云散月明谁点缀,天容海色本澄清-第二次blog作业
云散月明谁点缀,天容海色本澄清--第二次blog作业🔭
前言:
又到了blog的总结时间,我想,也许对于我们普通的学生来说,初学Java多态时,总觉得那些父类引用指向子类对象的代码,像一场晦涩的哑谜。编译器沉默地注视着我手忙脚乱地调试,而IDE里鲜红的报错提示像午夜的路灯,照着我这个迷途的初学者。 记得某个调试到凌晨的夜晚,当我终于让重写的方法正确调用时,屏幕上的输出忽然变得清晰起来,仿佛拨开了层层代码的迷雾。那一刻,我想起那句"云散月明谁点缀"——原来晦涩难懂的语法规则背后,藏着的是一轮皎洁的月光,只待我耐心拨开浮云,便能看见它的温柔照耀。 现在想来,编程路上的困惑,不过是成长必经的夜色。而每一次顿悟,都是月光终于穿透云层,洒在键盘上的时刻,那是我才发现,原来--天容海色本澄清🌙
本次blog我们分成三个题目的分类讨论,先来看第一个,点线面问题的两次重构:

初见这道题时,我还是懵懂的,不了解多态,继承的含义,看着题目给的三个element分别使用了三次,不免产生了深深的疑惑,于是便去仔细了解了一下继承/多态:
有一位同学给我举了一个例子,我觉得非常生动:
继承:白嫖父类的代码,还能自己加功能或改功能。
class 老爸的支付宝 {
void 扫码付款()
{ System.out.println("付款成功!");
} }
class 我的支付宝 extends 老爸的支付宝
{ // extends 就是继承! void 发红包()
{ System.out.println("红包已塞钱!");
} // 新增功能 @Override void 扫码付款()
{ // 改进老爸的旧功能 System.out.println("请先按指纹~");
super.扫码付款(); // 调老爸原来的方法
} }
(在这里用父类子类就很生动形象了😁)
那么多态呢?
多态:同一个方法名,干不同的事
多态就像「同样的按钮,按出不同效果」
多态和继承就像"遥控器"和"电器"
万能遥控器(Element类),它可以控制各种电器。所有电器都必须有"开/关"功能(display()方法)。
现在有几种电器:
电灯(Point 类):按开关会亮灯 💡
空调(Line 类):按开关会吹冷风 ❄️
电视(Plane 类):按开关会播放节目 📺
多态:父类引用统一调用,但实际执行看子类具体实现;
那么在结合第一次代码的基础上
我们进行一个类图的大致分析:
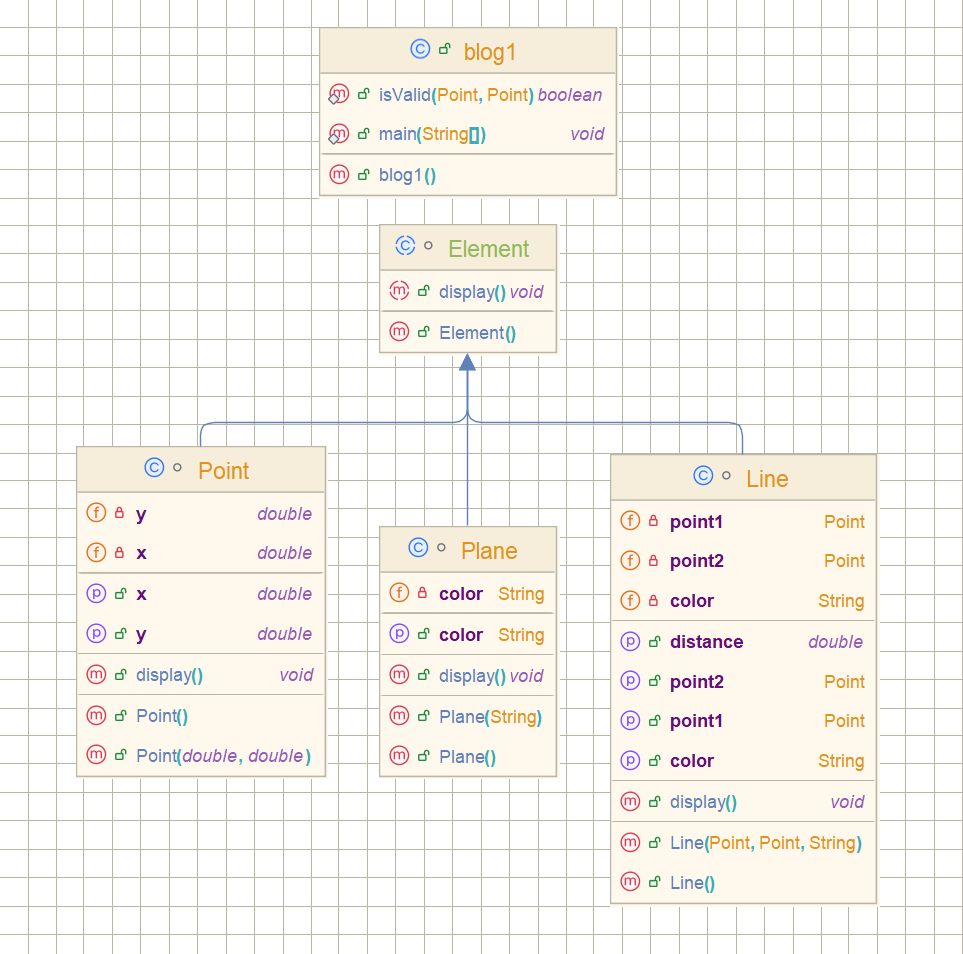
在这个程序里,Element就是我的魔法棒:
指向Point时,display()变成坐标打印机
指向Line时,display()化身线段测量仪
指向Plane时,display()又成了颜色播报员
Element接口就是我和三个类之间的秘密暗号,不管它们内部怎么折腾,只要遵守display()这个约定,我就能用统一的方式唤醒它们的不同能力😁。
在知道这些核心内容后,我们就能够成功写出这道题的代码:
点我折叠哦^-^
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
Point p1 = new Point(sc.nextDouble(), sc.nextDouble());
Point p2 = new Point(sc.nextDouble(), sc.nextDouble());
sc.nextLine();
String color = sc.nextLine();
if (isValid(p1,p2)) {
Line l = new Line(p1, p2, color);
Plane plane = new Plane(color);
Element element;
element = p1;
element.display();
element = p2;
element.display();
element = l;
element.display();
element = plane;
element.display();
} else {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
}
public static boolean isValid(Point p1, Point p2) {
return (p1.getX() > 0 && p1.getX() <= 200) &&
(p2.getX() > 0 && p2.getX() <= 200) &&
(p1.getY() > 0 && p1.getY() <= 200) &&
(p2.getY() > 0 && p2.getY() <= 200);
}
}
/*学渣的挣扎与理解:多态和继承就像"遥控器"和"电器"
万能遥控器(Element类),它可以控制各种电器。所有电器都必须有"开/关"功能(display()方法)。
现在有几种电器:
电灯(Point类)
空调(Line类)
电视(Plane类)*/
abstract class Element {
{
public abstract void display();
}
class Point extends Element {
private double x;
private double y;
public Point() {}
public Point(double x, double y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public double getX() {
return x;
}
public void setX(double x) {
this.x = x;
}
public double getY() {
return y;
}
public void setY(double y) {
this.y = y;
}
@Override
public void display() {
System.out.printf("(%.2f,%.2f)\n", x, y);
}
}
class Line extends Element {
private Point point1;
private Point point2;
private String color;
public Line() {}
public Line(Point point1, Point point2, String color) {
this.point1 = point1;
this.point2 = point2;
this.color = color;
}
public Point getPoint1() {
return point1;
}
public void setPoint1(Point point1) {
this.point1 = point1;
}
public Point getPoint2() {
return point2;
}
public void setPoint2(Point point2) {
this.point2 = point2;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public double getDistance() {
double dx = point2.getX() - point1.getX();
double dy = point2.getY() - point1.getY();
return Math.sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy);
}
@Override
public void display() {
System.out.printf("The line's color is:%s\n", color);
System.out.println("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:");
point1.display();
System.out.println("The line's end point's Coordinate is:");
point2.display();
System.out.printf("The line's length is:%.2f\n", getDistance());
}
}
class Plane extends Element {
private String color;
public Plane() {}
public Plane(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
@Override
public void display() {
System.out.printf("The Plane's color is:%s\n", color);
}
}
那我们来看第二个部分--魔方🗜
第一阶段:初读题目(这都是啥跟啥)
第一次看到这个题目时,我的表情是这样的:😳
类太多:Solid、RubikCube、SquareCube、RegularPyramidCube...类名都好长,而且我还看不懂什么意思!!!!
