JavaScript入门笔记
JavaScript
@author:伏月廿柒
内部引入、外部引入
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Demo01</title>
<!-- script标签内,写JavaScript代码 -->
<script>
alert('Hello World!'); //弹窗
</script>
<!-- 外部引入 -->
<!-- 注意:script标签必须成对出现(闭合) -->
<script src="../js/Demo01.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div></div>
<script></script>
</body>
</html>
alert('你好!')
语法入门
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Demo02</title>
<script>
//JavaScript严格区分大小写
// 1.定义变量 变量类型 变量名 = 变量值
var num = 1;
//alert(num);
// 2.条件控制
if (num < 2){
alert("ture");
}else {
alert("other");
}
// 3.在浏览器控制台打印
console.log(num);
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
数据类型
变量
var num
number
js不区分小数和整数,Number
123 //整数
123.1 //浮点数
1.123e3 //科学计数法
-99 //复数
NaN //not a number
Infinity //无线大
字符串
'abc' abc"
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Demo04</title>
<script>
'use strict';
// 1、字符串正常使用单引号
// 2、转义字符
// \'
// \n
// \t
// \u4e2d Unicode字符(\u####)
// \x41 Ascll字符
console.log('\''); // ‘
console.log('a\nb');
console.log('\u4e2d'); // 中
console.log('\x41'); // A
// 3、多行字符串编写
let msg = `hello
world
你好
`;
console.log(msg);
// 4、模板字符串
let name = "小明";
let age = 3;
let msg2 = `你好,${name}`;
console.log(msg2); // 你好,小明
// 5、字符串长度
var student = "student";
console.log(student.length); // 7
// 6、字符串可变性,不可变
// 7、大小写转换
console.log(student.toUpperCase()); // STUDENT
console.log(student.toLowerCase()); // student
// 8、获取指定字符下标
console.log(student.indexOf('t')); // 1
// 9、截取字符串
console.log(student.substring(1,3)); // 第一个到第三个之间 tu
console.log(student.substring(1)); // 第一个到最后一个之间 tudent
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
布尔值
true false
逻辑运算
&& || !
比较运算符
= 赋值
== 等于(类型不一样,值一样,也会判断为true)
=== 绝对等于(类型一样,值也一样,才会判断为true)
注:1、NaN === NaN,NaN与所有的数值都不相等,包括自己
只能通过isNaN(NaN)来判断这个数是否为NaN
2、浮点数问题
console.log((1/3) === (1 - 2/3)) //false
// 尽量避免使用浮点数进行运算,存在精度问题!
// 绝对值比较
console.log(Math.abs((1/3) === (1 - 2/3)) < 0.00000001) //true
null 和 undefined
null 空
undefined 未定义
数组
js中数组的数值不需要是相同类型
var arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 'hello', null, true]
// 如果取数组下标越界了,会返回 undefined
// 数组长度
console.log(arr.length); // 8
// 数组元素可变
arr[0] = 0;
console.log(arr); // [0, 2, 3, 4, 5, 'hello', null, true]
// 数组长度可变,即arr.length可赋值
// 变长
arr.length = 10;
console.log(arr.length); // 10
console.log(arr); // [0, 2, 3, 4, 5, 'hello', null, true, empty x 4]
console.log(arr[9]); // undefined
// 变短
arr.length = 2;
console.log(arr.length); // 2
console.log(arr); // [0, 2]
// indexOf,查找元素返回下标
console.log(arr.indexOf(2)); // 1
//字符串"1"和数字1是不同的,不代表同一个元素
arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, "1", "2"];
console.log(1); // 0
console.log("1"); // 5
// slice() 截取Array的一部分,返回一个新数组
var fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Lemon", "Apple", "Mango"];
var citrus = fruits.slice(1, 3);
console.log(citrus); // ["Orange", "Lemon"]
// push(), pop()
// push() 方法向数组末尾添加新元素,并返回新长度
var fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];
fruits.push("Kiwi");
console.log(fruits); // ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango", "Kiwi"]
// pop() 方法移除数组的最后一个元素,并返回该元素
fruits.pop();
console.log(fruits); // ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"]
