实验1
源代码
task.1
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
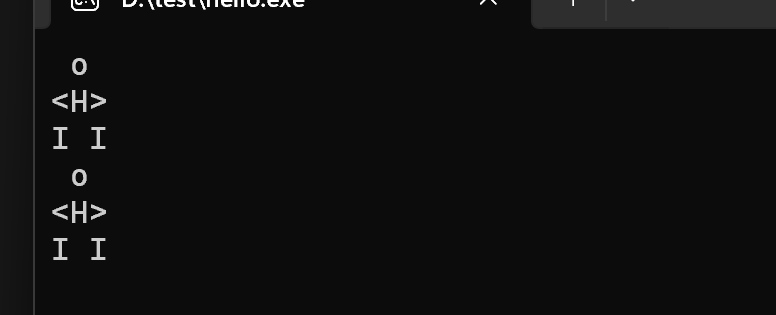
printf(" o \n");
printf("<H>\n");
printf("I I\n");
system("pause");
return 0;
}
task1_1.c
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
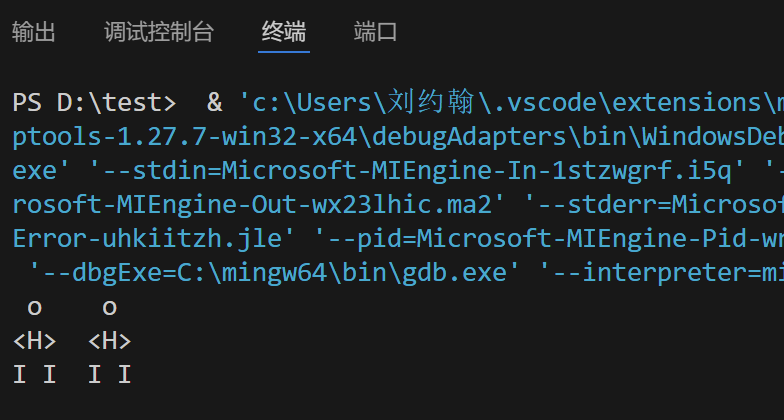
{ printf(" o \n");
printf("<H>\n");
printf("I I\n");
printf(" o \n");
printf("<H>\n");
printf("I I\n");
system("pause");
return 0;
}
task1_2.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
printf(" o o \n");
printf("<H> <H>\n");
printf("I I I I\n");
system("pause");
return 0;
}
实验结果截图
![屏幕截图 2025-09-26 093527]()
![image]()
![屏幕截图 2025-09-26 233213]()
实验2
源代码
task2.c
include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
double a, b, c;
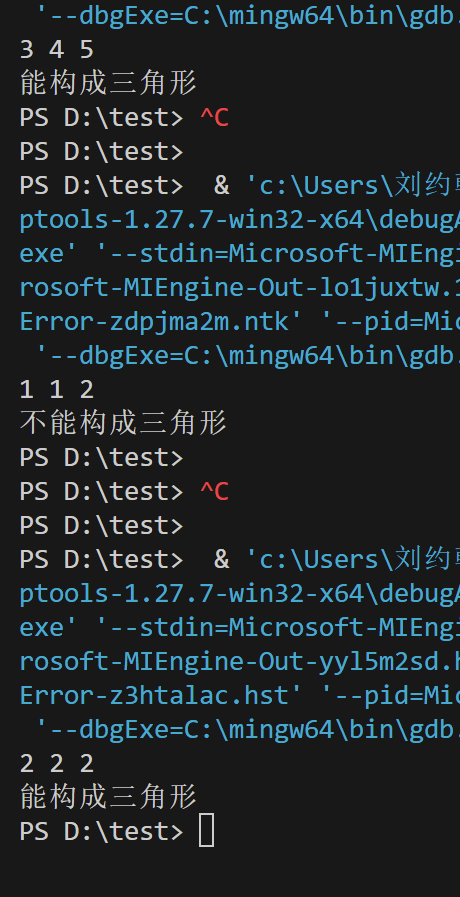
scanf("%lf%lf%lf", &a, &b, &c);
if (a + b > c && a + c > b && b + c > a)
printf("能构成三角形\n");
else
printf("不能构成三角形\n");
return 0;
}
实验结果截图
![屏幕截图 2025-09-27 150743]()
实验3
源代码
task3.c
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char ans1, ans2;
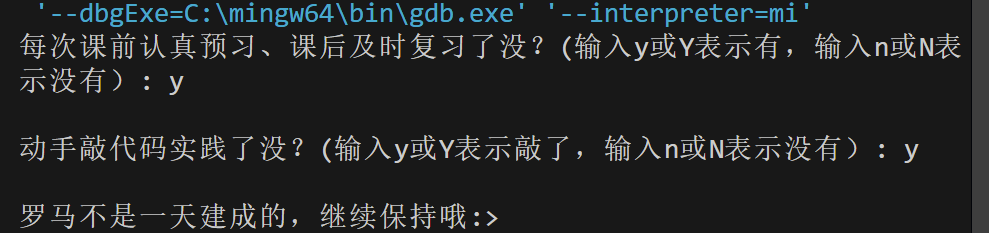
printf("每次课前认真预习、课后及时复习了没?(输入y或Y表示有,输入n或N表示没有): ");
ans1 = getchar();
getchar(); // 吸收回车符
printf("\n动手敲代码实践了没?(输入y或Y表示敲了,输入n或N表示没有): ");
