2024 Summer_Camp 做题总结 上
P1020 [NOIP1999 提高组] 导弹拦截
思路
设 \(dp_i\) 表示前 \(i\) 个数,最长不降子序列的长度,我们知道枚举求法的时间复杂度为 \(O(n^2)\),这是不能接受的,所以考虑二分。
设 \(f_i\) 表示所有最长不降子序列长度为 \(i\)中,它的结尾中最大的数。
证明:\(f_i < f_{i - 1}\)。
若有一个长度为 \(i - 1\) 的最长不降子序列,它的结尾最大,如果它能转移,那么它后面的数一定小于等于当前这个最大值,即小于 \(f_{i - 1}\),如果它不能转移,那么是由其他小于最大值结尾的去转移,必定它后面的数小于这个序列结尾,小于 \(f_{i - 1}\),所以无论如何,\(f_i < f_{i - 1}\)。
所以,\(f\) 数组是单调不增的,可以二分,对于一个需要转移的 \(dp\) 数组,二分最后一个大于当前高度的 \(f_i\),此时 \(i\) 为最长的满足要求的最长不降自序列,更新 \(dp\) 和 \(f\)。
对于第二个问题,拦截所有导弹,最少的装置数,我们考虑枚举每一个导弹,记录 \(g_i\) 装置拦截的最后一个导弹的高度,如果此时有一个导弹高度为 \(h_i\) 那么用最小的能满足拦截需求的 \(g_i\) 拦截,显然 \(g_i\) 是单调不减的,也可用二分快速查找 \(g_i\) 更新答案。
代码
点击查看代码
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
inline int read(){register int x = 0, f = 1;register char c = getchar();while (c < '0' || c > '9'){if (c == '-') f = -1;c = getchar();}while (c >= '0' && c <= '9'){x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (c ^ 48);c = getchar();}return x * f;}
inline void write(int x){if (x < 0) putchar('-'), x = -x;if (x > 9) write(x / 10);putchar(x % 10 + '0');}
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int n, x, ans1, ans2;
int a[N], dp[N], f[N], g[N];
int main(){
while(cin >> x) a[++n] = x;
f[0] = 0x7fffffff;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
int l = 1, r = i - 1;
while (l <= r){
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if (f[mid] >= a[i]) l = mid + 1;
else r = mid - 1;
}
dp[i] = max(1, max(dp[i], r + 1));
f[dp[i]] = max(f[dp[i]], a[i]);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) ans1 = max(ans1, dp[i]);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
if (g[ans2] < a[i]){
g[++ans2] = a[i];
continue;
}
int l = 1, r = ans2;
while (l <= r){
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if (g[mid] >= a[i]) r = mid - 1;
else l = mid + 1;
}
g[l] = a[i];
}
cout << ans1 << '\n' << ans2 << endl;
return 0;
}
P1091 [NOIP2004 提高组] 合唱队形
思路
简单 \(dp\),左右两边各做一次最长上升子序列,枚举同学,统计答案。
代码
点击查看代码
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
inline int read(){register int x = 0, f = 1;register char c = getchar();while (c < '0' || c > '9'){if (c == '-') f = -1;c = getchar();}while (c >= '0' && c <= '9'){x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (c ^ 48);c = getchar();}return x * f;}
inline void write(int x){if (x < 0) putchar('-'), x = -x;if (x > 9) write(x / 10);putchar(x % 10 + '0');}
const int N = 110;
int n, ans = 0x7fffffff;
int a[N], dp1[N], dp2[N];
int main(){
n = read();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) a[i] = read();
dp1[1] = 1, dp2[n] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++){
for (int j = 1; j < i; j++){
if (a[i] > a[j]) dp1[i] = max(1, max(dp1[i], dp1[j] + 1));
else dp1[i] = max(1, dp1[i]);
}
}
for (int i = n - 1; i; i--){
for (int j = n; j > i; j--){
if (a[i] > a[j]) dp2[i] = max(1, max(dp2[i], dp2[j] + 1));
else dp2[i] = max(1, dp2[i]);
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) ans = min(ans, n - dp1[i] - dp2[i] + 1);