关系复杂:既有继承又有组合,还有抽象类
公式劝退:看到√3、√2这些数学公式直接头大
内心OS:"这到底是编程题还是数学题啊?"
第二阶段:尝试理解类图吧
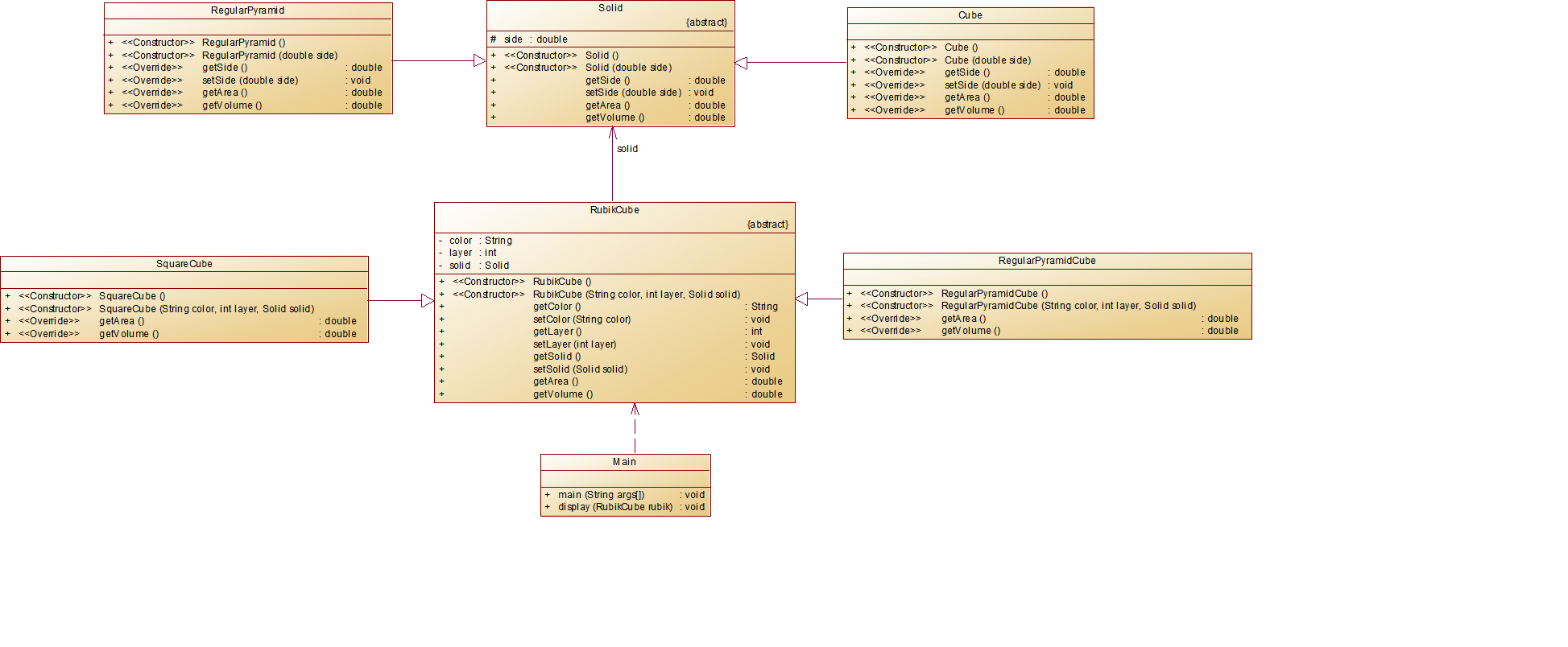
(地铁,老人,手机..)
最让我弄不懂的,还是这个solid类到底是干啥的,觉得这个类很多余:"直接写Cube和Pyramid不就行了吗?"
后来发现它的精妙之处:
相当于制定了一套"几何体标准"
任何几何体想要加入这个体系,必须:
要有边长(side属性)
能计算表面积和体积(实现两个抽象方法)
以规范的格式规定我必须去计算每一个小立体的表面积,体积;
欸,那为什么RubikCube会继承于solid类呢?看着旁边另外两个继承,我似乎一下子醍醐灌顶,这道题的思路大抵就是:
先用Solid规范每一个小的立体,然后传给"魔方类"
再根据魔方类为主类,去重新计算正方体和三棱锥的相关信息,就像是一层层拼起来,Solid和RubikCube更像是,监督?
简直是层层递进,妙,实在是妙啊!
继承的优点在这个程序中体现
代码复用:
所有子类共享Solid中定义的side属性和getter/setter方法
不需要在每个子类中重复定义这些基本内容
多态性:
display()方法接收RubilkCube参数,但可以处理任何子类对象
运行时根据实际对象类型调用相应的方法实现
扩展性:
可以轻松添加新的立体形状或魔方类型,只需继承相应基类
不需要修改现有代码,符合开闭原则
抽象与具体分离:
高层代码(如Main)只需要知道RubilkCube的接口
具体实现细节隐藏在子类中
那我们一起来看一下这道题的代码吧!
^-^防伪标识
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
String color = input.next();
int layer = input.nextInt();
double side = input.nextDouble();
RubilkCube cube1 = new SquareCube(color, layer,new Cube(side));
color = input.next();
layer = input.nextInt();
side = input.nextDouble();
RubilkCube cube2 = new RegularPyramidCube(color, layer,new RegularPyramid(side));
display(cube1);
display(cube2);
}
static void display(RubilkCube cube) {
System.out.println(cube.getColor());
// 输出表面积(通过组合的Solid对象计算)
System.out.printf("%.2f\n", cube.getArea());
// 输出体积(通过组合的Solid对象计算)
System.out.printf("%.2f\n", cube.getVolume());
}
}
abstract class Solid {
protected double side;
public Solid(){}
public Solid(double side) {
this.side = side;
}
public double getSide() {
return side;
}
public void setSide(double side) {
this.side = side;
}
public abstract double getArea();
public abstract double getVolume();
}
class RegularPyramid extends Solid{
public RegularPyramid() {
}
public RegularPyramid(double size) {
super(size);
}
@Override
public double getSide() {
return super.getSide();
}
@Override
public void setSide(double side) {
super.setSide(side);
}
@Override
public double getVolume() {
return Math.sqrt(3)*getSide()*getSide()*getSide()/36;//根号三*a三次方/36
}
@Override
public double getArea() {
return Math.sqrt(3)*getSide()*getSide();
}
}
class Cube extends Solid{
public Cube(){}
public Cube(double side){
super(side);
}
@Override
public double getSide() {
return super.getSide();
}
@Override
public void setSide(double side) {
super.setSide(side);
}
@Override
public double getArea() {
return getSide()*getSide()*6;
}
@Override
public double getVolume() {
return getSide()*getSide()*getSide();
}
}
abstract class RubilkCube extends Solid{
protected String color;
protected int layer;
protected Solid solid;
public RubilkCube() {}
public RubilkCube(String color, int layer, Solid solid) {
this.color = color;
this.layer = layer;
this.solid = solid;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public int getLayer() {
return layer;
}
public void setLayer(int layer) {
this.layer = layer;
}
public Solid getSolid() {
return solid;
}
public void setSolid(Solid solid) {
this.solid = solid;
}
}
class SquareCube extends RubilkCube {
public SquareCube() {}
public SquareCube(String color, int layer,Solid solid) {
super(color, layer, solid);
}
@Override
public double getArea(){
// 步骤1:获取阶数(层数)→ 来自父类RubikCube的属性
int layers = this.getLayer();
// 步骤2:获取单元正方体的边长 → 来自组合的Cube对象
double unitSide = this.getSolid().getSide();
// 步骤3:计算实际魔方边长(放大后的边长)
double actualSide = layers * unitSide;
// 步骤4:套用正方体表面积公式
return 6 * actualSide * actualSide;
}
@Override
public double getVolume() {
double actualSide = this.getSolid().getSide()*this.getLayer();
return Math.pow(actualSide, 3);
}
}
class RegularPyramidCube extends RubilkCube {
public RegularPyramidCube() {
}
public RegularPyramidCube(String color, int layer, Solid solid) {
super(color, layer, solid);
}
@Override
public double getArea() {
int layers = this.getLayer();
double unitSide = this.getSolid().getSide();
double actualSide = layers * unitSide;
return Math.sqrt(3) * actualSide * actualSide;
}
@Override
public double getVolume() {
double actualSide = this.getLayer() * this.getSolid().getSide();
// 正三棱锥体积公式:√2/12 × 边长³
return (Math.sqrt(2)/12) * Math.pow(actualSide, 3);
}
}
那么最后分享两个踩坑心得吧!
