NCHU OOP BLOG-1
1. 前言
第一次使用Java实现任务
在高中接触了VB语言,在大一接触了C/C++,Python语言,大二的时候只大致了解过Java的语法。
在这之前也只是稍微学习了有关类的知识,知道类的概念和使用,希望通过Java和这门课程系统全面地学习面对对象编程的思想。
对于前三次的作业:
第一次作业的作用主要是熟悉Java的语法;
第二次作业需要用到数组,String类等常用的API;
第三次作业考察到正则表达式的使用,以及注意Java的计算精度问题。
2. 设计与分析
2.1. practice 2
2.1.1. 字母-数字转换
-
思路:
循环遍历str判断是否合法;
如果某个字符的ASCii码值不在'a'和'z'之间即是不合法的字符串。 -
实现:
//字母-数字转换
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.lang.Math;
class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
String s;
s = in.nextLine();
boolean f=true;
s = s.toLowerCase();
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++){
if(s.charAt(i)<'a'||s.charAt(i)>'z'){
f=false;
break;
}
}
if(f){
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++){
System.out.print(s.charAt(i)-'a'+1);
}
}
else{
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
}
}
2.1.2. 串口字符解析
-
思路:
一个信号由起始位(1),数据位(8),奇偶判断位(1),结束位(1)共 11 位组成;
当位数不足11时,不足以一个信号,特判结束;
设置一个ok代表有无信号出现,在结束时特判;
先判断结束位是否为1,在判断奇偶位的正确性(注意:当数据位1的个数为奇数时,奇偶位为0,反之则为1);
以上均满足则输出数据; -
实现:
//串口字符解析
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.lang.Math;
class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
String s;
s = in.nextLine();
if(s.length()<11){
System.out.println("null data");
}
if(s.matches("^[1]*$")){
System.out.println("null data");
}
int st=0,index=1,sum=0;
boolean parity = false, validate = false;
for(int i=0;i<s.length()-10;i++){
if(s.charAt(i) == '0'){
System.out.print(index+":");
index++;
if(s.charAt(i+10)!='1'){
validate = false;
}
else{
validate = true;
sum=0;
for(int j=i+1;j<i+9;j++){
if(s.charAt(j)=='1')sum++;
}
if(sum%2==0){
if(s.charAt(i+9)!='1')
parity = false;
else
parity = true;
}
else{
if(s.charAt(i+9)!='0')
parity = false;
else
parity = true;
}
}
if(validate){
if(parity){
for(int j=i+1;j<i+9;j++) System.out.print(s.charAt(j));
System.out.println();
}
else
System.out.println("parity check error");
}
else{
System.out.println("validate error");
}
i+=10;
}
}
}
}
2.1.3. String的格式判断与内容提取
-
思路:
特判掉输入字符串长度小于8的样例;
- 学生为17,18,19,20届软件学院人员,所以学号前四位在(2020,1920,1820,1720)中;
- 只要有一个学号不合法直接结束程序;
-
实现:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.lang.Math;
class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
String s, ans = "";
ArrayList<String> dic = new ArrayList<String>();
boolean flag = true;
s = in.nextLine();
int size = 0;
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++){
if(s.charAt(i)<'0'||s.charAt(i)>'9'){
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
return;
}
}
if(s.length()%8!=0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
return;
}
for(int i=0;i<s.length()-7;i+=4){
ans = "";
flag = true;
for(int j=1;j<=8;j++){
if(s.charAt(i+j-1)<'0'||s.charAt(i+j-1)>'9'){
flag=false;
break;
}
ans += s.charAt(i+j-1);
}
