C语言综合研究与高强度程序设计训练综合研究0
第一题
分别定义 char 型、int 型、long 型、float 型、double 型数据,并打印出各类型数据的值。
代码
void test01() {
int i_num = 1;
char c_num = 'H';
long l_num = 327688;
float f_num = 1.0e9;
double d_num = 2.4e9;
printf("\nint num : %d", i_num);
printf("\nchar num : %d", c_num);
printf("\nlong num : %ld", l_num);
printf("\nfloat num : %f", f_num);
printf("\ndouble num : %e", d_num);
}
结果:

第二题
题目
阅读以下材料,按步骤进行实践:
C 语言集成开发环境 Tc.exe 自带有调试功能。调试方法如下:
(1)表达式查看(快捷键 Ctrl+F7)在 Tc.exe 开发环境中的 Break/watch 菜单中添加
或者删除表达式查看。(2)断点操作(快捷键 Ctrl+F8)在 Tc.exe 开发环境中的 Break/watch 菜单中添加或
者删除断点。
(3)单步执行—不进入函数(快捷键 F8)。
(4)单步执行—进入函数(快捷键 F7)。
(5)执行到断点处(快捷键 Ctrl+F9)。
程序一实现的功能:从 0 到 19 中依次找到所有偶数并将这个偶数乘以 2 后得到的结果
打印到屏幕上。
过程
对于程序一进行如下调试:
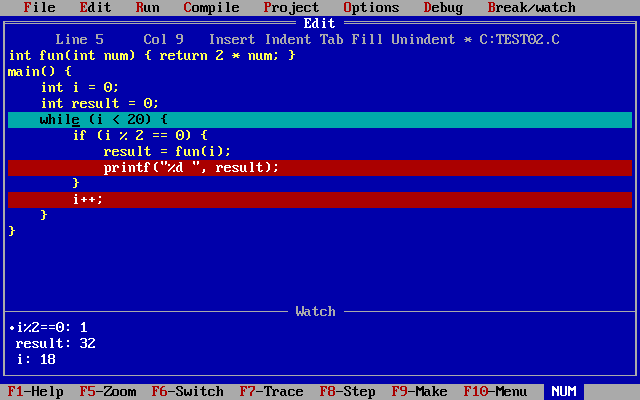
(1)添加对 i,result,i%2==0 的值的查看,然后用单步调试(F7,F8)查看这三者的值,
观察是否和自己预判的一样。
可以看到和预测结果一致
(2)在(1)中表达式查看的基础上,在 printf("%d ", result)和 i++两行处处添加断点(光
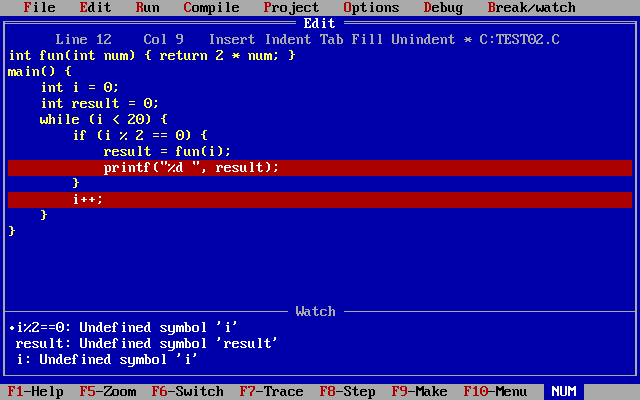
标置于这一行按下 Ctrl+F8 即可),然后按 Ctrl+F9 进行断点调试。查看 i,result,i%2==0
的值是否和自己预判的一样。
通过下图可以知道可自己预判的一致
添加完查看和断点
断点调试
第三题
题目
给定的一个班的 C 语言成绩为:
short results[] = {55, 80, 71, 72, 87, 90, 95, 100, 96, 87,
76, 100, 50, 83, 80, 65, 70, 69, 80, 88,
91, 98, 96, 76, 89};
将这些成绩进行统计,90 ~ 100 的为 A,80 ~ 89 的为 B,70 ~ 79 的为 C,60 ~ 69 的为
D,60 以下的为 E。
在屏幕上打印输出每个成绩段的人数,即最终输出应该为:
A:8
B:8
C:5
D:2
E:2
注:分别使用“if...else 语句”与“swith...case 语句”实现。
代码
void test03() {
short results[] = {55, 80, 71, 72, 87, 90, 95, 100, 96, 87,
76, 100, 50, 83, 80, 65, 70, 69, 80, 88,
91, 98, 96, 76, 89};
int res[5]={0};
//switch...case
for(int i = 0 ; i<(sizeof(results)/sizeof(results[0])) ; i++){
switch (results[i]/10) {
case 0:
case 1:
case 2:
case 3:
case 4:
case 5:res[4]++;break;
case 6:res[3]++;break;
case 7:res[2]++;break;
case 8:res[1]++;break;
case 9:
case 10:res[0]++;break;
default:printf("error val");
}
}
printf("\n switch...case");
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
printf("\n %c : %d",'A'+i,res[i]);
res[i]=0;
}
//if...else
for (int i = 0; i <(sizeof(results)/sizeof(results[0])) ; ++i) {
if((results[i]/10)<=5){
res[4]++;
} else if ((results[i]/10)<=6){
res[3]++;
} else if ((results[i]/10)<=7){
res[2]++;
} else if ((results[i]/10)<=8){
res[1]++;
} else if ((results[i]/10)<=10){
res[0]++;
} else{
printf("error val");
}
}
printf("\n if...else");
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
printf("\n %c : %d",'A'+i,res[i]);
res[i]=0;
}
};
结果

