JUC完结
深入理解CAS
什么是CAS
package com.cedric.JUC.cas;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
public class CASDemo {
// CAS compareAndSet:比较并交换
public static void main(String[] args) {
AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(2020);
// 期望、更新
// public final boolean compareAndSet(int expect,int update)
// 如果我的期望值达到了,那么久更新,否则就不更新,CAS是CPU并发原语
System.out.println(atomicInteger.compareAndSet(2020, 2021));
System.out.println(atomicInteger.get());
System.out.println(atomicInteger.compareAndSet(2021, 2022));
System.out.println(atomicInteger.get());
}
}
Unsafe类
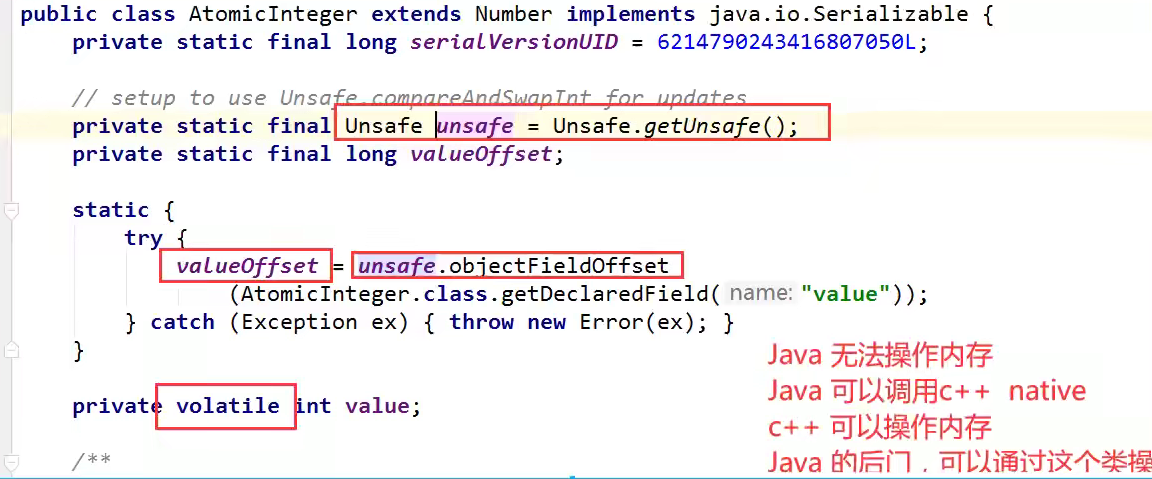
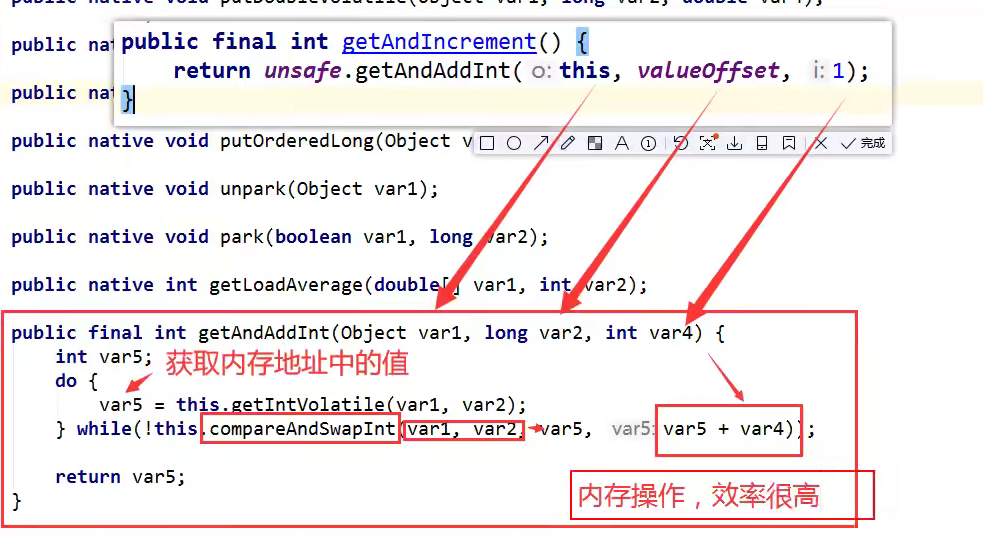

CAS:比较当前工作内存中的值和主内存中的值,如果这个值是期望的,那么则执行,如果不是,就一直循环
缺点:
1.循环会耗时
2.一次性只能保证一个共享变量的原子性
3.ABA问题
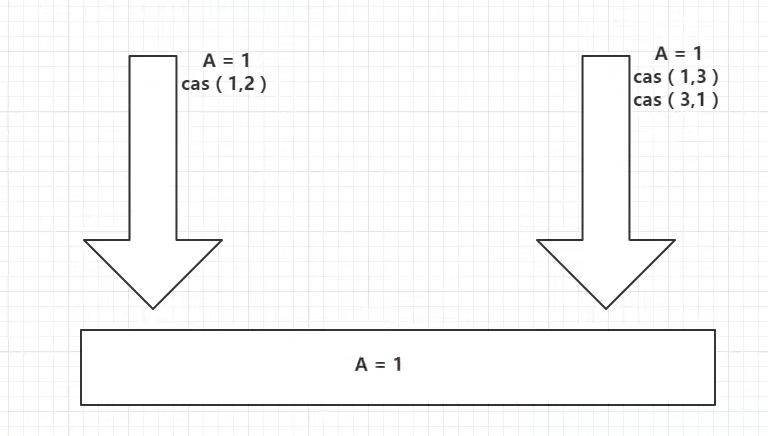
CAS:ABA问题(狸猫换太子)
package com.cedric.JUC.cas;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
public class CASDemo {
// CAS compareAndSet:比较并交换
public static void main(String[] args) {
AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(2020);
// 期望、更新
// public final boolean compareAndSet(int expect,int update)
// 如果我的期望值达到了,那么久更新,否则就不更新,CAS是CPU并发原语
// ===============================捣乱的线程================
System.out.println(atomicInteger.compareAndSet(2020, 2021));
System.out.println(atomicInteger.get());
System.out.println(atomicInteger.compareAndSet(2021, 2020));
System.out.println(atomicInteger.get());
// =====================期望的线程=========================
System.out.println(atomicInteger.compareAndSet(2020, 9999));
System.out.println(atomicInteger.get());
}
}
原子引用
解决ABA问题,引入原子引用,对应思想:乐观锁
带版本号的原子操作
package com.cedric.JUC.cas;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicStampedReference;