// push(), pop()都会改变数组长度
// unshift(), shift()
// unshift() 方法将新项添加到数组的开头,并返回新的长度
var fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];
fruits.unshift("Kiwi");
console.log(fruits); // ["Kiwi", "Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"]
// shift() 方法移除数组的第一个元素,并返回该元素。
fruits.shift();
console.log(fruits); // ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"]
// unshift(), shift()都会改变数组长度
// sort() 排序
var arr = ["B", "A", "C"];
arr.sort();
console.log(arr); // ["A", "B", "C"]
// reverse() 反转
var arr = ["A", "B", "C"];
arr.reverse();
console.log(arr); // ["C", "B", "A"]
// concat() 拼接,返回新数组
var arr = ["A", "B", "C"];
var newarr = arr.concst([1, 2, 3]);
console.log(newarr); // ["A", "B", "C",1, 2, 3]
console.log(arr); // ["A", "B", "C"]
// join 使用特定字符串连接
var arr = ["A", "B", "C"];
var str = arr.join('-');
console.log(str); // "C-B-A"
// 多维数组
var arr = [[1, 2], [3, 4], ["5", "6"]];
console.log(arr[1][1]); // 4
// fill() 填充
var arr = ["A", "B", "C"];
arr.fill(1);
console.log(arr); //[1, 1, 1]
// splice() 向/从数组添加/删除项目,并返回删除的项目
// splice()与slice()区别,splice()会改变原数组,slice()不会
var arr3 = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,"f1","f2"];
var arr4 = arr3.splice(2,3); // 删除第三个元素以后的三个数组元素(包含第三个元素)
console.log(arr4); // [3,4,5];
console.log(arr3); // [1,2,6,7,"f1","f2"]; 原始数组被改变
var arr5 = arr3.splice(2,0,"wu","leon"); // 从第2位开始删除0个元素,插入"wu","leon"
console.log(arr5); // [] 返回空数组
console.log(arr3); // [1, 2, "wu", "leon", 6, 7, "f1", "f2"]; 原始数组被改变
var arr6 = arr3.splice(2,3,"xiao","long"); // 从第2位开始删除3个元素,插入"xiao","long"
console.log(arr6); // ["wu", "leon", 6]
console.log(arr3); // [1, 2, "xiao", "long", 7, "f1", "f2"]
var arr7 = arr3.splice(2); // 从第三个元素开始删除所有的元素
console.log(arr7); // ["xiao", "long", 7, "f1", "f2"]
console.log(arr3); // [1, 2]
// find() 通过指定函数筛选数组中第一个符合的元素的值并返回
// find() 不会改变原始数组
// find() 不对空数组执行该函数
var ages = [3, 10, 17, 20, 6, 50];
function checkAdult(age) {
return age >= 18;
}
console.log(ages.find(checkAdult)); // 20
对象
若干个键值对
var person = {
name : "xiaoming",
age : 3,
tags : ['js', 'Java', 'Web', '...']
}
取对象的值
JavaScript所有的建都是字符串
person.name
>"xiaoming"
person.age
>3
person['age']
>3
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Demo05</title>
<script>
'use strict';
// var 对象名 = {
// 属性名: 属性值,
// 属性名: 属性值,
// 属性名: 属性值
// }
var person = {
name : "xiaoming",
age : 3,
email : "123456@emial.com",
score : 0
}
// 对象赋值
person.name = "xiaohong";
console.log(person.name); // xiaohong
// 使用不存在的属性
console.log(person.abc); // undefined
// delete 动态删除属性
delete person.name;
console.log(person.name); // undefined
// 动态添加(直接给新的属性添加值)
person.sex = "男";
console.log(person.sex); // 男
// in 判断一个属性值是否在这个对象中
console.log('age' in person); // true
// hasOwnProperty() 判断一个属性是否是这个对象自身拥有
console.log(person.hasOwnProperty('toString')); // false
console.log(person.hasOwnProperty('age')); // true
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
标准对象
typeof 123
"number"
typeof '123'
"string"
typeof true
"boolean"
typeof NaN
"number"
typeof []
"object"
typeof {}
"object"
typeof Math.abs
"function"
严格检查模式 strict
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Demo03</title>
<!--
'use strict';严格检查模式,预防JavaScript的随意性导致产生的一些问题
必须写在JavaScript的第一行!
