MyBatis
框架概述
三层架构
mvc:web开发中,使用mvc架构模式。m:数据,v:视图,c:控制器
c控制器:接受请求,调用servlet对象,显示请求的处理结果,当前使用servlet作为控制器
v视图:现在使用jsp,html,css,js。显示请求的处理结果,把m中的数据显示出来
m数据:来自数据库mysql,来自文件,来自网络
mvc作用:
1)实现解耦和
2)让mvc各司其职
3)使得系统扩展更好,更容易维护
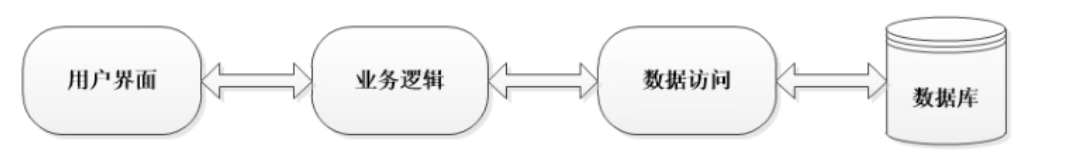
三层架构:
1.界面层(视图层):接受用户的请求,调用service,显示请求的处理结果。包含了jsp,html,servlet等对象,对应 的包controller
2.业务逻辑层:处理业务逻辑,使用算法处理数据的,把数据返回给界面层。对应的是service包,和包中的很多xxServive类
3.持久层(数据库访问层):访问数据库,或者读取文件,访问网络,获取数据。对应的包是dao。dao包中很多的StudentDao....
三层架构请求的处理流程
用户发起请求---->界面层---->业务逻辑层---->持久层---->数据库(mysql)
为什么要使用三层?
1.结构清晰、耦合度低,各层分工明确
2.可维护性高,可扩展性强
3.有利于标准化
4.开发人员可以只关注整个结构中的其中某一层的功能实现
5.有利于各层逻辑的复用
三层架构模式和框架
每一层对应着一个框架
1)界面层---SpringMVC
2)业务层---Spring
3)持久层---MyBatis
框架
1)什么是框架(framework)
框架:就是一个软件,完成了部分的功能。软件中的类和类之间的方法调用都已经规定好了。通过这些类可以完成某些功能。框架看作是模板
框架是可以升级、改造的,框架是安全的。
框架解决的问题
1)框架能实现技术的整合
2)提高开发效率,降低难度
JDBC访问数据库的优缺点
优点:直观、好理解
缺点:
1.创建很多对象 Connection,Statement,ResultSet
2.注册驱动
3.执行sql语句
4.把ResultSet转为Java对象
5.关闭资源
6.sql语句和业务逻辑代码混在一起
MyBatis框架
什么是Mybatis?
是一个持久层框架,原名是ibatis,2013改名为MyBatis.MyBatis可以操作数据库,对数据执行增删改查,看作是高级的jdbc。解决jdbc的缺点
MyBatis能做什么?
1)注册驱动
2)创建jdbc中使用的Connection,Statement,ResultSet
3)执行sql语句,得到ResultSet
4)处理ResultSet,把记录集中的数据转换为java对象,同时还能把java对象放入到List集合
5)关闭资源
6)实现sql语句和java代码的解耦合
MyBatis的官网:http://mybatis.org/spring/zh/index.html
MyBatis入门
第一个例子
实现步骤:
0.创建student表(id,name,email,age) 1.新建maven项目 2.修改pom.xml 1)加入mybatis依赖,mysql驱动,junit 2)在< buide>加入插件资源 3.创建实体类Student。定义属性,属性名与列名保持一致 4.创建Dao接口,定义操作数据库的方法 5.创建xml文件(mapper文件),写sql语句。 mybatis框架推荐是把sql语句和java代码分开 mapper文件:定义和dao接口在同一个目录,一个表一个mapper文件 6.创建mybatis的主配置文件(xml文件):有一个,放在resource目录下 1)定义创建连接实例的数据源(DataSource)对象 2)指定其他mapper文件的位置 7.创建测试的内容 使用main方法,测试mybatis访问数据库 也可以使用junit访问数据库
代码实现
<!--mybatis的依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.1</version>
</dependency>
<!--mysql驱动-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.26</version>
</dependency>
<!--单元测试-->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.11</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<!--资源插件:处理src/main/java目录中的xml-->
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/java</directory><!--所在的目录-->
<includes><!--包括目录下的.properties .xml文件都会被扫描-->
<include>**/*.properties</include>
<include>**/*.xml</include>
</includes>
<filtering>false</filtering>
</resource>
</resources>
</build>
public interface StudentDao {
//查询一个学生
Student selectStudentById(Integer id);
//添加学生
//返回值int:表示本次操作影响的数据库行数
int insertStudent(Student student);
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.cedric.dao.StudentDao">
<!-- <select id="selectBlog" resultType="Blog">
select * from Blog where id = #{id}
</select>-->
<!--查询一个学生student
<select>:表示查询操作,里面是select语句
id:要执行的sql语句的唯一标识,是一个自定义字符串
