线段树 篇一(势能线段树)
目录
势能线段树
前言
一种对修改加以次数限制的线段树
之前写一个区间开平方的题的时候看到的一种 小清新线段树 但是没有继续看这一类的
现在又回头看 发现同属于一类 也就是 势能线段树
学习一下 顺便记笔记
这个大概是第一篇 其他的等基本看完再整合一下
势能线段树
我们知道的是线段树可以通过打标记的方式快速的处理区间问题 通过标记的下传以及合并统计对询问的影响
但是总会有些 毒瘤 的题目 其区间的操作并不能通过标记实现 比如区间开方 区间取模...
但这些操作存在一些性质 使每一个元素被修改的次数有一个上限
所以就有了势能线段树
在线段树的每个节点上记录一个值 表示区间内的每一个元素是否已经达到了修改上限 修改的时候直接冲着叶子节点修改 中途如果遇到达到上限的点 就直接返回
其他的操作与线段树无异
题目
P4145 上帝造题的七分钟2 / 花神游历各国
题面:

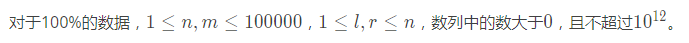
思路:
注意到 \(0\) 和 \(1\) 开平方是不变的 而且看数据范围 极限数据开方次数也不会超过六次 所以我们多维护一个区间的最大值 当这个值大于一的时候就直接递归到子节点进行更改即可
代码:
/*
Time: 3.21
Worker: Blank_space
Source: P4145 上帝造题的七分钟2 / 花神游历各国
*/
/*--------------------------------------------*/
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#define int long long
#define Max(x, y) ((x) > (y) ? (x) : (y))
#define Min(x, y) ((x) < (y) ? (x) : (y))
#define Abs(x) ((x) < 0 ? -(x) : (x))
/*--------------------------------------头文件*/
const int A = 1e4 + 7;
const int B = 1e5 + 7;
const int C = 1e6 + 7;
const int D = 1e7 + 7;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
/*------------------------------------常量定义*/
int n, m, a[B];
/*------------------------------------变量定义*/
inline int read() {
int x = 0, f = 1; char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9') {if(ch == '-') f = -1; ch = getchar();}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (ch ^ 48); ch = getchar();}
return x * f;
}
/*----------------------------------------快读*/
namespace Seg {
#define ls(x) x << 1
#define rs(x) x << 1 | 1
struct node {int l, r, mid, sum, max;}t[B << 2];
void push_up(int p) {
t[p].sum = t[ls(p)].sum + t[rs(p)].sum;
t[p].max = Max(t[ls(p)].max, t[rs(p)].max);
}
void build(int p, int l, int r) {
t[p].l = l; t[p].r = r; t[p].mid = l + r >> 1;
if(l == r) {t[p].sum = t[p].max = a[l]; return ;}
build(ls(p), l, t[p].mid); build(rs(p), t[p].mid + 1, r);
push_up(p);
}
void up_date(int p, int l, int r) {
if(t[p].l == t[p].r && l <= t[p].l && t[p].r <= r) {t[p].sum = t[p].max = std::sqrt(t[p].sum); return ;}
if(l <= t[p].mid && t[ls(p)].max > 1) up_date(ls(p), l, r);
if(r > t[p].mid && t[rs(p)].max > 1) up_date(rs(p), l, r);
push_up(p);
}
int query(int p, int l, int r) {
if(l <= t[p].l && t[p].r <= r) return t[p].sum; int res = 0;
if(l <= t[p].mid) res += query(ls(p), l, r); if(r > t[p].mid) res += query(rs(p), l, r);
return res;
}
}
/*----------------------------------------函数*/
signed main() {
n = read();
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) a[i] = read();
Seg::build(1, 1, n); m = read();
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
int opt = read(), l = read(), r = read();
if(l > r) std::swap(l, r);
if(opt) printf("%lld\n", Seg::query(1, l, r));
else Seg::up_date(1, l, r);
}
return 0;
}
CF438D The Child and Sequence
题面:

思路:
同样维护最大值 当这个值大于等于模数的时候在进行修改即可
代码:
/*
Time: 3.21
Worker: Blank_space
Source: CF438D The Child and Sequence
*/
/*--------------------------------------------*/
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#define int long long
#define Max(x, y) ((x) > (y) ? (x) : (y))
#define Min(x, y) ((x) < (y) ? (x) : (y))
#define Abs(x) ((x) < 0 ? -(x) : (x))
/*--------------------------------------头文件*/
const int A = 1e4 + 7;
const int B = 1e5 + 7;
const int C = 1e6 + 7;
const int D = 1e7 + 7;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
/*------------------------------------常量定义*/
int n, m, a[B];
/*------------------------------------变量定义*/
inline int read() {
int x = 0, f = 1; char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9') {if(ch == '-') f = -1; ch = getchar();}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (ch ^ 48); ch = getchar();}
return x * f;
}
/*----------------------------------------快读*/
namespace Seg {
#define ls(x) x << 1
#define rs(x) x << 1 | 1
struct node {int l, r, mid, sum, max;}t[B << 2];
void push_up(int p) {
t[p].sum = t[ls(p)].sum + t[rs(p)].sum;
t[p].max = Max(t[ls(p)].max, t[rs(p)].max);
}
void build(int p, int l, int r) {
t[p].l = l; t[p].r = r; t[p].mid = l + r >> 1;
if(l == r) {t[p].sum = t[p].max = a[l]; return ;}
build(ls(p), l, t[p].mid); build(rs(p), t[p].mid + 1, r);
push_up(p);
}
void up_date1(int p, int q, int k) {
if(t[p].l == q && t[p].r == q) {t[p].sum = t[p].max = k; return ;}
if(q <= t[p].mid) up_date1(ls(p), q, k); else up_date1(rs(p), q, k);
push_up(p);
}
void up_date2(int p, int l, int r, int k) {
if(t[p].l == t[p].r && l <= t[p].l && t[p].r <= r) {t[p].sum = t[p].max = t[p].sum % k; return ;}
if(l <= t[p].mid && t[ls(p)].max >= k) up_date2(ls(p), l, r, k);
if(r > t[p].mid && t[rs(p)].max >= k) up_date2(rs(p), l, r, k);
push_up(p);
}
int query(int p, int l, int r) {
if(l <= t[p].l && t[p].r <= r) return t[p].sum; int res = 0;
if(l <= t[p].mid) res += query(ls(p), l, r); if(r > t[p].mid) res += query(rs(p), l, r);
return res;
}
}
/*----------------------------------------函数*/
signed main() {
n = read(); m = read();
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) a[i] = read();
Seg::build(1, 1, n);
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
int opt = read(), x = read(), y = read();
if(opt == 1) printf("%lld\n", Seg::query(1, x, y));
if(opt == 2) {int z = read(); Seg::up_date2(1, x, y, z);}
if(opt == 3) Seg::up_date1(1, x, y);
}
return 0;
}
CF920F SUM and REPLACE
题面:

思路:
直接暴力求出 \(10^6\) 范围内所有数约数的个数 同样维护最大值 当这个值小于三的时候没有修改的意义(修改后还是原数) 直接暴力修改即可
代码:
/*
Time: 3.21
Worker: Blank_space
Source: CF920F SUM and REPLACE
*/
/*--------------------------------------------*/
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#define int long long
#define Max(x, y) ((x) > (y) ? (x) : (y))
#define Min(x, y) ((x) < (y) ? (x) : (y))
#define Abs(x) ((x) < 0 ? -(x) : (x))
/*--------------------------------------头文件*/
const int A = 1e4 + 7;
const int B = 1e5 + 7;
const int C = 1e6 + 7;
const int D = 1e7 + 7;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
/*------------------------------------常量定义*/
int n, m, a[B << 2], d[C];
/*------------------------------------变量定义*/
inline int read() {
int x = 0, f = 1; char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9') {if(ch == '-') f = -1; ch = getchar();}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (ch ^ 48); ch = getchar();}
return x * f;
}
/*----------------------------------------快读*/
namespace Seg {
#define ls(x) x << 1
#define rs(x) x << 1 | 1
struct node {int l, r, mid, sum, max;}t[B << 4];
void push_up(int p) {
t[p].sum = t[ls(p)].sum + t[rs(p)].sum;
t[p].max = Max(t[ls(p)].max, t[rs(p)].max);
}
void build(int p, int l, int r) {
t[p].l = l; t[p].r = r; t[p].mid = l + r >> 1;
if(l == r) {t[p].sum = t[p].max = a[l]; return ;}
build(ls(p), l, t[p].mid); build(rs(p), t[p].mid + 1, r);
push_up(p);
}
void up_date(int p, int l, int r) {
if(t[p].l == t[p].r && l <= t[p].l && t[p].r <= r) {t[p].sum = t[p].max = d[t[p].sum]; return ;}
if(l <= t[p].mid && t[ls(p)].max > 2) up_date(ls(p), l, r);
if(r > t[p].mid && t[rs(p)].max > 2) up_date(rs(p), l, r);
push_up(p);
}
int query(int p, int l, int r) {
if(l <= t[p].l && t[p].r <= r) return t[p].sum; int res = 0;
if(l <= t[p].mid) res += query(ls(p), l, r); if(r > t[p].mid) res += query(rs(p), l, r);
return res;
}
}
/*----------------------------------------函数*/
signed main() {
n = read(); m = read();
for(int i = 1; i <= 1e6; i++)
for(int j = i; j <= 1e6; j += i) d[j]++;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) a[i] = read();
Seg::build(1, 1, n);
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
int opt = read(), x = read(), y = read();
if(opt == 1) Seg::up_date(1, x, y);
if(opt == 2) printf("%lld\n", Seg::query(1, x, y));
}
return 0;
}
后记
本来以为能弄完的 但是下午没有时间了 可能晚上也没有了...
只能以后再说 近期会把线段树的都看一下的
还有: 感谢 : https://blog.csdn.net/Daniel__d/article/details/105104831
—— \(end\)


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号