在
System.out.println(cube.getColor());
// 输出表面积(通过组合的Solid对象计算)
System.out.printf("%.2f\n", cube.getArea());
// 输出体积(通过组合的Solid对象计算)
System.out.printf("%.2f\n", cube.getVolume());
这里,我第一次写的代码是:cube.getSolid().getVolume(),结果输出的数字刚好是每一个小方块的信息
而这两种方法的核心差异就在于:
cube.getVolume() 调用链: 1. 访问 SquareCube 的 getVolume() 方法 2. 计算实际边长:2.0(side) × 3(layer) = 6.0 3. 返回 6.0³ = 216.0
cube.getSolid().getVolume() 调用链: 1. 获取 solid 引用 → Cube对象 2. 调用 Cube 的 getVolume() 3. 返回 2.0³ = 8.0
因为RubilkCube cube1 = new SquareCube(color, layer,new Cube(side));和RubilkCube cube2 = new RegularPyramidCube(color, layer,new RegularPyramid(side));
已经明确了我的调用路径会去找谁,所以直接一次getVolume就能找到拼装后的结果啦!
那么我们来到,字数最多,解释最复杂,但是也能够攻克的最后一个,航空货运题✈️
ok,点开这道题,发现题目要求是pdf,两眼一黑😇
https://images.ptausercontent.com/499d204b-fcef-4610-a9ca-c8fbf5e346d9.pdf
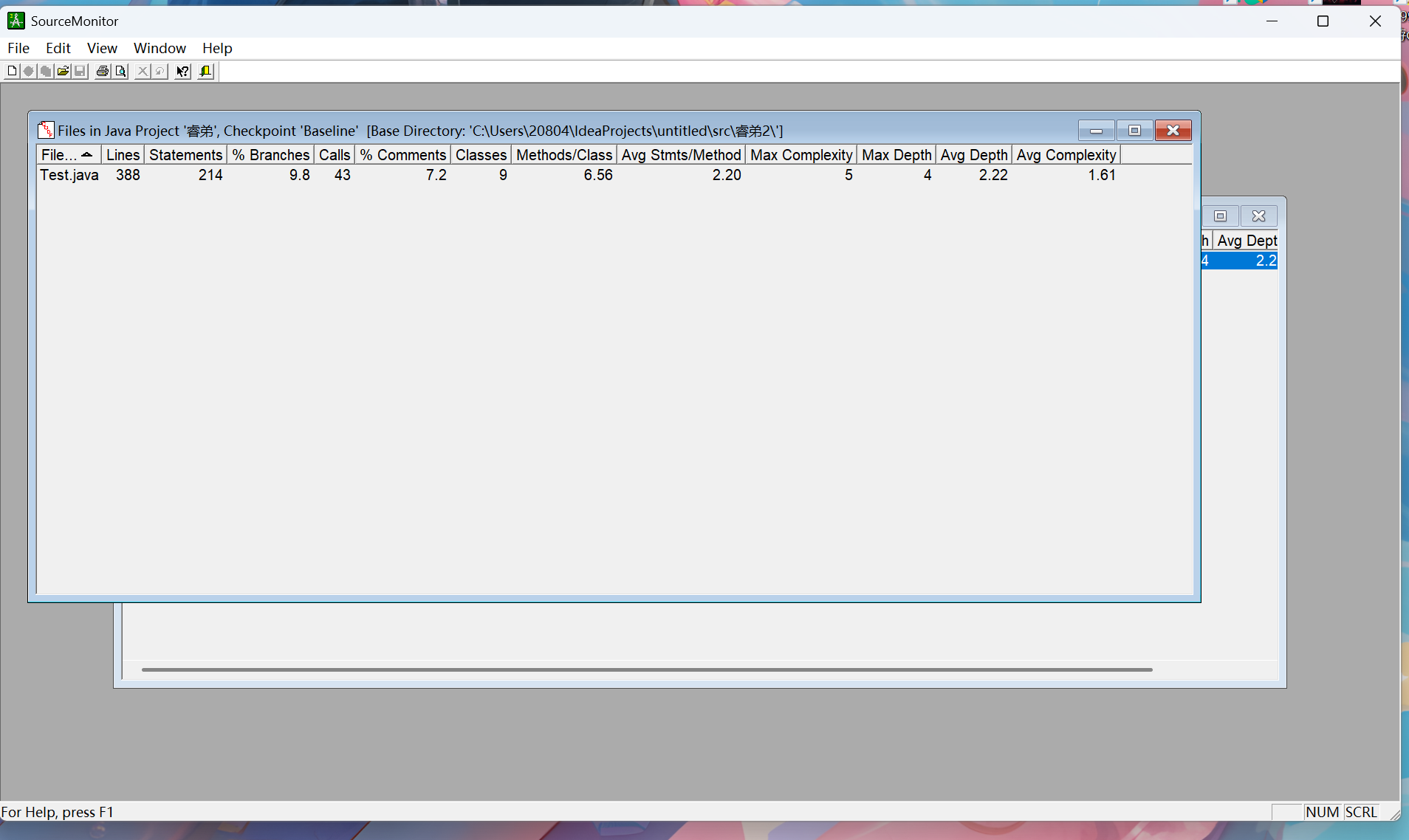
老样子,我们先来看两组图表数据:
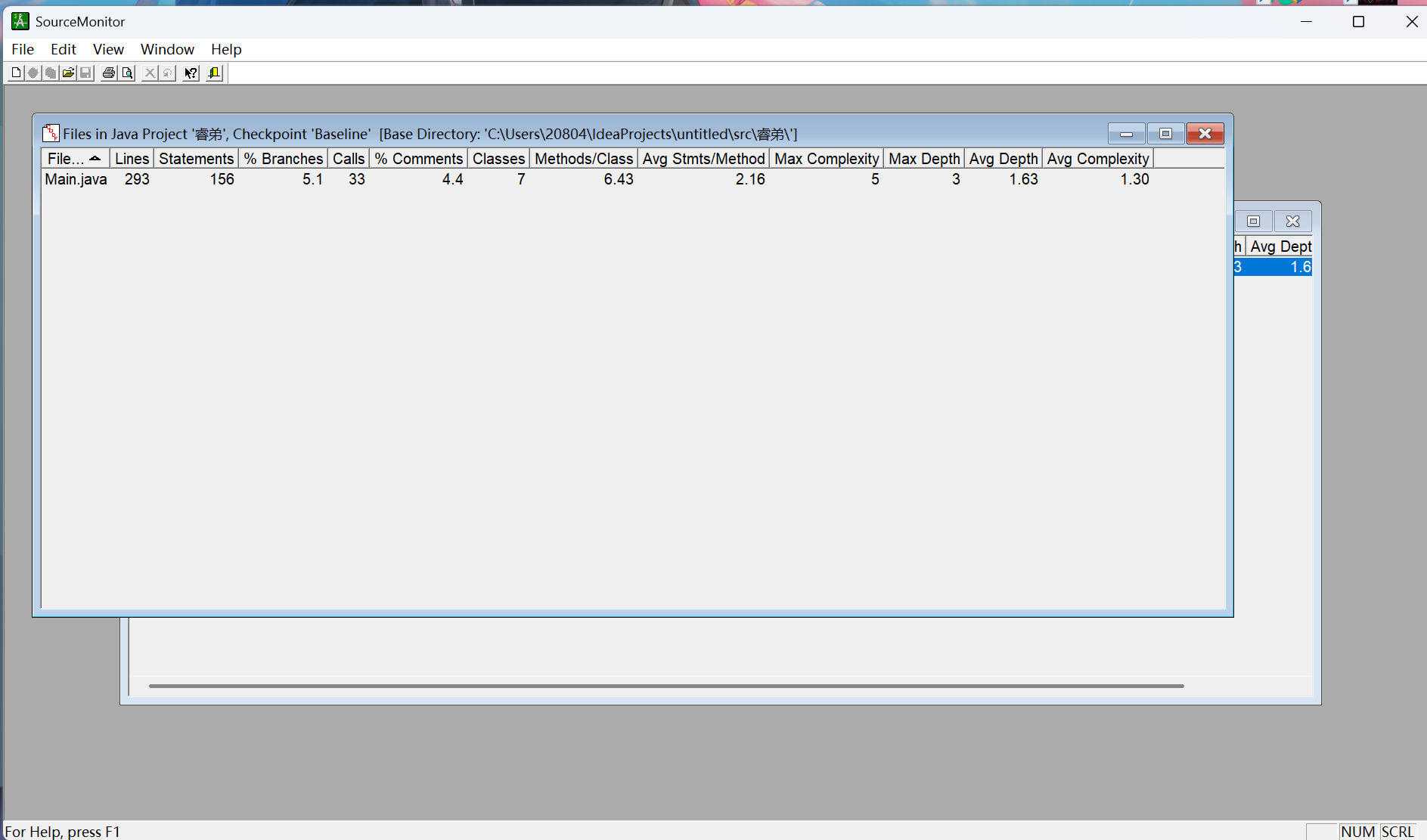
Lines:代码行数,Main.java有 293 行 。
Statements:语句数量,共 156 条语句。
% Branches:分支语句占比,为 5.1% 。
Calls:方法调用次数,为 33 次。