推荐使用dao接口中的方法名称
resultType:告诉mybatis,执行sql语句,把数据赋值给那个类型的java对象
resultType的值现在使用java对象的全限定名称
#{studentId}:占位符
-->
<select id="selectStudentById" resultType="com.cedric.domain.Student">
select id,name,email,age from student where id=#{studentId}
</select>
<!--添加insert
insert into student values (1003,"王五","wangwu@123.com",38)
如果传入给mybatis是一个java对象,使用#{属性名} 获取此属性的值
属性值如果放到#{}占位符的位置,mybatis执行此属性 对应getxxx()
例如 #{id},执行getId{}
-->
<insert id="insertStudent">
insert into student values (#{id},#{name},#{email},#{age})
</insert>
</mapper>
<!--
1.约束文件
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"
约束文件作用:定义和限制当前文件中可以使用的标签和属性,以及标签出现的顺序
2.mapper是根标签
namespace: 命名空间,必须有值,不能为空,唯一值
推荐使用Dao接口的全限定名称
作用: 参与识别sql语句的作用
3.在mapper里面可以写<insert>,<update>,<delete>,<select>等标签
<insert>里面是 insert语句,表示执行的insert操作
其余几个标签与之相似
-->
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<!--设置日志-->
<settings>
<setting name="logImpl" value="STDOUT_LOGGING"/>
</settings>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<!--配置数据源:创建Connection对象-->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<!--driver:驱动的内容-->
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/>
<!--数据库的url-->
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springdb?useUnicode=true&
characterEncoding=utf-8"/>
<!--用户名-->
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<!--密码-->
<property name="password" value="cedric1010"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<!--
指定其他mapper文件的位置
指定其他mapper文件的目的是找到其他文件的sql语句
-->
<mappers>
<!--
使用mapper的resource属性指定mapper文件的路径
这个路径是从target/classes路径开启的
使用注意:
resource="mapper文件的路径,使用 \ 分割路径“
一个mapper resource指定一个mapper文件
-->
<mapper resource="com\cedric\dao\StudentDao.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
package com.cedric;
import com.cedric.domain.Student;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class MyTest {
// 测试mybatis执行sql语句
@Test
public void testSelectStudentById() throws IOException {
// 调用mybatis某个对象的方法,执行mapper文件中的sql语句
// mybatis核心类:SqlSessionFactory
// 1.定义mybatis主配置文件的位置,从类路径开始的相对路径
String config = "mybatis.xml";
// 2.读取主配置文件,使用mybatis框架中的Resources类
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(config);
// 3.创建SqlSessionFactory对象,使用SqlSessionFactoryBuidler类
SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
// 4.获取SqlSession对象
SqlSession session = factory.openSession();
//5.指定要执行的sql语句的id
// sql的id = namespace+"." + select|update|insert|delete标签的id属性值
String sqlId = "com.cedric.dao.StudentDao"+"."+"selectStudentById";
// 6.通过SqlSession的方法,执行sql语句
Student student = session.selectOne(sqlId);
System.out.println("使用mybatis查询一个学生:" + student);
// 7.关闭SqlSession对象
session.close();
}
// 测试mybatis执行sql语句
@Test
