IO
创建文件
package file;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class demo1{
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file=new File("file.txt");//要创建File对象
try{
file.createNewFile();//用的是createNewFile()方法
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//在指定路径创建文件
package file;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class createFilesTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {//在指定路径创建不存在的file1.txt
File file=new File("E:\\Software Storage\\Edge download\\file1.txt");
try{
file.createNewFile();
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}

创建文件夹
package file;
import java.io.File;
public class createFilesTest{
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file=new File("E:\\test");//在E盘创建了不存在的test文件夹
if (file.mkdir()){//file.mkdir()就是创建单个文件夹的方法
System.out.println("The Directory is created");
}else {
System.out.println("Directory cannot be created");
}
}
}
//多级文件夹
File file=new File("E:\\test1\\test2\\test3");
if (file.mkdirs()){//file.mkdirs()就是创建多级文件夹的方法
System.out.println("Directories are created");
}else {
System.out.println("Directories cannot be created");
}
复制文件
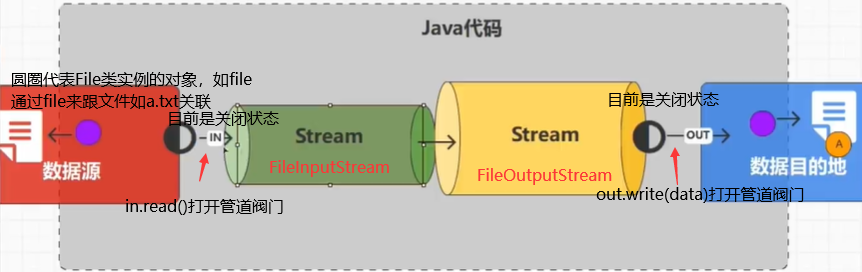
package Map;
import java.io.*;
public class demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//源文件对象
File srcFile = new File("D:\\Programme\\code\\JavaSE\\public\\a.txt");
//目的文件对象(自动生成)
File desFile = new File("D:\\Programme\\code\\JavaSE\\public\\b.txt");
FileInputStream in = null;//文件输入流(管道对象)
FileOutputStream out = null;//文件输出流(管道对象)
try{
in = new FileInputStream(srcFile);
out = new FileOutputStream(desFile);
//打开阀门,流转数据(输入)
int data = in.read();//读取源文件的一个字节的信息
//打开阀门,流转数据(输出)
out.write(data);//将信息写入目的文件
}catch (IOException e){
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
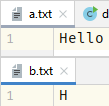
说明输入输出流管道的阀门在传输一个字节的信息后会自动关闭,所以需要用循环来传输完a.txt的信息
package Map;
import java.io.*;
public class demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//源文件对象
File srcFile = new File("D:\\Programme\\code\\JavaSE\\public\\a.txt");
//目的文件对象(自动生成)
File desFile = new File("D:\\Programme\\code\\JavaSE\\public\\b.txt");
FileInputStream in = null;//文件输入流(管道对象)
FileOutputStream out = null;//文件输出流(管道对象)
try {
in = new FileInputStream(srcFile);
out = new FileOutputStream(desFile);
int data = -1;//默认文件已读取完毕
while ((data = in.read()) != -1) {//in.read()当读取完最后一个数据还读取时会返回-1
out.write(data);
//read和write方法会打开输入和输出流管道的阀门
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
if (in != null) {//可能读取的是空指针,此时不应该关掉阀门
try {
in.close();//用完就关
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
if (out != null) {//可能读取的是空指针,此时不应该关掉阀门
try {
out.close();//用完就关
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
}
缓冲流
上面那种逐个字节读取再逐个字节写入的方式效率太低了,可以用缓冲流来提高效率。
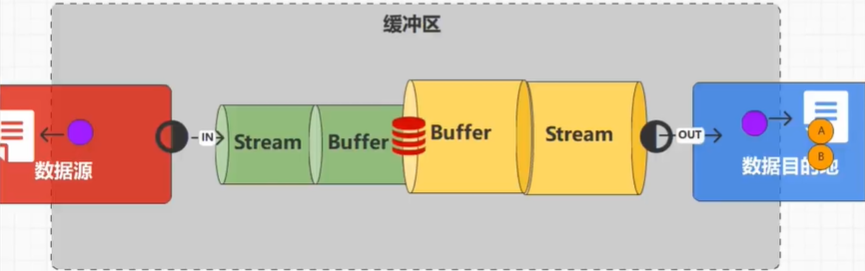
在输入流和输出流管道之前分别加个buffer输入流管道和buffer输出流管道
两个缓冲流管道中还有个缓冲区,像个红色的水桶,用来存放数据。一般用byte[]来定义这个缓冲区
默认大小是8192byte即8*1024byte即8kb
package Map;
import java.io.*;
public class demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//源文件对象
File srcFile = new File("D:\\Programme\\code\\JavaSE\\public\\a.txt");
//目的文件对象(自动生成)
File desFile = new File("D:\\Programme\\code\\JavaSE\\public\\b.txt");
FileInputStream in = null;//文件输入流(管道对象)
FileOutputStream out = null;//文件输出流(管道对象)
BufferedInputStream bufferIn = null;//缓冲输入流(管道对象)