if(ans.substring(0, 4).equals("2020") && flag) {
if(ans.substring(4, 6).equals("61") || ans.substring(4, 6).equals("17"))
dic.add(ans.substring(4, 8));
}
}
for(int i=0;i<dic.size();i++){
if(i==0) System.out.print(dic.get(i));
else System.out.print(' '+dic.get(i));
}
}
}
复杂度分析
为简洁起见,本次练习只分析第二题:
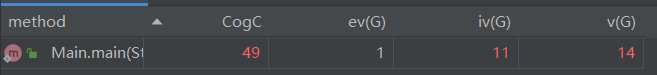
主函数复杂度较高
2.2. practice 3
2.2.1. 点线形系列1-计算两点之间的距离
-
思路:
-
首先使用正则表达式"[1]?(0|(0\.\d+)?|[1-9][0-9]*(\.\d+)?)$"判断非法情况;
-
调用String类的split方法分割字符串,如果点数不为2则输出"wrong number of points";
-
计算两点的欧式距离,并输出。
-
-
实现:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
String s;
s = in.nextLine();
String[] point;
point = s.split(" ");
String[] num;
for(String each:point) {
//正则表达式
num=each.split(",");
for(String j:num) {
if (!j.matches("^[+-]?(0|(0\\.\\d+)?|[1-9][0-9]*(\\.\\d+)?)$")) {
System.out.print("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
if(point.length!=2){
System.out.println("wrong number of points");
return;
}
double[] x = new double[2];
double[] y = new double[2];
int cnt=0;
for(String each:point){
double xx, yy;
String[] p = each.split(",");
xx = Double.parseDouble(p[0]);
yy = Double.parseDouble(p[1]);
x[cnt] = xx;
y[cnt] = yy;
cnt++;
}
double ans=0;
ans = Math.sqrt((x[0]-x[1])*(x[0]-x[1])+(y[0]-y[1])*(y[0]-y[1]));
System.out.println(ans);
}
}
2.2.2. 点线形系列2-线的计算
-
思路:
-
判断非法情况和2.2.1类似;
-
op == 1:根据两点坐标计算斜率,注意特判x[0]==x[1]的情况;
-
op == 2:用点到直线的距离公式计算第一个点到后两点构成的直线的距离,注意直线方程要使用Ax+By+C=0的形式,不然会因为误差造成测试点拿不满;
-
op == 3:使用三点中任意两点来计算直线方程,然后将第三点的坐标代入直线方程,如果等于0则说明在直线上;
-
op == 4:判断两条直线的斜率和截距是否同时相等就好了,注意判断相等时要将除法改为乘法;
-
op == 5:联立两条直线方程
$$
\begin{cases}
A1x+B1y+C1=0\
A2x+B2y+C2=0
\end{cases}$$
其中A1=y1-y0,B1=x0-x1,C1=x0y1-x1y0;A2=y3-y2,B2=x2-x3,C2=x2y3-x3y2。
解得:
$$
\begin{cases}
x=(C1B2-B1C2)/(A1B2-A2B1)\
y=(A1C2-A2C1)/(A1B2-A2B1)
\end{cases}$$
-
-
实现:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static boolean check(double[] x, double[] y){
for(int i=0;i<x.length;i++){
for(int j=i+1;j<x.length;j++){
if(x[i]==x[j] && y[i]==y[j]){
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
public static double cal_dis(double[] x, double[] y){
double x1 = x[0], y1 = y[0];
double x2 = x[1], y2 = y[1], x3 = x[2], y3 = y[2];
double A = y3 - y2;
double B = x2 - x3;
double C = x3*y2 - y3*x2;
double distance = (Math.abs(A*x1 + B*y1 + C)) / (Math.sqrt(A*A + B*B));
return distance;
}
public static boolean check_line(double[] x, double[] y){
double k1,k2;
k1=(y[1]-y[0])/(x[1]-x[0]);
k2=(y[2]-y[1])/(x[2]-x[1]);
return k1==k2;
}
public static boolean check_parr(double[] x, double[] y){
double k1,k2;
k1=(y[3]-y[2])/(x[3]-x[2]);
k2=(y[1]-y[0])/(x[1]-x[0]);
return k1==k2;
}
public static double[] cal_union(double[] x, double[] y){
double a1 = y[1]-y[0], b1 = x[0]-x[1], c1 = x[0]*y[1]-x[1]*y[0];