public void testSelectStudentById2() throws IOException {
// 调用mybatis某个对象的方法,执行mapper文件中的sql语句
// mybatis核心类:SqlSessionFactory
// 1.定义mybatis主配置文件的位置,从类路径开始的相对路径
String config = "mybatis.xml";
// 2.读取主配置文件,使用mybatis框架中的Resources类
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(config);
// 3.创建SqlSessionFactory对象,使用SqlSessionFactoryBuidler类
SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
// 4.获取SqlSession对象
SqlSession session = factory.openSession();
//5.指定要执行的sql语句的id
// sql的id = namespace+"." + select|update|insert|delete标签的id属性值
String sqlId = "com.cedric.dao.StudentDao"+"."+"selectStudentById";
// 6.通过SqlSession的方法,执行sql语句
Student student = session.selectOne(sqlId,1002);
System.out.println("使用mybatis查询一个学生:" + student);
// 7.关闭SqlSession对象
session.close();
}
@Test
public void testInsertStudent() throws IOException {
String config = "mybatis.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(config);
SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
// 指定要执行的sql语句的id
SqlSession session = factory.openSession();
// sql的id = namespace+"." + select|update|insert|delete标签的id属性值
String sqlId = "com.cedric.dao.StudentDao"+"."+"insertStudent";
// 通过SqlSession的方法,执行sql语句
Student student = new Student();
student.setId(1005);
student.setName("马超");
student.setEmail("machao@qq.com");
student.setAge(1500);
int count = session.insert(sqlId,student);
System.out.println("使用mybatis添加一个学生,count = " + count);
//mybatis默认执行的sql语句是 手动画提交事务模式,在做insert update delete后需要提交事务
session.commit();
session.close();
}
}
概念
1.自动提交:当你的sql语句执行完毕之后,提交事务。数据库更新操作直接保存到数据
2.手动提交事务:在你需要提交事务的位置,执行方法,提交事务或者回滚事务
MyBatis重要对象
1)Resources:mybatis框架中的对象,一个作用 读取主配置文件信息
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis.xml");
2)SqlSessionFactoryBuilder:负责创建SqlSessionFactory对象
SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
3)SqlSessionFactory:重要对象
SqlSessionFactory是重量级对象:创建此对象需要使用更多的资源和时间,项目中有一个就行
SqlSessionFactory接口:作用是SqlSession的工厂,就是创建SqlSession对象
DefaultSqlSessionFactory实现类
public class DefaultSqlSessionFactory implements SqlSessionFactory(){ }
SqlSessionFactory接口中的方法
openSession(boolean):获取一个默认的Sql'Session对象,默认是需要手动提交事务的(true,false)
4)SqlSession对象
SqlSession对象就是通过SqlSessionFactory获取的,SqlSession本身是接口
DefaultSqlSession:实现类
public class DefaultSqlSession implements SqlSession{ }
SqlSession作用是提供了大量的执行sql语句的方法:
selectOne selectList selectMap insert update delete commit rollback
注意:SqlSession对象不是线程安全的,使用步骤:
1.在方法的内部,执行sql语句之前,先获取SqlSession对象
2.在调用SqlSession的方法,执行sql语句
3.关闭SqlSession对象,执行SqlSession.close()
使用工具类和模板
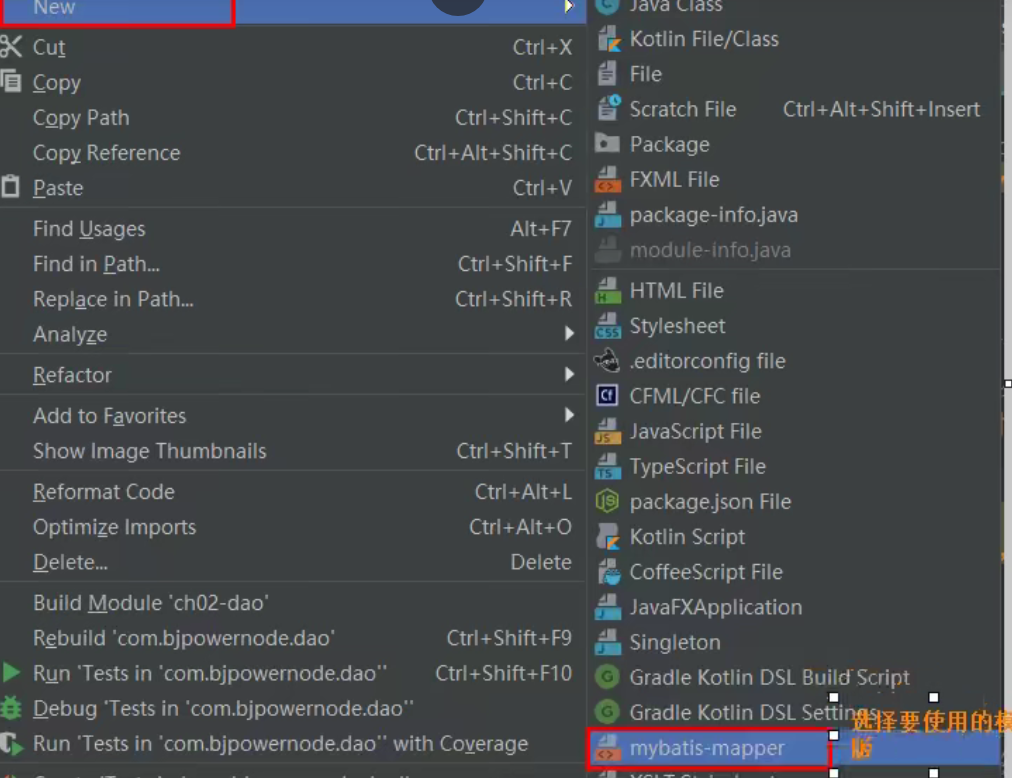
1)创建模板,mapper文件模板和mybatis主配置模板
创建模板的步骤:
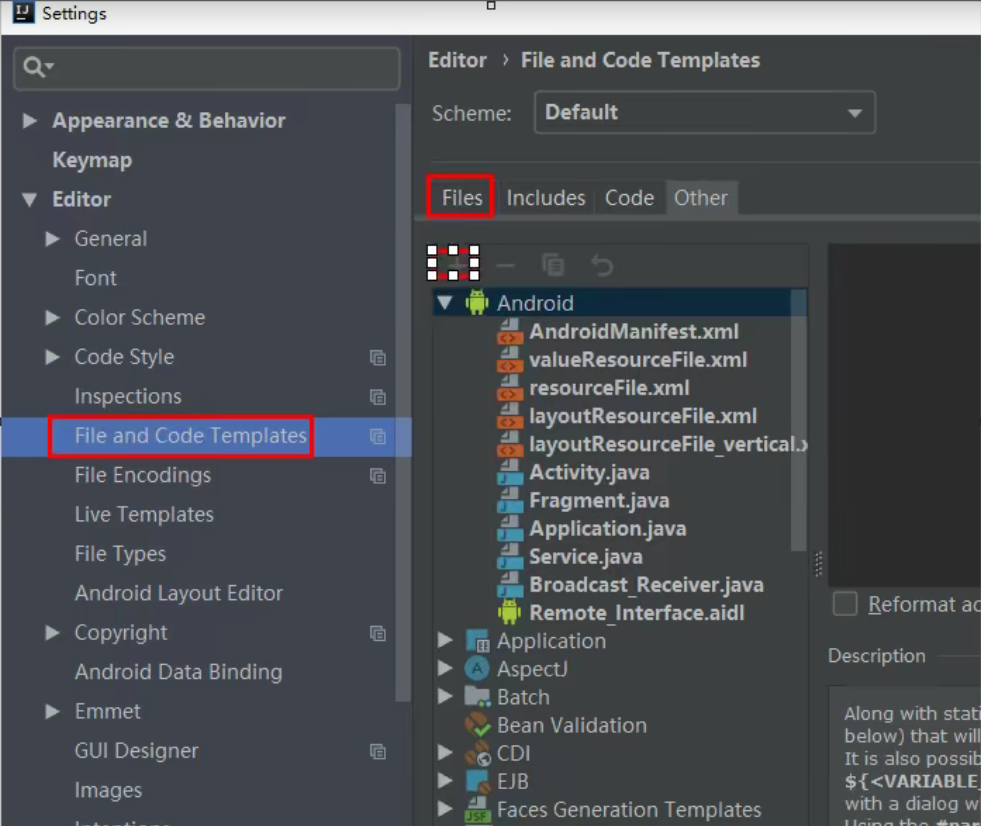
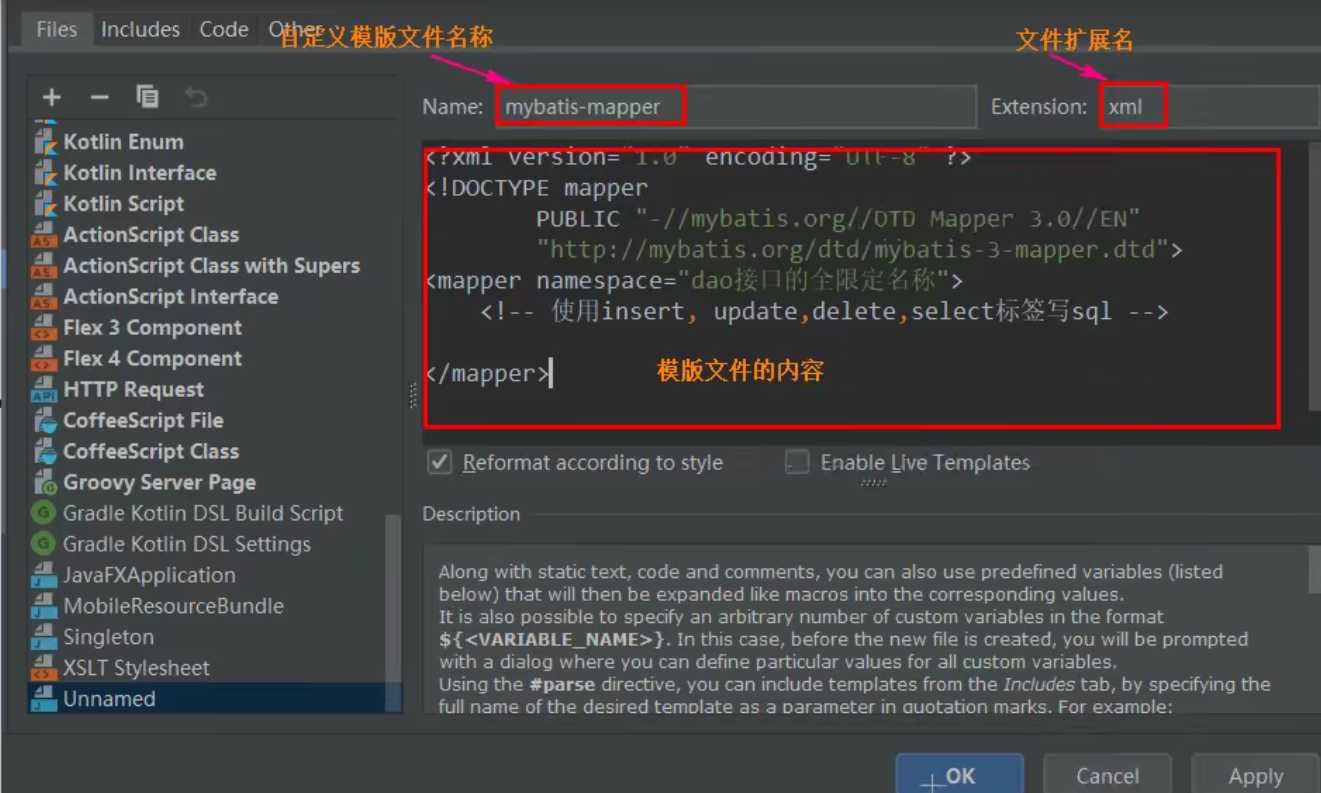
创建文件选择使用的模板
MyBatis的Dao代理