ans2 = getchar();
if ((ans1 == 'y' || ans1 == 'Y') && (ans2 == 'y' || ans2 == 'Y'))
printf("\n罗马不是一天建成的,继续保持哦:>\n");
else
printf("\n罗马不是一天毁灭的,我们来建设吧\n");
return 0;
}
实验结果截图
![屏幕截图 2025-09-27 151152]()
![屏幕截图 2025-09-27 151310]()
![屏幕截图 2025-09-27 151319]()
回答问题
第一个问题输入后按回车,程序会直接跳过第二个问题的,直接显示最后的结果 第一个 getchar() 读取了用户输入的字符 输入缓冲区中还剩下了'\n' 如果没有line9的 getchar() 来吸收这个'\n',那么第二个 getchar() 会直接读这个'\n' 导致第二个问题的答案被自动赋值为'\n',程序跳过用户第二次输入
实验4
源代码
task4.c
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
double x, y;
char c1, c2, c3;
int a1, a2, a3;
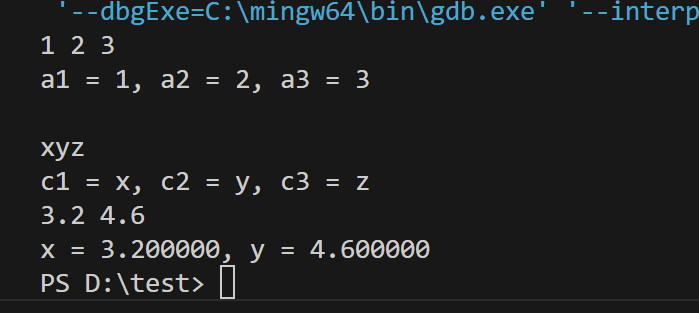
scanf("%d%d%d", &a1, &a2, &a3);
printf("a1 = %d, a2 = %d, a3 = %d\n", a1, a2, a3);
scanf("%c%c%c", &c1, &c2, &c3);
printf("c1 = %c, c2 = %c, c3 = %c\n", c1, c2, c3);
scanf("%lf%lf", &x, &y);
printf("x = %f, y = %lf\n", x, y);
return 0;
}
实验结果截图
![屏幕截图 2025-09-27 152732]()
实验5
源代码
task5.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int main()
{
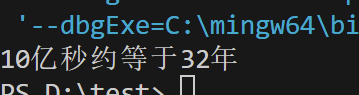
double seconds = 1000000000;
double seconds_per_year = 365 * 24 * 60 * 60;
double years = seconds / seconds_per_year;
int year = (int)(years + 0.5);
printf("10亿秒约等于%d年\n", year);
return 0;
}
实验结果截图
![屏幕截图 2025-09-27 153546]()
实验6
源代码