double a2 = y[3]-y[2], b2 = x[2]-x[3], c2 = x[2]*y[3]-x[3]*y[2];
double[] ans = new double[2];
ans[0] = (c1*b2-b1*c2)/(a1*b2-a2*b1);
ans[1] = (a1*c2-a2*c1)/(a1*b2-a2*b1);
return ans;
}
public static boolean check_coin(double[] ans, double[] x, double[] y){
double x1 = x[0], y1 = y[0], x2 = x[1], y2 = y[1];
double x3 = x[2], y3 = y[2], x4 = x[3], y4 = y[3];
double t;
if(x1>x2) {
t = x1;
x1 = x2;
x2 = t;
}
if(y1>y2){
t = y1;
y1 = y2;
y2 = t;
}
if(x3>x4){
t = x3;
x3 = x4;
x4 = t;
}
if(y3>y4){
t = y3;
y3 = y4;
y4 = t;
}
if(ans[0]>x1&&ans[0]<x2&&ans[1]>y1&&ans[1]<y2)return true;
if(ans[0]>x3&&ans[0]<x4&&ans[1]>y3&&ans[1]<y4)return true;
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
String s = in.nextLine();
if(!s.matches("^[1-5][:](([+-]?(0|(0\\.\\d+)|[1-9][0-9]*(\\.\\d+)?))[,]([+-]?(0|(0\\.\\d+)|[1-9][0-9]*(\\.\\d+)?))\\s?)+$")){
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
return;
}
String a[] = s.split(":");
String[] points = a[1].split(" ");
String[] num;
int op = Integer.parseInt(a[0]);
int cnt=0;
if(op==1){
if(points.length!=2){
System.out.println("wrong number of points");
return;
}
double[] x = new double[2];
double[] y = new double[2];
for(String point:points){
num = point.split(",");
x[cnt] = Double.parseDouble(num[0]);
y[cnt] = Double.parseDouble(num[1]);
cnt++;
}
if(!check(x, y)){
System.out.println("points coincide");
return;
}
if(x[0]==x[1]){
System.out.println("Slope does not exist");
}
else{
double ans;
ans=(y[0]-y[1])/(x[0]-x[1]);
System.out.println(ans);
}
}
else if(op==2){
if(points.length!=3){
System.out.println("wrong number of points");
return;
}
double[] x = new double[3];
double[] y = new double[3];
for(String point:points){
num = point.split(",");
x[cnt] = Double.parseDouble(num[0]);
y[cnt] = Double.parseDouble(num[1]);
cnt++;
}
if(!check(x, y)){
System.out.println("points coincide");
return;
}
System.out.println(cal_dis(x,y));
}
else if(op==3){
if(points.length!=3){
System.out.println("wrong number of points");
return;
}
double[] x = new double[3];
double[] y = new double[3];
for(String point:points){
num = point.split(",");
x[cnt] = Double.parseDouble(num[0]);
y[cnt] = Double.parseDouble(num[1]);
cnt++;
}
if(!check(x, y)){
System.out.println("points coincide");
return;
}
if(x[0]==x[1]&&x[1]==x[2]){
System.out.println("true");
}
else{
System.out.println(check_line(x,y));
}
}
else if(op==4){
if(points.length!=4){
System.out.println("wrong number of points");
return;
}
double[] x = new double[4];
double[] y = new double[4];
for(String point:points){
num = point.split(",");
x[cnt] = Double.parseDouble(num[0]);
y[cnt] = Double.parseDouble(num[1]);
cnt++;
}
if(!check(x, y)){
System.out.println("points coincide");
return;
}