Dao代理
mybatis提供代理
mybatis创建Dao接口的实现类对象,完成对sql语句的执行。mybatis创建一个对象代替你的dao实现功能
使用mybatis代理的要求
1)mapper文件中的namepace一定是dao接口的全限定名称
2)mapper文件中标签的id是dao接口方法名称
mybatis代理的实现方式
使用SqlSession对象的方法getMapper(dao.class)
例如:现在又StudentDao接口
String config = "mybatis.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(config);
SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSession session = factory.openSession();
StudentDao dao = session.getMapper(StudentDao.class);
Student stu = dao.selectById(1001);
// 上面的代码中
StudentDao dao = session.getMapper(StudentDao.class);
//等同于
StudentDao dao = new StudentDaoImpl();
理解参数
理解参数是:通过java程序把数据传入到mapper文件中的sql语句。参数主要是指dao接口方法的形参
parameterType
parpameterType:表示参数的类型,指定dao方法的形参数据类型。这个形参的数据类型是给mybatis使用
mybatis再给sql语句的参数赋值时使用
第一个用法 :java类型的全限定类型名称 parameterType=“integer”
第二个用法:mybatis定义的java类型的别名 paramterType = “int”
parameterType:mybatis通过反射机制可以获取 dao接口方法参数的类型,可以不写
<select id="selectById" parameterType="integer"
resultType="com.cedric.domain.Student">
select id,name,email,age from student where id=#{studentId}
</select>
dao接口方法是一个简单类型的参数
//dao接口的方法形参是一个简单类型
//简单类型:java基本数据类型和String
Student selectByEmail(String email);
<!--
dao接口是一个简单类型的参数
mapper文件,获取这个参数值,使用#{任意字符}
-->
<select id="selectByEmail" resultType="com.cedric.domain.Student">
select id,name,email,age from student where email=#{studentEmail}
</select>
dao接口方法有多个简单类型的参数
@Param:命名参数,在方法的形参前面使用的,定义参数名,这个名称可以用在mapper文件中
/*
多个简单类型的参数
使用@Param命名参数,注解是mybatis提供的
位置:在形参定义的前面
属性:value 自定义的参数名称
*/
List<Student> selectByNameOrAge(@Param("myname") String name,
@Param("myage") Integer age
);
<!--
多个简单类型的参数
当使用了@Param命名后,例如@Param("myname")
在mapper中,使用#{命名的参数},例如#{myname}
-->
<select id="selectByNameOrAge" resultType="com.cedric.domain.Student">
select id,name,email,age from student where name=#{myname} or age=#{myage}
</select>
dao接口方法使用一个对象作为参数
方法的形参是一个java对象。这个java对象表示多个参数。使用对象的属性值作为参数使用
dao接口中的方法定义
public class Student(){
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String email;
private Integer age;
// set | get方法
}
public class QueryParam {
private Object p1;
private Object p2;
// set | get方法
}
dao接口中的方法定义
/**
* 一个java对象作为参数(对象有属性,每个属性有set get方法)
*/
List<Student> selectByObject(Student student);
List<Student> selectByQueryParam(QueryParam queryParam);
mapper文件
<!--
一个java对象作为方法的参数,使用对象的属性作为参数值使用
简单的语法:#{属性名} mybatis调用此属性的get方法获取属性值
-->
<select id="selectByObject" resultType="com.cedric.domain.Student">
select id,name,email,age from student where name=#{name} or age=#{age}
</select>
<select id="selectByQueryParam" resultType="com.cedric.domain.Student">
select id,name,email,age from student where name=#{p1} or age=#{p2}
</select>
dao接口中多个简单类型参数
参数位置:dao接口中方法的形参列表,从左往右,参数位置是0,1,2...
