1 import numpy as np
2 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
3 import math
4
5 from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
6
7 xmin=-5
8 xmax=5
9 ymin=-5
10 ymax=5
11 N=1000
12 X=np.linspace(xmin,xmax,N)
13 Y=np.linspace(ymin,ymax,N)
14 X, Y = np.meshgrid(X, Y)
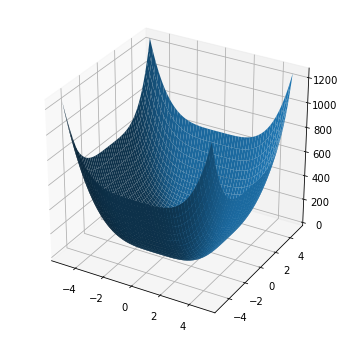
15 Z = X**4 + Y**4
16
17 fig = plt.figure(figsize=(6,6))
18 ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
19
20 # Plot a 3D surface
21 ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z)
22
23 plt.show()
24
25 plt.figure()
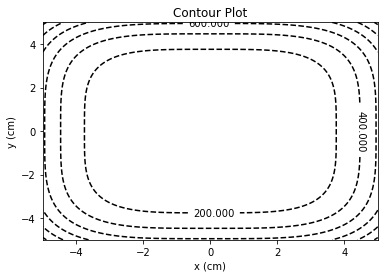
26 cp = plt.contour(X, Y, Z, colors='black', linestyles='dashed')
27 plt.clabel(cp, inline=True,
28 fontsize=10)
29 plt.title('Contour Plot')
30 plt.xlabel('x (cm)')
31 plt.ylabel('y (cm)')
32 plt.show()
![]()
![]()
1 for j in range(N):
2 for i in range(0,N):
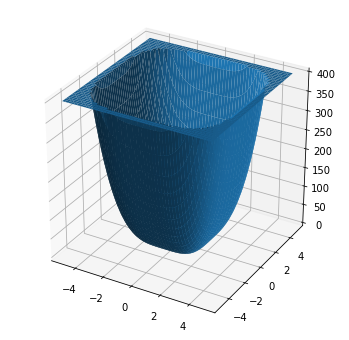
3 if Z[i,j] > 400:
4 Z[i,j] = 400 # replace the data greater than 400 with 400
5
6 fig = plt.figure(figsize=(6,6))
7 ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
8
9 # Plot a 3D surface
10 ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z)
![]()
1 # The rectangles method
2 vol_whole = ((xmax-xmin)**2)*400
3 def rectangle(X,Y,N):
4 d = X[1]-X[0]
5 vol = 0
6 for i in range(0,N):
7 vol += Y[i]
8 vol *= d
9 return vol
10
11 s = np.zeros(N)
12 for i in range(0,N): # integrate in x surface first
13 s[i] = rectangle(X[i,:],Z[i,:],N) # s is the surface area
14 vol = rectangle(Y[:,0],s,N) # integrate in y surface. This volume is the part under the water surface, not the water volume
15
16 vol_true = vol_whole - vol # you should use whole volume under 400 to minus the volume under the water surface
17 print('volume by rectangle is: ', vol_true)
volume by rectangle is: 19696.675605448814
1 # Simpson’s method
2 def simps(X,Y,N):
3 d = X[1]-X[0]
4 val_a = 0
5 val_b = 0
6 for i in range(N):
7 if i ==0 or i == N-1:
8 pass
9 else:
10 if i % 2 == 1:
11 val_a += 4*Y[i]
12 else:
13 val_b += 2*Y[i]
14 return (d/3)*(Y[0]+Y[N-1]+val_a+val_b)
15
16 s = np.zeros(N)
17 for i in range(N): # integrate in x surface first
18 s[i] = simps(X[i,:],Z[i,:],N) # s is the surface area
19 vol = simps(Y[:,0],s,N) # integrate in y surface
20
21 vol_true = vol_whole - vol
22 print('volume by Simpson is: ', vol_true)
volume by Simpson is: 19803.484672329087
1 # SciPy
2 import scipy.integrate as integrate
3
4 vol_whole = ((xmax-xmin)**2)*400
5 dx=X[0,1]-X[0,0]
6 dy=Y[1,0]-Y[0,0]
7 s=np.zeros(N)
8 for i in range(N):
9 s[i]=integrate.simps(Z[:,i],dx=dx)
10 Volume_Simpson=integrate.simps(s,dx=dy)
11 vol = vol_whole - Volume_Simpson
12 print('volume by Scipy is: ', vol)
volume by Scipy is: 19776.795765649047


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号