if((x[0]==x[1]&&x[2]==x[3])||(x[0]==x[2]&&x[1]==x[3])||(x[0]==x[3]&&x[1]==x[2])){
System.out.println("true");
}
else{
System.out.println(check_parr(x,y));
}
}
else{
if(points.length!=4){
System.out.println("wrong number of points");
return;
}
double[] x = new double[4];
double[] y = new double[4];
double[] ans;
for(String point:points){
num = point.split(",");
x[cnt] = Double.parseDouble(num[0]);
y[cnt] = Double.parseDouble(num[1]);
cnt++;
}
if(!check(x, y)){
System.out.println("points coincide");
return;
}
if((x[0]==x[1]&&x[2]==x[3])||(x[0]==x[2]&&x[1]==x[3])||(x[0]==x[3]&&x[1]==x[2])||check_parr(x,y)){
System.out.println("is parallel lines,have no intersection point");
}
else{
ans = cal_union(x,y);
System.out.print(ans[0]+","+ans[1]+" ");
System.out.println(check_coin(ans, x, y));
}
}
}
}
2.2.3. 点线形系列3-三角形的计算
-
思路:
-
前几点和前两题差不多,相当于初始化操作
-
op == 1:首先判断是否为等腰三角形,若是继续判断是否为等边三角形,若否直接输出"false false";
-
op == 2:周长和重心直接求,求面积用海伦公式误差最小;
-
op == 3:使用勾股定理的推广来判断三角形类型,三边中若有一种情况满足$a2$+$b2$==$c2$则为直角三角形,三边中若有一种情况满足$a2$+$b2$<$c2$则为钝角三角形,若三种情况都满足$a2$+$b2$>$c^2$则为锐角三角形,注意判断相等时要考虑误差;
-
op == 4:使用第二题中求交点的公式计算出两个交点(如果存在的话),然后找出可以和两个交点构成三角形的那个点(将三角形三个顶点坐标代入交线方程,如果某两个点得到的正负一致,则取剩余的那个点),求出该三角形的面积,记为$s_1$,用大三角形的面积$s$减去$s_1$即可得到剩余面积$s_2$;
-
op == 5:首先判断点是否在三角形三条边上,若不在则判断在三角形内外,用面积法判断最为简单,不妨设三角形三个顶点分别为$A,B,C$,需要判断的点为$O$,记$S_{AOB}=S_1,S_{AOC}=S_2,S_{BOC}=S_3$,大三角形面积为$S$,若$S_1+S_2+S_3==S$则说明该点在三角形内部。
-
-
实现:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static boolean check_trangle(double[] x, double[] y){
double a,b,c;
a = Math.sqrt((x[0]-x[1])*(x[0]-x[1])+(y[0]-y[1])*(y[0]-y[1]));
b = Math.sqrt((x[0]-x[2])*(x[0]-x[2])+(y[0]-y[2])*(y[0]-y[2]));
c = Math.sqrt((x[2]-x[1])*(x[2]-x[1])+(y[2]-y[1])*(y[2]-y[1]));
if((a+b<=c)||(a+c<=b)||(b+c<=a))return false;
return true;
}
public static boolean check_isosceles(double[] x,double[] y){
double a1,a2,a3;
a1 = Math.sqrt((x[0]-x[1])*(x[0]-x[1])+(y[0]-y[1])*(y[0]-y[1]));
a2 = Math.sqrt((x[0]-x[2])*(x[0]-x[2])+(y[0]-y[2])*(y[0]-y[2]));
a3 = Math.sqrt((x[2]-x[1])*(x[2]-x[1])+(y[2]-y[1])*(y[2]-y[1]));
if(Math.abs(a1-a2)<=0.1||Math.abs(a1-a3)<=0.1||Math.abs(a2-a3)<=0.1)return true;
return false;
}
public static boolean check_equilateral(double[] x, double[] y){
double a1,a2,a3;
a1 = Math.sqrt((x[0]-x[1])*(x[0]-x[1])+(y[0]-y[1])*(y[0]-y[1]));
a2 = Math.sqrt((x[0]-x[2])*(x[0]-x[2])+(y[0]-y[2])*(y[0]-y[2]));
a3 = Math.sqrt((x[2]-x[1])*(x[2]-x[1])+(y[2]-y[1])*(y[2]-y[1]));
if(Math.abs(a1-a2)<=0.1&&Math.abs(a1-a3)<=0.1&&Math.abs(a2-a3)<=0.1)return true;
return false;
}
public static double cal_C(double[] x, double[] y){
double a1,a2,a3;
a1 = Math.sqrt((x[0]-x[1])*(x[0]-x[1])+(y[0]-y[1])*(y[0]-y[1]));
a2 = Math.sqrt((x[0]-x[2])*(x[0]-x[2])+(y[0]-y[2])*(y[0]-y[2]));
a3 = Math.sqrt((x[2]-x[1])*(x[2]-x[1])+(y[2]-y[1])*(y[2]-y[1]));