public class CASDemo {
// AtomicStampedReference 注意:如果泛型是一个包装类,注意对象的引用问题
// 正常在业务中,这里面比较的都是一个个对象
static AtomicStampedReference<Integer> atomicStampedReference = new AtomicStampedReference<>(1,1);
// CAS compareAndSet:比较并交换
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(() -> {
int stamp = atomicStampedReference.getStamp();
System.out.println("a1 =>" + stamp);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(atomicStampedReference.compareAndSet(1,2, atomicStampedReference.getStamp(), atomicStampedReference.getStamp() + 1));
System.out.println("a2=>" + atomicStampedReference.getStamp());
System.out.println(atomicStampedReference.compareAndSet(2, 1, atomicStampedReference.getStamp(), atomicStampedReference.getStamp() + 1));
System.out.println("a3=>" + atomicStampedReference.getStamp());
},"a").start();
new Thread( () -> {
int stamp = atomicStampedReference.getStamp();
System.out.println("b1 =>" + stamp);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(atomicStampedReference.compareAndSet(1,6,stamp,stamp+1));
System.out.println("b2=>" + atomicStampedReference.getStamp());
},"b").start();
}
}
注意:
Integer使用了对象缓存机制,默认范围是-128 ~ 127,推荐使用静态工厂方法valueOf获取实例对象,而不是new,因为valueOf使用缓存,而new一定会创建新的对象分配新的内存空间;

各种锁的理解
1.公平锁、非公平锁
公平锁:非常公平,不能够插队,必须先来后到
非公平锁:非常不公平,可以插队(默认都是非公平)
public ReentrantLock() {
sync = new NonfairSync();
}
public ReentrantLock(boolean fair) {
sync = fair ? new FairSync() : new NonfairSync();
}
2.可重入锁
可重入锁(递归锁)
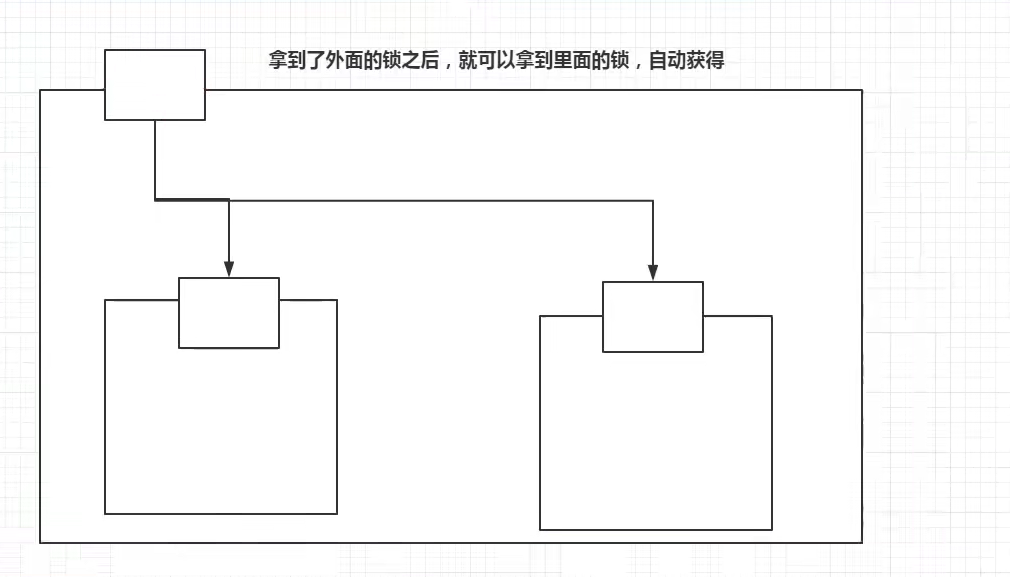
Synchronized
package com.cedric.JUC.lock;
//Synchronized
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Phone phone = new Phone();
new Thread(()->{
phone.sms();
},"A").start();
new Thread(() -> {
phone.sms();
