2022-2-12剑指offer day2
题1:
输入一个链表的头节点,从尾到头反过来返回每个节点的值(用数组返回)。
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,3,2] 输出:[2,3,1]
限制:
0 <= 链表长度 <= 10000
1 /** 2 * Definition for singly-linked list. 3 * public class ListNode { 4 * int val; 5 * ListNode next; 6 * ListNode(int x) { val = x; } 7 * } 8 */ 9 class Solution { 10 11 // public int[] reversePrint(ListNode head) { 12 // List<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>(); 13 // while (head!=null) { 14 // list.add(head.val); 15 // head=head.next; 16 // } 17 // int n=list.size(); 18 // int[] a=new int[n]; 19 // for (int i=n-1;i>=0;i--) a[i]=list.get(n-i-1); 20 // return a; 21 // } 22 23 24 public int[] reversePrint(ListNode head) { 25 if (head==null) return new int[]{}; 26 int[] a=reversePrint(head.next); 27 int[] res=new int[a.length+1]; 28 res[res.length-1]=head.val; 29 for (int i=0;i<a.length;i++) { 30 res[i]=a[i]; 31 } 32 return res; 33 } 34 }
思路:方法1,递归,将当前节点拼在新的数组后面。方法二,遍历链表,倒序填充在数组中。
题2:
定义一个函数,输入一个链表的头节点,反转该链表并输出反转后链表的头节点。
示例:
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL 输出: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL
限制:
0 <= 节点个数 <= 5000
1 /** 2 * Definition for singly-linked list. 3 * public class ListNode { 4 * int val; 5 * ListNode next; 6 * ListNode(int x) { val = x; } 7 * } 8 */ 9 class Solution { 10 public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) { 11 // 如果head空或者下一个为空直接返回head 12 if (head==null||head.next==null) return head; 13 // 记录当前节点的下一个 14 ListNode temp=head.next; 15 // 除当前节点外 反转后的头节点 16 ListNode tail=reverseList(head.next); 17 // 将原来节点的反转 18 temp.next=head; 19 // 新的结尾加上null 20 head.next=null; 21 return tail; 22 } 23 24 25 }