cout << ans;
return 0;
}
P1095 [NOIP2007 普及组] 守望者的逃离
思路
简单 \(dp\),设 \(dp_{i,j}\) 表示时间为 \(i\),魔法值为 \(j\) 时跑得最远的距离,由于数组开不下,所以使用滚动数组。
代码
点击查看代码
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
inline int read(){register int x = 0, f = 1;register char c = getchar();while (c < '0' || c > '9'){if (c == '-') f = -1;c = getchar();}while (c >= '0' && c <= '9'){x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (c ^ 48);c = getchar();}return x * f;}
inline void write(int x){if (x < 0) putchar('-'), x = -x;if (x > 9) write(x / 10);putchar(x % 10 + '0');}
const int M = 1e3 + 10;
int n, s, t, p, ans;
int dp[2][M];
int main(){
n = read(), s = read(), t = read();
for (int i = 1; i <= t; i++){
for (int j = 0; j <= n; j++){
dp[p][j] = max(dp[p][j], dp[p ^ 1][j] + 17);
if (j + 10 <= n) dp[p][j] = max(dp[p][j], dp[p ^ 1][j + 10] + 60);
if (j - 4 >= 0) dp[p][j] = max(dp[p][j], dp[p ^ 1][j - 4]);
if (dp[p][j] >= s){
cout << "Yes\n" << i;
return 0;
}
}
p ^= 1;
}
cout << "No\n";
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) ans = max(ans, dp[p ^ 1][i]);
cout << ans;
return 0;
}
P1868 饥饿的奶牛
思路
有点难度的 \(dp\),设 \(dp_i\) 表示前 \(i\) 个区间,组成的最大长度。
转移方程式为 \(dp_i = \max(dp_i, dp_{i - 1}, dp_j + r - l + 1)\),解释:前 \(i\) 个区间组成的最大长度,要么本身,要么前 \(i - 1\) 个区间组成的最大长度,要么是区间右端小于当前区间左端的右端最大的那个区间加上当前区间的长度,这个区间可以通过按照右端点排序再二分找到。
代码
点击查看代码
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
inline int read(){register int x = 0, f = 1;register char c = getchar();while (c < '0' || c > '9'){if (c == '-') f = -1;c = getchar();}while (c >= '0' && c <= '9'){x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (c ^ 48);c = getchar();}return x * f;}
inline void write(int x){if (x < 0) putchar('-'), x = -x;if (x > 9) write(x / 10);putchar(x % 10 + '0');}
const int N = 1.5e5 + 10;
int n, ans;
int dp[N];
struct node{
int l, r;
}a[N];
bool cmp(const node &a, const node &b){
if (a.r != b.r) return a.r < b.r;
return a.l < b.l;
}
int main(){
n = read();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) a[i] = (node){read(), read()};
sort(a + 1, a + n + 1, cmp);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) dp[i] = a[i].r - a[i].l + 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++){
int l = 1, r = i - 1;
while (l <= r){
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if (a[mid].r >= a[i].l) r = mid - 1;
else l = mid + 1;
}
dp[i] = max(dp[i], max(dp[i - 1], dp[r] + a[i].r - a[i].l + 1));
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) ans = max(ans, dp[i]);
cout << ans;
return 0;
}
P2439 [SDOI2005] 阶梯教室设备利用
思路
双倍经验,同上,注意区间长度定义和区间合并边界条件。
代码
点击查看代码
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
inline int read(){register int x = 0, f = 1;register char c = getchar();while (c < '0' || c > '9'){if (c == '-') f = -1;c = getchar();}while (c >= '0' && c <= '9'){x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (c ^ 48);c = getchar();}return x * f;}