第四题
题目
在屏幕上输出一个九九乘法表。
注:分别使用 for 循环和 while 循环实现。
代码
void test04() {
printf("\n ***************** for ***************** \n");
for (int i = 1; i <= 9; ++i) {
for (int j = 1; j <= i; ++j) {
printf("%d*%d=%d \t",j,i,i*j);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n ***************** while ******************* \n");
int i = 1;
while (i<=9){
int j = 1;
while (j<=i){
printf("%d*%d=%d \t",j,i,i*j);
++j;
}
printf("\n");
++i;
}
}
结果

第五题
题目
用 if...else 语句与 goto 语句分别构造 while 循环结构和 do...while 循环结构。
while 循环结构:
int count = 0;
while(count < 10)
{
printf("%d ", count);
count++;
}
do...while 循环结构:
int count = 0;
do
{
count++;
printf("%d ", count++);
}
while(count < 10)
分析
do while 先执行一次循环,然后判断是否满足条件再决定是否 goto
while 先 goto 到 判断语句 然后判断是否满足条件再决定是否 goto
代码
void test05() {
printf("do..while\n");
int count = 0;
do_while_loop:
count++;
printf(" %d ", count++);
if (count < 10) {
goto do_while_loop;
}
printf("\n");
printf("while\n");
count = 0;
goto while_bg;
while_loop:
printf(" %d ", count++);
while_bg:
if (count < 10) {
goto while_loop;
}
}
结果

第六题
题目
改正程序二中出现的所有语法错误,让程序没有任何的错误和警告。
程序二:
void func1(char);
int func2(char);
main()
{
int c = 0;
for(c = 1; c <= 9; c++)
{
func1(c);
printf("%d ", c);
}
printf("\n");
func2(c);
}
int fun1(char x)
{
retrun x+0x30;
}
int fun2(int x) {
x = fun1(x);
printf("%x");
}
结果
- fun1(char)->func1(int)
- fun2->func2
- retrun->return
- fun2 中的
printf("%x")改为printf("%x",x);
第七题
设计一个子函数,实现交换两个变量的值。
注意:指针(*,&,...)的运用。
代码
void test07_subfun(int *a,int *b){
int tmp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = tmp;
}
void test07(){
int a=1,b=2;
printf("before exchange\n");
printf("a=%d , b=%d",a,b);
test07_subfun(&a,&b);
printf("\nafter exchange\n");
printf("a=%d , b=%d",a,b);
}
结果

第八题
设计一个包含学生语、数、外三科成绩的结构体。定义 3 个此类型的结构体变量来存储
下列数据:
Tom: 语文 109, 数学 120, 外语 130;
Jack: 语文 95, 数学 140, 外语 99;
Mary: 语文 130, 数学 100, 外语 140;
通过调用结构体变量的各个数据项来计算出他们每一个人的总分,并打印出来。
注意:结构体(struct,...)的运用。
代码
typedef struct{
float chinese;
float math;
float english;
}score;
void test08(){
score Tom={109,120,130},Jack={95,140,99},Mary={130,100,140};
printf("Tom: %f\n",Tom.chinese+Tom.english+Tom.math);
printf("Jack: %f\n",Jack.chinese+Jack.english+Jack.math);
printf("Mary: %f\n",Mary.chinese+Mary.english+Mary.math);
}
结果

第九题
char daytable[2][13]={
{0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31},
{0,31,29,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}
};
以上定义的是一年 12 个月每个月的天数,其中 daytable[0]表示平年每个月的天数,
daytable[1]表示闰年每个月的天数。
设计一个子函数:int day_of_year(int year, int month, int day){}将给定的 x 年 x 月 x 日转
化为 x 年中的第几天的表示形式。
提示:闰年判定公式(year%4 == 0 && year%100 !=0) || (year %400 == 0)
此判定公式为“真(1)”时是闰年,“假(0)”时为平年。
注意:数组、运算符(+,-,*,/,%,&&,||,...)的运用。
代码
int day_of_year(int year, int month, int day) {
char daytable[2][13] = {
{0, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31},
{0, 31, 29, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31}
};
if (month > 12 || day > 31 || day < 0 || year < 0) {
return 0;
} else {
//闰 平 年
// 1 闰
if ((year%4 == 0 && year%100 !=0) || (year %400 == 0)){
for (int i =0 ; i< month ; i++){
day += daytable[1][i];
}
} else{ // 0 平
for (int i =0 ; i< month ; i++){
day += daytable[0][i];
}
}
}
return day;
}
void test09() {
int day = day_of_year(2020,3,0);
printf("the %d day of %d",day,2020);
}
结果

第十题
运用 Turbo C 的调试方法找出程序三中存在的错误,并修正程序。
程序三定义了一个新的结构体类型 struct Date。功能实现为用户输入时间修改指令来修
改对应的年、月、日的值。
实验过程
- 在TC 中编译完后运行

- 可以看到与预期结果不相符
- 添加断点 和 对 data 的查看
- 运行到断点后,接着输入
m 10然后观察 data 的值是否正确
- 可以看到data的值为10表示输入数据正确
- 接下来看处理数据是否正确

- 可以发现data在传参是就发生错误
- 观察
setDate(&date, type, (int)&data); - 可以看到传递的为data的地址而不是data 修改 为
setDate(&date, type,data);然后在运行
- 可以看到值传递正确
- 编译链接生成可执行文件后运行可以正确执行预期功能



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号