宏(Macro)的使用
一、宏定义
- 几个特殊的宏
C语言规定了几个特殊的宏:__FILE__ 、 __LINE__ 、 __func__。
macro.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
printf("Now, we will check macro:__FILE__, __LINE__, __func__\n");
printf("__FILE__:%s\n", __FILE__);
printf("__LINE__:%d\n", __LINE__);
printf("__func__:%s\n", __func__);
return 0;
}

__FILE__: 以字符串形式(%s)表示当前文件名称
__LINE__: 以整数形式(%d)表示当前行号
__func__: 以字符串形式(%s)表示当前函数名
- 宏变量
我们可以用变量形式来定义一个常量,例如:const double PI = 3.14。
但我们不一般不用上述这样的做,而是用宏定义一个明示常量,例如:#define PI 3.14 。
- 宏函数
我们定义一个简单的函数,例如:
int max(int a, int b)
{
return (a > b ? a : b);
}
但一般我们不这样做,而是使用宏函数,例如:#define MAX(a,b) ((a)>(b)?(a):(b))。
对于函数max比较的结果只能是整型,而宏函数MAX可以比较任一类型。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#define MAX(a,b) ((a)>(b)?(a):(b))
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
/* macro function MAX */
double a = 10.0, b = 25.5;
printf("The larger one of a and b is:%.1lf\n", MAX(a, b));
const char *c = "34.1";
const char *d = "78.5";
printf("The larger one of c and d is:%s\n", MAX(c, d));
return 0;
}

二、条件编译
- 涉及到条件编译的关键字
#ifdef:如果后面的宏已定义,则编译接下来的代码块
#ifndef:如果后面的宏没有定义,则编译接下来的代码块
#if: 如果后面的常量表达式为真,则编译接下来的代码块
#elif: 可以与#if、#else结合使用,使用方法类似:if 、elseif、 else
#else: 可以与#if、#ifdef、#ifndef结合使用
#elif:标志条件编译块的结束,凡是涉及到条件编译都要以它作为结尾,不能省略
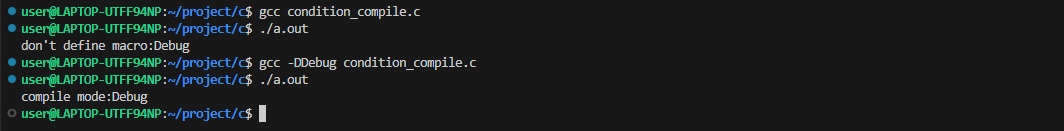
条件编译可以通过用户在gcc编译时传入宏到源文件,决定编译分支,例如:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
#ifdef Debug
printf("compile mode:Debug\n");
#else
printf("don't define macro:Debug\n");
#endif
return 0;
}
三、防止头文件重复包含
user.h
#ifndef __USER_H__
#define __USER_H__
void print_hello(void);
//...
#endif


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号