file=new File("E:\\java练习\\createFile_Demo.txt");
try {
// 判断文件是否存在
if(file.isFile()){
file.delete();
file.createNewFile();
}else {
// 创建文件
file.createNewFile();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//--------------------- 字节输出流-------------------------------
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(file,true);
//1.write(); 按单个字节输出。
out.write(97);
out.write("\r\n".getBytes()); // 换行
//2.write(byte[] b) 按字节数组输出 。
byte[] bytes = {97,98,99,100,101,102}; // 创建byte类型数组
out.write(bytes); // 把数组里的字节写入文件中
out.write("\r\n".getBytes()); // 换行
//3.write(| byte[] b, int off, int len) 按字节数组 并指数组中开始和结束的长度 输出。
out.write(bytes,2,3); //在数组的第二个坐标开始写,写入长度为3个
out.close();
System.out.println("写入完成");
}
}
2.FileInputStream 字节输入流
1.概念
已字节的方式 将硬盘中的文件读取到程序中。
2.构造方法
3.示例
2.字符流
1.FileWriter 写入字符流
1.概念
已字符的方式 将硬盘中的文件读取到 程序中。
2.构造方法
3.示例
2.FileReader 读取字符流
1.概念
已字符的方式 将程序中的文件读取到 。硬盘中。

 posted on
posted on

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号