Codeforces Round #333 DIV2
D:
A function 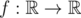 is called Lipschitz continuous if there is a real constant K such that the inequality |f(x) - f(y)| ≤ K·|x - y| holds for all
is called Lipschitz continuous if there is a real constant K such that the inequality |f(x) - f(y)| ≤ K·|x - y| holds for all 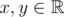 . We'll deal with a more... discrete version of this term.
. We'll deal with a more... discrete version of this term.
For an array 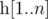 , we define it's Lipschitz constant
, we define it's Lipschitz constant 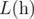 as follows:
as follows:
- if n < 2,
![]()
- if n ≥ 2,
![]() over all 1 ≤ i < j ≤ n
over all 1 ≤ i < j ≤ n
In other words, 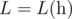 is the smallest non-negative integer such that |h[i] - h[j]| ≤ L·|i - j| holds for all 1 ≤ i, j ≤ n.
is the smallest non-negative integer such that |h[i] - h[j]| ≤ L·|i - j| holds for all 1 ≤ i, j ≤ n.
You are given an array  of size n and q queries of the form [l, r]. For each query, consider the subarray
of size n and q queries of the form [l, r]. For each query, consider the subarray 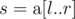 ; determine the sum of Lipschitz constants of all subarrays of
; determine the sum of Lipschitz constants of all subarrays of  .
.
The first line of the input contains two space-separated integers n and q (2 ≤ n ≤ 100 000 and 1 ≤ q ≤ 100) — the number of elements in array  and the number of queries respectively.
and the number of queries respectively.
The second line contains n space-separated integers 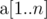 (
(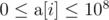 ).
).
The following q lines describe queries. The i-th of those lines contains two space-separated integers li and ri (1 ≤ li < ri ≤ n).
Print the answers to all queries in the order in which they are given in the input. For the i-th query, print one line containing a single integer — the sum of Lipschitz constants of all subarrays of 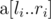 .
.
10 4
1 5 2 9 1 3 4 2 1 7
2 4
3 8
7 10
1 9
17
82
23
210
7 6
5 7 7 4 6 6 2
1 2
2 3
2 6
1 7
4 7
3 5
2
0
22
59
16
8
In the first query of the first sample, the Lipschitz constants of subarrays of  with length at least 2 are:
with length at least 2 are:
The answer to the query is their sum.
思路是;虽然题目说了很多定义,但是基本都是把人弄晕的。
一定是相邻的两个点的最值 ,可以对应在二维坐标上YY 一下。
然后由数组a[I]->得到B[I];
之后就变成统计问题了;
给一个数组B;
比如:3,2,5,7,8,4,9
求 所有子数组最大值得和;
你可以对一个I 求出I 左边范围 比如L,A[L].,A[L+1]...A[I]<A[I];(注意是小于)
右边 I R,A[I+1],A[I+2]..A[R]<=A[I](注意大于等于)
符号要注意 如果都是大于等于就会重复算(我这里错了几百遍
写得很丑
1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 3 using namespace std; 4 typedef long long ll; 5 6 #define N 123456 7 8 9 int a[N],L[N],R[N]; 10 int b[N],n; 11 12 int dp[N][20]; 13 14 15 void init() 16 { 17 int k=log(n)/log(2.0); 18 for (int i=1;i<=n;i++) 19 dp[i][0]=b[i]; 20 21 for (int j=1;j<=k;j++) 22 for (int i=1;i+(1<<(j-1))-1<=n;i++) 23 dp[i][j]=max(dp[i][j-1],dp[i+(1<<(j-1))][j-1]); 24 } 25 26 int rmq(int l,int r) 27 { 28 int k=log(r-l+1)/log(2.0); 29 return max(dp[l][k],dp[r-(1<<k)+1][k]); 30 } 31 32 int main() 33 { 34 int q; 35 scanf("%d%d",&n,&q); 36 for (int i=1;i<=n;i++) 37 scanf("%d",&a[i]); 38 39 n--; 40 for (int i=1;i<=n;i++) 41 b[i]=abs(a[i+1]-a[i]); 42 init(); 43 44 for (int i=1;i<=n;i++) 45 { 46 int l=1,r=i; 47 L[i]=i; 48 for (int _=1;_<20;_++) 49 { 50 int mid=(l+r)/2; 51 if (rmq(mid,i-1)<b[i]) 52 L[i]=mid,r=mid; 53 else l=mid+1; 54 } 55 56 l=i,r=n; 57 for (int _=1;_<20;_++) 58 { 59 int mid=(l+r)/2; 60 if (rmq(i,mid)<=b[i]) 61 R[i]=mid,l=mid+1; 62 else r=mid; 63 } 64 } 65 66 // for (int i=1;i<=n;i++) 67 // cout<<L[i]<<" "<<R[i]<<endl; 68 69 70 while (q--) 71 { 72 int l,r; 73 scanf("%d%d",&l,&r); 74 75 ll ans=0; 76 r--; 77 for (int i=l;i<=r;i++) 78 // ll tmp=(ll) (i-max(l,L[i])+1)*(min(r,R[i])-i+1); 79 // cout<<tmp<<endl; 80 ans+=(ll)(i-max(l,L[i])+1)*(min(r,R[i])-i+1)*b[i]; 81 82 cout<<ans<<endl; 83 // printf("%I64d\n",ans); 84 } 85 86 87 return 0; 88 }
