深入理解系统调用
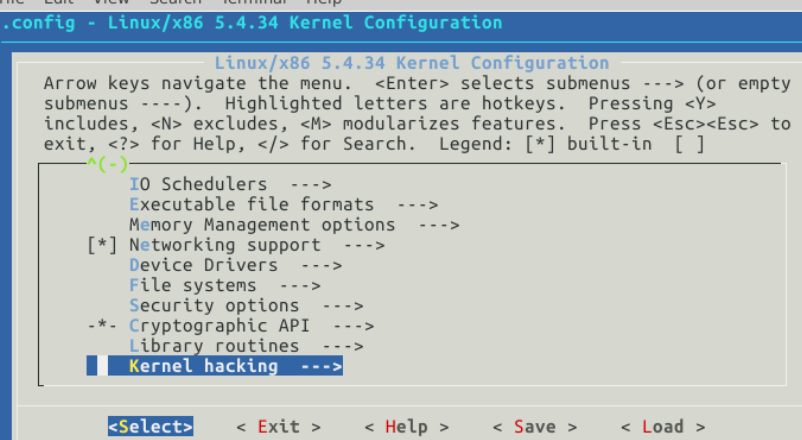
配置内核编译选项并编译内核
make defconfig # Default configuration is based on 'x86_64_defconfig' make menuconfig # 打开debug相关选项 Kernel hacking ---> Compile-time checks and compiler options ---> [*] Compile the kernel with debug info [*] Provide GDB scripts for kernel debugging [*] Kernel debugging # 关闭KASLR,否则会导致打断点失败 Processor type and features ----> [] Randomize the address of the kernel image (KASLR) make -j$(nproc) # nproc gives the number of CPU cores/threads available # 测试⼀下内核能不能正常加载运⾏,因为没有⽂件系统终会kernel panic qemu-system-x86_64 -kernel arch/x86/boot/bzImage # 此时应该不能正常运行
制作根文件系统
axel -n 20 https://busybox.net/downloads/busybox-1.31.1.tar.bz2 tar -jxvf busybox-1.31.1.tar.bz2 cd busybox-1.31.1 make menuconfig #记得要编译成静态链接,不⽤动态链接库。 Settings ---> [*] Build static binary (no shared libs) #然后编译安装,默认会安装到源码⽬录下的 _install ⽬录中。 make -j$(nproc) && make install
准备init脚本⽂件放在根⽂件系统跟⽬录下(rootfs/init),添加如下内容到init⽂件
#!/bin/sh mount -t proc none /proc mount -t sysfs none /sys echo "Welcome My OS!" echo "-------------------" cd home /bin/sh
给init脚本增加可执行权限
chmod +x init
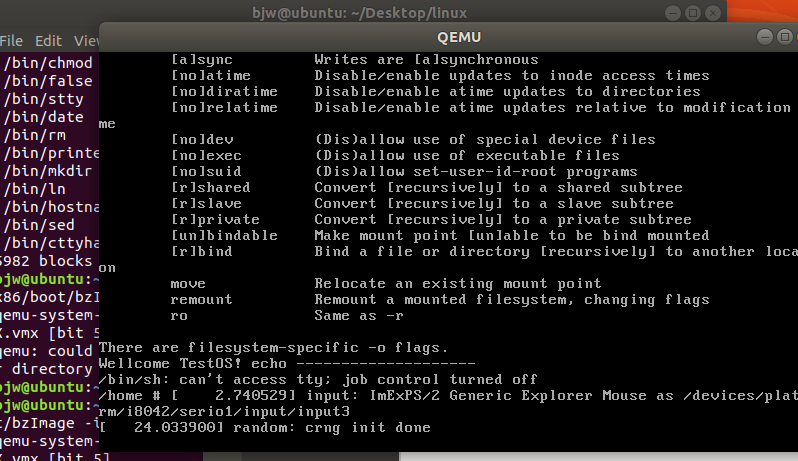
内核启动完成后执⾏init脚本
查看系统调用

95号为umask
内核处理函数为__x64_sys_umask
写一段代码调用
int main()
{
asm volatile(
"movl $0x5f,%eax\n\t"
"syscall\n\t" );
return 0;
}
跟踪调试Linux内核 启动gdb

查看调用堆栈 entry_SYSCALL_64是系统调用的入口,有保存现场,调用对应的内核处理函数、恢复现场、系统调用返回等功能

swapgs指令用于保存现场

rax存储了系统调用号。通过系统调用表调用相应的系统调用函数,然后将返回值存入rcx寄存器中
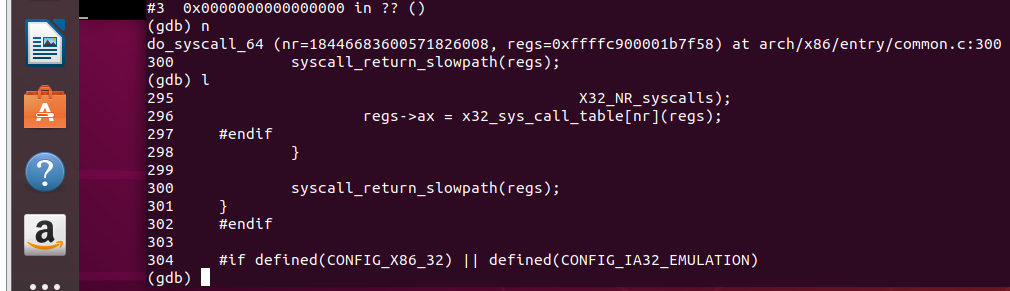
恢复现场

总结
在对应的系统调用入口entry_SYSCALL_64中,执行swapgs保存现场,然后do_syscall_64函数根据rax寄存器中的系统调用号找到对应的系统调用__x64_sys_umask,系统调用函数执行完毕后,返回ENTRY(entry_SYSCALL_64)方法,恢复现场。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号