BufferedOutputStream bufferOut = null;//缓冲输出流(管道对象)
try {
in = new FileInputStream(srcFile);
out = new FileOutputStream(desFile);
bufferIn = new BufferedInputStream(in);//对接文件输入流管道
bufferOut = new BufferedOutputStream(out);//对接文件输出流管道
byte[] cache = new byte[1024];//缓冲区(水桶),容量设为1024byte
int data = -1;//默认文件已读取完毕
/*先把读到的数据放进缓冲区cache中,read()当读取完最后一个数据还读取时会返回-1*/
while ((data = bufferIn.read(cache)) != -1) {
bufferOut.write(cache,0,data);
/*再把缓冲区的数据写入目的文件,从第一个字节开始写,直到写到data的长度为止
就是水桶还没装满,只装了一半,这时不应该从头写入到尾。应该写到一半(长度为data)就停
*/
//read和write方法会打开输入和输出流管道的阀门
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
if (bufferIn != null) {//可能读取的是空指针,此时不应该关掉阀门
try {
bufferIn.close();//用完就关
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
if (bufferOut != null) {//可能读取的是空指针,此时不应该关掉阀门
try {
bufferOut.close();//用完就关
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
}
采用缓冲流读写文件的效率更为高效,原本读写大小为100的文件,需要交互100次
而现在用缓冲流(假设水桶大小设为20)读写,只需要交互5次。
FileInputStream的in阀门从源文件中读取20个byte到水桶cache中才关闭阀门,水桶满了后,
FileOutputStream的out阀门会从cache中写入20byte到目的文件,然后关闭阀门
再次FileInputStream读取20byte到cache中,FileOutputStream写入20byte到目的文件,共循环5次
字符流
我们读取文件之后最常见的操作其实是字符串操作,而不是一个个字节的操作。比如源文件的内容是Hello,我们想添加内容zhangsan
肯定是把字符串加上去更合理,而不是一个个字节传输过去。
一个个字节传输可以做到,将字符串转换成字节数组,再将数组中的每一个字节写入到文件中。
字符管道对象就提供了更便捷的操作,操作字符而不是字节
package Map;
import java.io.*;
public class demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//源文件对象
File srcFile = new File("D:\\Programme\\code\\JavaSE\\public\\a.txt");
//目的文件对象(自动生成)
File desFile = new File("D:\\Programme\\code\\JavaSE\\public\\b.txt");
BufferedReader reader = null;//字符输入流(管道对象)
PrintWriter writer = null;//字符输出流(管道对象)
// PrintWriter与BufferedWriter类似且效果更好
try {
//通过字符的方式读取文件
reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(srcFile));//BufferedReader需要传FileReader对象的
writer = new PrintWriter(desFile);
//开启阀门,输入数据
//读取源文件中一行的数据(字符串)
String line = null;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
/*readLine()返回一行的字符串,如果结果不为空说明还在读取数据*/
writer.println(line);//放到字符输出管道
System.out.println(line);
/*
Hello
world
而不是ascii码*/
}
//刷写数据
writer.flush();//不管满没满都把数据写入目的文件
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
if (reader != null) {//可能读取的是空指针,此时不应该关掉阀门
try {
reader.close();//用完就关
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
if (writer != null) {//可能读取的是空指针,此时不应该关掉阀门
writer.close();
}
}
}
}
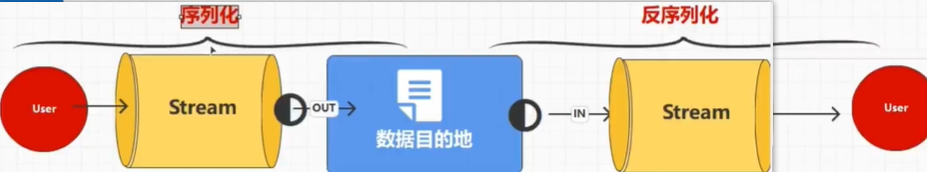
序列化
字符串能进行文件读写是因为字符串底层是字符,而字符能用字节来表示。
对象也可以,类在编译后叫字节码文件,类编译后才能构建对象,即对象在内存中存储的也是字节
要想把对象写入文件中和从文件中取出对象,需要通过对象流管道实现
如果把内存中的对象通过管道写到文件当中,即把对象变成字节,这个过程称作序列化
而把字节变成对象的过程称为反序列化
package Map;
import java.io.*;
public class demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//数据文件对象
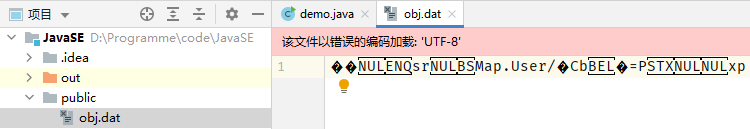
File file = new File("D:\\Programme\\code\\JavaSE\\public\\obj.dat");
//对象输出流(管道对象)
ObjectOutputStream objOut = null;//类和对象分开写是为了抛出异常
FileOutputStream out = null;
//对象输入流(管道对象)
ObjectInputStream objIn = null;
FileInputStream in = null;
try {
out = new FileOutputStream(file);
objOut = new ObjectOutputStream(out);//需要传入文件输出对象
User user = new User();//要序列化的对象
objOut.writeObject(user);//把对象写入对象输出管道
objOut.flush();//将管道的数据写入文件中
in = new FileInputStream(file);
objIn = new ObjectInputStream(in);//对接管道,图少画了文件的输入/出管道
try {
Object o = objIn.readObject();//从文件中读取出对象
System.out.println(o);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {//不知道对象的类型