语法格式:#{args},#{args}
dao接口的方法
/**
* 使用位置获取参数
*/
List<Student> selectByPosition(String name,Integer age);
<!--
使用位置获取参数值,dao接口方法是多个简单类型的参数
语法:#{arg0},#{arg1}
-->
<select id="selectByPosition" resultType="com.cedric.domain.Student">
select id,name,email,age from student where name=#{arg0} or age=#{arg1}
</select>
dao接口参数是一个Map
map作为dao接口的参数,使用key获取参数值,mapper文件中,语法格式#{key}
/**
* 使用map作为参数
*/
List<Student> selectStudentByMap(Map<String,Object> map);
mapper文件
<!--
使用Map传递参数
在mapper文件中,获取map的值,是通过key获取的,语法:#{key}
-->
<select id="selectStudentByMap" resultType="com.cedric.domain.Student">
select id,name,email,age from student where name=#{myname} or age=#{myage}
</select>
更新举例(update delete类似)
int updateStudent(Student student);
<!--更新-->
<update id="updateStudent">
update student set name=#{name},email=#{email} where id=#{id}
</update>
@Test
public void testUpdate() throws IOException {
String config = "mybatis.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(config);
SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSession session = factory.openSession();
StudentMapper dao = session.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
// 使用map传递参数
Student student = new Student();
student.setName("不知火舞");
student.setEmail("buzhihuowu@qq.com");
student.setAge(80);
student.setId(1002);
int rows = dao.updateStudent(student);
session.commit();
System.out.println("更新学生的rows-->" + rows);
session.close();
}
$和#的区别
(#占位符
语法:#{字符}
mybatis处理#{}使用jdbc对象是PrepareStatement对象
<select id="selectStudentById" resultType="com.cedric.domain.Student">
select id,name,email,age from student where id=#{studentId}
</select>
mybatis创建PrepareStatement对象,执行sql语句
String sql = "select id,name,email,age from student where id=?":
PrepareStatment pst = conn.prepareStatment(sql);
pst.setInt(1,1001); //传递参数
ResultSet rs = pst.executeQuery(); //执行sql语句
(#{})特点:
1)使用PrepareStatment对象,执行sql语句,效率高
2)使用的PrepareStatment对象,能避免sql注入,sql语句执行更安全
3)#{}常常作为列值使用,位于等号的右侧,#{}位置的值和数据类型有关
$占位符
语法:${字符}
mybatis执行${}占位符的sql语句
<select id="selectStudentById" resultType="com.cedric.domain.Student">
select id,name,email,age from student where id=${studentId}
</select>
${}表示字符串连接,把sql语句的其他内容和${}内容使用字符串(+)连接的方式连在一起
String sql = select id,name,email,age from student where id + "1001":
mybatis创建Statement对象,执行sql语句
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement(sql);
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery();
${}的特点
1)使用Statement对象,执行sql语句,效率低
2)${}占位符的值,使用字符串连接方式,有sql注入的风险
3)${}数据是原样使用的,不会区分数据类型
4)${}常用作表名或者列名,在能保证数据安全的情况下使用${}
封装MyBatis输出结果
封装输出结果:Mybatis执行sql语句,得到ResultSet,转为java对象
resultType
resultType属性:在执行select时使用,作为select标签的属性出现
resultType表示结果类型,mysql执行sql语句,得到java对象的类型。它的值有两种
1)java类型的全限定名称 2)使用别名
1.resultType:表示java的自定义对象
Student selectStudentById( Integer studentId);
<select id="selectStudentById" resultType="com.cedric.domain.Student">
select id,name,email,age from student where id=#{studentId}
</select>
resultType:现在使用java类型的全限定名称。表示的意思mybatis执行sql,把ResultSet中的数据转为Student类型的对象。mybatis会做一下操作:
1.调用com.cedric.domain.Student的无参数构造方法,创建对象
Student student = new Student(); //使用反射创建对象
2.同名的列赋值给同名的属性
Student.setId(rs.getInt("id"));
Student.setName(rs.getString("name"));
3.得到java对象,如果dao接口返回值时List集合,mybatis把student对象放入到List集合
所以执行 Student student = dao.selectById(1001);得到数据库中 id=1001这行数据,
这行数据的列值,赋给了student对象的属性,得到student对象就相当于时id = 1001这行数据
2.resultType表示简单类型
dao方法
long countStudent();
mapper文件
<select id="countStudent" resultType="java.lang.Long">
select count(*) from student
</select>
3.resultType:表示一个map结构
//查询结果返回一个Map
Map<Object,Object> selectMap(@Param("studentId") Integer id);
<!--
执行sql得到一个map集合的数据,mybatis执行sql,把ResultSet转为map
sql执行结果,列名做map的key,列值作为value
sql执行得到是一行记录,转为map结构是正确的
dao接口返回的是一个map,sql语句最多能获取一行记录,多于一行则报错
-->
<select id="selectMap" resultType="java.util.HashMap">
select id,name from student where id=#{studentId}
</select>
练习题:
输入一个省份id 得到省份id 省份name 城市id 城市名称
public class ProvinceCity {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Integer cid;
private String cname;
set | get方法
toString方法
````
````java