task6_1.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int main()
{
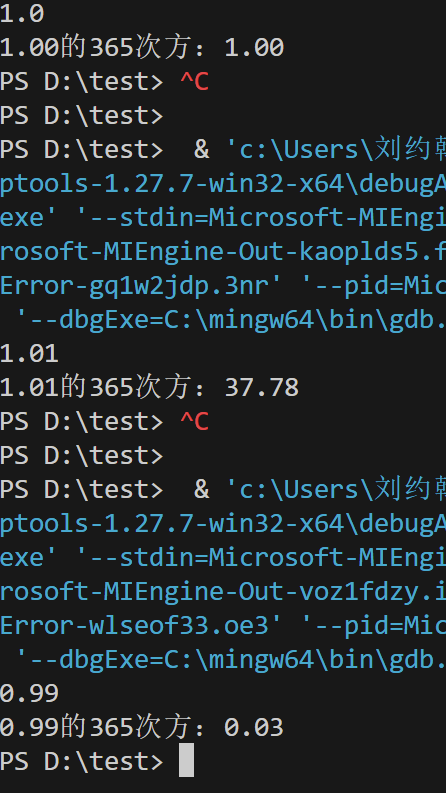
double x, ans;
scanf("%lf", &x);
ans = pow(x, 365);
printf("%.2f的365次方:%.2f\n", x, ans);
return 0;
}
task6_2.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int main()
{
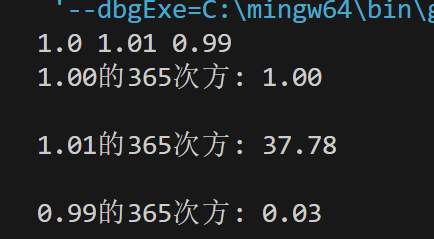
double x, ans;
while (scanf("%lf", &x) != EOF)
{
ans = pow(x, 365);
printf("%.2f的365次方: %.2f\n", x, ans);
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
实验结果截图
![屏幕截图 2025-09-27 154448]()
![屏幕截图 2025-09-27 154821]()
实验7
源代码
task7.c
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
double c, f;
while (scanf("%lf", &c) != EOF)
{
f = 9.0 / 5 * c + 32;
printf("摄氏度c = %.2f时,华氏度f = %.2f\n", c, f);
}
return 0;
}
实验结果截图
![屏幕截图 2025-09-27 155305]()
实验8
源代码
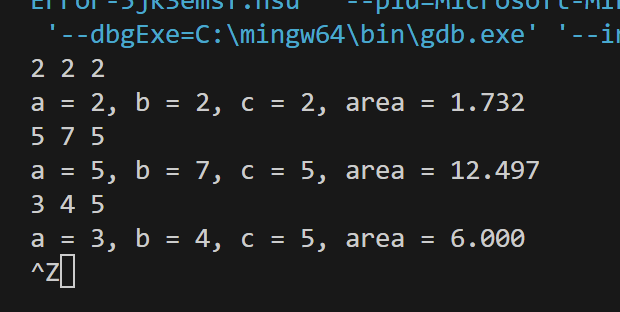
task8.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int main()
{
double a, b, c, s, area;
while (scanf("%lf%lf%lf", &a, &b, &c) != EOF)
{
s = (a + b + c) / 2;
area = sqrt(s * (s - a) * (s - b) * (s - c));
printf("a = %.0f, b = %.0f, c = %.0f, area = %.3f\n", a, b, c, area);
}
return 0;
}
实验结果截图
![屏幕截图 2025-09-27 155631]()







 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号