inline void write(int x){if (x < 0) putchar('-'), x = -x;if (x > 9) write(x / 10);putchar(x % 10 + '0');}
const int N = 1e4 + 10;
int n, ans;
int dp[N];
struct node{
int l, r;
}a[N];
bool cmp(const node &a, const node &b){
if (a.r != b.r) return a.r < b.r;
return a.l < b.l;
}
int main(){
n = read();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) a[i] = (node){read(), read()};
sort(a + 1, a + n + 1, cmp);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) dp[i] = a[i].r - a[i].l;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++){
int l = 1, r = i - 1;
while (l <= r){
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if (a[mid].r > a[i].l) r = mid - 1;
else l = mid + 1;
}
dp[i] = max(dp[i], max(dp[i - 1], dp[r] + a[i].r - a[i].l));
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) ans = max(ans, dp[i]);
cout << ans;
return 0;
}
P1896 [SCOI2005] 互不侵犯
思路
经典状压 \(dp\),设 \(dp_{i,j,k}\) 表示第 \(i\) 行,状态为 \(j\),总共放了 \(k\) 个国王。
预处理合法状态,枚举每个状态和上一行的状态,判断是否冲突,如果不冲突就转移。
代码
点击查看代码
#include<iostream>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
inline int read(){register int x = 0, f = 1;register char c = getchar();while (c < '0' || c > '9'){if (c == '-') f = -1;c = getchar();}while (c >= '0' && c <= '9'){x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (c ^ 48);c = getchar();}return x * f;}
inline void write(int x){if (x < 0) putchar('-'), x = -x;if (x > 9) write(x / 10);putchar(x % 10 + '0');}
const int N = 10, M = (1 << N) + 10, K = N * N;
int n, k, m, st[M], king[M], ans;
int dp[N][M][K];
signed main(){
n = read(), k = read();
for (int i = 0; i < (1 << n); i++){
if (i & (i << 1)) continue;
int sum = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++){
if (i & (1 << j)) sum++;
}
st[++m] = i;
king[m] = sum;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) dp[1][i][king[i]] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++){
for (int j = 0; j <= k; j++){
for (int p = 1; p <= m; p++){
for (int q = 1; q <= m; q++){
if ((st[p] << 1) & st[q] || st[p] & st[q] || st[p] & (st[q] << 1)) continue;
if (j - king[q] >= 0) dp[i][p][j] += dp[i - 1][q][j - king[p]];
}
}
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) ans += dp[n][i][k];
cout << ans;
return 0;
}
P1879 [USACO06NOV] Corn Fields G
思路
和上面一题十分类似,都是状压 \(dp\),但是判断不同,共有两种判断,第一:枚举当前这一行的状态要与本行要求相符,第二:上下左右无连续的 \(1\)。
代码
点击查看代码
#include<iostream>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
inline int read(){register int x = 0, f = 1;register char c = getchar();while (c < '0' || c > '9'){if (c == '-') f = -1;c = getchar();}while (c >= '0' && c <= '9'){x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (c ^ 48);c = getchar();}return x * f;}
inline void write(int x){if (x < 0) putchar('-'), x = -x;if (x > 9) write(x / 10);putchar(x % 10 + '0');}
const int N = 15, M = (1 << N) + 10, mod = 100000000;
int n, m, k, ans;
int cms[N], dp[N][M], st[N];
signed main(){