},"B").start();
}
}
class Phone{
public synchronized void sms(){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "sms");
call(); // 这里也有锁
}
public synchronized void call(){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " call");
}
}
Lock
package com.cedric.JUC.lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Phone2 phone = new Phone2();
new Thread(()->{
phone.sms();
},"A").start();
new Thread(() -> {
phone.sms();
},"B").start();
}
}
class Phone2{
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
public void sms(){
lock.lock(); // 细节问题:Lock.lock();lock.unlock(); // lock 锁必须配对,否则就会死在里面
lock.lock();
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "sms");
call(); // 这里也有锁
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void call(){
lock.lock();
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " call");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
3.自旋锁
spinlock
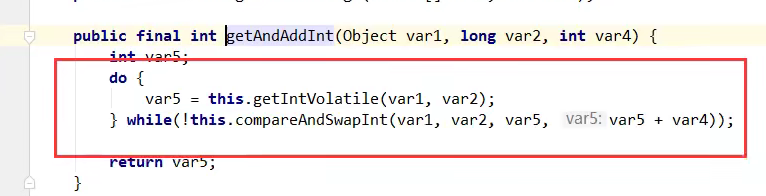
自定义锁测试
package com.cedric.JUC.lock;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicReference;
public class spinlockDemo {
AtomicReference<Thread> atomicReference = new AtomicReference<>();
// 加锁
public void myLock(){
Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "==> myLock");
// 自旋锁
while(!atomicReference.compareAndSet(null,thread)){
}
}
// 解锁
public void myUnlock(){
Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "==> myUnlock");
atomicReference.compareAndSet(thread,null);
}
}
测试
package com.cedric.JUC.lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Phone2 phone = new Phone2();
new Thread(()->{
phone.sms();
},"A").start();
new Thread(() -> {
phone.sms();
},"B").start();
}
}
class Phone2{