% Comments:注释占比,4.4% 。
Classes:类的数量,有 7 个类。
Methods/Class:平均每个类的方法数,为 6.43 。
Avg Stmts/Method:平均每个方法的语句数,2.16 条 。
Max Complexity:方法的最大复杂度,为 5 。
Max Depth:最大嵌套深度,为 3 。
Avg Depth:平均嵌套深度,1.63 。
Avg Complexity:平均复杂度,1.30 。
组合关系的实际应用 在基础练习中,我们学习到SquareCube应该组合Cube而不是继承它。货运系统将这个原则发挥得更加充分:
Order类组合了Cargo、Flight等多个业务对象
每个类职责单一,通过组合完成复杂功能
特别值得注意的是calCargoWeight工具类的设计,将体积计算完全独立封装
多态机制的进阶使用 相比基础练习中简单的display()抽象,货运系统的calculateRate接口展现了更专业的多态应用:
通过策略模式实现费率计算
不同的Rate实现类可以自由替换
业务逻辑与具体实现完全解耦
其实仔细观察发现,逻辑上来说并不复杂,只不过是很多数据堆砌在了一起,我们在仔细拆解后可以得到以下思考:
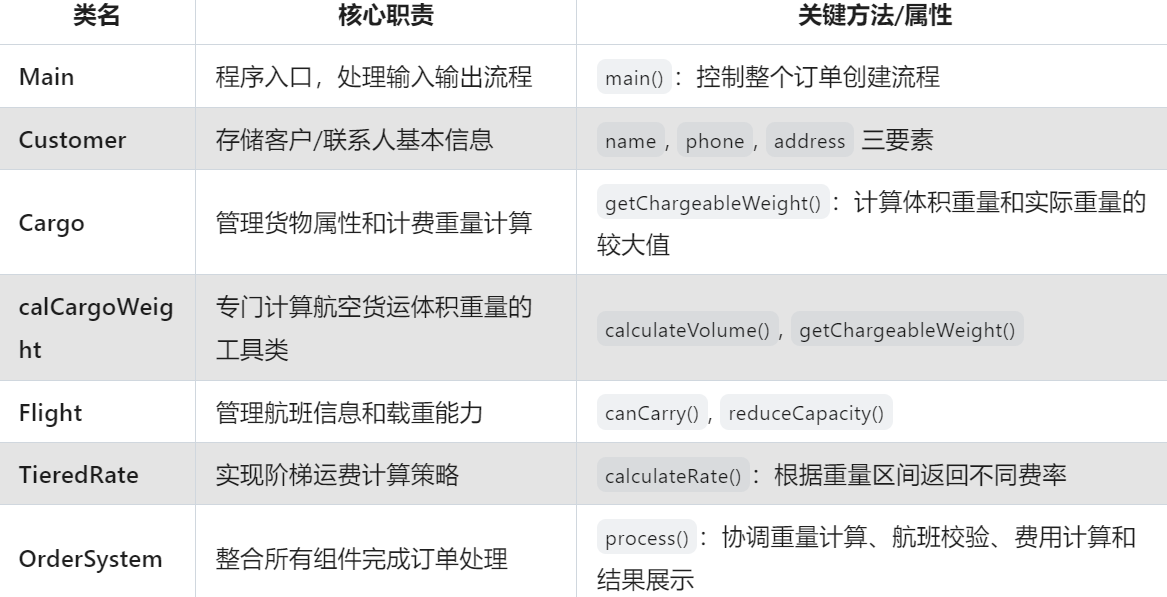
其中,我们的OrderSystem类持有:
多个Cargo对象(List集合)
单个Flight对象
三个Customer对象(客户、发件人、收件人)
一个TieredRate策略对象
一个calCargoWeight计算工具
接口实现关系:
TieredRate实现了calculateRate接口
OrderSystem依赖接口而非具体实现
计费重量计算流程:
OrderSystem遍历所有Cargo
每个Cargo调用calCargoWeight计算体积重量
比较实际重量和体积重量取较大值
运费计算流程:
根据Cargo提供的计费重量
TieredRate按重量区间选择费率
累加所有货物的运费
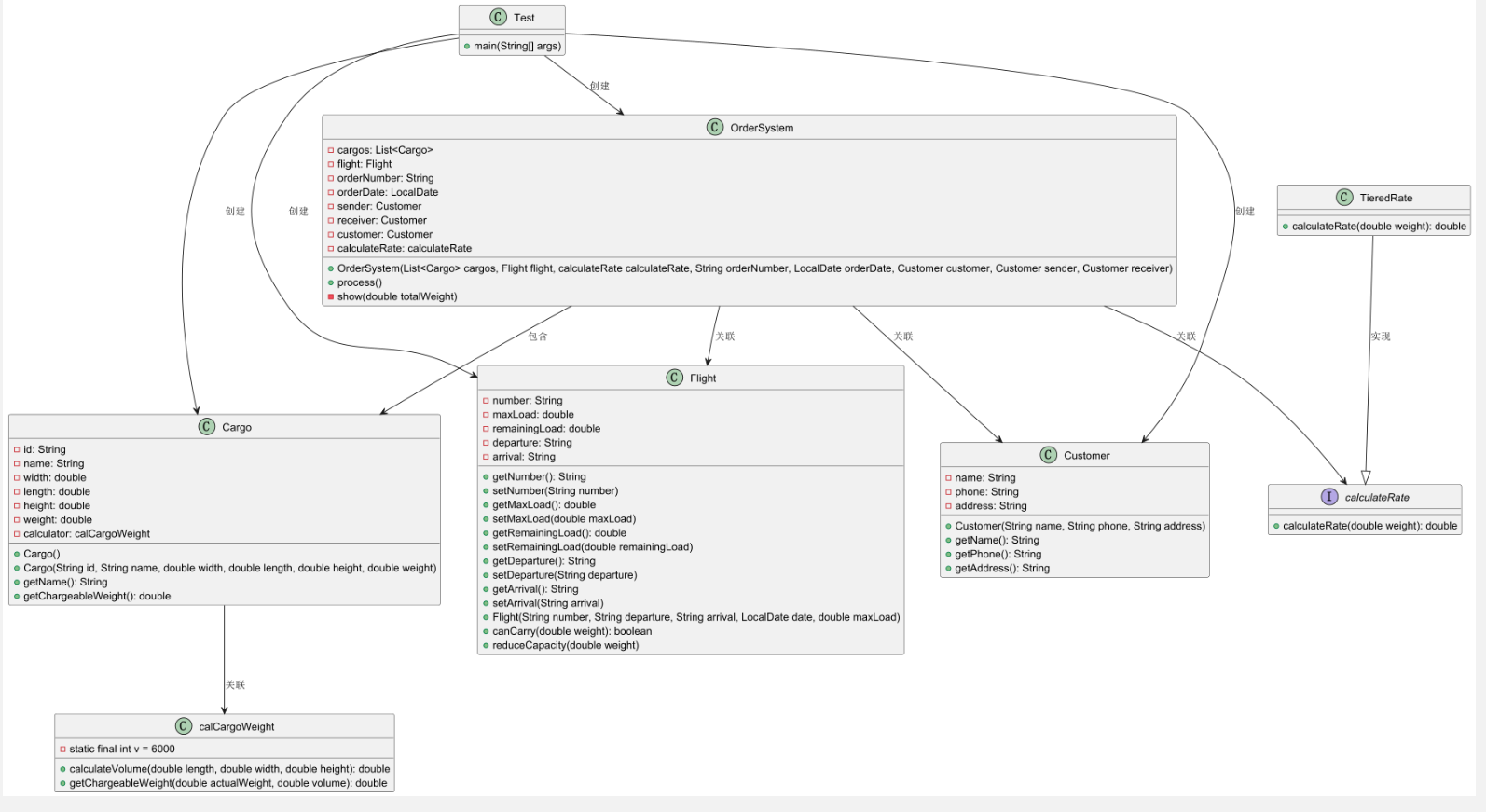
我们的类图如下:
在这道题目中,其实只要结合题目给的提示,梳理清楚逻辑,在前几道题目的铺垫上,会发现其实并没有那么复杂,不过我还是犯了一些小错误💩(在PTA上我也注释了这个错误,投机取巧的后果非常可怕啊!)
