数据库语句的简单应用3(实验5)
一、嵌套查询
1.不相关子查询的执行过程:
1)先执行内层查询,将内层查询的结果返回到外层查询的where条件中。
2)执行外层查询,得到最终结果.
2.相关子查询的执行过程:
1)首先将外层查询表的第一条记录为当前记录
2)将当前记录与内层查询相关的列值传入内层查询的条件中
3)执行内层查询,将结果返回到外层查询的where子句中,若该子句的条件为真,则将外层表的当前记录放入到结果表中;若该where子句的条件为假,则不把外层表的当前记录放入到结果表中,即放弃该记录。
4)然后再取外层查询表的下一条记录为当前记录。若有记录则转到2步;若无记录(外层表的所有记录循环处理完毕),则结束
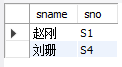
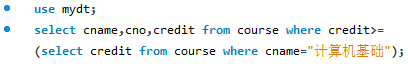
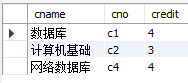
1.带比较运算符的子查询

2.带in(或 not in)谓词的子查询
use mydt;
select sname from student where sno in( //查询所有选修c3课程的学生的姓名
select sno from sc where cno='c3');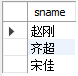
3.带any/all谓词的子查询
注意:不可以出现=all的情况,比如说sex,可知sex的all为{'男','女'},如果一个取之等于all的话,可想而知是没有人满足这个条件的
use mydt;/*查询所有选修c3课程的学生的姓名*/
select sname from student where sno=any
(select sno from sc where cno='c3');

use mydt;
/*查询没有选修c3课程的学生的姓名*/
select sname from student where sno<>all
(select sno from sc where cno='c3');

4.带exists(或者not exists)谓词的子查询
注意:含有这两个谓词的语句一般都是相关子查询
use mydt;
/*查询没有选修c3课程的学生的姓名*/
select sname from student where exists
(select * from sc where cno='c3' and sno=student.sno);
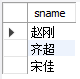
use mydt;
/*查询选修了全部课程的学生姓名*/
select sname from student where not exists
(select * from course where not exists(
select * from sc where student.sno=sc.sno and course.cno=cno));
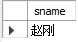
use mydt;
/*查询至少选修了学生s3选修的全部课程的学生的学号,不包括s3*/
select distinct sno from sc scx where scx.sno<>'s3'and not exists(
select * from sc scy where scy.sno='s3' and not exists(
select * from sc scz where scz.sno=scx.sno and scy.cno=scz.cno));
二、集合查询
1.语句结构:
select 语句1 union | intersect | minus select 语句2;/*注:mysql中不支持intersect和minus
1.union
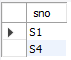
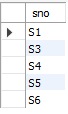
use mydt;
/*查询选修了c1课程或者c3课程的学号*/
select sno from sc where cno='c1'
union
select sno from sc where cno='c3';
2.intersect
3.minus
三、多表查询的等价形式
1.多表查询的多种等价形式总结:
1)自然连接(显示和隐式)
2)in嵌套
3)any/all嵌套及其等价的表达
4)exists嵌套
5)多种混合形式
2.多表查询的否定形式
1)minus集合查询
2)not in嵌套
3)<>all嵌套
4)not exists嵌套



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号