e.printStackTrace();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
if (objOut != null) {//可能读取的是空指针,此时不应该关掉阀门
try {
objOut.close();//用完就关
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
}
class User implements Serializable{//实现了Serializable接口的类才能被序列化
}

重命名文件/文件夹
//相同目录下命名文件
package file;
import java.io.File;
public class reNameFilesTest{
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file=new File("E:\\a\\file1.txt");
File NewFile=new File("E:\\a\\file2.txt");
file.renameTo(NewFile);
//1.如果a目录不存在,则返回false。
//2.如果file1.txt不存在,则返回false。
//3.如果file1.txt、file2.txt都存在,则返回false。
//4.如果file1.txt存在,file2.txt不存在,则返回true,成功执行。
}
}
//不同目录下重命名文件
package file;
import java.io.File;
public class reNameFilesTest1{
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file=new File("E:\\a\\file1.txt");
File NewFile1=new File("D:\\b\\file3.txt");
file.renameTo(NewFile1);
//1.如果a、b目录不存在,则返回false。
//2.如果file1.txt不存在,则返回false。
//3.如果file1.txt、file3.txt都存在,则返回false。
//4.如果a、b目录存在,file1.txt存在,file3.txt不存在,则返回true,成功执行。
// 并且file1.txt会移动到D:\b\,重命名为file3.txt。
}
}
//相同目录下重命名文件夹
package file;
import java.io.File;
public class reNameFoldersTest{
public static void main(String[] args) {
File folder=new File("E:\\a\\a1");
File folder1=new File("E:\\a\\a2");
folder.renameTo(folder1);
//1.如果a目录不存在,则返回false。
//2.如果a1目录不存在,则返回false。
//3.如果a1、a2目录都存在,则返回false。
//4.如果a1存在,a2不存在,则返回true,成功执行。
//不同目录下重命名文件夹,只能在同一盘符下运行
package file;
import java.io.File;
public class createFilesTest{
public static void main(String[] args) {
File folder=new File("E:\\a\\a1");
File folder2=new File("E:\\b\\b2");
folder.renameTo(folder2);
//1.如果a、b目录不存在,则返回false。
//2.如果a1不存在,则返回false。
//3.如果a1、b2都存在,则返回false。
//4.如果a、b目录存在,a1存在,b2不存在,则返回true,成功执行。
// 并且a1会移动到E:\b\,重命名为b2。
}
}
}
}
编辑文件
package file;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {//FileWriter创建对象也要在try中进行
FileWriter writer=new FileWriter("file.txt");
writer.write("hello world");//write()方法
writer.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
读取文件内容
package file;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class demo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try{
File file=new File("file.txt");
Scanner scanner=new Scanner(file);//扫描file的内容
while (scanner.hasNextLine()){
String content=scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println(content);
}
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
读取文件信息
package file;
import java.io.File;
public class demo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file=new File("file.txt");
if (file.exists()){
System.out.println("File Name:"+file.getName());
System.out.println("File AbsolutePath:"+file.getAbsolutePath());
System.out.println("Readable:"+file.canRead());
System.out.println("Writeable:"+file.canWrite());
System.out.println("File Size:"+file.length());
}else {
System.out.println("The File does not exist");
}
}
}
读取文件夹信息
package file;
import java.io.File;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class showFiles {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file=new File("E:\\a");
//用数组方法获取当前目录下的所有文件及文件夹的绝对路径
File[] fs = file.listFiles();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(fs));
System.out.println("=========================================");
//用增强for循环获取当前目录下的所有文件及文件夹的绝对路径
File[] fss = file.listFiles();
for (File f : fss){
System.out.println(f);