n = read(), m = read();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++){
bool x = read();
cms[i] = (cms[i] << 1) + x;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < (1 << m); i++){
if (i & (i << 1)) continue;
st[++k] = i;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++){
if ((cms[1] | st[i]) != cms[1]) continue;
dp[1][i] = 1;
}
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++){
for (int p = 1; p <= k; p++){
for (int q = 1; q <= k; q++){
if ((cms[i] | st[q]) != cms[i] || (cms[i - 1] | st[p]) != cms[i - 1] || st[p] & st[q]) continue;
dp[i][q] = (dp[i][q] + dp[i - 1][p]) % mod;
}
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) ans = (ans + dp[n][i]) % mod;
cout << ans;
return 0;
}
P2704 [NOI2001] 炮兵阵地
思路
经典的状压 \(dp\),但要考虑两行的状态,不然考虑不了上上行与这行的是否冲突。
代码
点击查看代码
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
inline int read(){register int x = 0, f = 1;register char c = getchar();while (c < '0' || c > '9'){if (c == '-') f = -1;c = getchar();}while (c >= '0' && c <= '9'){x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (c ^ 48);c = getchar();}return x * f;}
inline void write(int x){if (x < 0) putchar('-'), x = -x;if (x > 9) write(x / 10);putchar(x % 10 + '0');}
const int N = 110;
int n, m, k, ans;
int cms[N], st[N], bomb[N], dp[N][N][N];
int main(){
n = read(), m = read();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++){
char c;
cin >> c;
if (c == 'P') cms[i] = (cms[i] << 1) + 1;
else cms[i] = (cms[i] << 1);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < (1 << m); i++){
if ((i << 1) & i || (i << 2) & i) continue;
st[++k] = i;
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) if (i & (1 << j)) bomb[k]++;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++){
for (int j = 1; j <= k; j++){
if ((cms[1] | st[i]) != cms[1] || (cms[2] | st[j]) != cms[2]) continue;
dp[1][i][j] = bomb[i];
}
}
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++){
for (int p = 1; p <= k; p++){
for (int q = 1; q <= k; q++){
for (int l = 1; l <= k; l++){
if (st[p] & st[q] || st[q] & st[l] || st[p] & st[l] || (cms[i] | st[p]) != cms[i] || (cms[i - 1] | st[q]) != cms[i - 1] || (cms[i - 2] | st[l]) != cms[i - 2]) continue;
dp[i][p][q] = max(dp[i][p][q], dp[i - 1][q][l] + bomb[p]);
}
}
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++){
for (int j = 1; j <= k; j++){
if (st[i] & st[j]) continue;
ans = max(ans, dp[n][i][j]);
}
}
cout << ans;
return 0;
}
P2986 [USACO10MAR] Great Cow Gathering G
思路
简单换根 \(dp\),秒了。
代码
点击查看代码
#include<iostream>
#include<climits>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
inline int read(){register int x = 0, f = 1;register char c = getchar();while (c < '0' || c > '9'){if (c == '-') f = -1;c = getchar();}while (c >= '0' && c <= '9'){x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (c ^ 48);c = getchar();}return x * f;}
inline void write(int x){if (x < 0) putchar('-'), x = -x;if (x > 9) write(x / 10);putchar(x % 10 + '0');}
