总结算法中常见的二叉树问题
1.遍历二叉树
说到二叉树,最开始就要提到二叉树的遍历了。遍历分为递归版和非递归版,这里先说一下递归版。
但其实递归版也没什么好说的,就是把我们打印节点或者收集节点的时间放在了不同地方就能实现了。
这里说到非递归版,这里我想说的是,当用到先序遍历或者中序遍历后序遍历,都是用到栈辅助,这样子我们就能到一个节点两次,实现遍历。当我们想要按层遍历的时候,是用到队列来辅助的。遍历的时候,先压左,再压右,当队列不为空的时候,继续弹出头部,弹出的时候如果有左孩子就压入左孩子,如果有右孩子,就压入右孩子。
记住一个规律,普通遍历用栈,按层遍历用队列。
实现二叉树的序列化和反序列化
public static class Node { public int value; public Node left; public Node right; public Node(int data) { this.value = data; } } public static String serialByPre(Node head) { if (head == null) { return "#!"; } String res = head.value + "!"; res += serialByPre(head.left); res += serialByPre(head.right); return res; } //反序列化 public static Node reconByPreString(String preStr) { String[] values = preStr.split("!"); Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<String>(); for (int i = 0; i != values.length; i++) { queue.offer(values[i]); } return reconPreOrder(queue); } //给我一个队列,我返回二叉树 public static Node reconPreOrder(Queue<String> queue) { String value = queue.poll(); if (value.equals("#")) { return null; } Node head = new Node(Integer.valueOf(value)); head.left = reconPreOrder(queue); head.right = reconPreOrder(queue); return head; }
使用队列实现按层遍历也有两个题目,一个是判断一棵二叉树是否完全二叉树,计算一棵完全二叉树的大小。
判断一棵树是否为完全二叉树(按层遍历)
1)如果有右无左,则直接返回false
2)如果左右不全,则接下来遇到的所有节点都为叶子节点
2.Morris算法
Morris算法就是把递归过程省略了,也把辅助结构栈也给省略了,把二叉树中的空指针给利用起来,实现更快的遍历。
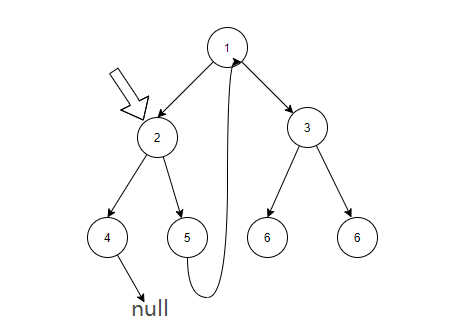
1)记录当前结点为cur。
如果cur无左孩子,cur向右移动(cur = cur.right);
2)如果cur有左孩子,找到cur左子树上最右的节点,记为mostRight.
①如果mostRight的right指针指向空,让其指向cur,cur向左移动;
②如果mostRight的right指针不指向空,cur先向右移动,再让mostRight的right指向null.
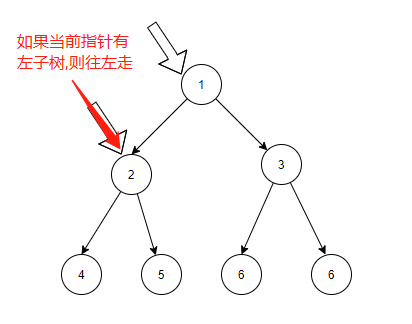
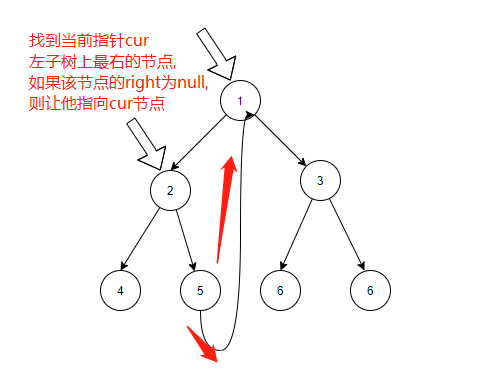
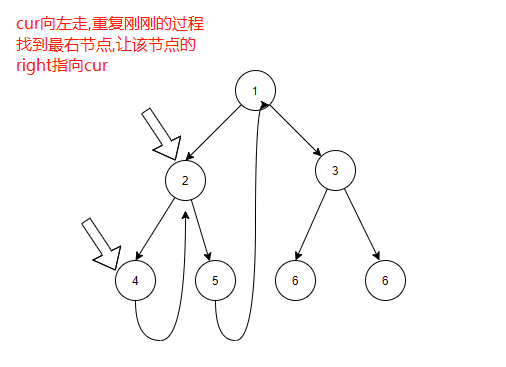
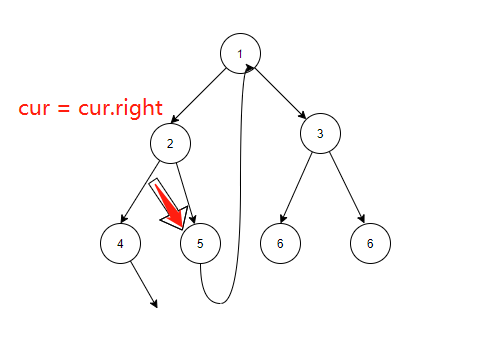
从图可以看出,其实就是cur指针在不断地向左跳,然后沿途创建那条很长的指针
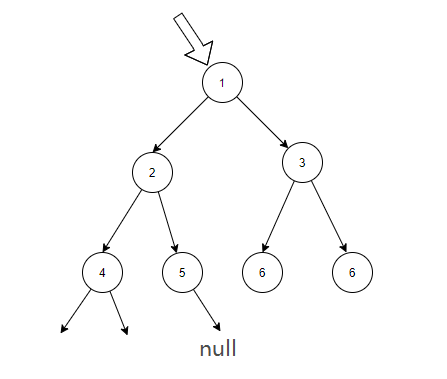
接下来就是,当cur指针的左子树为空时,此时向右跳,也就是 cur = cur.right。而因为我们刚刚沿途创建的指针,我们在向右跳的时候,其实也是在往上跳。
往右跳的过程就是顺着我们创建的“长指针”往上跳,再沿途把“长指针”恢复原样。
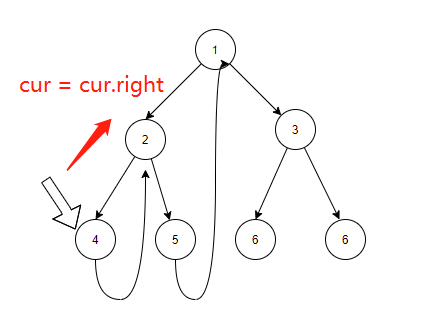