return a1+a2+a3;
}
public static double cal_S(double[] x,double[] y){
double a1,a2,a3;
a1 = Math.sqrt((x[0]-x[1])*(x[0]-x[1])+(y[0]-y[1])*(y[0]-y[1]));
a2 = Math.sqrt((x[0]-x[2])*(x[0]-x[2])+(y[0]-y[2])*(y[0]-y[2]));
a3 = Math.sqrt((x[2]-x[1])*(x[2]-x[1])+(y[2]-y[1])*(y[2]-y[1]));
double p = (a1+a2+a3)/2;
return Math.sqrt(p*(p-a1)*(p-a2)*(p-a3));
}
public static double[] cal_core(double[] x,double[] y){
double[] ans = new double[2];
ans[0] = (x[0]+x[1]+x[2])/3;
ans[1] = (y[0]+y[1]+y[2])/3;
return ans;
}
public static void print_Dec(double ans){
String res = String.format("%.6f",ans);
res = res.replaceAll("0+?$", "");//删掉尾数为0的字符
res = res.replaceAll("[.]$", "");//结尾如果是小数点,则去掉
if(res.indexOf('.')==-1){
res+=".0";
}
System.out.print(res);
}
public static boolean check_obtuse(double[] x,double[] y){
double a,b,c;
a = Math.sqrt((x[0]-x[1])*(x[0]-x[1])+(y[0]-y[1])*(y[0]-y[1]));
b = Math.sqrt((x[0]-x[2])*(x[0]-x[2])+(y[0]-y[2])*(y[0]-y[2]));
c = Math.sqrt((x[2]-x[1])*(x[2]-x[1])+(y[2]-y[1])*(y[2]-y[1]));
if(a * a + b * b - c * c <= -0.1 || c * c + a * a - b * b <= -0.1|| b * b + c * c - a * a <= -0.1)return true;
return false;
}
public static boolean check_right(double[] x,double[] y){
double a,b,c;
a = Math.sqrt((x[0]-x[1])*(x[0]-x[1])+(y[0]-y[1])*(y[0]-y[1]));
b = Math.sqrt((x[0]-x[2])*(x[0]-x[2])+(y[0]-y[2])*(y[0]-y[2]));
c = Math.sqrt((x[2]-x[1])*(x[2]-x[1])+(y[2]-y[1])*(y[2]-y[1]));
if(Math.abs(a * a + b * b - c * c) < 0.1 || Math.abs(c * c + a * a - b * b) < 0.1|| Math.abs(b * b + c * c - a * a) < 0.1)return true;
return false;
}
public static boolean check_acute(double[] x,double[] y){
double a,b,c;
a = Math.sqrt((x[0]-x[1])*(x[0]-x[1])+(y[0]-y[1])*(y[0]-y[1]));
b = Math.sqrt((x[0]-x[2])*(x[0]-x[2])+(y[0]-y[2])*(y[0]-y[2]));
c = Math.sqrt((x[2]-x[1])*(x[2]-x[1])+(y[2]-y[1])*(y[2]-y[1]));
if(a * a + b * b - c * c >= 0.1 && a * a + c * c - b * b >= 0.1 && c * c + b * b - a * a >= 0.1)return true;
return false;
}
public static boolean on_edge(double x0, double y0, double[] x, double[] y){
double A,B,C;
A = y[1]-y[0];
B = x[0]-x[1];
C = y[0]*(x[1]-x[0])-x[0]*(y[1]-y[0]);
return x0 * A + B * y0 + C == 0;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
String s = in.nextLine();
if(!s.matches("^[1-5][:](([+-]?(0|(0\\.\\d+)|[1-9][0-9]*(\\.\\d+)?))[,]([+-]?(0|(0\\.\\d+)|[1-9][0-9]*(\\.\\d+)?))\\s?)+")){
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
return;
}
String a[] = s.split(":");
String[] points = a[1].split(" ");
String[] num;
int op = Integer.parseInt(a[0]);
int cnt=0;
if(op==1){
if(points.length!=3){
System.out.println("wrong number of points");
return;
}
double[] x = new double[3];
double[] y = new double[3];
for(String point:points){
num = point.split(",");