局部变量建议都使用let去定义~
-->
<script>
'use strict';
//全局变量
let i=1;
//ES6 let
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
流程控制
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Demo06</title>
<script>
'use strict'
// if 判断
var age = 3;
if (age > 0 && age < 1) {
alert("kuwa~");
} else if (age < 3){
alert("huhu~");
} else {
alert("haha~");
}
// while 循环
// 有可能一次也不执行
while (age < 10) {
age += 1;
console.log(age);
}
// 一定会执行一次
do {
age += 1;
console.log(age);
} while (age < 10)
// for 循环
for (let i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
console.log(i);
}
// forEach 循环
var age = [12, 3 , 5 ,6 ,99];
age.forEach(function (value) {
console.log(value);
})
// for…in 循环(数组,对象)
var num;
for(num in age) {
console.log(age[num]);
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
Map和Set
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Demo07</title>
<script>
'use strict';
// ES6 Map 键值对结构,方便快速查找
// 学生成绩,学生名字
// var names = ["tom", "jack", "lisa"];
// var scores = [100, 90, 80];
var map = new Map([["tom", 100], ["jack", 90], ["lisa", 80]]);
var name = map.get("tom"); // 通过key获得value
console.log(name); // 100
map.set('admin', 60); // 添加或修改
console.log(map); // [["tom", 100], ["jack", 90], ["lisa", 80], ["admin", 60]]
map.delete('tom'); // 删除
console.log(map); // [["jack", 90], ["lisa", 80], ["admin", 60]]
// ES6 Set 无序不重复的集合
var set = new Set([3, 1, 1, 1, 2]);
console.log(set); // [3, 1, 2] set可以去重
set.add(4); // 添加
console.log(set); // [3, 1, 2, 4]
set.delete(2); // 删除
console.log(set); // [3, 1, 4]
console.log(set.has(3)); // true 判断是否包含某个元素
// iterator
// 遍历数组
var x;
var arr = [3, 4, 5];
for (x in arr) {
console.log(x); // for…in 返回下标
}
for (x of arr) {
console.log(x); // for…of 返回value
}
// 遍历map
for (x of map) {
console.log(x); // for…of 返回value
}
// 遍历set
for (x of set) {
console.log(x); // for…of 返回value
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
函数
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Demo08</title>
<script>
// 定义函数
// 方法一
function abs(x) {
if (x >= 0) {
return x;
}else {
return -x;
}
}
console.log(abs(-10)); // 10
// 方法二
// function(x){} 匿名函数
// 可以把匿名函数的值赋给变量(eg. abs)通过变量(eg. abs)调用
var abs = function(x) {
if (x >= 0) {
return x;
}else {
return -x;
}
}
// 调用函数
var a = abs(-10);
console.log(a); // 10
console.log(abs()); // NaN
// 手动抛出异常
function checkNum(x) {
if (typeof x!= 'number') {
throw 'Not a Number';
} else {
return x;
}
}
console.log(checkNum("a")); // Not a Number
//抛出异常后,后面函数不再执行,其他script标签的函数可继续执行
function isContinue() {
console.log("continue");
}
isContinue();
</script>
<script>
// arguments 代表传递进来的所有参数,是一个数组
var numArgu = function(x) {
console.log(x);
for (var i = 0; i < arguments.length; i++) {
console.log(arguments[i]);
}
}
numArgu(123, 12, 56, 78, 98, 1); // 123 12 56 78 98 1
// ...rest 代表除了已定义的参数(eg. a,b)之外的所有参数,是一个数组
// ES6新特性 注:...rest只能写在最后面
function aaa(a,b,...rest) {
console.log("a=>" + a);
console.log("b=>" + b);
console.log("rest=>" + rest);
}
aaa(1, 3, 6, 99, 895, 0); // a=>1 b=>3 rest=>[6,99,895,0]
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
变量的作用域
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Demo09</title>
<script>
// var定义的变量有作用域限制
function test1() {
var x = 1;
x = x + 1;
}
// 在函数体内定义的变量,则在函数体外不可以使用 (闭包可以实现函数体内变量外用)
// console.log(x = x + 2); // Uncaught ReferenceError: x is not defined
// 两个函数体内如果使用了相同的变量名,并不冲突
function test2() {
var x = 1;
x = x + 1;
}
// 内部函数可以调用外部函数的变量,反之不行
function test3() {
var x = 1;
function test4() {
var y = x + 1;
console.log(y);
}
test4(); // 2
var z = y + 1;
console.log(z);
}
// test3(); // Uncaught ReferenceError: y is not defined
// 内部函数和外部函数如果使用了相同的变量名,并不冲突
// 运行时,内部函数由内向外查找并调用变量
function test5() {
var x = 1;
function test6() {
var x = 'A';
console.log('inner=' + x);
}
console.log('outer=' + x); // outer=1
test6(); // inner=A
}
test5();
// 全局变量
var abc = '全局变量';
function test7() {
console.log(abc); // 全局变量
}
test7();
// 所有全局变量都自动绑定在window对象下
console.log(window.abc); // 全局变量
// console.lg()、alert() 等函数也属于window对象下
window.console.log(window.abc);
var old_console = window.console.log;
old_console(123); // 123
// 可以使console.log()等函数失效
window.console.log = function() {
}
window.console.log(123); // (空)
// 恢复
window.console.log = old_console;
window.console.log(456); // 456
// let 局部作用域 ES6
function test8() {
for (var j = 0; j < 100; j++) {
console.log(j); // 1~100
}
console.log(j+1); // 101 var定义的变量在for循环外依然可以调用
for (let i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
console.log(i); // 1~100
}
// console.log(i+1); // Uncaught ReferenceError: i is not defined
}
test8();
// const 常量 ES6
const PI = '3.14'; // 只读变量不可更改
console.log(PI);
// PI = '123'; // Uncaught TypeError: Assignment to constant variable.
