RoI Pooling
RoI
在 Fast R-CNN 中提出了 RoI 层的具体概念及其反向传播函数. RoI 层的功能就是要解决卷积层不同尺寸的输出与全连接层固定尺寸输入的连接问题而设计.
卷积层可以对任意尺寸的数据进行处理, 而全连接层的输入尺寸是确定的. 因此, 连接卷积层与全连接层需要进行特殊设计, 一个好的连接结构必须拥有以下三个性质:
- 输入尺寸的可变性;
- 输出尺寸的确定性;
- 反向传播可计算性.
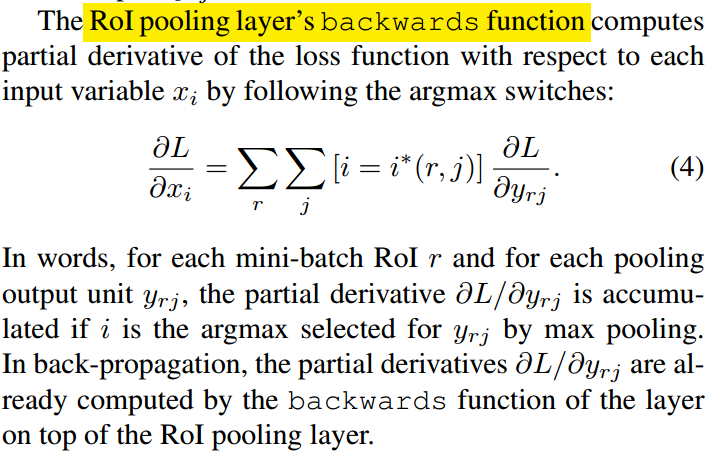
对于 RoIPooling 反向传播函数原文说明如下:
通过实际案例介绍RoI的原理:

输入的原始尺寸: \(input\_shape = (1, 5, 8)\)
输出核的尺寸: \(out\_size = (2, 3)\)
最终输出尺寸为 \((1, 2, 3)\)
从左到右从上到下进行编号: 1~6
第1个区域的最大值为: 18
第2个区域的最大值为: 21
第3个区域的最大值为: 23
第4个区域的最大值为: 34
第5个区域的最大值为: 37
第6个区域的最大值为: 39
则输出结果为:
[[[18., 21., 23.]
[34., 37., 39.]]]
RoI 代码
为了有助于理解 RoI 的逻辑, 给出 RoIPooling 的 numpy 实现如下:
# 为了更直观的理解 RoI, 未检测数据的安全性及异常处理
import numpy as np
class RoIMaxPooling2d(object): # torch.nn.AdaptiveMaxPool2d
def __init__(self, out_size):
self.w, self.h = out_size # (w, h)
def __call__(self, x: np.ndarray):
(channels, width, height) = x.shape # (channels, width, height)
out = np.zeros([channels, self.w, self.h])
grid_w = (width + self.w - 1) // self.w
grid_h = (height + self.h - 1) // self.h
for ch in range(channels): # channels
for iw in range(self.w): # width
sw, ew = self.update_index(iw, grid_w)
for ih in range(self.h): # height
sh, eh = self.update_index(ih, grid_h)
out[ch, iw, ih] = np.max(x[ch][sw:ew, sh:eh])
return out
def backwards(self):
# TODO: MaxPooling2d 的反向传播函数
pass
@staticmethod
def update_index(idx, grid):
start = idx * grid
end = start + grid
return start, end
input0 = np.array(range(80)).reshape([2, 5, 8])
output0 = RoIMaxPooling2d((2, 3))(input0)
print('input0:\n', input0)
print('output0:\n', output0)
print('out_shape: ', output0.shape)
输出结果如下:
input0:
[[[ 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7]
[ 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15]
[16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23]
[24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31]
[32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39]]
[[40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47]
[48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55]
[56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63]
[64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71]
[72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79]]]
output0:
[[[18. 21. 23.]
[34. 37. 39.]]
[[58. 61. 63.]
[74. 77. 79.]]]
out_shape: (2, 2, 3)




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号