x[cnt] = Double.parseDouble(num[0]);
y[cnt] = Double.parseDouble(num[1]);
cnt++;
}
if(!check_trangle(x,y)){
System.out.println("data error");
return;
}
if(check_isosceles(x,y)){
System.out.print("true ");
}
else{
System.out.print("false ");
}
if(check_equilateral(x,y)){
System.out.println("true");
}
else{
System.out.println("false");
}
}
else if(op==2){
if(points.length!=3){
System.out.println("wrong number of points");
return;
}
double[] x = new double[3];
double[] y = new double[3];
double[] ans = new double[2];
for(String point:points){
num = point.split(",");
x[cnt] = Double.parseDouble(num[0]);
y[cnt] = Double.parseDouble(num[1]);
cnt++;
}
if(!check_trangle(x,y)){
System.out.println("data error");
return;
}
print_Dec(cal_C(x,y));
System.out.print(" ");
print_Dec(cal_S(x,y));
System.out.print(" ");
ans = cal_core(x,y);
print_Dec(ans[0]);
System.out.print(",");
print_Dec(ans[1]);
}
else if(op==3){
if(points.length!=3){
System.out.println("wrong number of points");
return;
}
double[] x = new double[3];
double[] y = new double[3];
for(String point:points){
num = point.split(",");
x[cnt] = Double.parseDouble(num[0]);
y[cnt] = Double.parseDouble(num[1]);
cnt++;
}
if(!check_trangle(x,y)){
System.out.println("data error");
return;
}
System.out.println(check_obtuse(x,y)+" "+check_right(x,y)+" "+check_acute(x,y));
}
else if(op==4){
if(points.length!=5){
System.out.println("wrong number of points");
return;
}
String[] v = points[0].split(",");
double x1,x2,y1,y2,x3,y3,x4,y4,x5,y5;
x1 = Double.parseDouble(v[0]);
y1 = Double.parseDouble(v[1]);
String[] u = points[1].split(",");
x2 = Double.parseDouble(u[0]);
y2 = Double.parseDouble(u[1]);
String[] w = points[2].split(",");
x3 = Double.parseDouble(w[0]);
y3 = Double.parseDouble(w[1]);
String[] p = points[3].split(",");
x4 = Double.parseDouble(p[0]);
y4 = Double.parseDouble(p[1]);
String[] q = points[4].split(",");
x5 = Double.parseDouble(q[0]);
y5 = Double.parseDouble(q[1]);
if(x1==x2&&y1==y2){
System.out.println("points coincide");
return;
}
if(gongxian(x3,x4,x5,y3,y4,y5)==1){
System.out.println("data error");
return;
}
if(gongxian(x3,x4,x1,y3,y4,y1)==1&&gongxian(x3,x4,x2,y3,y4,y2)==1||gongxian(x5,x4,x1,y5,y4,y1)==1&&gongxian(x5,x4,x2,y5,y4,y2)==1||gongxian(x3,x5,x1,y3,y5,y1)==1&&gongxian(x3,x5,x2,y3,y5,y2)==1){
System.out.print("The point is on the edge of the triangle");
return;
}
jiequ_mianji(x1,x2,x3,x4,x5,y1,y2,y3,y4,y5);
}
else{
if(points.length!=4){
System.out.println("wrong number of points");
return;
}
double x0,y0;
double[] x = new double[3];
double[] y = new double[3];
num = points[0].split(",");
x0 = Double.parseDouble(num[0]);
y0 = Double.parseDouble(num[1]);
for(int i=1;i<points.length;i++){
num = points[i].split(",");