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int n, ans = LONG_LONG_MAX;
int sz[N], dp[N];
struct edge{
int v, nxt, w;
}e[N << 1];
int head[N], cnt;
void add(int u, int v, int w){
e[++cnt] = (edge){v, head[u], w};
head[u] = cnt;
}
void dfs(int u, int fa){
for (int i = head[u]; i; i = e[i].nxt){
int v = e[i].v;
if (v == fa) continue;
dfs(v, u);
sz[u] += sz[v];
dp[1] += sz[v] * e[i].w;
}
}
void f(int u, int fa){
for (int i = head[u]; i; i = e[i].nxt){
int v = e[i].v;
if (v == fa) continue;
dp[v] = dp[u] - sz[v] * e[i].w + (sz[1] - sz[v]) * e[i].w;
f(v, u);
}
}
signed main(){
n = read();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) sz[i] = read();
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++){
int u = read(), v = read(), w = read();
add(u, v, w), add(v, u, w);
}
dfs(1, 0);
f(1, 0);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) ans = min(ans, dp[i]);
cout << ans;
return 0;
}
[ARC125E] Snack
思路
看到这道题,很容易想到最大流,建边也很好想,如下图:
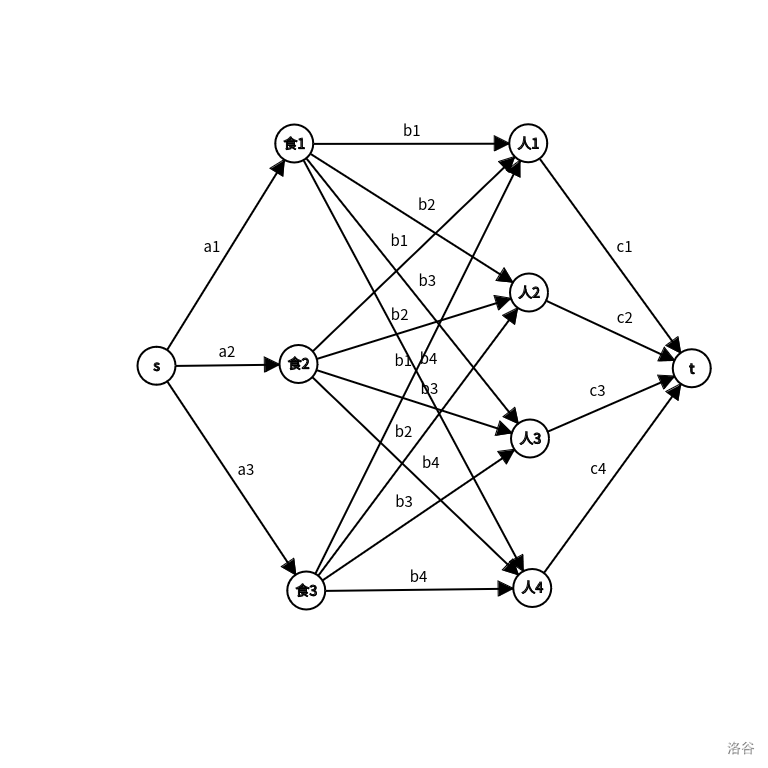
但是,建这么多的边会有问题,就是时间复杂度太高,跑不了网络流,所以我们换一种思路。
有一个重要的结论就是:最大流 \(=\) 最小割。
证明可以看这里,这里不证明了。
于是题目就转化为了对于上面这张图求最小割。
我们发现,我们要割掉左边一些零食点集与 \(s\) 的连边,同理割掉右边一些人的点集与 \(t\) 的边,再割掉中间某些 \(b_i\) 的边。
我们可以将这个过程看成删掉左右两边某些点,再删掉中间的某些边,有一个非常妙的性质就是,删掉左右两边的某些点后,必须将没删掉的那些点之间的所有连边全部删除才能保证图不联通,因为对于每一个零食,都对每个人连了边。
设左边零食删去的点集为 \(A\),右边人删去的点集为 \(c\),那么答案就为下面式子的最小值:
\(|A|\) 表示 \(A\) 集合的大小。
进一步地,我们将式子后面的两坨改一下,变为求下面式子的最小值:
让我们感性理解一下,左边为删掉某些零食点集的贡献,右边为选枚举人的点集中的所有点,要么删掉这个人,要么删掉左边剩余零食点集与这个人的所有 \(b_i\) 的边,由于要求最小割,所以取两者中的最小值保证图不联通。
于是题目就变为快速求上面这个式子。
首先我们枚举 \(A\) 集合的大小,在当前大小下,肯定选择的点是 \(s\) 与之连边 \(a_i\) 最小的几个,于是先对 \(a_i\) 排序。
如何快速求式子右边那一坨,将 \(\frac{c_i}{b_i}\) 求出来,设 \(x_i = \frac{c_i}{b_i}\),这样当 \(n-|A|=x_i\) 时,\(b_i(n-|A|)=c_i\),当 \(n-|A|<x_i\) 时,取 \(b_i(n-|A|)\),当 \(n-|A|>x_i\) 时,取 \(c_i\)(当然 \(x_i\) 可能为小数,可以将 \(x_i+1\) 向下取整,看到后面就明白了)。
接下来思路就很明确了,每次枚举到一个 \(n-|A|\),后面那个式子有些保持不变,有些超过了临界点,改变了数值,所以以 \(x_i\) 为第一关键字从小到大排序,求出 \(b_i\) 与 \(c_i\) 的前缀和,每次二分大于等于 \(n-|A|\) 的 \(x_i\) 的位置,前面的还是 \(b_i(n-|A|)\),后面的是 \(c_i\),利用前缀和统计答案(这时 \(x_i+1\) 就有用了,因为浮点数范围太小,\(x_i+1\) 后二分到这个临界点随便取 \(b_i\) 还是 \(c_i\) 都是同样的结果)。
代码
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<climits>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
inline int read(){register int x = 0, f = 1;register char c = getchar();while (c < '0' || c > '9'){if (c == '-') f = -1;c = getchar();}while (c >= '0' && c <= '9'){x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (c ^ 48);c = getchar();}return x * f;}
inline void write(int x){if (x < 0) putchar('-'), x = -x;if (x > 9) write(x / 10);putchar(x % 10 + '0');}
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
int n, m, sum, ans = LONG_LONG_MAX;
int a[N], qc[N], qb[N];
struct node{
int x, b, c;
bool operator < (const node &w) const{
return x < w.x;
}
}p[N];
signed main(){
n = read(), m = read();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) a[i] = read();