我们来看一下:

为什么会有这个反思呢?很简单,我们来看一下题目要求的输入:

会发现,其实这里不光只有两个人,其实还有第三个人!
没错,他就是我们的--郭靖!
为什么我要单独把他拎出来呢?
我的心路历程belike:在第一行的System.out中,我们输出的其实是郭靖的相关信息,如果只创建两个"送件人"和"收货人",那我们第一行的郭靖的信息怎么办呢?那我偷个懒,直接在show方法之前输出一行不就行了?但是这样却是拆东墙,补西墙,一直有问题😇
因为,除了我们的送件人和收件人,我们的郭靖应该是本次货运的"客户",他的信息我们需要单独去创建一个类进行打印,这就导致,如果我想在主函数里偷懒,直接打印郭靖的信息的话,会让信息打印顺序有误,那有人会说了,你把打印郭靖信息的代码放到输出信息前面不就好了吗?事实并非如此,因为我们还要有货物超重的判断,这样会导致先打印郭靖的信息,然后再输出货物超重!!!
那没办法了,只能老老实实的建立一个郭靖了!
然后跟其他的输出内容使用一样的格式,一起出来,那我们来看一下最后的代码吧:
^-^我又来咯
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
//客户基本信息与取件人收件人的输入中间隔了很多,所以不太好放到customer类里面,所以我直接在后面作了单独一行去打印
//没错,我打脸了,这样失败了,因为在输出错误提示的时候,我发现先把郭靖打上去了,所以重新创建了一个customer作为存储郭靖信息的地方
String custId = scanner.nextLine();
String custName = scanner.nextLine();
String custPhone = scanner.nextLine();
String custAddress = scanner.nextLine();
Customer customer = new Customer(custName, custPhone, custAddress);
//货物数量
int cargoCount = Integer.parseInt(scanner.nextLine());
List<Cargo> cargos = new ArrayList<>();
//读取货物数据
for (int i = 0; i < cargoCount; i++) {
String id = scanner.nextLine();
String name = scanner.nextLine();
double width = Double.parseDouble(scanner.nextLine());
double length = Double.parseDouble(scanner.nextLine());
double height = Double.parseDouble(scanner.nextLine());
double weight = Double.parseDouble(scanner.nextLine());
cargos.add(new Cargo(id, name, width, length, height, weight));
}
//读取航班信息
String flightNumber = scanner.nextLine();
String departure = scanner.nextLine();
String arrival = scanner.nextLine();
LocalDate flightDate = LocalDate.parse(scanner.nextLine());
double maxLoad = Double.parseDouble(scanner.nextLine());
Flight flight = new Flight(flightNumber, departure, arrival,
flightDate, maxLoad);
// 读取订单信息(洪七公和黄药师)
String orderNumber = scanner.nextLine();
LocalDate orderDate = LocalDate.parse(scanner.nextLine());
// 读取发件人信息(南昌大学、洪七公、18907912325)
String senderAddr = scanner.nextLine();
String senderName = scanner.nextLine();
String senderPhone = scanner.nextLine();
Customer sender = new Customer(senderName, senderPhone, senderAddr);
// 读取收件人信息(北京大学、黄药师、13607912546)
String receiverAddr = scanner.nextLine();
String receiverName = scanner.nextLine();
String receiverPhone = scanner.nextLine();
Customer receiver = new Customer(receiverName, receiverPhone, receiverAddr);
// 创建订单系统时传递 Customer 对象
OrderSystem orderSystem = new OrderSystem(
cargos,
flight,
new TieredRate(),
orderNumber,
orderDate,
customer,
sender,
receiver
);
//System.out.println("客户:" + custName+ "(" + custPhone + ")订单信息如下:");
orderSystem.process();
}
}
class Flight {
private String number;
private double maxLoad;
private double remainingLoad;
private String departure;
private String arrival;
public String getNumber() {
return number;
}
public void setNumber(String number) {
this.number = number;
}
public double getMaxLoad() {
return maxLoad;
}
public void setMaxLoad(double maxLoad) {
this.maxLoad = maxLoad;
}
public double getRemainingLoad() {
return remainingLoad;
}
public void setRemainingLoad(double remainingLoad) {
this.remainingLoad = remainingLoad;
}
public String getDeparture() {
return departure;
}
public void setDeparture(String departure) {
this.departure = departure;
}
public String getArrival() {
return arrival;
}
public void setArrival(String arrival) {
this.arrival = arrival;
}
public Flight(String number, String departure, String arrival,LocalDate date, double maxLoad) {
this.number = number;
this.maxLoad = maxLoad;
this.remainingLoad = maxLoad;
this.departure = departure;
this.arrival = arrival;
}
public boolean canCarry(double weight) {
return weight <= remainingLoad;
}
public void reduceCapacity(double weight) {
remainingLoad -= weight;
}
}
class Cargo {
private String id;
private String name;
private double width;
private double length;
private double height;
private double weight;
private calCargoWeight calculator = new calCargoWeight();
public Cargo() {}
public Cargo(String id, String name, double width, double length,double height, double weight) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.width = width;
this.length = length;
this.height = height;
this.weight = weight;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public double getChargeableWeight() {
//calCargoWeight calculator = new calCargoWeight();
double volume = calculator.calculateVolume(length, width, height);
return calculator.getChargeableWeight(weight, volume);
}
}
class calCargoWeight {
private static final int v = 6000;
public double calculateVolume(double length, double width, double height) {
return (length * width * height) / v;
}
public double getChargeableWeight(double actualWeight, double volume) {
return Math.max(actualWeight, volume);
}
}
class TieredRate implements calculateRate {
@Override
public double calculateRate(double weight) {
if (weight < 20) return 35;
else if (weight < 50) return 30;
else if (weight < 100) return 25;
else return 15;
}
}
interface calculateRate {
public abstract double calculateRate(double weight);
}
class OrderSystem {
private List<Cargo> cargos;
private Flight flight;
private String orderNumber;
private LocalDate orderDate;
private Customer sender;
private Customer receiver;
private Customer customer;
private calculateRate calculateRate;
public OrderSystem(List<Cargo> cargos, Flight flight, calculateRate calculateRate,