x[cnt] = Double.parseDouble(num[0]);
y[cnt] = Double.parseDouble(num[1]);
cnt++;
}
if(!check_trangle(x,y)){
System.out.println("data error");
return;
}
double[] ix = new double[2], iy = new double[2];
ix[0] = x[0];
ix[1] = x[1];
iy[0] = y[0];
iy[1] = y[1];
if(on_edge(x0,y0,ix,iy)&&x0>=Math.min(ix[0],ix[1])&&x0<=Math.max(ix[0],ix[1])&&y0>=Math.min(iy[0],iy[1])&&y0<=Math.max(iy[0],iy[1])){
System.out.println("on the triangle");
return;
}
ix[0] = x[0];
ix[1] = x[2];
iy[0] = y[0];
iy[1] = y[2];
if(on_edge(x0,y0,ix,iy)&&x0>=Math.min(ix[0],ix[1])&&x0<=Math.max(ix[0],ix[1])&&y0>=Math.min(iy[0],iy[1])&&y0<=Math.max(iy[0],iy[1])){
System.out.println("on the triangle");
return;
}
ix[0] = x[1];
ix[1] = x[2];
iy[0] = y[1];
iy[1] = y[2];
if(on_edge(x0,y0,ix,iy)&&x0>=Math.min(ix[0],ix[1])&&x0<=Math.max(ix[0],ix[1])&&y0>=Math.min(iy[0],iy[1])&&y0<=Math.max(iy[0],iy[1])){
System.out.println("on the triangle");
return;
}
double[] sx = new double[3], sy = new double[3];
sx[0] = x0;sy[0] = y0;
double s1,s2,s3;
sx[1] = x[0];sy[1] = y[0];
sx[2] = x[1];sy[2] = y[1];
s1 = cal_S(sx,sy);
sx[1] = x[0];sy[1] = y[0];
sx[2] = x[2];sy[2] = y[2];
s2 = cal_S(sx,sy);
sx[1] = x[1];sy[1] = y[1];
sx[2] = x[2];sy[2] = y[2];
s3 = cal_S(sx,sy);
if(Math.abs(s1+s2+s3-cal_S(x,y))<0.00001){
System.out.println("in the triangle");
}
else{
System.out.println("outof the triangle");
}
}
}
public static int gongxian(double x1,double x2,double x3,double y1,double y2,double y3){
double k1,b1,c1;
k1 = y2-y1;
b1 = x1-x2;
c1 = x2*y1-x1*y2;
if(k1*x3+b1*y3+c1==0){
return 1;
}
else{
if(k1*x3+b1*y3+c1<0){
return -1;
}
else{
return 0;
}
}
}
public static void jiequ_mianji(double x1,double x2,double x3,double x4,double x5,double y1,double y2,double y3,double y4,double y5){
double c1,c2,c3,c4,k1,k2,k3,k4,b1,b2,b3,b4,p0,q0,p1,q1,p2,q2;
k1 = y2-y1;
b1 = x1-x2;
c1 = x2*y1-x1*y2;
k2 = y4-y3;
b2 = x3-x4;
c2 = x4*y3-x3*y4;
k3 = y5-y3;
b3 = x3-x5;
c3 = x5*y3-x3*y5;
k4 = y5-y4;
b4 = x4-x5;
c4 = x5*y4-x4*y5;
if(k2*b1-k1*b2!=0){
p0 = ((b2*c1-b1*c2) / (k2*b1-k1*b2));
q0 = ((k1*c2-k2*c1) / (k2*b1-k1*b2));
}
else{
p0=999999999.;
q0=9999999.;
}
if(k3*b1-k1*b3!=0){
p1 = (b3*c1-b1*c3)/(k3*b1-k1*b3);
q1 = (k1*c3-k3*c1)/(k3*b1-k1*b3);
}
else{
p1=99999999.;
q1=9999999.;
}
if(k4*b1-k1*b4!=0){
p2 = (b4*c1-b1*c4)/(k4*b1-k1*b4);
q2 = (k1*c4-k4*c1)/(k4*b1-k1*b4);
}
else{
p2=99999999999.;
q2=999999999.;
}
double s1=0,s2,s0;
s0=mianji(x3,x4,x5,y3,y4,y5);
if(p0==p1&&q0==q1){
s1 = 0.5*juli_pp(p0,p2,q0,q2)*juli_px(x4,x1,x2,y4,y1,y2);
}
else if(p1==p2&&q1==q2){
s1 = 0.5*juli_pp(p0,p1,q0,q1)*juli_px(x3,x1,x2,y3,y1,y2);
}
else if(p0==p2&&q0==q2){
s1 = 0.5*juli_pp(p0,p1,q0,q1)*juli_px(x3,x1,x2,y3,y1,y2);
}
else {
if (xianduannei(x3, x4, p0, y3, y4, q0)) {
if (xianduannei(x3, x5, p1, y3, y5, q1)) {