public static void morrisPre(Node head) { if (head == null) { return; } Node cur1 = head; Node cur2 = null; while (cur1 != null) { cur2 = cur1.left; //当前孩子有左孩子 if (cur2 != null) { //找到最右节点 while (cur2.right != null && cur2.right != cur1) { cur2 = cur2.right; } //如果最右节点的右指针为空,则让它指向cur.然后cur向左移动 if (cur2.right == null) { cur2.right = cur1; System.out.print(cur1.value + " "); cur1 = cur1.left; continue; } else { cur2.right = null; } } else { System.out.print(cur1.value + " "); } cur1 = cur1.right; } System.out.println(); }
Morris算法的先序中序遍历也是不同到达节点时机。但是后序的话不一样,因为Morris算法没有到达一个节点三次,所以我们只针对有左孩子的节点,当到达一个节点第二次的时候,逆序遍历该节点的左孩子的右边界。
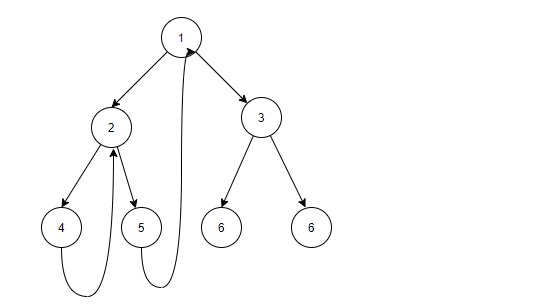
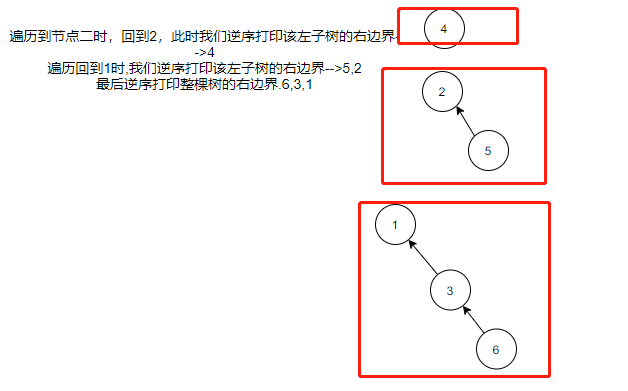
逆序打印比较麻烦,就需要我们去改链表的方向,遍历后再改回来
3.找最低公共祖先
4.找到最大的搜索二叉子树
首先我们最大搜索二叉树有三种可能(列可能性)
①包括自己节点为最大搜索二叉树;
②节点的左子树为最大搜索二叉树;
③节点的右子树为最大搜索二叉树。
所以我们要分析要返回的是什么类型,我们的返回值应该为(size,最大搜索二叉树的头结点,搜索二叉树的最大值,搜索二叉树的最小值)
public static class Node { public int value; public Node left; public Node right; public Node(int data) { this.value = data; } } public static int getBiggestSubBSTSize(Node head){ if(head == null) return 0; return process(head).size; } public static class ReturnType{ public int size; public Node head; public int min; public int max; public ReturnType(int size,Node head,int min,int max){ this.size = size; this.head = head; this.min = min; this.max = max; } } public static ReturnType process(Node head){ if(head == null){ return null; } ReturnType leftReturnType = process(head.left); ReturnType rightReturnType = process(head.right); int p1 = leftReturnType.size; int p2 = rightReturnType.size; int includeHead = 0; if (leftReturnType.head == head.left && rightReturnType.head == head.right && leftReturnType.max < head.value && rightReturnType.min > head.value) { includeHead = p1+p2+1; } int maxSize = Math.max(Math.max(p1, p2),includeHead); Node bSTHead = p1 > p2 ? leftReturnType.head : rightReturnType.head; if (maxSize == includeHead) { bSTHead = head; } return new ReturnType(maxSize, bSTHead, Math.min(Math.min(leftReturnType.min,rightReturnType.min),head.value), Math.max(Math.max(leftReturnType.max,rightReturnType.max),head.value)); }

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号