思路: 递归。具体见注释。
题3:
请实现 copyRandomList 函数,复制一个复杂链表。在复杂链表中,每个节点除了有一个 next 指针指向下一个节点,还有一个 random 指针指向链表中的任意节点或者 null。
示例 1:
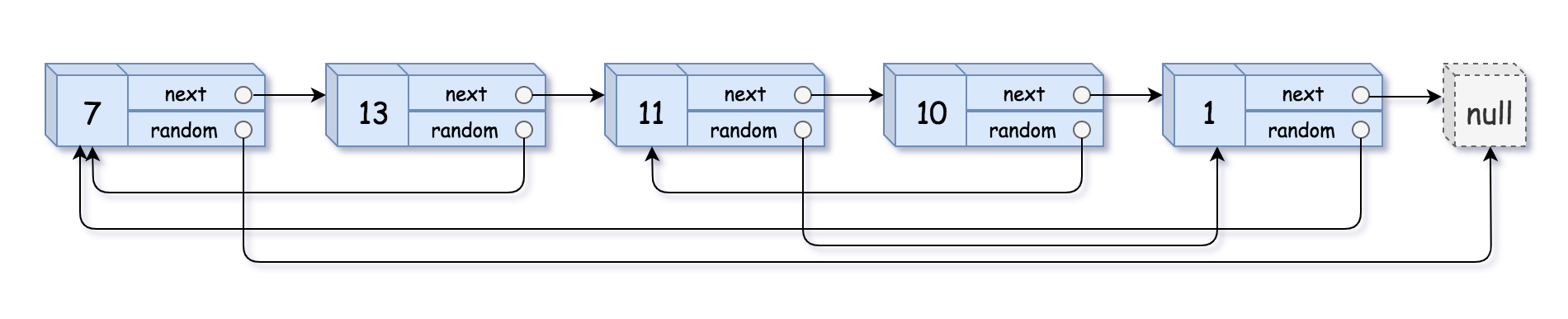
输入:head = [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]] 输出:[[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
示例 2:
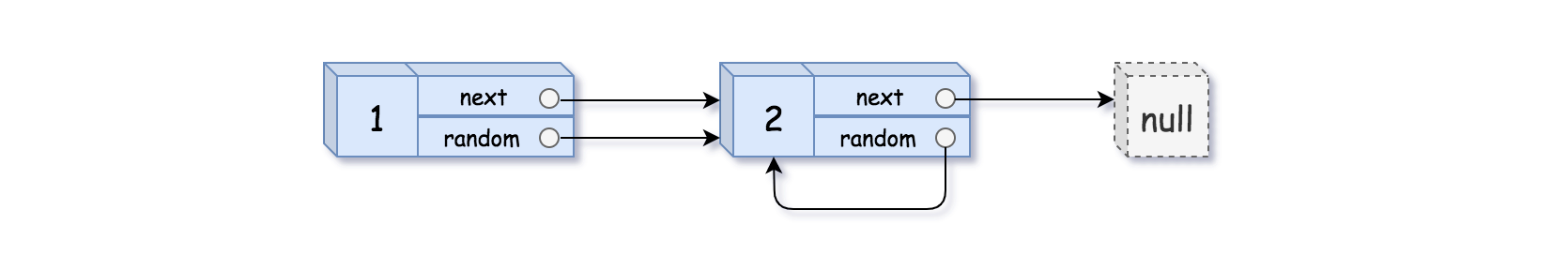
输入:head = [[1,1],[2,1]] 输出:[[1,1],[2,1]]
示例 3:
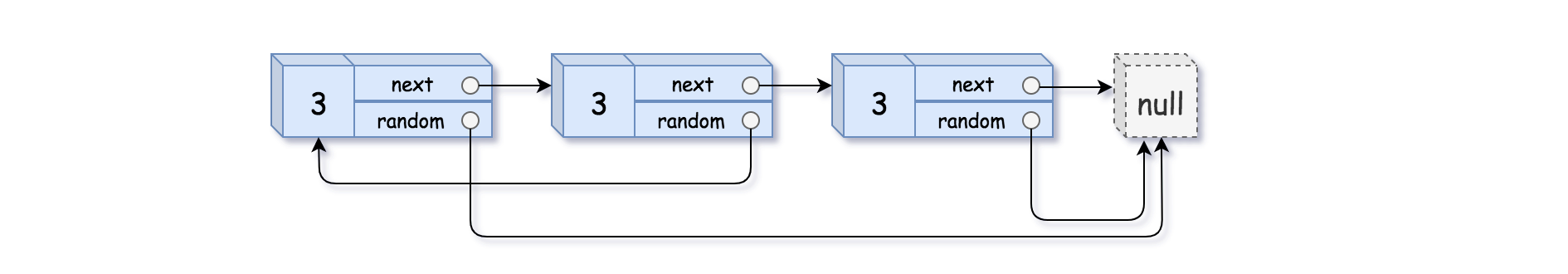
输入:head = [[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]] 输出:[[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
示例 4:
输入:head = [] 输出:[] 解释:给定的链表为空(空指针),因此返回 null。
提示:
-10000 <= Node.val <= 10000Node.random为空(null)或指向链表中的节点。- 节点数目不超过 1000 。
1 /* 2 // Definition for a Node. 3 class Node { 4 int val; 5 Node next; 6 Node random; 7 8 public Node(int val) { 9 this.val = val; 10 this.next = null; 11 this.random = null; 12 } 13 } 14 */ 15 class Solution { 16 public Node copyRandomList(Node head) { 17 if (head==null) return head; 18 Node temp=head; 19 while (temp!=null) { 20 Node behind=temp.next; 21 Node cross=new Node(temp.val); 22 temp.next=cross; 23 cross.next=behind; 24 temp=behind; 25 } 26 temp=head; 27 while (temp!=null) { 28 if (temp.random!=null) temp.next.random=temp.random.next; 29 temp=temp.next.next; 30 } 31 Node dummy=head.next; 32 Node p1=head,p2=head.next; 33 while (p2.next!=null) { 34 p1.next=p1.next.next; 35 p2.next=p2.next.next; 36 p1=p1.next; 37 p2=p2.next; 38 } 39 p1.next=null; 40 return dummy; 41 } 42 }
思路:第一次遍历在原来的链表后面先添加一个相同的节点。第二次遍历,将新节点的ranbom复制到对应的新节点上。第三次遍历,将复制链表和原链表分开。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号