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
方法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Demo10</title>
<script>
function getAge() {
var now = new Date().getFullYear();
return now - this.birth;
}
// 方法 (就是把函数放在对象里面)
var student = {
name : 'xiaoming',
birth : 2020,
// 定义方法
age : function() {
var now = new Date().getFullYear();
// this 表示当前对象的一个引用
return now - this.birth;
},
age2 : getAge,
}
console.log("age=" + student.age()); // age=2
console.log("age2=" + student.age2()); // age2=2 this指向调用它的那个对象
console.log("getAge=" + getAge()); // getAge=NaN this无法指向
// apply()
var age3 = getAge.apply(student,[]); // this指向了student,参数为空
console.log("age3=" + age3); // age3=2
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
Date 日期对象
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Demo11</title>
<script>
var now = new Date();
console.log(now); // Thu Mar 10 2022 20:23:26 GMT+0800 (中国标准时间)
// 获取基础时间信息
now.getFullYear(); // 年
now.getMonth(); // 月 0~11 代表月
now.getDate(); // 日
now.getDay(); // 星期
now.getHours(); // 时
now.getMinutes(); // 分
now.getSeconds(); // 秒
now.getTime(); // 时间戳 全世界统一 1970.1.1 00:00:00 至今的毫秒数
// 时间戳转换
console.log(new Date(1578106175991)); // Sat Jan 04 2020 10:49:35 GMT+0800 (中国标准时间)
// 获取本地时间
// 注:now.toLocaleString() 是方法不是属性
console.log(now.toLocaleString()); // 2022/3/10 20:55:01
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
JSON对象
- JSON(JavaScript Object Notation) 是一种轻量级的数据交换格式
- 简洁和清晰的层次结构使得 JSON 成为理想的数据交换语言
- 易于人阅读和编写,同时也易于机器解析和生成,并有效地提升网络传输效率。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Demo12</title>
<script>
var user = {
name : "xiaoming",
age : 3,
sex : "男"
}
// 对象转化JSON字符串
var jsonUser = JSON.stringify(user);
console.log(jsonUser); // {"name":"xiaoming","age":3,"sex":"男"}
// JSON字符串转化对象
var obj = JSON.parse('{"name":"xiaoming","age":3,"sex":"男"}');
console.log(obj); // {name : "xiaoming", age : 3, sex : "男"}
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
面向对象编程
原型继承
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Demo13</title>
<script>
var student = {
name : "name",
age : 3,
run : function() {
console.log(this.name + " run……")
}
}
var xiaoming = {
name : "xiaoming"
}
// student是原型,将xiaoming指向了student
xiaoming.__proto__ = student;
xiaoming.run(); // xiaoming run……
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
class继承
- ES6引入
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Demo14</title>
<script>
function Student(name) {
this.name = name;
}
// 给Student新增一个方法(ES6之前)
// prototype 原型
Student.prototype.hello = function() {
console.log(this.name + " hello");
