python的线程笔记
一、简单的创建线程
def foo(n):
print(n)
sleep(1)
t1 = threading.Thread(target=foo,args=(1,))
t1.start()
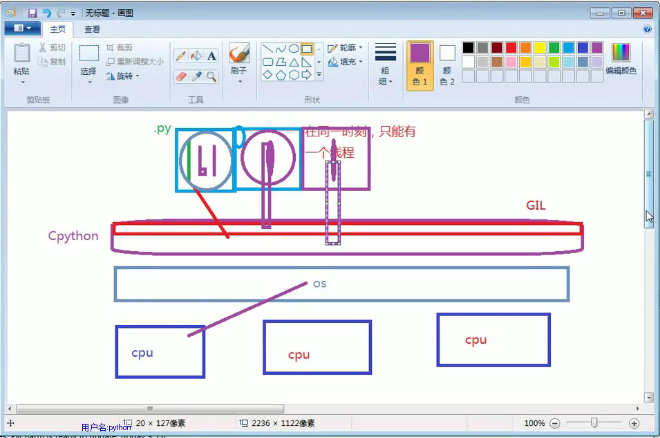
二、GIL--->全局解释器锁
就是因为有GIL的原因 所以python解释器才只能处理一个线程
所以python真正意义上是单线程的
三、结论
假如任务是IO密集型的可以用多线程
假如是计算密集型的就不能用多线程,或者改用c写
四、join()方法--》线程阻塞作用,只有当前线程运行结束后向后执行
五、Daemon --》守护进程
t.setDaemon(True)方式调用
守护哪个线程,要等其他线程结束,进程结束,守护的线程不一样结束了
六、线程同步(第一把锁)
lock = threading.Lock()
lock.acquire()---》
temp = num
sleep(0.2)
num = temp-1
print(num)
lock.release()----》
七、死锁问题(第二把锁)
使用lock = threading.Rlock()方式解决
八:信号量(第三把锁)semaphore
import threading
from builtins import range, print
from time import sleep
class myThread(threading.Thread):
def run(self):
semaphore.acquire()
print(self.name)
# sleep(1)
semaphore.release()
if __name__ == '__main__':
semaphore = threading.BoundedSemaphore(5)
threads = []
for i in range(100):
threads.append(myThread())
for t in threads:
t.start()
九、条件变量(第四八锁)Condition()--》可进行线程间通信
import threading
import time
from builtins import print, len, range
from random import randint
class Producer(threading.Thread):
def run(self):
global L
while True:
val = randint(0,100)
print('生产者-->',val,'--->',L)
lock_conn.acquire()
L.append(val)
lock_conn.notify() #唤醒
lock_conn.release()
time.sleep(3)
class Consumer(threading.Thread):
def run(self):
global L
while True:
lock_conn.acquire()
if len(L) == 0:
lock_conn.wait()#等待
print('消费--》',L[0],'-->',L)
del L[0]
lock_conn.release
time.sleep(1)
L = []
lock_conn = threading.Condition()
threads = []
if __name__ == '__main__':
for i in range(5):
threads.append(Producer())
threads.append(Consumer())
for t in threads:
t.start()
![]()
import threading
from builtins import print, range
from time import sleep
class Boss(threading.Thread):
def run(self):
print('今天要加班到22:00,大家辛苦了!!!')
event.isSet() or event.set()
sleep(5)
print('十点了 下班了。。。。。。')
event.isSet() or event.set()
class Worker(threading.Thread):
def run(self):
event.wait()
print('打工太苦命了。。。。。')
sleep(1)
event.clear()
event.wait()
print('终于 下班了。。。。。')
event.clear()
events = []
event = threading.Event()
if __name__ == '__main__':
for i in range(5):
events.append(Worker())
events.append(Boss())
for t in events:
t.start()
10、队列(本身具有锁,可实现数据安全)
FIFO:先进先出
LIFO:后进先出





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号