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) p[i].b = read();
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) p[i].c = read();
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) p[i].x = p[i].c / p[i].b + 1;
sort(a + 1, a + n + 1);
sort(p + 1, p + m + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) qc[i] = qc[i - 1] + p[i].c, qb[i] = qb[i - 1] + p[i].b;
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++){
sum += a[i];
int y = n - i;
int l = 1, r = m;
while (l <= r){
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if (y >= p[mid].x){
l = mid + 1;
}else{
r = mid - 1;
}
}
ans = min(ans, sum + qc[r] + (qb[m] - qb[r]) * y);
}
cout << ans;
return 0;
}
Palindrome Numbers
从 ABC363D 来的。
思路
我们假设将 \(n\) 加上一,那么样例就变为以下的状况:
2 -> 1
13 -> 33
25 -> 151
很好理解,就是我们把 \(0\) 当成第一个回文数。
于是我们开始寻找规律。
当最高位为 \(0\) 到 \(9\) 之间的数时,将最高位减一,再反转,此时的回文数的位数是奇数个。
例如:
25->15
15->151
当最高位为 \(1\) 时,要分两种情况,第一种是最高位是 \(1\),第二位不是 \(0\),此时把最高位去掉,再反转,此时回文数的位数是偶数个。
例如:
13->3
3->33
但如果第二位是 \(0\) 呢,很简单,用第一种讨论的方法,前两位看成是 \(10\),减一后变为 \(9\),再反转,此时回文数的位数也是奇数个。
例如:
100->90
90->909
以上就是讨论的结果,剩下的就是模拟了。
代码
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
inline int read(){register int x = 0, f = 1;register char c = getchar();while (c < '0' || c > '9'){if (c == '-') f = -1;c = getchar();}while (c >= '0' && c <= '9'){x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (c ^ 48);c = getchar();}return x * f;}
inline void write(int x){if (x < 0) putchar('-'), x = -x;if (x > 9) write(x / 10);putchar(x % 10 + '0');}
int n, k, cnt;
unsigned long long s = 1;
int qpow(int a, int b){
int ans = 1;
while (b){
if (b & 1) ans *= a;
a *= a;
b >>= 1;
}
return ans;
}
signed main(){
while (1){
k = n = read(), s = 1, cnt = 0;
if (n == 0) return 0;
k++, n++;
if (n >= 1 && n <= 10){
cout << n - 1 << '\n';
continue;
}
while (k){
k /= 10;
cnt++;
s *= 10;
}
if (n % s == 0){
cout << 9;
for (int i = 1; i < (cnt - 2) * 2; i++) cout << 0;
cout << 9;
cout << '\n';
continue;
}
if (n % s != 0) s /= 10;
if (n / s != 1){
n -= qpow(10, cnt - 1);
cout << n;
n /= 10;
while (n){
cout << n % 10;
n /= 10;
}
cout << '\n';
continue;
}
if (n / s == 1 && (n - qpow(10, cnt - 1)) / (s / 10) == 0){
n -= qpow(10, cnt - 2);
cout << n;
n /= 10;
while (n){
cout << n % 10;
n /= 10;
}
cout << '\n';
continue;
}
if (n / s == 1 && (n - qpow(10, cnt - 1)) / (s / 10) != 0){
n -= qpow(10, cnt - 1);
cout << n;
while (n){
cout << n % 10;
n /= 10;
}
cout << '\n';
continue;
}
}
return 0;
}
后记
总之,这种题目可以通过转换后找规律的方法通过,具体规律见这个。
Mathematical Problem
思路
这道题目需要分类讨论一下,首先当 \(n = 2\) 时,直接去掉前导零,输出答案。
当 \(n > 2\) 时,枚举有两个字符的断点,将每个段的数存下来,去掉前导零,如果某个段有 \(0\),那么答案就是 \(0\),如果没有 \(0\),那么如果某个段有 \(1\) 时,肯定与前面或者后面的数相乘,这样才能让答案最小。
接下来就是模拟的时间。
代码
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
inline int read(){register int x = 0, f = 1;register char c = getchar();while (c < '0' || c > '9'){if (c == '-') f = -1;c = getchar();}while (c >= '0' && c <= '9'){x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (c ^ 48);c = getchar();}return x * f;}