String orderNumber, LocalDate orderDate,Customer customer,Customer sender, Customer receiver) {
this.cargos = cargos;
this.flight = flight;
this.calculateRate = calculateRate;
this.orderNumber = orderNumber;
this.orderDate = orderDate;
this.sender = sender;
this.receiver = receiver;
this.customer = customer;
}
public void process() {
double totalWeight = 0;
for (Cargo cargo : cargos) {
totalWeight += cargo.getChargeableWeight();
}
if (!flight.canCarry(totalWeight)) {
System.out.printf("The flight with flight number:%s has exceeded its load capacity and cannot carry the order.\n",
flight.getNumber());
System.exit(0);
}
flight.reduceCapacity(totalWeight);
show(totalWeight);
}
private void show(double totalWeight){
double totalPayment = 0;
//这里把原来的第一行输出删掉了,因为发现郭靖变成了内谁
//就是这里,删不掉,还得是在这块打印啊!突然发现自己上面的方法好像是投机取巧,因为只有在这里打印才算是满足那个单一职责
System.out.println("客户:" +customer.getName() + "(" + customer.getPhone() + ")订单信息如下:");
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------");
System.out.println("航班号:" + flight.getNumber());
System.out.println("订单号:" + orderNumber);
System.out.println("订单日期:" + orderDate);
System.out.println("发件人姓名:" + sender.getName());
System.out.println("发件人电话:" + sender.getPhone());
System.out.println("发件人地址:" + sender.getAddress());
System.out.println("收件人姓名:" + receiver.getName());
System.out.println("收件人电话:" + receiver.getPhone());
System.out.println("收件人地址:" + receiver.getAddress());
System.out.println("订单总重量(kg):" + totalWeight);
for (Cargo cargo : cargos) {
double weight = cargo.getChargeableWeight();
double rate = calculateRate.calculateRate(weight);
double payment = weight * rate;
totalPayment += payment;
}
System.out.printf("微信支付金额:%.1f\n", totalPayment);
System.out.println("\n货物明细如下:");
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------");
System.out.println("明细编号\t货物名称\t计费重量\t计费费率\t应交运费");
int index = 1;
for (Cargo cargo : cargos) {
double weight = cargo.getChargeableWeight();
double rate = calculateRate.calculateRate(weight);
double payment = weight * rate;
System.out.printf("%d\t%s\t%.1f\t%.1f\t%.1f\n",index++, cargo.getName(), weight, rate, payment);
}
}
}
class Customer {
private String name;
private String phone;
private String address;
public Customer(String name, String phone, String address) {
this.name = name;
this.phone = phone;
this.address = address;
}
public String getName() { return name; }
public String getPhone() { return phone; }
public String getAddress() { return address; }
}
那我们来看迭代后的下一题:https://images.ptausercontent.com/499d204b-fcef-4610-a9ca-c8fbf5e346d9.pdf
(地铁,老人,手机*2...😶)
秉持着以不变应万变的思想,我们先来大致看一下迭代后的要求与第一次哪里有不同:

第一个就是费率与之前的计算方式有改变,分了更多的类,这部分好改,我们可以定义一个接口,分别去重写三种方法,对应三种不同的计算方法:
interface calculateRate {
public abstract double calculateRate(double weight);
}
//普通类货物
class NormalRate implements calculateRate {
@Override
public double calculateRate(double weight) {
if (weight < 20) return 35;
else if (weight < 50) return 30;
else if (weight < 100) return 25;
else return 15;
}
}
//加急类货物
class ExpediteRate implements calculateRate {
@Override
public double calculateRate(double weight) {
if (weight < 20) return 60;
else if (weight < 50) return 50;
else if (weight < 100) return 40;
else return 30;
}
}
// 危险类货物
class DangerousRate implements calculateRate {
@Override
public double calculateRate(double weight) {
if (weight < 20) return 80;
else if (weight < 50) return 50;
else if (weight < 100) return 30;
else return 20;
}
}
那么第二个变化的地方就是我们的支付方式,这是题目明确要求的添加的类,这里也不难,我们只需要将对应的英文输出对应的中文的支付方式,再给他计算后的货物总费用即可:
class Payment {
private String method; // Wechat/ALiPay/Cash
private double amount;
public Payment(String method, double amount) {
this.method = method;
this.amount = amount;
}
public String getPaymentInfo() {
String methodName = switch (method) {
case "Wechat" -> "微信";
case "ALiPay" -> "支付宝";
case "Cash" -> "现金";
default -> "未知";
};
return methodName + "支付金额:" + String.format("%.1f", amount);
}
}
那么最后一个地方,也是让我思考颇多,收益匪浅的地方.段老师在群里给我们这样的提示:

那意味着我的第一次的ordersystem类就要拆成两个类了,那么为什么单独一个类来处理订单不好呢?
如果一个类的话,这个类将要处理:
- 订单元数据管理
- 客户关系维护
- 货物详细计算
- 航班容量检查
- 费用计算和折扣应用
分成两个类来处理:
Order类:
负责订单整体管理
处理订单级别的操作(如总费用计算、折扣应用、航班容量检查)
协调订单与客户、航班等外部实体的关系
OrderItem类:
专注于单个货物项的处理
计算单个货物的计费重量和运费
维护货物与费率策略的关系
这种分离让每个类只关注自己的核心职责,避免了"上帝类"的出现。
这就让代码具有了更好的封装性和内聚性:
Order不需要了解货物计费的细节,只需通过OrderItem接口获取结果
OrderItem封装了所有与单个货物相关的计算逻辑,变化不会影响Order
修改货物计费方式(如增加新的费率策略)只需修改OrderItem,不影响订单主逻辑
在实际业务中:
- 客服查询订单状态 → 只需要Order信息
- 仓库处理发货 → 主要关注OrderItem
- 财务对账 → 需要Order汇总和Item明细
分析到这,我再看平常点外卖的订单,似乎对这个生活中不起眼的细节有了更加深刻的理解..😎
那么到了最后,让我们一起来看一下代码的最终实现吧!
最后的代码啦,辛苦批阅^-^
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String custType = scanner.nextLine();
String custId = scanner.nextLine();
String custName = scanner.nextLine();
String custPhone = scanner.nextLine();
String custAddress = scanner.nextLine();
Customer customer = new Customer(custName, custPhone, custAddress, custType);
String cargoType = scanner.nextLine();
calculateRate rateStrategy;
if ("Expedite".equals(cargoType)) {
rateStrategy = new ExpediteRate();
} else if ("Dangerous".equals(cargoType)) {
rateStrategy = new DangerousRate();
} else {
rateStrategy = new NormalRate(); //默认普通货物
}
//货物数量
int cargoCount = Integer.parseInt(scanner.nextLine());
List<Cargo> cargos = new ArrayList<>();
//读取货物数据
for (int i = 0; i < cargoCount; i++) {
String id = scanner.nextLine();
