SpringCloud注册中心
1. 引言
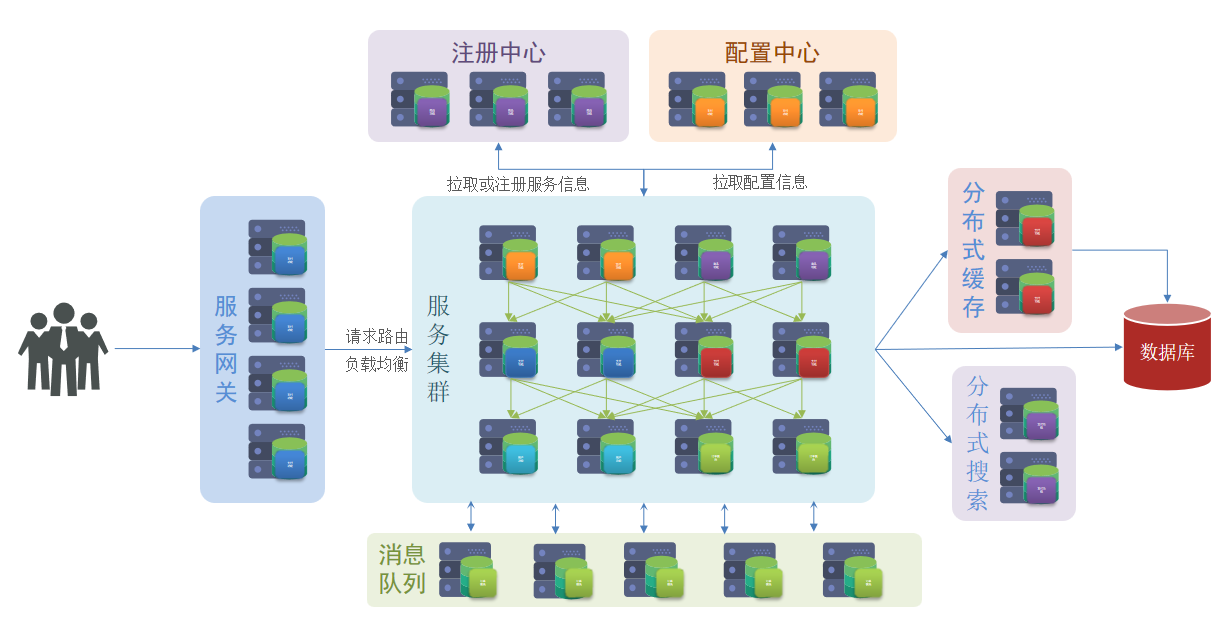
总体微服务流程类似:
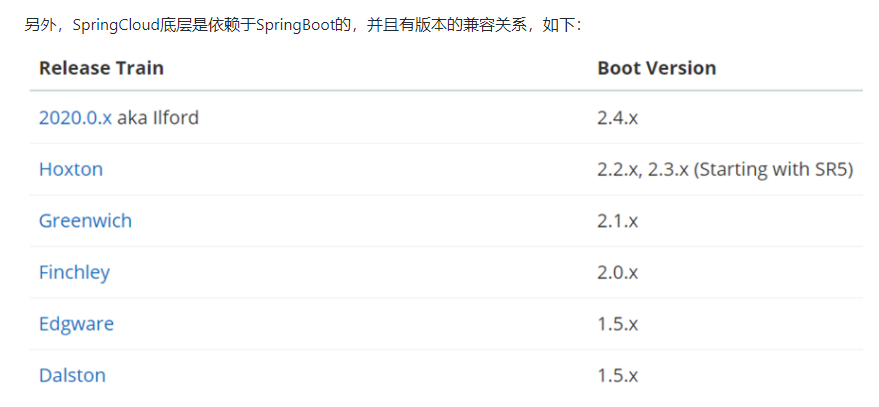
SpringCloud是基于SpringBoot的,所以会存在版本的兼容性问题,
1.5. 远程调用
因为不同的服务部署在不同的机器上,所以我们需要使用远程调用的方式去获取数据(把RestTemplate注册进IOC容器中)
@Bean
public RestTemplate restTemplate(){
return new RestTemplate();
}
-------------------------------------
// 设定url
String url = "http://localhost:8081/user/" + order.getUserId();
// 发送get请求
ResponseEntity<User> forEntity = restTemplate.getForEntity(url, User.class);
// 获取对象
User body = forEntity.getBody();
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
//需要参数的请求
// 设定url,使用{}占位
String url = "http://localhost:8081/user?id={id}&name={name}";
// 发送get请求,最后传入id和name
ResponseEntity<User> forEntity = restTemplate.getForEntity(url, User.class,1,"xx");
// 获取对象
User body = forEntity.getBody();
2. 注册中心
对于多个微服务,我们要知道每个微服务的地址(ip+port),使用注册中心可以帮助我们记录下每个服务的地址(集群也可以,帮助我们从集群中按照规则获取一个可用的地址)。代码中只需要知道微服务的名字就可以通过注册中心获取ip+port
【1. 启动注册中心。 2. 把所有的微服务注册进注册中心中。】
注册中心一般分为两种:Eureka 和 Nacos
