实验2
实验任务1
代码
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<time.h>
#define N 5
#define N1 80
#define N2 35
int main()
{
int cnt;
int random_major, random_no;
srand(time(NULL));
cnt = 0;
while (cnt < N)
{
random_major = rand() % 2;
if (random_major)
{
random_no = rand() % N1 + 1;
printf("20256343%04d\n", random_no);
}
else
{
random_no = rand() % N2 + 1;
printf("20256136%04d\n", random_no);
}
cnt++;
}
return 0;
}
运行截图
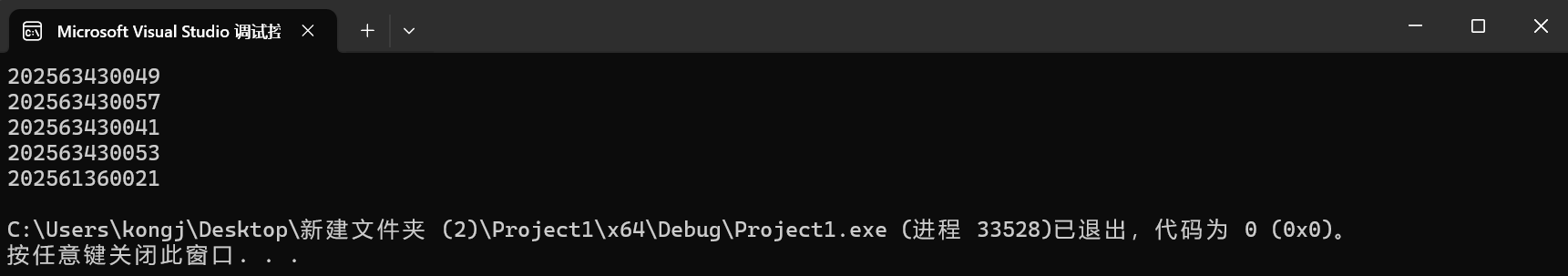
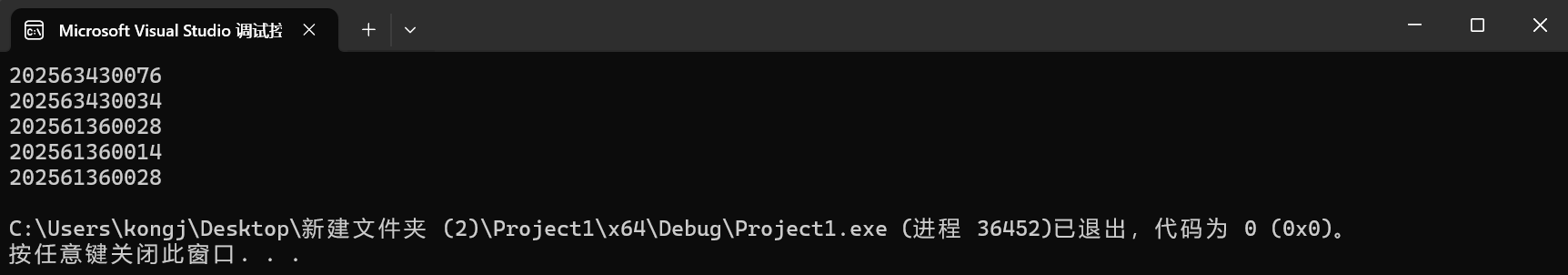
问题
问题1
保证每次运行得到的结果不同
问题2
随机在班级(网安和计科)内抽五名学生的学号(不过计科应该是2025631600xx而不是2025613600xx)
实验任务2