List<ProvinceCity> selectProvinceCityList(Integer provinceId);
<mapper namespace="com.cedric.dao.ProvinceDao">
<!--使用insert,update,delete,select标签写sql-->
<select id="selectProvinceCityList" resultType="com.cedric.query.ProvinceCity">
select p.id,p.name,c.id cid,c.name cname
from province p inner join city c on p.id = c.provinceid where p.id=#{pid}
</select>
</mapper>
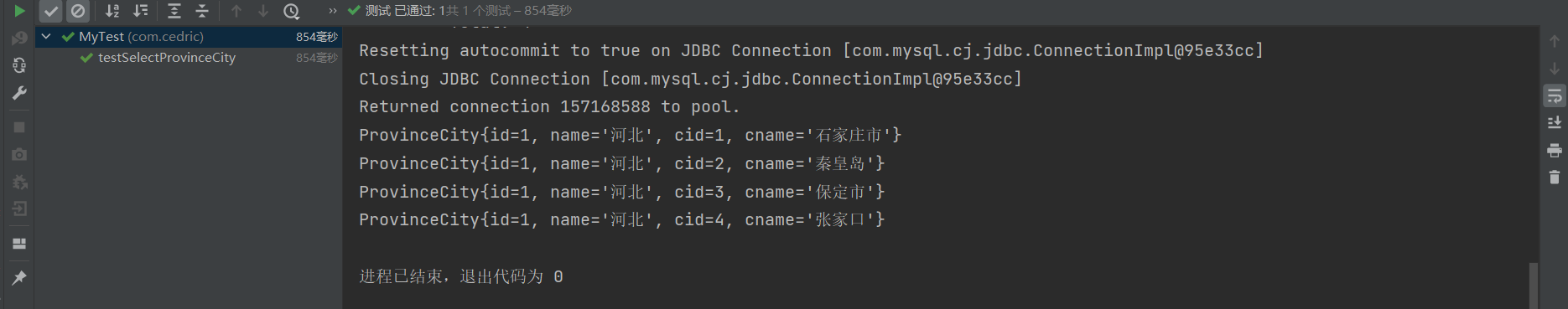
@Test
public void testSelectProvinceCity() throws IOException {
String config = "mybatis.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(config);
SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSession session = factory.openSession();
ProvinceDao dao = session.getMapper(ProvinceDao.class);
List<ProvinceCity> list = dao.selectProvinceCityList(1);
session.close();
list.forEach(p -> System.out.println(p));
}
运行结果:
resultMap
resuktMap:结果映射。自定义列名和java对象属性的对应关系。常用在列名和属性名不同的情况
用法:
1.先定义resultMap标签,指定列名和属性名称对应关系
2.在select标签使用resultMap属性,指定上面定义的resultMap的id值
<!--
id:给resultMap的映射关系起个名称,唯一值
type:java类型的全限定名称
-->
<resultMap id="customMap" type="com.cedric.query.CustomObject">
<!--定义列名和属性名对应-->
<!--主键类型使用id标签-->
<id column="id" property="cid"/>
<!--非主键类型使用result标签-->
<result column="name" property="cname"/>
<!--列名和属性名相同不用定义-->
</resultMap>
<!--
使用resultMap属性,指定映射关系的id
resultMap和resultType不能同时使用 二选一
-->
<select id="selectById2" resultMap="customMap">
select * from student where id=#{stuid}
</select>
自定义别名
mybatis提供对java类型定义简短,好记的名称
自定义别名步骤:
1)在mybatis主配置文件,使用typeAliases标签声明别名
2)在mapper文件中,resultType="别名"
声明别名(mybatis主配值文件)
<!--声明别名-->
<typeAliases>
<!--
第一种语法格式
type:java类型的全限定名称(自定义类型)
alias:自定义名称
优点:别名可以自定义
缺点:每个类型必须单独定义
-->
<typeAlias type="com.cedric.domain.Student" alias="stu"/>
<typeAlias type="com.cedric.query.QueryParam" alias="qp"/>
<!--
第二种方式:
name:包名,mybatis会把这个包中所有类名作为别名(不用区分大小写)
优点:使用方便,一次给多个类定义别名
缺点:别名不能定义,必须是类名
-->
<package name="com.cedric.domain"/>
<package name="com.cedric.query"/>
mapper文件中使用
<select id="queryStudentOrderByColName" resultType="stu">
select * from student order by ${colname} desc
</select>
<select id="queryStudentOrderByColName" resultType="student">
select * from student order by ${colname} desc
</select>
列名和java对象属性名陈不一样解决方式
1)使用resultMap:自定义列名和属性名称对应关系
2)使用resultType:使用列别名,让别名和java对象属性名称一样
like
第一种方式:在java程序中,把like的内容组装好。把这个内容传入到sql语句
// like第一种方式
List<Student> selectLikeOne(@Param("name") String name);
mapper
<select id="selectLikeOne" resultType="com.cedric.domain.Student">
select id,name,email,age from student where name like #{name}
</select>
执行like
@Test
public void testSelectLikeOne() throws IOException {
String config = "mybatis.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(config);
SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSession sqlSession = factory.openSession();
StudentMapper dao = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
String name = "%关%";
List<Student> students = dao.selectLikeOne(name);
students.forEach(student -> System.out.println("student-->" + student));
}
第二种方式:在sql语句,组织like的内容
sql语句like的格式:where name like "%空格#{name}空格"
// like第二种方式
List<Student> selectLikeTwo(@Param("name") String name);
<select id="selectLikeTwo" resultType="com.cedric.domain.Student">
select id,name,email,age from student where name like "%" #{name} "%"
</select>
@Test
public void testSelectLikeTwo() throws IOException {
String config = "mybatis.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(config);
SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSession sqlSession = factory.openSession();
StudentMapper dao = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
String name = "关";
List<Student> students = dao.selectLikeTwo(name);
students.forEach(student -> System.out.println("student-->" + student));
}
动态sql
什么是动态sql:同一个dao方法,根据不同的条件可以表示不同的sql语句,主要是where部分有变化
使用mybatis提供的标签,实现动态sql的能力
使用动态sql的时候,dao方法的形参使用java对象
if
语法:
<if test="boolean判断结果">
sql 代码
</if>
在mapper文件中
<select id="selectStudent" resultType="com.cedric,domain.Student">
select * from student
<if test="条件">
sql语句
</if>
</select>
例子:
List<Student> selectIf(Student student);
