选择排序的实现以及如何编写测试 #CS61B-sp18-3.1
Selection Sort的思想:
就是在一系列数字中先找到一个最小的放在所有数字的第一个位置上,然后再从余下的数字里面找最小个放在余下的数字里的第一个位置上。
例如:
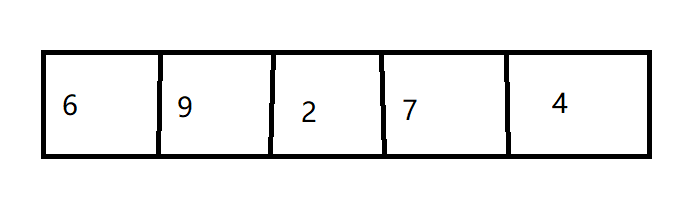
在这段数据里面我们找到最小的数字是2,它的下标是2,那么我们把它移到最前面,就变成
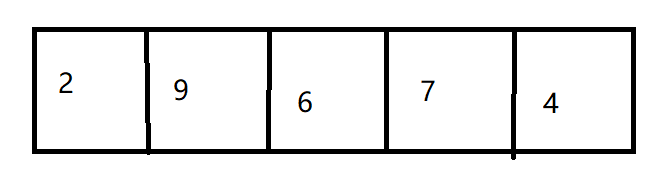
如此往复,直到所有的的全部排序完毕才算结束。
为了实现这一排序我们需要:
①逐个找到最小值的下标
②将最小值与位置靠前的元素交换
③将余下的所有完成交换
在CS61B中,Josh Hug使用了递归的方式来解决这个问题(他真的好喜欢递归- -!),具体代码实现如下:
/** * @author century */ public class Sort { public static void sort(String[] str) { // find the smallest item // move it to the front // selection sort the rest (using recursion?) sort(str,0); } /** * This is a helper method for the public method(sort) * @param str * @param start */ private static void sort(String[] str, int start) { if (start == str.length) { return; } int smallestIndex = findSmallest(str, start); swap(str, start, smallestIndex); sort(str, start + 1); } /** * return the smallest String item's index of this arr * @param str * @return smallestIndex */ public static int findSmallest(String[] str, int start) { int smallestIndex = start; for (int i = start; i < str.length; i += 1) { int comp = str[i].compareTo(str[smallestIndex]); if (comp < 0) { smallestIndex = i; } } return smallestIndex; } /** * swap the value of two different index * @param arr * @param a * @param b */ public static void swap(String[] arr, int a, int b) { String temp = arr[a]; arr[a] = arr[b]; arr[b] = temp; } }
另外在这门课里面,Josh Hug教给学生应该如何编写测试来验证自己所编写的代码的正确性。
编写测试的步骤是:
先导入JUnit的包,然后再把JUnit包中Assert类的所有方法给导入,之后只需要在每个测试方法上加上一个@Test注解,然后在内部编写具体的测试方法就vans了。
下面代码是关于上面选择排序的测试类:
import org.junit.Test; import static org.junit.Assert.*; /** * @author century */ public class TestSort { /** * Test the Sort.sort(String[] arr) */ @Test public void testSort() { String[] input = {"i","have","an","egg"}; String[] expected = {"an","egg","have","i"}; Sort.sort(input); assertArrayEquals(input, expected); } /** * Test the method (Sort.findSmallest) */ @Test public void testFindSmallest() { String[] input = {"i","have","an","egg"}; int expected = 2; int actual = Sort.findSmallest(input, 0); assertEquals(actual,expected); } /** * Test the method (Sort.swap) */ @Test public void testSwap() { String[] input = {"i","have","an","egg"}; String[] input2 = {"an","have","i","egg"}; int a = 0, b = 2; Sort.swap(input2, 0 , 2); assertArrayEquals(input, input2); } }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号