};
var abc = new Student("abc");
abc.hello(); // abc hello
// 给User新增一个方法(ES6之后)
class User {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
}
hello() {
console.log(this.name + " hello");
}
}
var xiaoming = new User("xiaoming");
var xiaohong = new User("xiaohong");
xiaohong.hello(); // xiaohong hello
// 继承
class newUser extends User {
constructor(name,grade) {
super(name); // super() 继承父类属性
this.grade = grade; // 定义子类自身属性
}
myGrade() {
console.log(this.name + " " + this.grade + "年级");
}
}
var xiaoli = new newUser("xiaoli",3);
xiaoli.myGrade(); // xiaoli 3年级
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
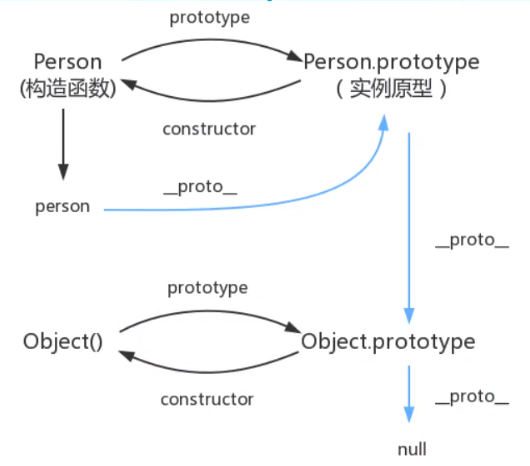
原型链
- 每个对象都可以有一个原型_proto_,这个原型还可以有它自己的原型,以此类推,形成一个原型链
- __proto__ 是原型链查询中实际用到的,它总是指向 prototype
- prototype 是函数所独有的,在定义构造函数时自动创建,它总是被 __proto__ 所指
操作BOM对象 (重点)
BOM:浏览器对象模型
- IE 6~11
- Chrome
- Safari
- FireFox
window
代表浏览器窗口
window.alert(1)
undefined
window.innerHeight
258
window.innerWidth
919
window.outerHeight
994
window.outerWidth
919
Navigator
封装了浏览器的信息
// 返回浏览器的名称
navigator.appName
'Netscape'
// 返回浏览器的平台和版本信息
navigator.appVersion
'5.0 (Linux; Android 6.0; Nexus 5 Build/MRA58N) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/100.0.4884.0 Mobile Safari/537.36 Edg/100.0.1181.0'
// 返回由客户机发送服务器的 user-agent 头部的值
navigator.userAgent
'Mozilla/5.0 (Linux; Android 6.0; Nexus 5 Build/MRA58N) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/100.0.4884.0 Mobile Safari/537.36 Edg/100.0.1181.0'
// 返回运行浏览器的操作系统平台
navigator.platform
'Linux x86_64'
注:navigator可以被人为修改,所以一般不使用这些属性来判断和编码
screen
屏幕尺寸
screen.width
1683
screen.height
946
location (重点)
代表当前页面的URL信息
location
Location {
// 设置或返回主机名和当前 URL 的端口号
host: "www.bilibili.com"
// 设置或返回完整的 URL
href: "https://www.bilibili.com/"
// 设置或返回当前 URL 的协议
protocol: "https:"
// 刷新网页 用法:location.reload()
reload: ƒ reload()
}
//设置新的地址
location.assign('https://www.baidu.com')
document
当前的页面,HTML DOM文档树
document.title
'哔哩哔哩 (゜-゜)つロ 干杯~-bilibili'
document.title='abc'
'abc'
获取具体的文档树节点
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Demo15</title>
</head>
<body>
<dl id="app">
<dt>Java</dt>
<dd>JavaSE</dd>
<dd>JavaEE</dd>
</dl>
<script>
var dl = document.getElementById('app');
console.log(dl);
</script>
</body>
</html>
获取cookie
document.cookie
'MicrosoftApplicationsTelemetryDeviceId=50064098-38d1-40ed-8587-16d34751e561; MSFPC=GUID=3f4b08025afe4c8f87c5c828a19d1225&HASH=3f4b&LV=202111&V=4&LU=1637417714744'
服务器端可以设置cookie:httpOnly 来防止cookie被劫持
history
浏览器的历史记录(不建议使用)
history.back() // 后退
history.forward() // 前进
操作DOM对象(重点)
浏览器网页就是一个DOM树形结构!
