流程控制
流程控制
- 分支结构
- while循环
一、流程控制即控制事物的执行流程
任何时候执行流程只有三种情况
1.顺序结构
自上而下依次运行
2.分支结构
在运行过程中根据条件的不同可能会执行不同的流程
3.循环结构
在运行过程中有些代码需要反复执行
二、必知必会
1.条件都会转成布尔值,从而决定子代码是否执行
2.在python中,使用缩进来表示代码的从属关系
3.并不是所有的代码都可以拥有子代码
4.同属于某个代码的多行子代码,必须要保持相同的缩进量
在python中推荐使用四个空格来缩进
ps:小技巧 上一行代码的结尾如果是冒号,那么下一行代码必缩进
三、分支结构
关键字:if
- 单if分支结构
if 条件:
条件成立之后执行的子代码块
# 如果年龄小于28,叫小姐姐
age = 36
if age < 28:
print('小姐姐好')
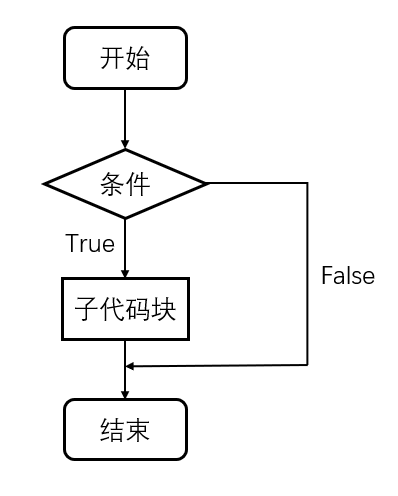
- if与else连用
if 条件:
条件成立之后执行的子代码块
else:
条件不成立的情况下执行的子代码块
ps:if与else连用,两者的子代码永远只会执行一个
# 如果年龄小于28,叫小姐姐,否则叫不好意思认错人了
age = 25
if age < 28:
print('小姐姐好')
else:
print('认错人了')

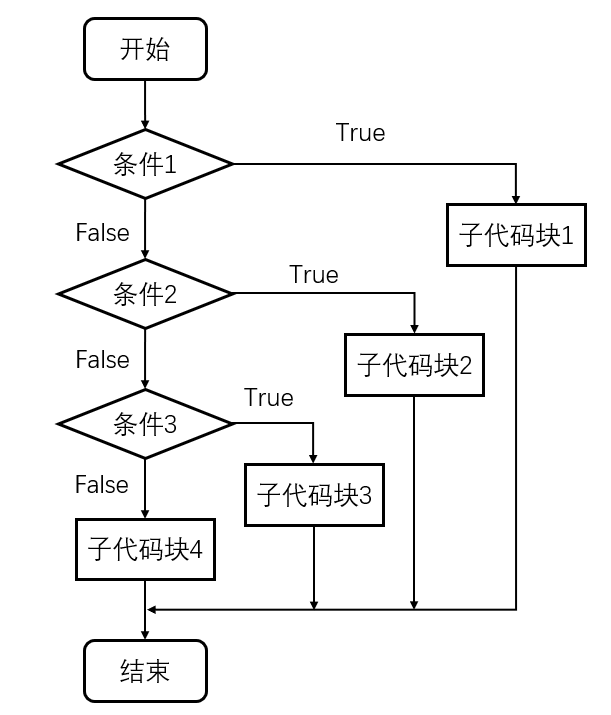
- if elif else三者连用
if 条件1:
条件1成立后执行的子代码块
elif 条件2:
条件1不成立,条件2成立之后执行的子代码块
elif 条件3:
条件1和2都不成立,条件3成立后执行的子代码块
...
else:
上述条件都不成立,执行的子代码块
# 根据成绩评判分类
# 大于90优秀,大于80良好,大于70一般,大于60及格,其他挂科
score = 79
if score > 90:
print('优秀')
elif score > 80:
print('良好')
elif score > 70:
print('一般')
elif score > 60:
print('及格')
else:
print('挂科')
- if判断嵌套
age = 26
height = 165
weight = 99
is_beautiful = True
is_success = True
if age < 28 and height > 160 and weight < 100 and is_beautiful:
print('小姐姐能否加个微信?')