代码
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int choice, quantity;
float total_price = 0, amount_paid, change;
while (1)
{
printf("\n自动饮料售卖机菜单:\n");
printf("1.可乐-3元/瓶\n");
printf("2.雪碧-3元/瓶\n");
printf("3.橙汁-5元/瓶\n");
printf("4.矿泉水-2元/瓶\n");
printf("0.退出购买流程\n");
printf("请输入饮料编号:");
scanf("%d", &choice);
if (choice == 0)
break;
if (choice < 1 || choice>4)
{
printf("无效的饮料编号,请重新输入。\n");
continue;
}
printf("请输入购买数量:");
scanf("%d", &quantity);
if (quantity < 0)
{
printf("购买数量不能为负数,请重新输入。\n");
continue;
}
if (choice == 1 || choice == 2)
total_price += 3 * quantity;
else if (choice == 3)
total_price += 5 * quantity;
else
total_price += 2 * quantity;
printf("请投入金额:");
scanf("%f", &amount_paid);
change = amount_paid - total_price;
printf("本次购买总价:%.2f元\n", total_price);
printf("找零:%.2f元\n", change);
total_price = 0;
}
printf("感谢您的购买,欢迎下次光临!\n");
return 0;
}
运行截图
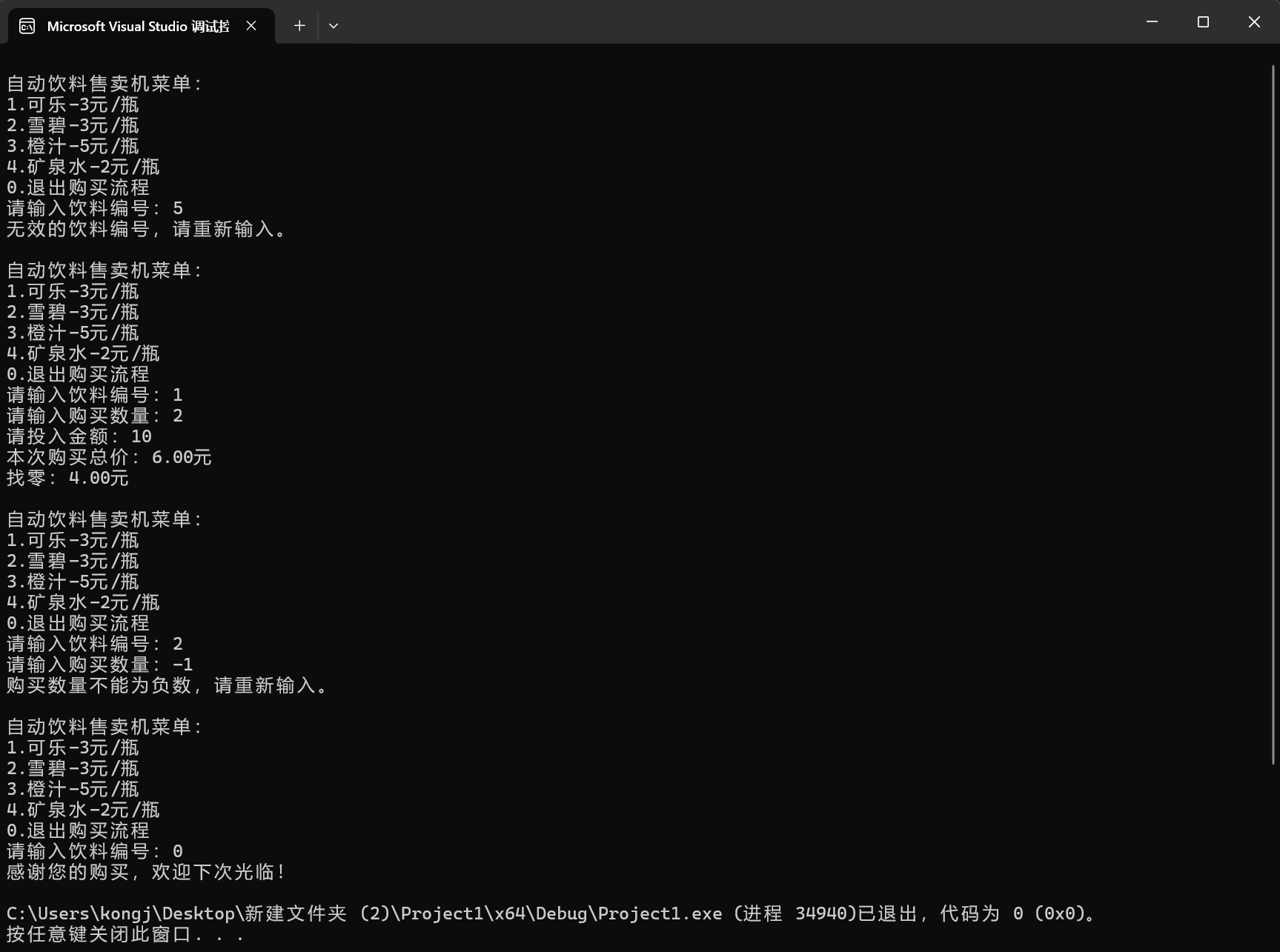
问题
问题1
如果去掉,那么第二次实际的总价就是第一次的总价和第二次理论上的总价之和,和我们想要的售货机的效果不符
问题2
终止此次循环开启下一次循环
实验任务3
代码
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
char ans;
while (scanf("%c", &ans) != EOF)
{
if (ans == 'r')
printf("stop!\n");
else if (ans == 'g')
printf("go go go\n");
else if (ans == 'y')