- 更新:更新DOM节点
- 遍历:通过遍历得到DOM节点
- 删除:删除DOM节点
- 增加:新增DOM节点
要操作一个DOM节点,就必须先获得这个DOM节点
获得DOM节点
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Demo16</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="father">
<h1>标题一</h1>
<p id="p1">p1</p>
<p class="p2">p2</p>
</div>
<script>
// 获取标签选择器
var h1 = document.getElementsByTagName('h1');
// 获取Id选择器
var p1 = document.getElementById('p1');
// 获取class选择器
var p2 = document.getElementsByClassName('p2');
var father = document.getElementById('father');
//获取父节点下全部子节点
var childrens = father.children;
// father.firstChild
// father.lastChild
</script>
</body>
</html>
更新DOM节点
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Demo17</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="id_1">abc</div>
<script>
var id_1 = document.getElementById('id_1');
// 操作文本
// innerText 修改节点文本
id_1.innerText = 'hello';
// innerHTML 修改节点文本,并解析文本中所带标签
id_1.innerHTML = '<strong>hello</strong>'
// 操作CSS
// style.xxx 修改节点style
id_1.style.color = 'red';
id_1.style.fontSize = '20px'; // 驼峰
id_1.style.padding = '10px';
</script>
</body>
</html>
删除DOM节点
需要先找到父元素,才能删除自己
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Demo18</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="father">
<h1 id="h1">标题一</h1>
<p id="p1">p1</p>
<p class="p2">p2</p>
<p id="p3">p3</p>
<p id="p4">p4</p>
</div>
<script>
// 通过Id选择器删除节点
var father = document.getElementById('father');
var p1 = document.getElementById('p1');
father.removeChild(p1); // 移除p1
// 通过父元素数组删除节点
// 依次删除father下元素
// 因为children数组是动态变化的,所以下标始终为0
father.removeChild(father.children[0]); // 移除h1
father.removeChild(father.children[0]); // 移除p2
father.removeChild(father.children[0]); // 移除p3
</script>
</body>
</html>
创建和插入DOM节点
如果一个DOM节点是空的,可以通过InnerHTML插入新元素,但如果已经存在元素,则不能使用innerHTML,否则将覆盖节点原内容
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Demo19</title>
</head>
<body>
<p id="js">JavaScript</p>
<div id="list">
<p id="se">JavaSE</p>
<p id="ee">JavaEE</p>
<p id="me">JavaME</p>
</div>
<script>
var js = document.getElementById('js');
var list = document.getElementById('list');
var se = document.getElementById('se');
var ee = document.getElementById('ee');
var me = document.getElementById('me');
// 追加
list.appendChild(js); // 将js插入到list的最后
// 创建新节点
var newP = document.createElement('p'); // 创建一个p标签
newP.id = 'newP';
newP.innerText = 'Hello,World!';
list.appendChild(newP);
// 创建标签节点
var myScript = document.createElement('script');
// 通过setAttribute可以设置任意的值
myScript.setAttribute('type', 'text/javascript');
list.appendChild(myScript);
// 插入节点
// insertBefore(newNode, targetNode) 头插
list.insertBefore(ee,se);
// 替换节点
// replaceChild(newNode, oldNode) 可以新建节点替换,也可以用已有节点替换
var css = document.createElement('p');
css.id = 'css';
css.innerText = 'CSS';
list.replaceChild(css,se);
</script>
</body>
</html>
操作表单(验证)
表单 form
- 文本框 text
- 下拉框 select
- 单选框 radio
- 多选框 checkbox
- 隐藏域 hidden
- 密码框 password
- ……
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Demo20</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="post">
<p>
<span>用户名:</span><input type="text" id="username">
</p>
<p>
<span>性别:</span>
<input type="radio" value="boy" name="sex" id="boy">男
<input type="radio" value="girl" name="sex" id="girl">女
<!-- 单选框、多选框的值不可变 -->
</p>
<p>
<input type="button" name="sure" id="sure" value="确定" onclick="print()">
</p>
</form>
<script>
var input_text = document.getElementById('username');
var boy_radio = document.getElementById('boy');
var girl_radio = document.getElementById('girl');
// 获取文本框的值
input_text.value;
// 修改文本框的值
input_text.value = '123';
// 获取单选框是否被选中
boy_radio.checked;
// 修改单选框的所选项
boy_radio.checked = true;
</script>
<script>
function print() {
console.log(input_text.value); // 123
console.log(boy_radio.checked); // true
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
提交表单
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Demo21</title>