<!--if
test:使用对象属性值作为条件
-->
<select id="selectIf" resultType="com.cedric.domain.Student">
<include refid="selectStudent"/>
where id=-1
<if test="name != null and name != ''">
or name = #{name}
</if>
<if test="age > 600">
or age < #{age}
</if>
</select>
@Test
public void testSelectIF() throws IOException {
String config = "mybatis.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(config);
SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSession session = factory.openSession();
// 获取dao的代理
StudentMapper dao = session.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
Student student = new Student();
/* student.setName("张飞");
student.setAge(1500);*/
student.setName(null);
student.setAge(1500);
List<Student> students = dao.selectIf(student);
students.forEach(student1 -> System.out.println("studens--->" + student1));
// 关闭SqlSession对象
session.close();
}
where标签
使用if标签时,容易引起sql语句语法错误。使用where标签解决if产生的语法问题
使用时where,里面是一个或多个if标签,当有一个if标签判断条件为true,where标签会转为WHERE关键字附加到sql语句的后面。如果if没有一个条件作为true,忽略where和里面的if
where标签删除和它最近的or或者and
<where>
<if test="条件1">sql语句1</if>
<if test="条件2">sql语句2</if>
</where>
例子:
<select id="selectWhere" resultType="com.cedric.domain.Student">
select <include refid="studentFiledList"></include> from student
<where>
<if test="name != null and name != ''">
name = #{name}
</if>
<if test="age > 600">
or age < #{age}
</if>
</where>
</select>
// where
List<Student> selectWhere(Student student);
@Test
public void testSelectWhere() throws IOException {
String config = "mybatis.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(config);
SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSession session = factory.openSession();
// 获取dao的代理
StudentMapper dao = session.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
Student student = new Student();
student.setName("关羽");
student.setAge(1500);
List<Student> students = dao.selectWhere(student);
students.forEach(student1 -> System.out.println("student--->" + student1));
}
foreach循环
使用foreach可以循环数组,list集合,一般使用在in语句中
语法:
<foreach collection="集合类型" open="开始的字符" close="结束的字符"
item="集合中的成员" separator="集合成员之间的分隔符">
#{item的值}
</foreach>
标签属性:
collection:表示,循环的对象是数组,还是list集合。如果dao接口方法的形参是数组
collection="array",如果dao接口形参是List,collection="list"
open:循环开始的字符 sql.append("(");
close:循环结束的字符 sql.append(")");
item:集合成员,自定义的变量 Integer item = idlist.get(i); // item是集合成员
separator:集合成员之间的分隔符 sql.append(","); // 集合成员之间的分隔符
#{item的值}:获取集合成员的值
第一种方式:
// forEach-1
List<Student> selectForEachOne(List<Integer> idList);
<!--foreach第一种方式,循环简单类型的List-->
<select id="selectForEachOne" resultType="com.cedric.domain.Student">
select * from student
<if test="list != null and list.size > 0">
where id in
<foreach collection="list" open="(" close=")" separator="," item="myid">
#{myid}
</foreach>
</if>
</select>
@Test
public void testSelectForEachOne() throws IOException {
String config = "mybatis.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(config);
SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSession session = factory.openSession();
// 获取dao的代理
StudentMapper dao = session.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
List<Integer> idList = new ArrayList<>();
idList.add(1001);
idList.add(1002);
idList.add(1003);
List<Student> students = dao.selectForEachOne(idList);
students.forEach(student1 -> System.out.println("student--->" + student1));
session.close();
}
第二种方式:
// forEach-2
List<Student> selectForEachTwo(List<Student> students);
<!--forEachList第二种方式,循环List<Student>-->
<select id="selectForEachTwo" resultType="com.cedric.domain.Student">
select * from student
<if test="list!=null and list.size > 0">
where id in
<foreach collection="list" open="(" close=")" separator="," item="stu">
#{stu.id}
</foreach>
</if>
</select>
@Test
public void testSelectForEachTwo() throws IOException {
String config = "mybatis.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(config);
SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSession session = factory.openSession();
// 获取dao的代理
StudentMapper dao = session.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