inline void write(int x){if (x < 0) putchar('-'), x = -x;if (x > 9) write(x / 10);putchar(x % 10 + '0');}
const int N = 25;
int T, n, ans;
char c[N];
int a[N];
int get(int l, int r){//去掉前导零,获得数字
int pos = l, res = 0;
for (pos = l; pos < r; pos++){
if (c[pos] != '0') break;
}
for (int i = pos; i <= r; i++) res = res * 10 + (c[i] - '0');
return res;
}
int main(){
T = read();
while (T--){
n = read(), ans = 0x7fffffff;
cin >> (c + 1);
if (n == 2){//特判
cout << get(1, n) << '\n';
continue;
}
bool flag = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++){
int cnt = 0;
bool f = 0;
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++){
if (j == i) a[++cnt] = get(j, j + 1), j++;
else a[++cnt] = get(j, j);
if (a[cnt] == 0){
f = 1;
cout << 0 << '\n';//有 0 答案最小就为 0
break;
}
}
if (f){
flag = 1;
break;
}
int res = 0;
bool d = 0;
for (int j = 1; j <= cnt; j++){
if (a[j] == 1){//有 1 相当于不加,乘起来还是为前面或后面的数的值
continue;
}else d = 1;
res += a[j];
}
if (!d) ans = min(ans, 1);//特判如果整个全为 1
else ans = min(ans, res);
}
if (flag) continue;
cout << ans << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
GCD-sequence
思路
先处理出每个 \(b_i\),接着从前往后和从后往前扫一遍,找到从前往后非递减的最远的位置 \(l\) 和从后往前非递减的最远的位置 \(r\)。
然后暴力枚举删除的 \(a_i\),此时位置是 \(i\),求出位置 \(i\) 相邻两个的最大公约数,即 \(k = \gcd(a_{i - 1}, a_{i + 1})\),将 \(b_i\) 与 \(b_{i - 1}\) 合并,它的上一个为 \(b_{i - 2}\),下一个为 \(b_{i + 1}\),判断 \(k\) 是否大于等于 \(b_{i - 2}\) 和是否小于等于 \(b_{i + 1}\),还要满足 \(i - 2\) 小于等于 \(l\),\(i + 1\) 大于等于 \(r\) 使前一段和后一段的非递减序列能与 \(k\) 拼接上。
接下来就是模拟时间。
代码
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
inline int read(){register int x = 0, f = 1;register char c = getchar();while (c < '0' || c > '9'){if (c == '-') f = -1;c = getchar();}while (c >= '0' && c <= '9'){x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (c ^ 48);c = getchar();}return x * f;}
inline void write(int x){if (x < 0) putchar('-'), x = -x;if (x > 9) write(x / 10);putchar(x % 10 + '0');}
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
int T, n;
int a[N], b[N], l, r;
int gcd(int x, int y){
return (y == 0 ? x : gcd(y, x % y));
}
signed main(){
T = read();
while (T--){
n = read();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) a[i] = read();
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) b[i] = gcd(a[i], a[i + 1]);
l = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++){
if (b[i - 1] <= b[i]) l = i;
else break;
}//找到最远前缀
r = n - 1;
for (int i = n - 2; i >= 1; i--){
if (b[i + 1] >= b[i]) r = i;
else break;
}//找到最远后缀
if (r <= 2 || l >= n - 2){
cout << "yes\n";
continue;
}
bool f = 0;
b[n] = 0x7fffffff, b[0] = 0;
for (int i = 2; i < n; i++){
int k = gcd(a[i - 1], a[i + 1]), li = max(i - 2, 0ll), ri = min(i + 1, n);
if (li <= l && ri >= r && k >= b[li] && k <= b[ri]){
cout << "yes\n";
f = 1;
break;
}//满足条件
}
if (!f) cout << "no\n";
}
return 0;
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号