s1 = 0.5 * juli_pp(p0, p1, q0, q1) * juli_px(x3, x1, x2, y3, y1, y2);
} else if (xianduannei(x4, x5, p2, y4, y5, q2)) {
s1 = 0.5 * juli_pp(p0, p2, q0, q2) * juli_px(x4, x1, x2, y4, y1, y2);
} else {
System.out.println("1");
return;
}
} else {
if (xianduannei(x3, x5, p1, y3, y5, q1)) {
if (xianduannei(x4, x5, p2, y4, y5, q2)) {
s1 = 0.5 * juli_pp(p1, p2, q1, q2) * juli_px(x5, x1, x2, y5, y1, y2);
} else {
System.out.print("1");
return;
}
} else {
System.out.print("0");
return;
}
}
}
s2 = s0 - s1;
if(s2<=0||s1<=0){
System.out.println("1");
return;
}
String S1,S2;
S1 = Double.toString(s1);
S2 = Double.toString(s2);
if(xiaoshuwei(S1)>6){
S1 = String.format("%.6f",s1);
s1 = Double.parseDouble(S1);
}
if(xiaoshuwei(S2)>6){
S2 = String.format("%.6f",s2);
s2 = Double.parseDouble(S2);
}
if(s2<s1){
System.out.print("2"+" "+s2+" "+s1);
}
else{
System.out.print("2"+" "+s1+" "+s2);
}
return;
}
public static int xiaoshuwei(String s){
String str1 = s.substring(0, s.indexOf("."));
String str2 = s.substring(str1.length()+1);
return str2.length();
}
public static double mianji(double x1,double x2,double x3,double y1,double y2,double y3){
return 0.5*juli_pp(x2,x3,y2,y3)*juli_px(x1,x2,x3,y1,y2,y3);
}
public static double juli_pp(double x1,double x2,double y1,double y2){
return Math.sqrt((x1-x2)*(x1-x2)+(y1-y2)*(y1-y2));
}
public static double juli_px(double x1,double x2,double x3,double y1,double y2,double y3){
if(x2==x3){
return Math.abs(x1-x2);
}
if(y2==y3){
return Math.abs(y1-y2);
}
double k = (y2-y3)/(x2-x3);
double b = y3-k*x3;
double ans = Math.abs((k*x1-y1+b)/Math.sqrt(k*k+1));
return ans;
}
public static boolean xianduannei(double x1,double x2,double x3,double y1,double y2,double y3){
if(((x3-x1)*(x3-x2)<0)||((y3-y1)*(y3-y2)<0)){
return true;
}
else return false;
}
}
复杂度分析
第一题:
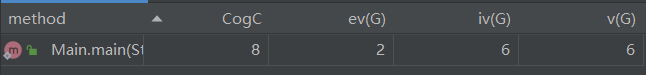
ok
第二题:
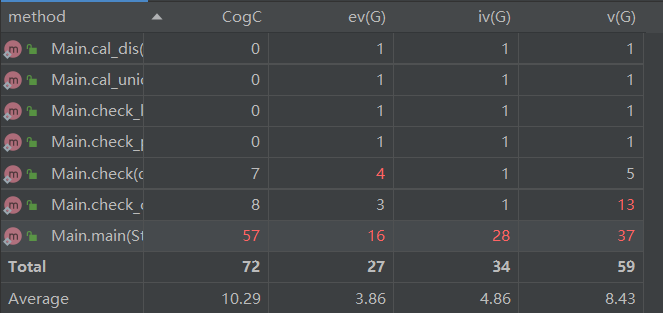
主函数复杂度较高
第三题:
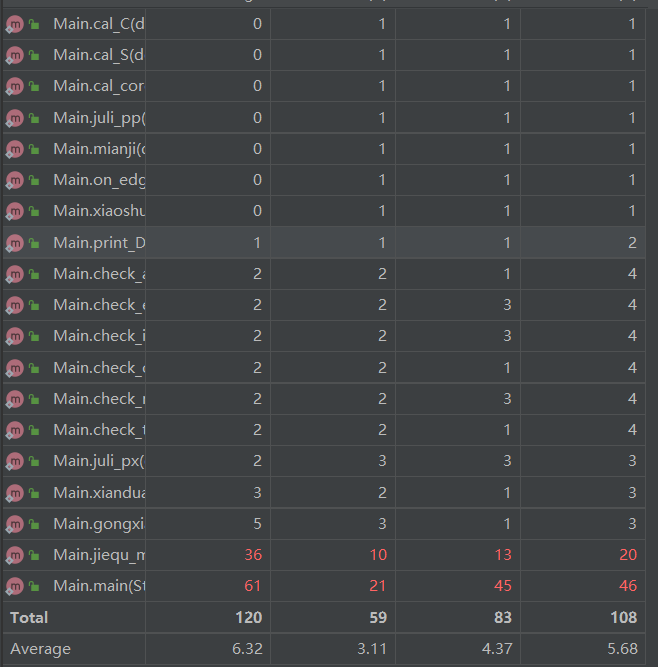
主函数复杂度较高
3. 踩坑心得
- 求点到直线的距离,如果直线方程为形如$y=kx+b$的形式,则会有几个点过不去,给这个问题也是折磨了很久;
- 判断是否构成直角三角形需要控制精度,即$a2+b2-c^2<0.01$;
- 使用面向过程的形式来完成,需要用到多次函数调用,代码一长容易乱,非常考验脑细胞...
4. 改进建议
由于平时不怎么用面向对象的形式写代码,再加上前几次作业都还比较简单,所以作业代码都是都面向过程的形式完成的,希望后面几次作业可以用面向对象的形式来完成,不然到结课还是写不好面向对象的代码。
5. 总结
关于java中的数组
Java中的数组属于定长数组,定义时需要给定数组长度,这使得面对动态增删时不太方便,所以Java又提供了ArrayList类,该类实现了数据结构中链表的功能,使得数组长度可以动态增加,方便了需要动态增加长度的任务。
关于java中String类的API
String作为经常使用的非一般类数据类型,内置API相当之多,但学习起来并不会太难,有时候只需要一个函数就能解决许多复杂的操作,使得代码更加简洁。
关于java中的类
Java中类特有一种构造函数,构造函数会在对象实例化时被调用。
类中的函数允许同名但是传入参数的不同的情况,使得“同一个函数”可以具有多个功能,这种函数重载功能大大加强了程序的可读性。
使用非一般类型类数组时,不仅要申请类数组空间,若要初始化类数组,则需要以对象的形式赋值,而不能使用形如
Person[] p = new Person[10];
p[0].a = 0; //此处会报空指针错误
p[0] = new Person(); //正确初始化 +- ↩︎



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号