printf("wait a minute\n");
else
printf("something must be wrong...\n");
getchar();
}
return 0;
}
运行截图
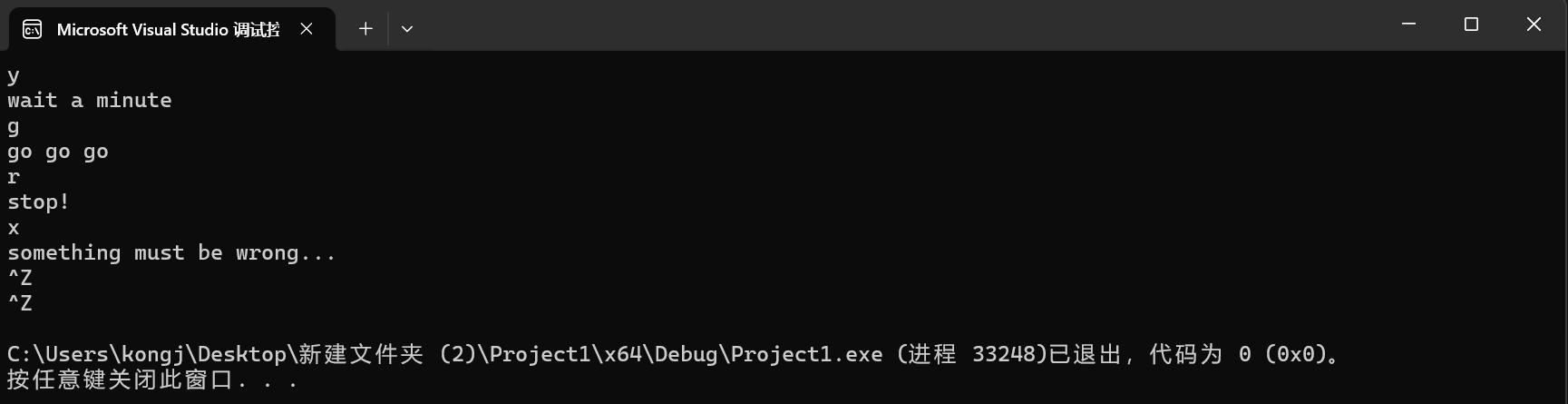
实验任务4
代码
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
double max, min, money, total;
max = 0;
min = 20000;
total = 0;
while (1)
{
scanf("%lf", &money);
if (money != -1)
{
if (money > max)
max = money;
if (money < min)
min = money;
total += money;
}
else
break;
}
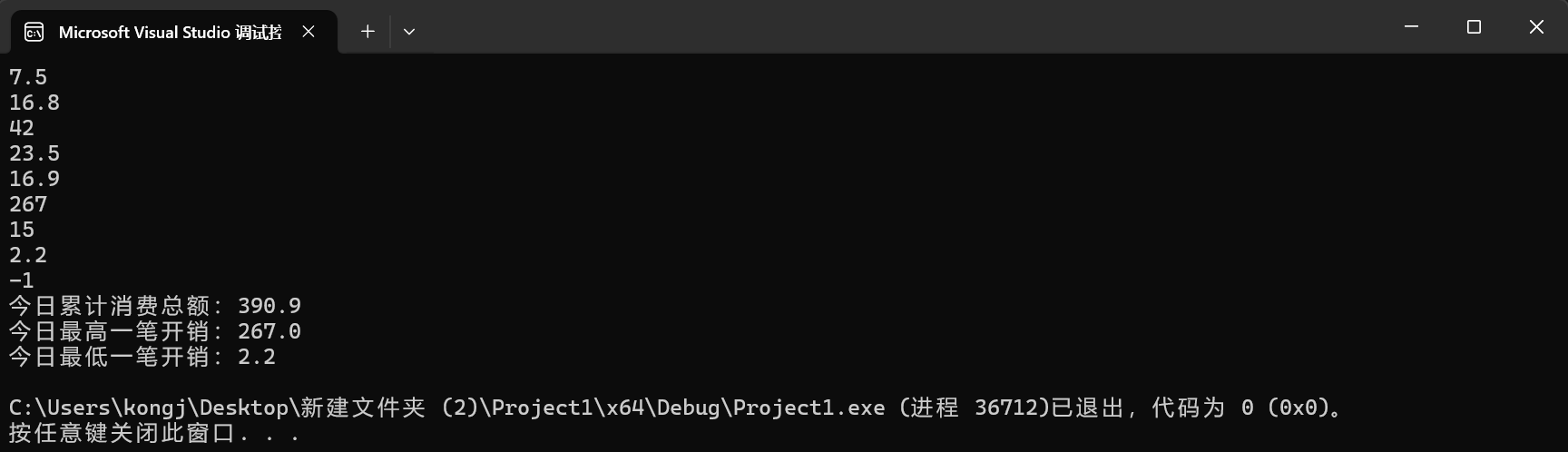
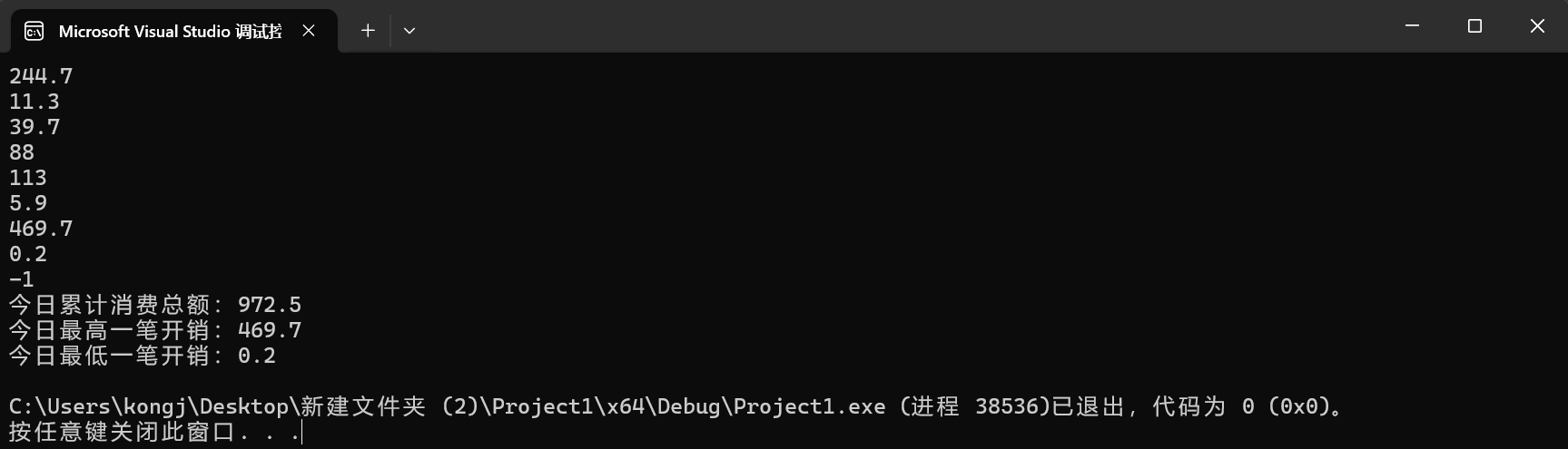
printf("今日累计消费总额:%.1f\n", total);
printf("今日最高一笔开销:%.1f\n", max);
printf("今日最低一笔开销:%.1f\n", min);