<!-- MD5工具类 -->
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/blueimp-md5/2.10.0/js/md5.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Demo21</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="post">
<p>
<span>用户名:</span><input type="text" id="username" name="username">
</p>
<p>
<span>密码:</span><input type="password" id="password" name="password">
</p>
<p>
<span>性别:</span>
<input type="radio" value="boy" name="sex" id="boy">男
<input type="radio" value="girl" name="sex" id="girl">女
</p>
<p>
<!-- 绑定事件 onclick 被点击 -->
<input type="submit" name="sure" id="sure" value="确定" onclick="print()">
</p>
</form>
<script>
var username = document.getElementById('username');
var password = document.getElementById('password');
var boy_radio = document.getElementById('boy');
var girl_radio = document.getElementById('girl');
</script>
<script>
function print() {
console.log(username.value);
console.log(password.value);
//MD5 算法
password.value = md5(password.value);
console.log(password.value);
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
jQuery
jQuery库,包含大量的JavaScript函数
jQuery导入及选择器
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Demo22</title>
<!-- cdn导入jQuery -->
<script src="http://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/jquery/1.8.0/jquery.min.js"></script>
<!-- 文件导入jQuery -->
<script src="../js/jquery-3.6.0.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<p></p>
<a href="" id="id-jquery">点击</a>
<div class="class-jquery"></div>
<script>
// 选择器同css选择器
// 写法:$(selector).action()
// 标签选择器
$('p').click(function() {
alert("Hello,jQuery!");
})
// Id选择器
$('#id-jquery').click(function() {
alert("Hello,jQuery!");
})
// class 类选择器
$('.class-jquery').click(function() {
alert("Hello,jQuery!");
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
jQuery事件
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Demo23</title>
<script src="../js/jquery-3.6.0.js"></script>
<style>
#divMove {
width: 500px;
height: 500px;
border: 1px solid black;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<a href="" id="id-jquery">点击</a>
<script>
// 鼠标事件
$('#id-jquery').mousedown(); // 按下左键
$('#id-jquery').mouseenter(); // 光标进入、穿过标签
$('#id-jquery').mouseleave(); // 光标离开标签
$('#id-jquery').mousemove(); // 光标移动标签
$('#id-jquery').mouseout(); // 光标离开标签
$('#id-jquery').mouseover(); // 光标进入、穿过标签
$('#id-jquery').mouseup(); // 释放、松开左键
// mouseleave 仅在指针离开被选元素时被触发
// mouseout 在指针离开被选元素或进入该元素的任意子元素时均会被触发
// mouseenter 仅在指针进入被选元素时被触发
// mouseover 在指针进入被选元素或进入该元素的任意子元素时也会被触发
</script>
<!-- 获取鼠标当前坐标 -->
mouse : <span id="mouseMove"></span>
<div id="divMove">
在此区域移动
</div>
<script>
// 当网页加载完毕之后,响应事件
// $(document).ready(function () { }) 简写如下
$(function () {
$('#divMove').mousemove(function (e) {
$('#mouseMove').text('x:' + e.pageX + ' y:' + e.pageY);
})
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
jQuery操作DOM元素
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Demo24</title>
<script src="../js/jquery-3.6.0.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<ul id="test-ul" style="font-size: 50px;">
<li class="js">JavaScript</li>
<li name="py">Python</li>
<li class="java">Java</li>
</ul>
<script>
// 节点文本操作
// 获取值
var js = $('#test-ul li[name=py]').text(); // 等同innerText
var py = $('#test-ul').html(); // 等同innerHTML
console.log(js); // Python
console.log(py); // <li class="js">JavaScript</li> <li name="py">Python</li>
// 设置值
$('#test-ul li[name=py]').text('PY');
$('#test-ul li[class=js]').html('<strong>JS</strong>');
// css操作
// 设置单个属性
$('#test-ul li[class=js]').css("color","blue");
// 设置多个属性
$('#test-ul li[name=py]').css({"color":"red", "fontSize":"30px"});
// 元素的显示和隐藏 ( 本质 display:none )
$('#test-ul li[class=java]').hide(); // 状态:隐藏
$('#test-ul li[class=java]').show(); // 状态:显示
// 切换显示/隐藏
$('#test-ul li[class=java]').toggle(); // 状态:隐藏
</script>
</body>
</html>



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号