作业 02 - 双层神经网络实现分类
双层神经网络
作业 01 只用了单层神经网络实现分类,这次用单隐藏层神经网络来实现
注:$\mathrm{\times}$ 代表正常的矩阵乘法,$\mathrm{*}$ 代表数乘或者矩阵对应位置相乘.
输入 $\mathrm{m}$ 个训练样本,每个样本有 $\mathrm{n[0]}$ 个特征
正向传播递推式
$\mathrm{X=(n[0], m)}$,
$\mathrm{w1 = (n[1], n[0])}$, $\mathrm{b1 = (n[1], 1)}$, $\mathrm{w2 = (1, n[1]), b2 = (1, 1)}$
$\mathrm{z1 = w1 \times X + b1}$, $\mathrm{a1 = tanh(z1)}$
$\mathrm{z2 = w2 \times a1 + b2}$, $\mathrm{a2 = sigmoid(z2)}$
反向传播递推式
$\mathrm{d(z2) = [a2[1] - Y[1], a2[2] - Y[2]......a2[m] - Y[m]]}$
$\mathrm{d(w2) = \frac{1}{m} d(z2) \times A^{T}}$
$\mathrm{d(b2) = \frac{1}{m} np.sum(d(z2), axis=1,keepdims=True)}$
$\mathrm{d(z1) = \frac{1}{m} (w2)^{T} \times d(z2) * tanh'(z1)}$
$\mathrm{d(w1) = \frac{1}{m} d(z1) X^{T}}$
$\mathrm{d(b1) = \frac{1}{m} np.sum(d(z1), axis=1,keepdims=True)}$
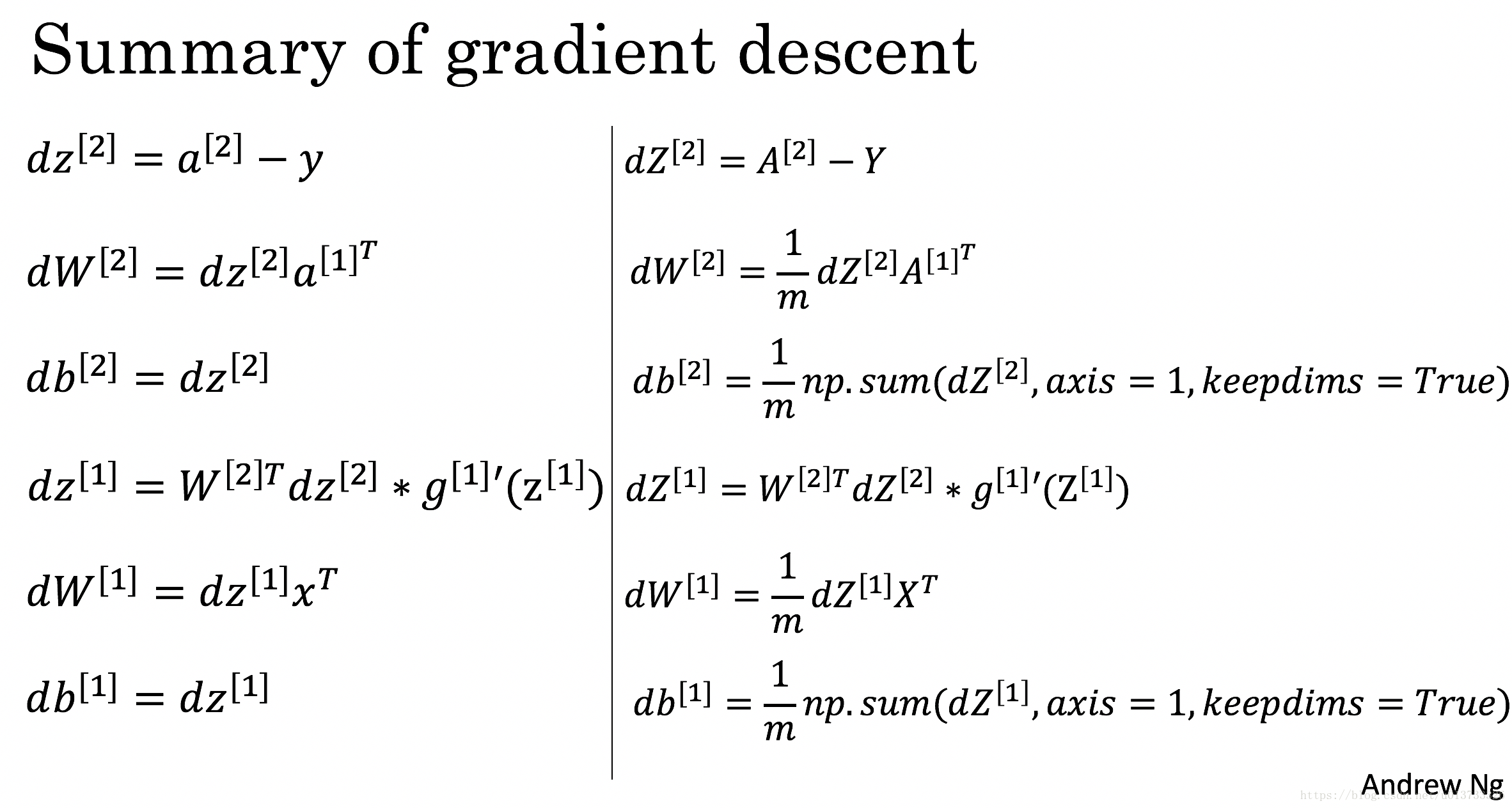
源自 Andrew Ng 的 PPT
代码实现
import numpy as np
import h5py
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from lr_utils import load_dataset
def sigmoid(x):
return 1 / (1.0 + np.exp(-x))
def tanh(x):
return (np.exp(x) - np.exp(-x)) / (np.exp(x) + np.exp(-x))
def dtanh(y):
return 1 - (y * y)
def neural_solve(train_x, train_y, n1, step = 100, lr = 0.009):
n0, m = train_x.shape
#w1, b1 = np.random.randn(n1, n0) * (1 / np.sqrt(m)), np.random.randn(n1, 1) * 0.01
#w2, b2 = np.random.randn(1, n1) * (1 / np.sqrt(n1)), np.random.randn(1, 1) * 0.01
w1, b1 = np.random.randn(n1, n0) * 0.001, np.random.randn(n1, 1) * 0.01
w2, b2 = np.random.randn(1, n1) * 0.5, np.random.randn(1, 1) * 0.01