return 0;
}
运行截图
实验任务5
代码
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a, b, c;
while (scanf("%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c) != EOF)
{
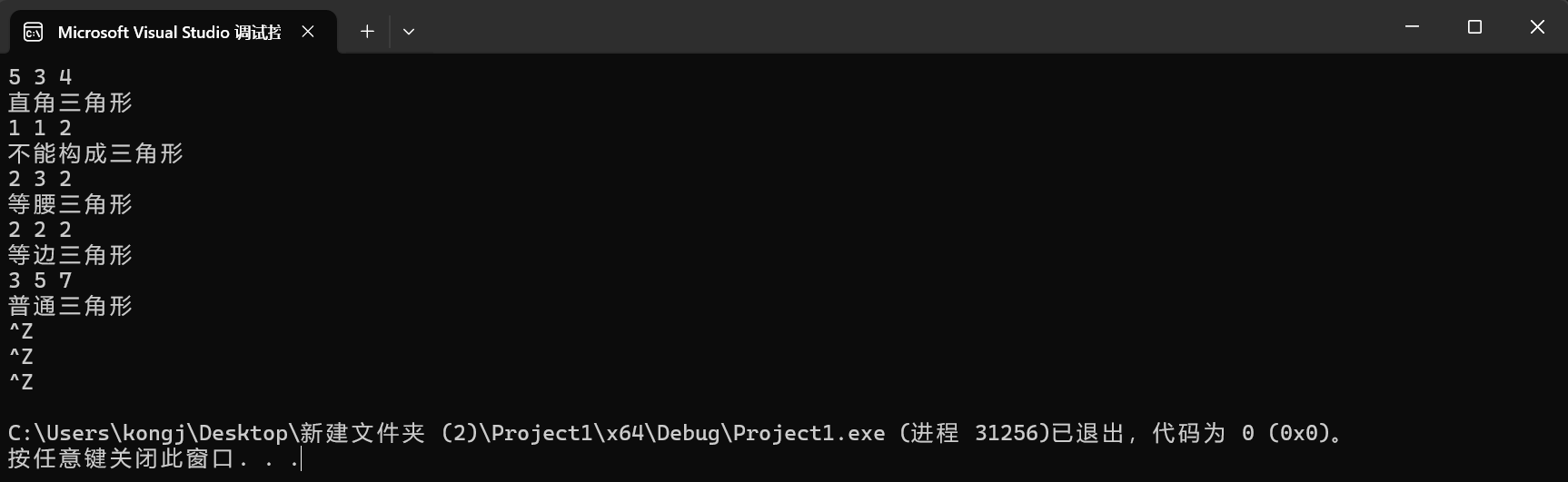
if (a + b <= c || a + c <= b || b + c <= a)
printf("不能构成三角形\n");
else if (a * a + b * b == c * c || a * a + c * c == b * b || b * b + c * c == a * a)
printf("直角三角形\n");
else if (a == b && b == c && a == c)
printf("等边三角形\n");
else if (a == b || b == c || a == c)
printf("等腰三角形\n");
else
printf("普通三角形\n");
}
return 0;
}
运行截图
实验任务6
代码
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<time.h>