String name = scanner.nextLine();
double width = Double.parseDouble(scanner.nextLine());
double length = Double.parseDouble(scanner.nextLine());
double height = Double.parseDouble(scanner.nextLine());
double weight = Double.parseDouble(scanner.nextLine());
cargos.add(new Cargo(id, name, width, length, height, weight, cargoType));
}
//读取航班信息
String flightNumber = scanner.nextLine();
String departure = scanner.nextLine();
String arrival = scanner.nextLine();
LocalDate flightDate = LocalDate.parse(scanner.nextLine());
double maxLoad = Double.parseDouble(scanner.nextLine());
Flight flight = new Flight(flightNumber, departure, arrival,
flightDate, maxLoad);
// 读取订单信息(洪七公和黄药师)
String orderNumber = scanner.nextLine();
LocalDate orderDate = LocalDate.parse(scanner.nextLine());
// 读取发件人信息(南昌大学、洪七公、18907912325)
String senderAddr = scanner.nextLine();
String senderName = scanner.nextLine();
String senderPhone = scanner.nextLine();
Customer sender = new Customer(senderName, senderPhone, senderAddr,null);
// 读取收件人信息(北京大学、黄药师、13607912546)
String receiverAddr = scanner.nextLine();
String receiverName = scanner.nextLine();
String receiverPhone = scanner.nextLine();
Customer receiver = new Customer(receiverName, receiverPhone, receiverAddr,null);
// 创建订单系统时传递 Customer 对象
Order order = new Order(
cargos,
flight,
rateStrategy,
orderNumber,
orderDate,
customer,
sender,
receiver
);
String paymentMethod = scanner.nextLine();
order.process(paymentMethod);
}
}
class Flight {
private String number;
private double maxLoad;
private double remainingLoad;
private String departure;
private String arrival;
public String getNumber() {
return number;
}
public void setNumber(String number) {
this.number = number;
}
public double getMaxLoad() {
return maxLoad;
}
public void setMaxLoad(double maxLoad) {
this.maxLoad = maxLoad;
}
public double getRemainingLoad() {
return remainingLoad;
}
public void setRemainingLoad(double remainingLoad) {
this.remainingLoad = remainingLoad;
}
public String getDeparture() {
return departure;
}
public void setDeparture(String departure) {
this.departure = departure;
}
public String getArrival() {
return arrival;
}
public void setArrival(String arrival) {
this.arrival = arrival;
}
public Flight(String number, String departure, String arrival,LocalDate date, double maxLoad) {
this.number = number;
this.maxLoad = maxLoad;
this.remainingLoad = maxLoad;
this.departure = departure;
this.arrival = arrival;
}
public boolean canCarry(double weight) {
return weight <= remainingLoad;
}
public void reduceCapacity(double weight) {
remainingLoad -= weight;
}
}
class Cargo {
private String id;
private String name;
private double width;
private double length;
private double height;
private double weight;
private String cargoType;
private calCargoWeight calculator = new calCargoWeight();
public Cargo() {}
public Cargo(String id, String name, double width, double length,double height, double weight ,String cargoType) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.width = width;
this.length = length;
this.height = height;
this.weight = weight;
this.cargoType = cargoType;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getCargoType() {
return cargoType;
}
public double getChargeableWeight() {
//calCargoWeight calculator = new calCargoWeight();
double volume = calculator.calculateVolume(length, width, height);
return calculator.getChargeableWeight(weight, volume);
}
}
class calCargoWeight {
private static final int v = 6000;
public double calculateVolume(double length, double width, double height) {
return (length * width * height) / v;
}
public double getChargeableWeight(double actualWeight, double volume) {
return Math.max(actualWeight, volume);
}
}
//普通类货物
class NormalRate implements calculateRate {
@Override
public double calculateRate(double weight) {
if (weight < 20) return 35;
else if (weight < 50) return 30;
else if (weight < 100) return 25;
else return 15;
}
}
//加急类货物
class ExpediteRate implements calculateRate {
@Override
public double calculateRate(double weight) {
if (weight < 20) return 60;
else if (weight < 50) return 50;
else if (weight < 100) return 40;
else return 30;
}
}
// 危险类货物
class DangerousRate implements calculateRate {
@Override
public double calculateRate(double weight) {
if (weight < 20) return 80;
else if (weight < 50) return 50;
else if (weight < 100) return 30;
else return 20;
}
}
interface calculateRate {
public abstract double calculateRate(double weight);
}
class OrderItem {
private Cargo cargo;
private double chargeableWeight;
private double rate;
private double payment;
public OrderItem(Cargo cargo, calculateRate rateStrategy) {
this.cargo = cargo;
this.chargeableWeight = cargo.getChargeableWeight();
this.rate = rateStrategy.calculateRate(chargeableWeight); // 关键:调用费率策略
this.payment = chargeableWeight * rate;
}
// Getter方法(供Order类调用)
public double getChargeableWeight() { return chargeableWeight; }
public double getPayment() { return payment; }
public String getCargoName() { return cargo.getName(); }
public double getRate() { return rate; }
}
class Order {
private String orderNumber;
private LocalDate orderDate;
private Customer customer;
private Customer sender;
private Customer receiver;
private Flight flight;
private List<OrderItem> orderItems; // 订单明细列表
private calculateRate rateStrategy; // 费率策略