2.1 Eureka
2.1.1 创建一个新的maven空模块
2.1.2 导入Eureka的starts(别忘了导入SpringCloud相关依赖)
<!-- springCloud -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-server</artifactId>
</dependency>
2.1.3 编写启动类【在@SpringBootApplication 注解标注的主类上加上 @EnableEurekaServer 注解】
2.1.4 编写yml配置文件
server:
port: 10086
spring:
application:
name: eureka-server
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://127.0.0.1:10086/eureka
2.1.5 给所有需要使用注册中心的模块添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
2.1.6 给所有需要使用注册中心的模块添加yml配置信息【设定名字和eureka的服务器地址】
spring:
application:
name: %自定义的name%
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://127.0.0.1:10086/eureka
2.1.7 给RestTemplate的@Bean方法上加上@LoadBalanced注解
@Bean
@LoadBalanced
public RestTemplate restTemplate(){
return new RestTemplate();
}
2.2 rabbion的负载均衡原理【要在需要消费其他微服务接口的微服务修改负载均衡的模式!】
2.2.1 @LoadBalanced

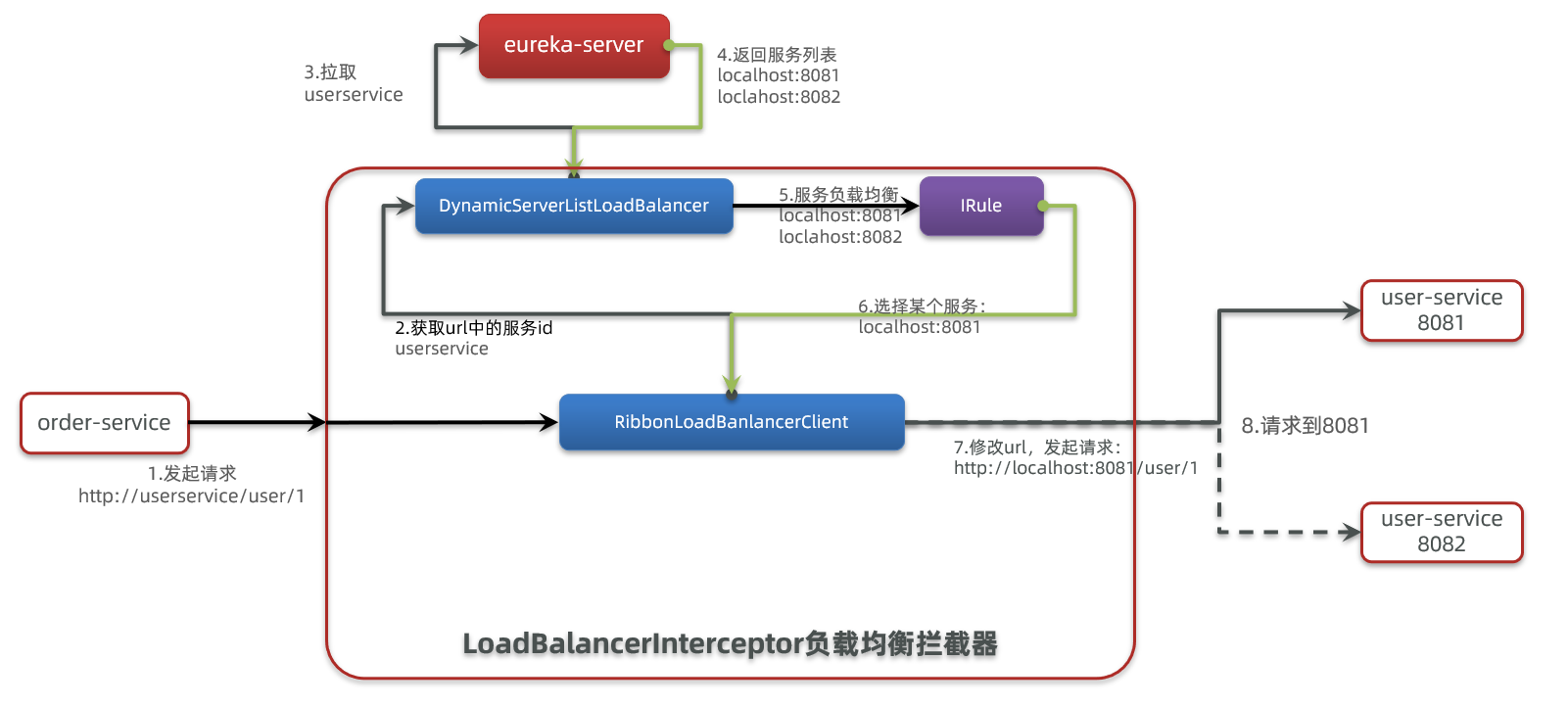
2.2.2 负载均衡的类型
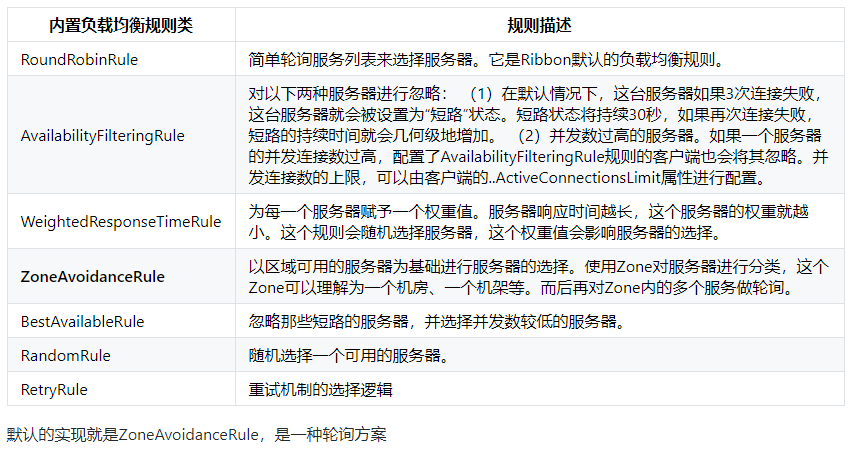
2.2.3 更改默认负载均衡规则【在消费者的yml文件里配置】