# w1(n1, n0), b1(n1, 1)
# w2(1, n1), b2(1, 1)
# X(n0, m), Y(1, m)
X , Y = train_x, train_y
for i in range(0, step + 1):
# 这些是向前传播.
z1 = np.dot(w1, X) + b1
a1 = tanh(z1)
z2 = np.dot(w2, a1) + b2
a2 = sigmoid(z2)
# 向后传播
dz2 = a2 - Y
dw2 = (1 / m) * np.dot(dz2, a1.T)
db2 = (1 / m) * np.sum(dz2, axis = 1, keepdims = True)
dz1 = (1 / m) * np.dot(w2.T, dz2) * dtanh(a1)
dw1 = (1 / m) * np.dot(dz1, X.T)
db1 = (1 / m) * np.sum(dz1, axis = 1, keepdims = True)
w1 -= lr * dw1
b1 -= lr * db1
w2 -= lr * dw2
b2 -= lr * db2
return w1, b1, w2, b2
def calculate(X, w1, b1, w2, b2):
z1 = np.dot(w1, X) + b1
a1 = tanh(z1)
z2 = np.dot(w2, a1) + b2
a2 = sigmoid(z2)
return a2
第二周作业
用双层神经网络实现对于猫的识别,训练数据正确率达到 $0.9$ 时测试数据达到了 $0.74$ 的正确率.
这里隐藏层开了 3 个节点.
import numpy as np
import h5py
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from lr_utils import load_dataset
def sigmoid(x):
return 1 / (1.0 + np.exp(-x))
def tanh(x):
return (np.exp(x) - np.exp(-x)) / (np.exp(x) + np.exp(-x))
def dtanh(y):
return 1 - (y * y)
def neural_solve(train_x, train_y, n1, step = 100, lr = 0.009):
n0, m = train_x.shape
#w1, b1 = np.random.randn(n1, n0) * (1 / np.sqrt(m)), np.random.randn(n1, 1) * 0.01
#w2, b2 = np.random.randn(1, n1) * (1 / np.sqrt(n1)), np.random.randn(1, 1) * 0.01
w1, b1 = np.random.randn(n1, n0) * 0.001, np.random.randn(n1, 1) * 0.01
w2, b2 = np.random.randn(1, n1) * 0.5, np.random.randn(1, 1) * 0.01
# w1(n1, n0), b1(n1, 1)
# w2(1, n1), b2(1, 1)
# X(n0, m), Y(1, m)
X , Y = train_x, train_y
for i in range(0, step + 1):