C:
In Absurdistan, there are n towns (numbered 1 through n) and m bidirectional railways. There is also an absurdly simple road network — for each pair of different towns x and y, there is a bidirectional road between towns x and y if and only if there is no railway between them. Travelling to a different town using one railway or one road always takes exactly one hour.
A train and a bus leave town 1 at the same time. They both have the same destination, town n, and don't make any stops on the way (but they can wait in town n). The train can move only along railways and the bus can move only along roads.
You've been asked to plan out routes for the vehicles; each route can use any road/railway multiple times. One of the most important aspects to consider is safety — in order to avoid accidents at railway crossings, the train and the bus must not arrive at the same town (except town n) simultaneously.
Under these constraints, what is the minimum number of hours needed for both vehicles to reach town n (the maximum of arrival times of the bus and the train)? Note, that bus and train are not required to arrive to the town n at the same moment of time, but are allowed to do so.
The first line of the input contains two integers n and m (2 ≤ n ≤ 400, 0 ≤ m ≤ n(n - 1) / 2) — the number of towns and the number of railways respectively.
Each of the next m lines contains two integers u and v, denoting a railway between towns u and v (1 ≤ u, v ≤ n, u ≠ v).
You may assume that there is at most one railway connecting any two towns.
Output one integer — the smallest possible time of the later vehicle's arrival in town n. If it's impossible for at least one of the vehicles to reach town n, output - 1.
4 2
1 3
3 4
2
4 6
1 2
1 3
1 4
2 3
2 4
3 4
-1
5 5
4 2
3 5
4 5
5 1
1 2
3
In the first sample, the train can take the route 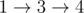 and the bus can take the route
and the bus can take the route  . Note that they can arrive at town 4 at the same time.
. Note that they can arrive at town 4 at the same time.
In the second sample, Absurdistan is ruled by railwaymen. There are no roads, so there's no way for the bus to reach town 4.
太无语了。
没想到,写了一个暴力的BFS 结果TLE了
真心不会读题。。
因为BUS或者 train总有一个 直接连接1-N,所以只要算另一个的最短路就好了O(n^2);
1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 const int inf=1<<29; 5 6 bool sb; 7 queue<int >q; 8 int dis[456]; 9 int mp[456][456]; 10 int n,m; 11 int dfs() 12 { 13 for(int i=0; i<n+1; i++) 14 dis[i]=inf; 15 q.push(1); 16 dis[1]=0; 17 while(!q.empty()) 18 { 19 int u=q.front(); 20 q.pop(); 21 for(int v=1; v<=n; v++) 22 { 23 if(sb&&!mp[u][v]) 24 { 25 if(dis[v]==inf) 26 { 27 dis[v]=dis[u]+1; 28 q.push(v); 29 } 30 } 31 else if(!sb&&mp[u][v]) 32 { 33 if(dis[v]==inf) 34 { 35 dis[v]=dis[u]+1; 36 q.push(v); 37 } 38 } 39 } 40 } 41 return dis[n]; 42 } 43 int main() 44 { 45 while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)!=EOF) 46 { 47 int x,y; 48 for(int i=0; i<m; i++) 49 { 50 scanf("%d%d",&x,&y); 51 mp[x][y]=1; 52 mp[y][x]=1; 53 if((x==n&&y==1)||(x==1&&y==n)) 54 sb=true; 55 56 } 57 int t=dfs(); 58 t=max(t,1); 59 if(t==inf) 60 printf("-1\n"); 61 else printf("%d\n",t); 62 63 } 64 }
B:
When Xellos was doing a practice course in university, he once had to measure the intensity of an effect that slowly approached equilibrium. A good way to determine the equilibrium intensity would be choosing a sufficiently large number of consecutive data points that seems as constant as possible and taking their average. Of course, with the usual sizes of data, it's nothing challenging — but why not make a similar programming contest problem while we're at it?