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
public void sms(){
lock.lock(); // 细节问题:Lock.lock();lock.unlock(); // lock 锁必须配对,否则就会死在里面
lock.lock();
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "sms");
call(); // 这里也有锁
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void call(){
lock.lock();
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " call");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
4.死锁
死锁是什么
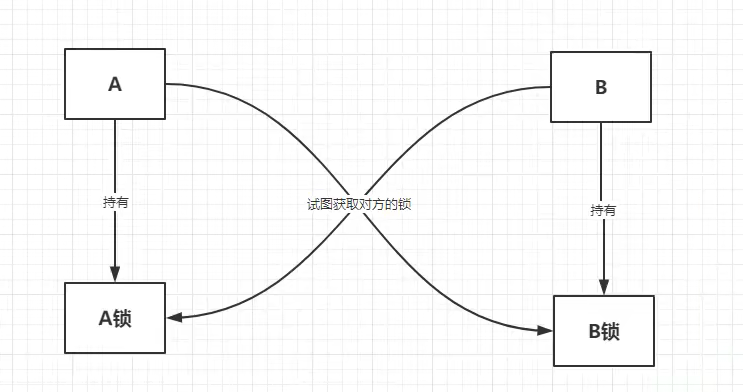
死锁产生的4个必要条件
1、互斥: 某种资源一次只允许一个进程访问,即该资源一旦分配给某个进程,其他进程就不能再访问,直到该进程访问结束。
2、占有且等待: 一个进程本身占有资源(一种或多种),同时还有资源未得到满足,正在等待其他进程释放该资源。
3、不可抢占: 别人已经占有了某项资源,你不能因为自己也需要该资源,就去把别人的资源抢过来。
4、循环等待: 存在一个进程链,使得每个进程都占有下一个进程所需的至少一种资源。
当以上四个条件均满足,必然会造成死锁,发生死锁的进程无法进行下去,它们所持有的资源也无法释放。这样会导致CPU的吞吐量下降。所以死锁情况是会浪费系统资源和影响计算机的使用性能的。那么,解决死锁问题就是相当有必要的了。
死锁测试,怎么排除死锁
package com.cedric.JUC.lock;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class DeadLock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String lockA = "lockA";
String lockB = "lockB";
new Thread(new MyThread(lockA,lockB),"T1").start();
new Thread(new MyThread(lockB,lockA),"T2").start();
}
}
class MyThread implements Runnable{
private String lockA;
private String lockB;
public MyThread(String lockA,String lockB){
this.lockA = lockA;
this.lockB = lockB;
}
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (lockA){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "lock:" + lockA + "=>get" + lockB);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (lockB){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "lock:" + lockB + "=> get" + lockA);
}
}
}
}
解决问题
1.使用jps -l 定位进程号
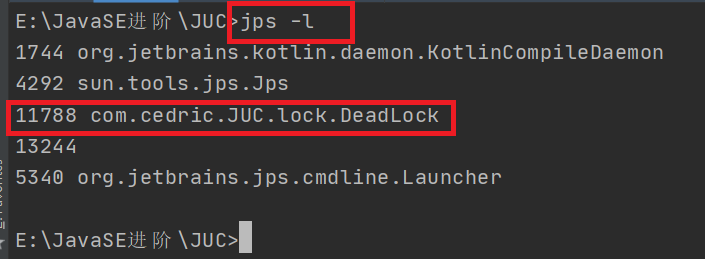
2.使用jstack进程号找到死锁问题



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号