int main()
{
int ans, ture, cnt;
srand(time(NULL));
ture = rand()%30+1;
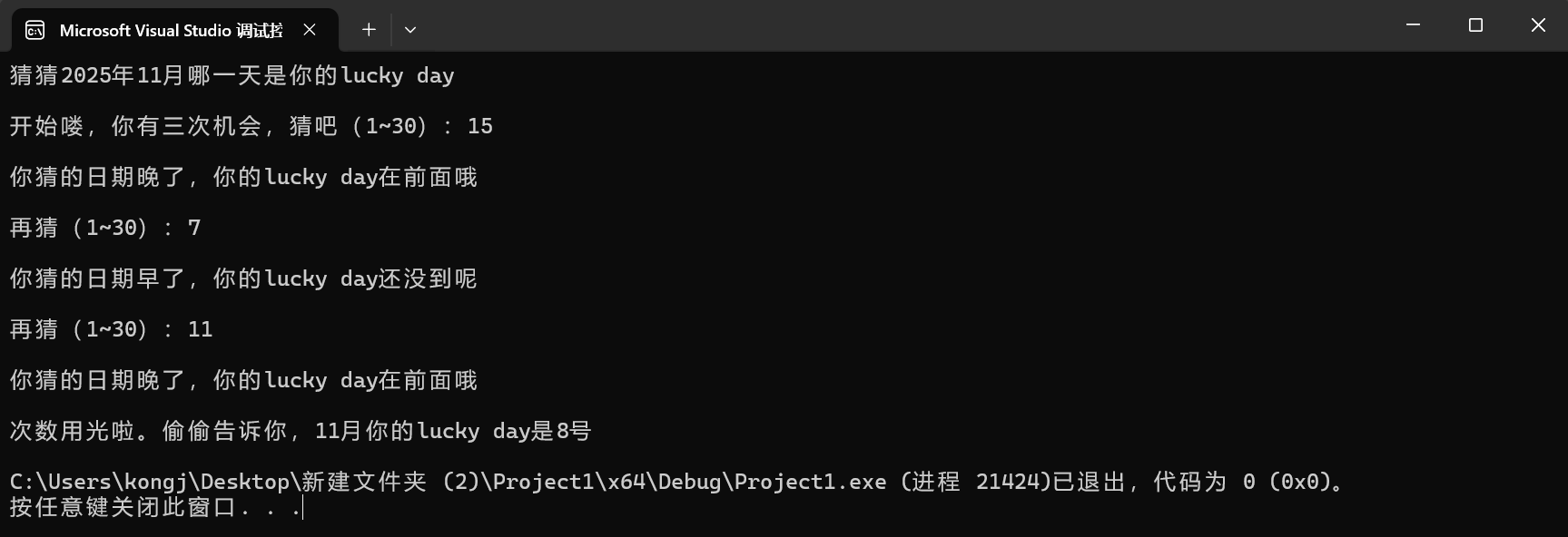
printf("猜猜2025年11月哪一天是你的lucky day\n");
printf("\n开始喽,你有三次机会,猜吧(1~30):");
scanf("%d", &ans);
cnt = 0;
while (cnt < 3)
{
if (ans == ture)
{
printf("\n哇,猜中了:)\n");
break;
}
else if (ans > ture)
printf("\n你猜的日期晚了,你的lucky day在前面哦\n");
else
printf("\n你猜的日期早了,你的lucky day还没到呢\n");
if (cnt == 2)
{
printf("\n次数用光啦。偷偷告诉你,11月你的lucky day是%d号\n", ture);
break;
}
printf("\n再猜(1~30):");
scanf("%d", &ans);
cnt += 1;
}
return 0;
}
运行截图




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号