# 这些是向前传播.
z1 = np.dot(w1, X) + b1
a1 = tanh(z1)
z2 = np.dot(w2, a1) + b2
a2 = sigmoid(z2)
# 向后传播
dz2 = a2 - Y
dw2 = (1 / m) * np.dot(dz2, a1.T)
db2 = (1 / m) * np.sum(dz2, axis = 1, keepdims = True)
dz1 = (1 / m) * np.dot(w2.T, dz2) * dtanh(a1)
dw1 = (1 / m) * np.dot(dz1, X.T)
db1 = (1 / m) * np.sum(dz1, axis = 1, keepdims = True)
w1 -= lr * dw1
b1 -= lr * db1
w2 -= lr * dw2
b2 -= lr * db2
return w1, b1, w2, b2
def calculate(X, w1, b1, w2, b2):
z1 = np.dot(w1, X) + b1
a1 = tanh(z1)
z2 = np.dot(w2, a1) + b2
a2 = sigmoid(z2)
return a2
train_x, train_y, test_x, test_y, classes = load_dataset()
train_x = train_x.reshape(train_x.shape[0], -1).T / 255
test_x = test_x.reshape(test_x.shape[0], -1).T / 255
cases = test_y.shape[1]
w1, b1, w2, b2 = neural_solve(train_x, train_y, 3, 9000, 0.008)
answer = calculate(test_x, w1, b1, w2, b2) >= 0.5
answer_test = calculate(train_x, w1, b1, w2, b2) >= 0.5
# print(answer)
"""
for i in range(cases):
print((int)(answer[0][i]), test_y[0][i])
"""
dd = 0
for i in range(train_y.shape[1]):
if(answer_test[0][i] == train_y[0][i]) :
dd += 1
print(dd / train_y.shape[1])
cc = 0
for i in range(cases):
if(answer[0][i] == test_y[0][i]):
cc += 1
print(cc / cases)
第三周作业
这次作业是对一个二维图形进行颜色的分类
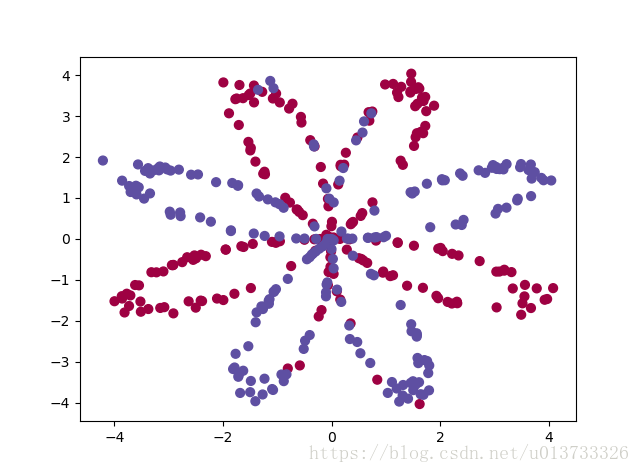
由于颜色的分布并不是线性的,所以直接用一层神经网络是无法完成高正确率的分类的.
即使对训练数据针对大量的训练,模型对于训练数据也只有 50% 的正确率.
使用双层神经网络可以让正确率提高到 87.5%, 神经网络是自己封装好的,直接调用即可.
神经网络:
import numpy as np
import h5py
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def sigmoid(x):
return 1 / (1.0 + np.exp(-x))
def tanh(x):
return (np.exp(x) - np.exp(-x)) / (np.exp(x) + np.exp(-x))
def dtanh(y):
return 1 - np.power(y, 2)
def neural_solve(train_x, train_y, n1, step = 100, lr = 0.009):
np.random.seed(233)
n0, m = train_x.shape
#w1, b1 = np.random.randn(n1, n0) * (1 / np.sqrt(m)), np.random.randn(n1, 1) * 0.01
#w2, b2 = np.random.randn(1, n1) * (1 / np.sqrt(n1)), np.random.randn(1, 1) * 0.01
w1, b1 = np.random.randn(n1, n0) * 0.01, np.random.randn(n1, 1) * 0.01
w2, b2 = np.random.randn(1, n1) * 0.01, np.random.randn(1, 1) * 0.01
# w1(n1, n0), b1(n1, 1)
# w2(1, n1), b2(1, 1)
# X(n0, m), Y(1, m)
X , Y = train_x, train_y
for i in range(0, step + 1):
# 这些是向前传播.
z1 = np.dot(w1, X) + b1
a1 = tanh(z1)
z2 = np.dot(w2, a1) + b2
a2 = sigmoid(z2)
# 向后传播
dz2 = a2 - Y
dw2 = (1 / m) * np.dot(dz2, a1.T)
db2 = (1 / m) * np.sum(dz2, axis = 1, keepdims = True)
dz1 = (1 / m) * np.dot(w2.T, dz2) * dtanh(a1)
dw1 = (1 / m) * np.dot(dz1, X.T)
db1 = (1 / m) * np.sum(dz1, axis = 1, keepdims = True)
w1 -= lr * dw1
b1 -= lr * db1
w2 -= lr * dw2
b2 -= lr * db2
return w1, b1, w2, b2
def calculate(X, w1, b1, w2, b2):
z1 = np.dot(w1, X) + b1
a1 = tanh(z1)
z2 = np.dot(w2, a1) + b2
a2 = sigmoid(z2)
return a2
调用代码
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from testCases import *
import sklearn
import sklearn.datasets
import sklearn.linear_model
from planar_utils import plot_decision_boundary, sigmoid, load_planar_dataset, load_extra_datasets
from a import neural_solve, calculate
np.random.seed(1)
X, Y = load_planar_dataset()
print("X 的形状: " + str(X.shape))
print("Y 的形状: " + str(Y.shape))
# X[0], X[1] -> Y
w1, b1, w2, b2 = neural_solve(X, Y, 4 , 40000, 1.2)
answer = calculate(X, w1, b1, w2, b2) >= 0.5
cc = 0
for i in range(400):
if answer[0][i] == Y[0][i]:
cc += 1
print("训练数据正确率:" + str(cc / 4) + "%")




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号