# 判断小姐姐是否会给微信
if is_success:
print('吃饭 看电影')
else:
print('加微信失败')
else:
print('可惜了')
四、while循环
1.语法结果
while 条件:
条件成立之后循环执行的子代码块
while True:
# 1.获取用户输入的用户名和密码
username = input('username>>>:')
password = input('password>>>:')
# 2.判断用户名和密码是否正确
if username == 'jason' and password == '123':
print('欢迎')
else:
print('登陆失败')
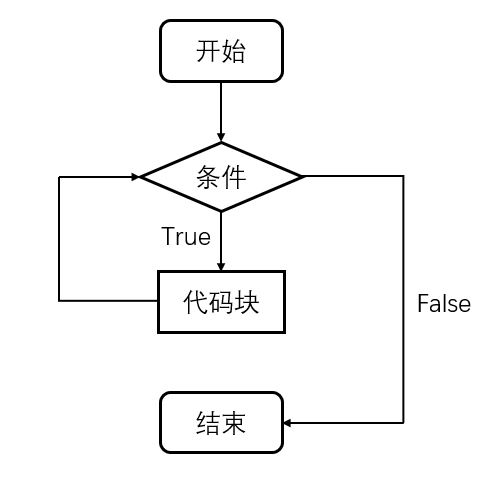
- while+break
break结束本层循环
while True:
# 1.获取用户输入的用户名和密码
username = input('username>>>:')
password = input('password>>>:')
# 2.判断用户名和密码是否正确
if username == 'jason' and password == '123':
print('欢迎')
# 直接结束本层循环
break
else:
print('登陆失败')
-
break本层的含义
while嵌套
while True:
# 1.获取用户输入的用户名和密码
username = input('username>>>:')
password = input('password>>>:')
# 2.判断用户名和密码是否正确
if username == 'jason' and password == '123':
print('欢迎')
while True:
cmd = input('请输入您的指令>>>:')
# 判断用户是否想退出
if cmd == 'q':
break
print('正在执行您的指令:%s' % cmd)
break
else:
print('登陆失败')
- 全局标志位
# 标志位的使用
flag = True
while flag:
# 1.获取用户输入的用户名和密码
username = input('username>>>:')
password = input('password>>>:')
# 2.判断用户名和密码是否正确
if username == 'jason' and password == '123':
print('欢迎')
while flag:
cmd = input('请输入您的指令>>>:')
# 判断用户是否想退出
if cmd == 'q':
flag = False
print('正在执行您的指令:%s' % cmd)
else:
print('登录失败')
-
猜年龄的游戏
普通要求
用户可以有三次猜错的机会,如果过程中猜对了就直接退出。
拔高要求
三次机会用完之后提示用户是否继续尝试,如果是则再给三次机会,如果否就直接结束。
real_age = '20'
count = 0
while count < 3:
age = input('请输入年龄:')
if age == real_age:
print('猜对了!')
break
else:
print('猜错了!')
count += 1
if count == 3:
answer = input('输入"y"继续尝试')
if answer == 'y':
print('继续')
count = 0
else:
print('结束')
-
while + continue
continue会让循环体代码直接回到条件判断处重新判断
# 1.一个起始变量 count = 0 # 2.循环 while count < 11: # 5.判断 如果count为4则不打印 if count == 4: count += 1 # 跳过本次循环 开始下一次循环 continue # 3.打印变量的值 print(count) # 4.变量值自增1 count += 1 -
while + else
当while循环没有被认为中断(break)的情况下才会走else
count = 0
while count < 5:
print(count)
count += 1
else:
print('啊啊啊') # 会执行else子代码
count = 0
while count < 5:
if count == 3:
break
print(count)
count += 1
else:
print('啊啊啊') # 不会执行else子代码
-
死循环
死循环会让CPU极度繁忙 甚至崩溃
while True:
print(1)


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号