You're given a sequence of n data points a1, ..., an. There aren't any big jumps between consecutive data points — for each 1 ≤ i < n, it's guaranteed that |ai + 1 - ai| ≤ 1.
A range [l, r] of data points is said to be almost constant if the difference between the largest and the smallest value in that range is at most 1. Formally, let M be the maximum and m the minimum value of ai for l ≤ i ≤ r; the range [l, r] is almost constant if M - m ≤ 1.
Find the length of the longest almost constant range.
The first line of the input contains a single integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 100 000) — the number of data points.
The second line contains n integers a1, a2, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 100 000).
Print a single number — the maximum length of an almost constant range of the given sequence.
5
1 2 3 3 2
4
11
5 4 5 5 6 7 8 8 8 7 6
5
In the first sample, the longest almost constant range is [2, 5]; its length (the number of data points in it) is 4.
In the second sample, there are three almost constant ranges of length 4: [1, 4], [6, 9] and [7, 10]; the only almost constant range of the maximum length 5 is [6, 10].
好像想复杂了
我是对于:for (int i=1;i<==n;i++)
{
二分Mid 值求出(i,mid)最大值-最小值的大小
}
好吧的确想多了、、、
或者随便set搞搞应该可以
1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 3 using namespace std; 4 #define N 500100 5 6 int maxl[N][20], minl[N][20]; 7 int n, m, a[N]; 8 9 int min(int a, int b) 10 { 11 if (a>b) return b; return a; 12 } 13 14 int max(int a, int b) 15 { 16 if (a>b) return a; return b; 17 } 18 19 void S_table() 20 { 21 int l = int(log((double)n)/log(2.0)); 22 for (int j=1;j<=l;j++) 23 { 24 for (int i=1; i + (1 << (j-1) ) - 1 <=n;++i) 25 { 26 maxl[i][j] = max(maxl[i][j-1], maxl[i + (1 << (j-1) )][j-1]); 27 minl[i][j] = min(minl[i][j-1], minl[i + (1 << (j-1) )][j-1]); 28 } 29 } 30 } 31 32 int rmq(int l, int r) 33 { 34 int k = int(log((double)(r-l+1))/log(2.0)); 35 int a1 = max(maxl[l][k], maxl[r - (1<<k) + 1][k]); 36 int a2 = min(minl[l][k], minl[r - (1<<k) + 1][k]); 37 return a1-a2; 38 //printf("Max: %d Min: %d\n", a1, a2); 39 } 40 41 42 43 int main() 44 { 45 46 cin>>n; 47 for (int i=1;i<=n;++i) 48 { 49 scanf("%d", &a[i]); 50 maxl[i][0] = minl[i][0] = a[i]; 51 } 52 S_table(); 53 54 55 int ans=1; 56 for (int i=1;i<=n;i++) 57 { 58 int l=i,r=n; 59 for (int _=1;_<40;_++) 60 { 61 int mid=(l+r)/2; 62 if (rmq(i,mid)<=1) l=mid+1,ans=max(ans,mid-i+1); 63 else r=mid; 64 } 65 //cout<<ans<<endl; 66 } 67 68 cout<<ans<<endl; 69 return 0; 70 }
A:题水



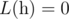
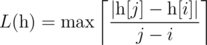 over all
over all 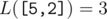
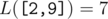

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号