List<Student> idList = new ArrayList<>();
Student s1 = new Student();
s1.setId(1007);
Student s2 = new Student();
s2.setId(1008);
idList.add(s1);
idList.add(s2);
List<Student> students = dao.selectForEachTwo(idList);
students.forEach(student1 -> System.out.println("student--->" + student1));
session.close();
}
sql标签
sql标签表示一段sql代码,可以是表名,几个字段,where条件都可以,可以在其他地方复用sql标签的内容
使用方式:
1)在mapper文件中定义 sql代码片段<sql id = "唯一字符串">部分sql语句</sql>
2)在其他的位置,使用include标签引用某个代码片段
例如:
<!--定义代码片段-->
<sql id="selectStudent">
select * from student
</sql>
<sql id="studentFiledList">
id,name,email
</sql>
<select id="selectIf" resultType="com.cedric.domain.Student">
<include refid="selectStudent"/>
where id=-1
<if test="name != null and name != ''">
or name = #{name}
</if>
<if test="age > 600">
or age < #{age}
</if>
</select>
<select id="selectWhere" resultType="com.cedric.domain.Student">
select <include refid="studentFiledList"></include> from student
<where>
<if test="name != null and name != ''">
name = #{name}
</if>
<if test="age > 600">
or age < #{age}
</if>
</where>
</select>
MyBatis配置文件
mybatis配置文件分为两大类:1 mybatis主配置文件;2 mybatis的mapper文件
1.mybatis主配值文件,提供mybatis全局设置的。包含的内容 日志,数据源,mapper文件位置
2.mapper文件:写sql语句的。一个表一个mapper文件
setting部分
setting是mybatis的全局设置,影响整个mybatis的运行,一般使用默认值就可以
typeAliase别名
设置别名
<!--声明别名-->
<typeAliases>
<!--
第一种语法格式
type:java类型的全限定名称(自定义类型)
alias:自定义名称
优点:别名可以自定义
缺点:每个类型必须单独定义
-->
<typeAlias type="com.cedric.domain.Student" alias="stu"/>
<typeAlias type="com.cedric.query.QueryParam" alias="qp"/>
<!--
第二种方式:
name:包名,mybatis会把这个包中所有类名作为别名(不用区分大小写)
优点:使用方便,一次给多个类定义别名
缺点:别名不能定义,必须是类名
-->
<package name="com.cedric.domain"/>
<package name="com.cedric.query"/>
</typeAliases>
配置环境
environments:环境标签,在他里面可以配置多个environment
属性:default,必须是某个environment的id属性值。表示mybatis默认连接的数据库
environment:表示一个数据库的连接信息
属性:id 自定义的环境的标识,唯一值
transactionManager:事务管理器
属性:type 表示事务管理器的类型
属性值:1)JDBC:使用connection对象,由mybatis自己完成事务的处理
2)MANAGER:管理,表示把事务的处理交给容器实现(由其他软件完成事务的提交,回滚)
dataSource:数据源,创建的Connection对象,连接数据库
属性:type 数据源的类型
属性值:1)POOLED,mybatis会在内存中创建pooledDataSource类,管理多个Connection连接对象,使用连接池
2)UNPOOLED,不使用连接池,mybatis创建一个UnPooledDataSource这个类,每次执行sql语句先创建Connection对象,再执行sql语句,最后关闭Connection、
3)JNDI:java的命名和目录服务
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<!--配置数据源:创建Connection对象-->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<!--driver:驱动的内容-->
<property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driver}"/>
<!--数据库的url-->
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<!--用户名-->
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<!--密码-->
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
使用数据库属性配置文件
需要把数据库的配置信息放到一个单独的文件中独立管理。这个文件扩展名是.properties在这个文件中,使用自定义的key=value的格式表示数据
使用步骤:
1.在resources目录下,创建xxx.properties
2.在文件中,使用key=value的格式定义数据
例如:jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springdb
3.在mybatis主配置文件,使用properties标签引用外部的属性配置文件
4.在使用值的位置,使用${key}获取key对应的value(等号右侧的值)
例子:
jdbc.properties
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springdb?useUnicode=true& characterEncoding=utf-8
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=cedric1010
mybatis主配置文件
<!--使用外部的属性配置文件
resource:指定类路径下的某个配置文件
-->
<properties resource="jdbc.properties"/>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<!--配置数据源:创建Connection对象-->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<!--driver:驱动的内容-->
<property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driver}"/>
<!--数据库的url-->
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<!--用户名-->
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<!--密码-->
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
mapper标签
使用mapper指定其他mapper文件的位置
mapper标签使用的格式有两种常用的方式
<mappers>
<!--
第一种方式:resources="mapper文件的路径"
优点:文件清晰,加载文件是明确的
文件的位置比较灵活
缺点:文件比较多,代码量会比较大,管理难度大
-->
<mapper resource="mapper/StudentMapper.xml"/>
<!--
第二种方式,使用<package>
name:包名,mapper文件所在的包名
特点:把这个包中所以的mapper文件一次加载
使用要求:
1.mapper文件和dao接口在同一目录
2.mapper文件和dao接口名称完全一样
-->
<package name="com.cedric.dao"/>
</mappers>



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号