userservice: # 给某个微服务配置负载均衡规则,这里是userservice服务
ribbon:
NFLoadBalancerRuleClassName: com.netflix.loadbalancer.RandomRule # 负载均衡规则
2.3 nacos
2.3.0 启动nacos
cmd运行
startup.cmd -m standalone
访问网址,密码和账号都是nacos
2.3.1 给父工程添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-alibaba-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>2.2.6.RELEASE</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
2.3.2 给被注册的微服务添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery</artifactId>
</dependency>
2.3.3 给被注册的微服务添加配置信息【nacos的服务器地址和集群,拉取ip地址时优先拉取同集群的】
spring:
application:
name: %自定义的name%
cloud:
nacos:
server-addr: localhost:8848
discovery:
cluster-name: HZ # 集群名称
ephemeral: true # 是否设置成临时实例 ,临时实例采用心跳机制探测,非临时实例采用nacos主动请求探测机制
2.4 总结
- Nacos与eureka的共同点
* 都支持服务注册和服务拉取
* 都支持服务提供者心跳方式做健康检测
- Nacos与Eureka的区别
* Nacos支持服务端主动检测提供者状态:临时实例采用心跳模式,非临时实例采用主动检测模式
* 临时实例心跳不正常会被剔除,非临时实例则不会被剔除
* Nacos支持服务列表变更的消息推送模式,服务列表更新更及时
* Nacos集群默认采用AP方式,当集群中存在非临时实例时,采用CP模式;Eureka采用AP方式


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号