}
System.out.println("=========================================");
//获取当前目录下的所有文件及文件夹,不带绝对路径
String[] fsss = file.list();
for (String f : fsss){
System.out.println(f);
}
}
}
删除文件
package file;
import java.io.File;
public class demo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file=new File("file.txt");
if (file.delete()){//删除对象的文件或者空文件夹
System.out.println(file.getName()+" is deleted");
}else {
System.out.println("Failed to delete the file");
}
}
}
实例
package file;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class demo {
private static final Scanner scanner1=new Scanner(System.in);//全局化
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sw=0;
boolean flag1=true;
boolean flag2=true;
txt();
while(flag1){
System.out.print("请输入对应数字:");
if (scanner1.hasNextInt()){
sw=scanner1.nextInt();
switch (sw){
case 1:
createFile();
break;
case 2:
editFile();
break;
case 3:
readFileContent();
break;
case 4:
readFileInformation();
break;
case 5:
deleteFile();
break;
case 0:
flag1=false;
scanner1.close();
System.out.println("已退出");
System.exit(0);//退出程序
break;
default:
System.out.println("输入错误");
break;
}
scanner1.nextLine();
System.out.print("是否继续?Y/N:");
String choose=scanner1.nextLine();
while(flag2){
if (choose.equals("n")||choose.equals("N")){//不可以choose=="n"
scanner1.close();
System.out.println("已退出");
flag1=false;
break;
}else if (choose.equals("y")||choose.equals("Y")){
txt();
break;
}else{
System.out.print("输入错误,是否继续?Y/N:");
choose=scanner1.nextLine();
}
}
}else {
System.out.println("输入错误,请重试。");
}
}
}
//文本
public static void txt(){
System.out.println("============");
System.out.println(" 操作 |按键");
System.out.println("创建文件| 1");
System.out.println("编辑文件| 2");
System.out.println("读取内容| 3");
System.out.println("读取信息| 4");
System.out.println("删除文件| 5");
System.out.println("退出操作| 0");
System.out.println("============");
}
//创建文件
public static void createFile(){
File file1=new File("file1.txt");
try {
file1.createNewFile();
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//编写文件
public static void editFile(){
try{
FileWriter write_file1=new FileWriter("file1.txt");
scanner1.nextLine();
System.out.print("请输入内容:");
String i=scanner1.next();
write_file1.write(i);
write_file1.close();
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//读取文件
public static void readFileContent(){
//读取内容
try{
File file1=new File("file1.txt");
Scanner scanner=new Scanner(file1);
if (scanner.hasNextLine()){
while (scanner.hasNextLine()){
String information=scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println(information);
}
scanner.close();
}else {
System.out.println("无信息");
}
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void readFileInformation(){
//读取信息
File file1=new File("file1.txt");
if (file1.exists()){
System.out.println("File Name:"+file1.getName());
System.out.println("Absolute Path:"+file1.getAbsolutePath());
System.out.println("Writeable:"+file1.canWrite());
System.out.println("Readable:"+file1.canRead());
System.out.println("File Size:"+file1.length());
}else{
System.out.println("The File is not exist");
}
}
//删除文件
public static void deleteFile(){
File file1=new File("file1.txt");
if (file1.delete()){
System.out.println(file1.getName()+" is deleted");
}else{
System.out.println("Failed to delete the file");
}
}
}





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号