// 构造函数
public Order(List<Cargo> cargos, Flight flight, calculateRate rateStrategy,
String orderNumber, LocalDate orderDate, Customer customer,
Customer sender, Customer receiver) {
this.orderNumber = orderNumber;
this.orderDate = orderDate;
this.customer = customer;
this.sender = sender;
this.receiver = receiver;
this.flight = flight;
this.rateStrategy = rateStrategy;
// 初始化订单明细
this.orderItems = new ArrayList<>();
for (Cargo cargo : cargos) {
orderItems.add(new OrderItem(cargo, rateStrategy));
}
}
// 处理订单核心逻辑
public void process(String paymentMethod) {
// 1. 计算总重量和原始运费
double totalWeight = 0;
double originalPayment = 0;
for (OrderItem item : orderItems) {
totalWeight += item.getChargeableWeight();
originalPayment += item.getPayment();
}
// 2. 应用客户折扣
double totalPayment = originalPayment;
if ("Corporate".equals(customer.getCustomerType())) {
totalPayment *= 0.8; // 集团用户8折
} else if ("Individual".equals(customer.getCustomerType())) {
totalPayment *= 0.9; // 个人用户9折
}
Payment payment = new Payment(paymentMethod, totalPayment);
//System.out.println(payment.getPaymentInfo());
// 3.检查航班载重
if (!flight.canCarry(totalWeight)) {
System.out.printf("The flight with flight number:%s has exceeded its load capacity and cannot carry the order.\n",
flight.getNumber());
System.exit(0);
}
// 4.更新航班剩余载重并显示结果
flight.reduceCapacity(totalWeight);
showOrderDetails(totalWeight, totalPayment,paymentMethod);
}
// 显示订单详情
private void showOrderDetails(double totalWeight, double totalPayment,String paymentMethod) {
// 打印订单基本信息
System.out.println("客户:" + customer.getName() + "(" + customer.getPhone() + ")订单信息如下:");
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------");
System.out.println("航班号:" + flight.getNumber());
System.out.println("订单号:" + orderNumber);
System.out.println("订单日期:" + orderDate);
System.out.println("发件人姓名:" + sender.getName());
System.out.println("发件人电话:" + sender.getPhone());
System.out.println("发件人地址:" + sender.getAddress());
System.out.println("收件人姓名:" + receiver.getName());
System.out.println("收件人电话:" + receiver.getPhone());
System.out.println("收件人地址:" + receiver.getAddress());
System.out.println("订单总重量(kg):" + totalWeight);
Payment payment = new Payment(paymentMethod, totalPayment);
System.out.println(payment.getPaymentInfo());
// 打印货物明细
System.out.println("\n货物明细如下:");
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------");
System.out.println("明细编号\t货物名称\t计费重量\t计费费率\t应交运费");
for (int i = 0; i < orderItems.size(); i++) {
OrderItem item = orderItems.get(i);
System.out.printf("%d\t%s\t%.1f\t%.1f\t%.1f\n",
i + 1,
item.getCargoName(),
item.getChargeableWeight(),
item.getRate(),
item.getPayment());
}
}
}
class Customer {
private String name;
private String phone;
private String address;
private String customerType;
public Customer(String name, String phone, String address, String customerType) {
this.name = name;
this.phone = phone;
this.address = address;
this.customerType = customerType;
}
public String getName() { return name; }
public String getPhone() { return phone; }
public String getAddress() { return address; }
public String getCustomerType() { return customerType; }
}
class Payment {
private String method; // Wechat/ALiPay/Cash
private double amount;
public Payment(String method, double amount) {
this.method = method;
this.amount = amount;
}
public String getPaymentInfo() {
String methodName = switch (method) {
case "Wechat" -> "微信";
case "ALiPay" -> "支付宝";
case "Cash" -> "现金";
default -> "未知";
};
return methodName + "支付金额:" + String.format("%.1f", amount);
}
}来大致的过一遍各类的职责与相互关系:
Main类:
作为程序入口,负责协调所有类的交互
创建并连接其他所有类的实例
Customer类:
被Order类持有(作为客户、发件人和收件人)
与Order类是一对多关系(一个客户可以有多个订单)
Cargo类:
被Order类通过OrderItem间接持有
与OrderItem是一对一关系
使用calCargoWeight类计算计费重量(组合关系)
Flight类:
被Order类持有
与Order类是一对多关系(一个航班可以承载多个订单)
Order类:
系统的核心类,协调多个其他类的交互
持有Customer(3个角色)、Flight、OrderItem集合和calculateRate策略
与Payment类协作处理支付
OrderItem类:
作为Order和Cargo之间的中介
使用calculateRate策略计算费用
calculateRate接口及其实现类:
策略模式实现,通过接口与OrderItem交互
三种实现:NormalRate、ExpediteRate、DangerousRate
Payment类:
被Order类使用来处理支付信息
与Order类是临时关联关系
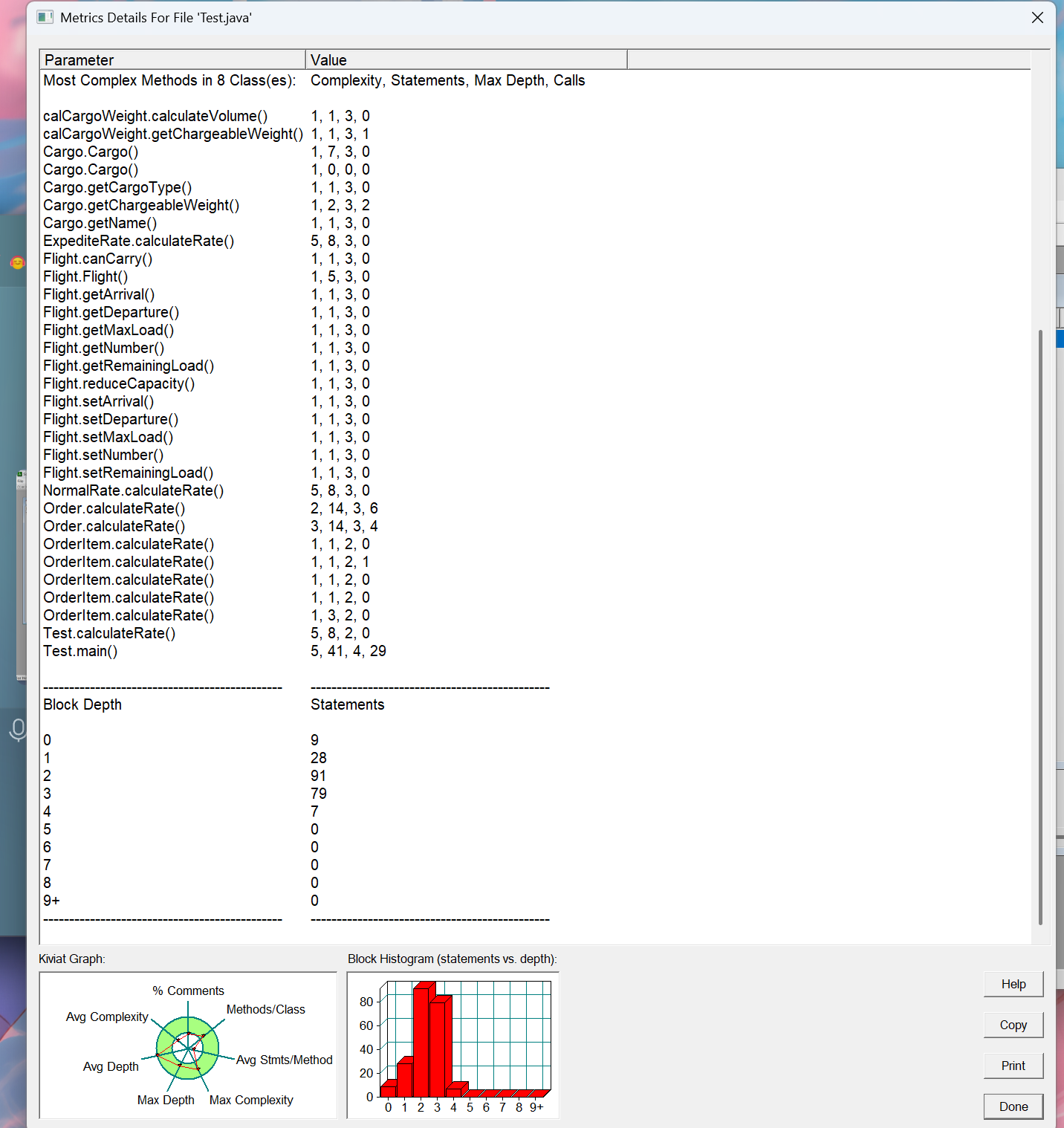
当我们分析图表,可以探索得到以下内容:
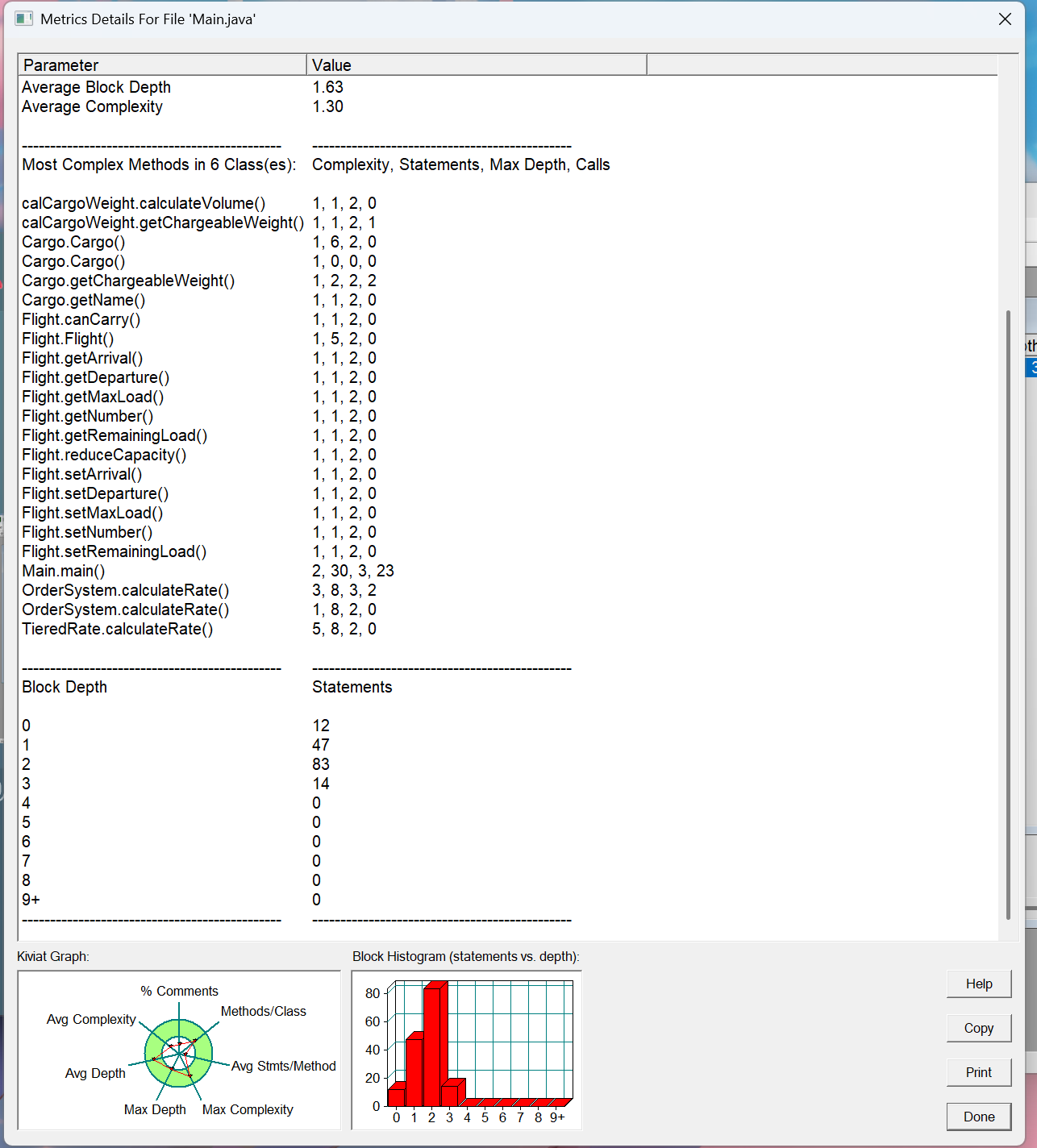
- 复杂度分布特征图中显示复杂度峰值为5级,出现在main方法和费率计算方法
这种分布表明核心业务逻辑集中在合理位置,没有出现复杂度失控
特别值得注意的是,工具类方法(如calculateVolume)保持最低复杂度1,验证了单一职责原则的贯彻 - 代码深度分析
深度3的代码块占比最大(79语句),对应OrderItem这一层级
深度4仅出现1次,显示系统避免了过度嵌套
这种"浅而宽"的分布是良好分层架构的典型特征,优于"深而窄"的调用链 - 方法质量矩阵
理想的方法应该位于"低复杂度+少语句数"区间
图中显示大多数方法落在理想区域,特别是:
工具类方法集中在左下角(复杂度1,语句3)
核心业务方法分布在中间区域(复杂度3-5,语句10-20)
仅main方法略显臃肿(41语句),但考虑到是入口方法尚可接受 - 架构健康指标
雷达图显示各项指标均衡发展,没有明显短板
特别突出的优势:
合理的抽象层次(Abstraction)
良好的封装性(Encapsulation)
可控的复杂度(Complexity) - 待改进点:
注释覆盖率(Comments)相对较低
个别方法可进一步分解
分层架构验证
深度0:架构定义层(9语句)
深度1:业务流程层(28语句)
深度2:业务实现层(91语句)
深度3:工具层(79语句) 这种金字塔结构完美匹配经典的分层架构模式,每层都有明确的职责边界。
又到了总结学习心得的时候:
在未来的代码学习和实践中,我将更加注重**架构设计**与**代码质量**的平衡。通过这次对Order与OrderItem分离设计的分析,我深刻体会到:
1. 分层思维:代码不是越少越好,而是职责越清晰越好。合理的分层能让系统更易维护、扩展和测试。
2. 度量驱动:学会借助工具(如复杂度分析、代码覆盖率)量化代码质量,而非仅凭直觉判断。
3. 设计原则落地:SOLID不是理论,而是实践指南。比如单一职责原则(SRP)直接决定了类该不该拆分。
4. 迭代优化:即使初期设计不够完美,也要通过重构逐步接近理想状态,而非追求一步到位。
未来写代码时,我会像建筑师一样思考——先规划结构,再填充细节,让每一行代码都有明确的归属和意义🥴。
---
编程如航海,有时迷雾重重,但好的设计就像灯塔,指引着代码的航向。当层层抽象拨云见日,当冗余逻辑被一一剥离,系统终会回归它最本真的模样——简洁、优雅、直指核心。
云散月明谁点缀,天容海色本澄清。好的代码亦如此,褪尽浮华后,唯留清澈逻辑,如皓月当空,海天一色🌙



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号