注解
注解的作用
1) 不是程序本身,可以对程序作出解释。(这一点跟注释没什么区别)
2) 可以被其他程序(比如:编译器等)读取。(注解信息处理流程,是注解和注释的重大区别,如果没有注解信息处理流程,则注解毫无意义)
注解的格式
1) 注解是以”@注释名”在代码中存在,还可以添加一些参数值,例如@SuppressWarnings(value=”unchecked”)
注解在哪里使用
1) 可以附加在 package,class,method,field 等上面,相当于给它们添加了额外的辅助信息,我们可以通过反射机制编程实现对这些元素的访问。
内置的注解
1) @Override :标识方法是重写的方法
public class TestAnnotation { @Override public String toString() { return super.toString(); } }
2) @Deprecated :标识的方法不建议使用
public class TestAnnotation { @Deprecated public void show(){ Date d=new Date(); System.out.println(d.getYear()); } }
3) @SuppressWarnings:用来抑制编译时的警告信息 需要提供参数才能正常使用,这些参数都是已经定义好的,我们只需要选择就可以了。
deprecation 使用了过时的类或方法的警告
unchecked 执行了未检查的转换时的警告,如使用集合时未指定泛型
fallthrough 当在使用 switch 语句使用时发生穿透
path 在类路径、源文件路径等中有不存在路径的警告
serial 当 在 可 序 列 化 的 类 上 缺 少
serialVersionUID 定义时的警告
finally 任何 finally 子句不能完成时的警告
all 关于以上所有情况的警告
public class TestAnnotation { @SuppressWarnings("all") public void method(){ List list=new ArrayList(); } @SuppressWarnings(value={"unchecked","path"}) public static void main(String[] args) { new TestAnnotation().show(); } }
自定义注解
自定义注解的语法
使 用 @interface 定 义 自 定 义 注 解 时 , 自 动 继 承 了java.lang.annotation.Annotation 接口
1) @interface 用来声明一个注解
2) 其中的每一个方法实际上是声明了一个配置参数
a) 方法的名称就是参数的名称
b) 返回值类型就是参数类型(返回值类型只能是基本类型、Class、String、enum)
c) 可以通过 default 来声明参数的默认值
d) 如果只有一个成员,一般参数名为 value
注意事项:注解元素必须要有值。我们定义注解元素时,经常使用空字符串,0 作为默认值。也经常使用负数(比如-1)表示不存在的含义
元注解
元注解的作用就是负责注解其他注解。在 Java 中定义了 4个标准的 meta-annotation 类型,它们被用来提供对其它annotation(注解) 类型作说明
这些类型和它们所支持的类在 java.lang.annotation 包中可以找到
1) @Target(目标)
2) @Retention(保留)
3) @Documented(记录)
4) @Inherited(继承)
@Target
作用:用于描述注解的使用范围(即被描述的注解可以用在什么地方)
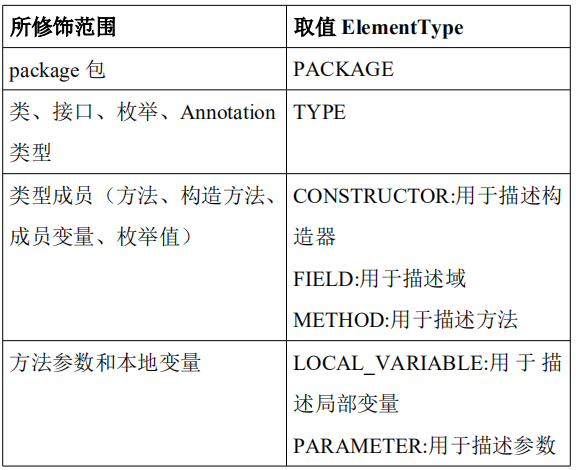
举例:
@Target(value=ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention
作用:表示需要在什么级别保存该注解信息,用于描述注解的生命周期
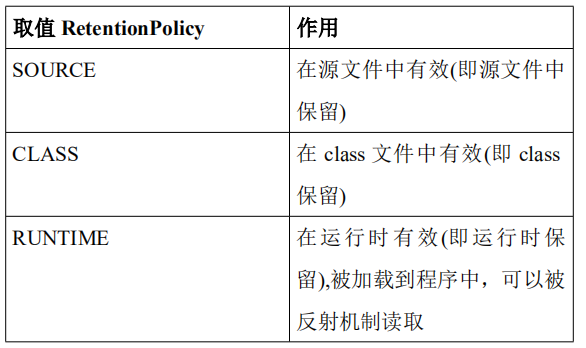
创建一个自定义注解
1 import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; 2 import java.lang.annotation.Retention; 3 import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; 4 import java.lang.annotation.Target; 5 6 @Target(ElementType.METHOD) 7 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) 8 public @interface MyAnnotation { 9 String stuName() default ""; 10 int age() default 0; 11 String [] school () default {"清华大学","北京大学"}; 12 }
如果自定义注解只有一个方法,则名字建议使用value
1 import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; 2 import java.lang.annotation.Retention; 3 import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; 4 import java.lang.annotation.Target; 5 6 @Target({ElementType.TYPE,ElementType.METHOD}) 7 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) 8 public @interface MyAnnotation2 { 9 String value(); 10 }
使用自定义注解
//@MyAnnotation 该注解只能应用到方法上 //@MyAnnotation2(value="aaaa") @MyAnnotation2("aaa") public class Test { @MyAnnotation(stuName="张小三") public void show(){ } @MyAnnotation(stuName="王一一",age=23,school={"浙江大学","北京艺术学院"}) public void method(){ } }
反射读取注解信息
ORM (Object Relationship Mapping) 对象关系映射
写程序用 Java 来写,存数据用数据库存储
1) 类与表结构对应
2) 属性和字段对应
3) 对象和记录对应
使用注解完成类和表结构的映射关系
功能描述
将Java中的Student类使用第三方程序通过读取注解生成数据库中的表
实现步骤
1) 编写 Student 类
2) 编写注解
3) 在类中使用注解
4) 通过解析程序将注解读取出来 (通过框架解析)
5) 拼接 SQL 语句,使用 JDBC 到数据库中执行创建表
类注解

