[ABC266Ex] Snuke Panic (2D) 题解
[ABC266Ex] Snuke Panic (2D) 题解
前言
前几天看到了这个,发现自己还真没仔细思考过。
做了两道题,把这个题当个总结。
思路
设 \(f_i\) 表示:在 \(T_i\) 走到第 \(i\) 个节点的最大收益。
有转移:\(f_i=\max \{f_j\} + A_i\)。
其中 \(j\) 需要满足:
- \(y_j\le y_i\)
- \(T_i\le T_i\)
- \(|x_i-x_j|+y_i-y_j\le T_i-T_j\)
第三条限制可以转化为:\(x_i-x_j+y_i-y_j\le T_i-T_j \land x_j-x_i+y_i-y_j\le T_i-T_j\)。
容易发现满足第三条限制一定满足第二条限制,所以有如下限制:
- \(y_i\ge y_j\)
- \(x_i+y_i-T_i\le x_j+y_j-T_j\)
- \(-x_i+y_i-T_i\le -x_j+y_j-T_j\)
然后其实就是三维偏序了。因为这些点没有顺序限制,所以在外层可以排序掉一维,第二维可以用 CDQ 分治处理,第三为用树状数组即可。值得注意的是,因为有初始的点 \((0,0)\),所以我们有 \(n+1\) 个点,离散化后树状数组应该跑到 \(n+1\)。
CDQ 实现的时候为什么和平常写的不太一样?
这里的“平常”指先把左右都递归下去再算贡献。
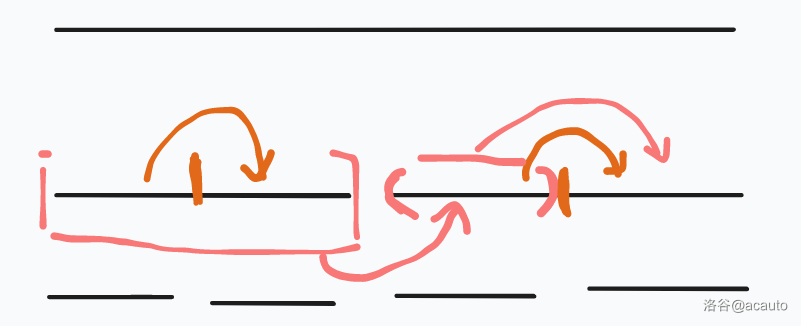
因为如果我们按平常的做法,其实是左右各自贡献,如下图中橙色。但这会出问题,我们更新最右边的时候用的是没有被左边更新的右端的左侧,所以错了。
粉色的顺序才应该是对的。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define IL inline
#define vec vector
#define bg begin
#define eb emplace_back
#define emp emplace
#define fi first
#define se second
#define mkp make_pair
#define lb lower_bound
#define ub upper_bound
using ubt = long long;
using uubt = unsigned long long;
using dub = double;
using pii = pair<int, int>;
using puu = pair<ubt, ubt>;
IL void ckx(int &x, const int &y) { (x < y) && (x = y); }
IL void ckm(int &x, const int &y) { (x > y) && (x = y); }
template <typename T = int>
IL T _R() {
T s = 0, w = 1;
char c = getchar();
while (!isdigit(c)) w = c == '-' ? -1 : 1, c = getchar();
while (isdigit(c)) s = s * 10 + c - 48, c = getchar();
return s * w;
}
const int inf = 1e18;
const int N = 1e5;
const int maxN = N + 3;
int n;
int f[maxN], id[maxN], fid[maxN];
int sot[maxN];
struct node {
int x, y, t;
int A;
int k1, k2;
IL void init() {
k1 = -x + sot[y] - t;
k2 = x + sot[y] - t;
}
IL friend bool operator < (const node &A, const node &B) {
if (A.k2 != B.k2) return A.k2 > B.k2;
if (A.k1 != B.k1) return A.k1 > B.k1;
if (A.y != B.y) return A.y < B.y;
if (A.t != B.t) return A.t < B.t;
assert(false);
}
IL friend bool operator <= (const node &A, const node &B) {
return !(B < A);
}
} a[maxN];
IL bool cmp(int i, int j) { return a[i] < a[j]; }
struct BIT {
int t[maxN];
IL void ins(int x, int b) {
for (; x <= n + 1; x += x & -x) ckx(t[x], b);
}
IL int ask(int x) {
int res = -inf;
for (; x > 0; x -= x & -x) ckx(res, t[x]);
return res;
}
IL void clr(int x) {
for (; x <= n + 1; x += x & -x) t[x] = -inf;
}
BIT() { memset(t, ~0x3f, sizeof(t)); }
} T;
void cdq(int l, int r) {
if (l == r) return;
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
cdq(l, mid);
for (int i = mid + 1; i <= r; i++) fid[i] = id[i];
sort(fid + mid + 1, fid + r + 1, cmp);
int t1 = l, t2 = mid + 1;
while (t1 <= mid && t2 <= r) {
if (a[id[t1]] <= a[fid[t2]]) {
T.ins(a[id[t1]].y, f[id[t1]]);
t1++;
} else {
ckx(f[fid[t2]], T.ask(a[fid[t2]].y) + a[fid[t2]].A);
t2++;
}
}
while (t2 <= r)
ckx(f[fid[t2]], T.ask(a[fid[t2]].y) + a[fid[t2]].A),
t2++;
for (int i = l; i <= mid; i++) T.clr(a[id[i]].y);
cdq(mid + 1, r);
stable_sort(id + l, id + r + 1, cmp);
}
signed main() {
n = _R();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
a[i].t = _R(), a[i].x = _R(), a[i].y = _R(), a[i].A = _R();
sot[i] = a[i].y;
}
sot[n + 1] = 0;
sort(sot + 1, sot + n + 2);
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
a[i].y = lb(sot + 1, sot + n + 2, a[i].y) - sot;
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
a[i].init();
sort(a, a + n + 1, [&](const auto &A, const auto &B) {
if (A.k1 != B.k1) return A.k1 > B.k1;
if (A.k2 != B.k2) return A.k2 > B.k2;
if (A.y != B.y) return A.y < B.y;
if (A.t != B.t) return A.t < B.t;
assert(false);
});
memset(f, ~0x3f, sizeof(f));
f[0] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) id[i] = i;
cdq(0, n);
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) ckx(ans, f[i]);
printf("%lld\n", ans);
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号