1 import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; 2 import java.lang.annotation.Retention; 3 import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; 4 import java.lang.annotation.Target; 5 6 @Target(ElementType.TYPE) //注解的使用范围 7 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) //在运行时起作用 8 public @interface SxtTable { 9 String value(); 10 }
属性注解

1 import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; 2 import java.lang.annotation.Retention; 3 import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; 4 import java.lang.annotation.Target; 5 6 @Target(ElementType.FIELD) 7 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) 8 public @interface SxtField {//属性的注解 9 String columnName(); //数据库中列的名称 10 String type(); //数据库中列的类型 11 int length(); //类型的长度 12 }
在类中使用注解

1 import com.bjsxt.annotation.SxtField; 2 import com.bjsxt.annotation.SxtTable; 3 4 @SxtTable("tb_student") 5 public class Student { 6 //私有属性 7 @SxtField(columnName="id",type="int",length=10) 8 private int id; 9 10 @SxtField(columnName="stuname",type="varchar",length=20) 11 private String stuName; 12 13 @SxtField(columnName="age",type="int",length=10) 14 private int age; 15 16 17 public int getId() { 18 return id; 19 } 20 public void setId(int id) { 21 this.id = id; 22 } 23 public String getStuName() { 24 return stuName; 25 } 26 public void setStuName(String stuName) { 27 this.stuName = stuName; 28 } 29 public int getAge() { 30 return age; 31 } 32 public void setAge(int age) { 33 this.age = age; 34 } 35 public Student(int id, String stuName, int age) { 36 super(); 37 this.id = id; 38 this.stuName = stuName; 39 this.age = age; 40 } 41 public Student() { 42 super(); 43 } 44 45 }
解析

1 import java.lang.annotation.Annotation; 2 import java.lang.reflect.Field; 3 4 import com.bjsxt.annotation.SxtField; 5 import com.bjsxt.annotation.SxtTable; 6 7 public class Test { 8 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 9 //(1)创建Student类的Class对象 10 Class clazz=Class.forName("com.chb.entity.Student"); 11 //(2)得到Student类的所有注解 12 Annotation [] annotations=clazz.getDeclaredAnnotations(); 13 for (Annotation a : annotations) { 14 System.out.println(a); 15 } 16 System.out.println("\n----------------------------"); 17 //(3)获取指定的注解 18 SxtTable st=(SxtTable) clazz.getDeclaredAnnotation(SxtTable.class); 19 System.out.println(st); 20 System.out.println("\n----------------------------"); 21 22 //(4)获取属性的注解 23 24 Field field=clazz.getDeclaredField("stuName"); 25 SxtField sf=field.getDeclaredAnnotation(SxtField.class); 26 System.out.println(sf.columnName()+"--"+sf.type()+"--"+sf.length()); 27 28 /**拼接SQL语句 DDL ,使用JDBC在数据库中执行,创建出了一张表,tb_student,表中的列就为id,stuname,age*/ 29 30 } 31 }




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号