day26-python-spider
day26-python-spider
python
线程
线程的分类:
- 内核线程:由操作系统内核创建和撤销
- 用户线程:不需要内核支持而在用户程序实现的线程
python中使用线程有两种方式
- 函数
- 用类来包装线程对象
函数
函数式:调用_thread模块中的start_new_thread()函数来产生新的线程
_thread.start_new_thread(function,args[,kwargs])
参数说明:
function:线程函数
args:传递给线程函数的参数,他必须是一个tuple类型
kwargs:可选参数
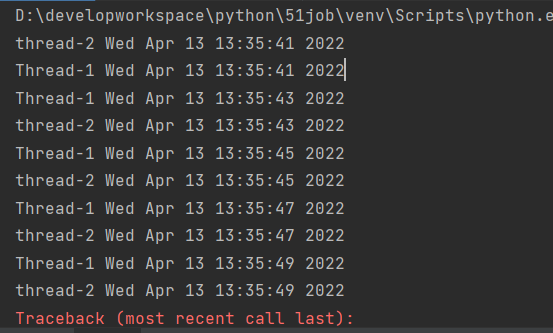
范例:
# 多线程
import _thread
import time
# 定义一个线程函数
def threadFunction(threadName,delay):
count=0
while count <5:
time.sleep(delay)
count +=1
print("%s %s" %(threadName,time.ctime(time.time())))
# 创建两个线程
try:
_thread.start_new_thread(threadFunction,("Thread-1",2))
_thread.start_new_thread(threadFunction,("thread-2",2))
except Exception as e:
print(e)
while 1:
pass
线程模块
Pyrhon3 通过两个标准库_thread 和 threading 提供对线程的支持。
_thread 提供了低级别、原始的线程以及一个简单的锁,它相对于threading模块的功能还是比较有限的
threading模块除了包含_thread模块中的所有方法外,还提供了其他方法
threading模块
- threading.currentThread():返回当前的线程变量
- thread.enumerate():返回一个包含正在运行的线程的list。正在运行指线程启动后、结束前,不包括启动前和终止后的线程。
- threading.activeCount():返回正在运行的线程数量,与len(threading.enumerate)) 有相同的结果
Thread类
除了使用方法外,线程模块同样提供了Thread类来处理线程
- run() 用来标识线程活动的方法
- start() 启动线程获得
- join([time]) 等待至线程终止。这阻塞用线程直至线程的join()方法被调用终止-正常退出或者抛出未处理的异常-或者是可选的超时发生。
- isAlive() 返回线程时候活动
- getName() 返回线程名
- setName() 设置线程名
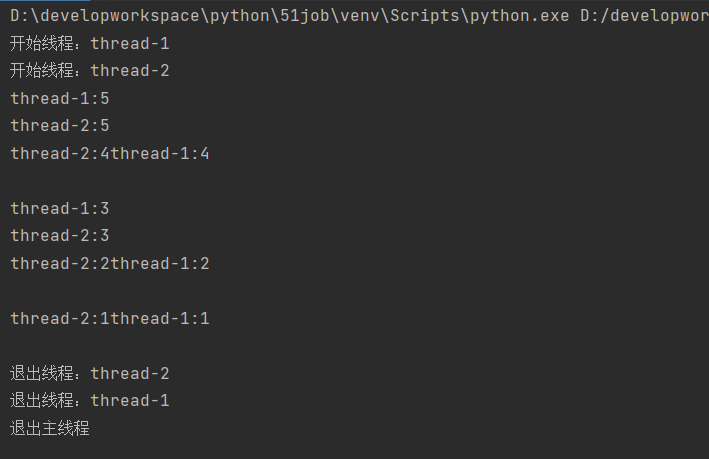
使用threading模块创建线程
import threading
import time
exitFlag=0
class MyThread(threading.Thread):
def __init__(self,threadId,name,delay):
threading.Thread.__init__(self)
self.threadId=threadId
self.name=name
self.delay=delay
def run(self):
print("开始线程:"+self.name)
printTime(self.name,self.delay,5)
print("退出线程:"+self.name)
def printTime(threadName,delay,counter):
while counter:
time.sleep(delay)
print("{}:{}".format(threadName,counter))
counter-=1
# 创建线程
thread1=MyThread(1,'thread-1',2)
thread2=MyThread(2,'thread-2',2)
# 开启线程
thread1.start()
thread2.start()
thread1.join()
thread2.join()
print("退出主线程")
线程同步
如果多个线程共同对某个数据修改,则可能出现不可预料的结果,为了保证数据的正确性,需要对多线程进行同步。
为了避免数据不同步,引入了锁的概念。
把线程任务放在锁里面,就能够保证数据的同步
锁的使用:
lock=threading.Lock()
lock.acquire() 获取锁
线程任务
lock.release() 释放锁
- lock=threading.Lock() 获取锁对象
- lock.acquire() 获取锁
- lock.release() 释放锁
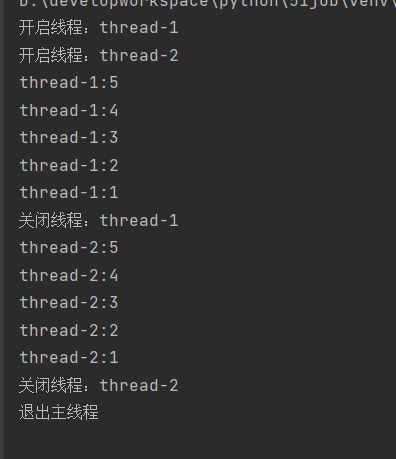
import threading
import time
class MyThread(threading.Thread):
def __init__(self,threadId,threadName,delay):
threading.Thread.__init__(self)
self.threadId=threadId
self.threadName=threadName
self.delay=delay
def run(self):
print("开启线程:"+self.threadName)
# 获取锁,用于线程同步
threadLock.acquire()
printTime(self.threadName,self.delay,5)
# 释放锁,让执行下一个线程
threadLock.release()
print("关闭线程:"+self.threadName)
def printTime(threadName,delay,counter):
while counter:
time.sleep(delay)
print("{}:{}".format(threadName,counter))
counter-=1
threadLock=threading.Lock()
threads=[]
# 创建线程
myThread01=MyThread(1,"thread-1",2)
myThread02=MyThread(2,"thread-2",2)
# 添加线程到列表中
threads.append(myThread01)
threads.append(myThread02)
# 启动线程
myThread01.start()
myThread02.start()
# 等待所有线程完成
for t in threads:
t.join()
print("退出主线程")
线程优先级队列
python的Queue模块中提供了同步的、线程安全的队列类,包括FIFO(先入先出)队列Queue,LIFO(后入先出)
队列LifoQueue
优先级队列PriorityQueue
这些队列都是先了锁原语,能够在多线程中直接使用,可以使用队列来实现线程间的同步
Queue模块中常用的方法
Queue.qsize() 返回队列的大小
Queue.empty() 如果队列为空,返回True,反之False
Queue.full() 如果队列满了,返回True,反之False
Queue.get(block,timeout) 获取队列,timeout等待时间
Queue.get_nowait() 相当于Queue.get(False)
Queue.put(item) 写入队列,timeout等待时间
Queue.put_nowait(item) 相当Queue.put(item,False)
QUeue.task_done() 在完成一项工作后,函数向任务以及完成的队列发送一个信号
Queue.join() 实际上意味着等到队列为空,再执行别的操作
多线程爬取网页信息实战
import queue
import threading
from fake_useragent import UserAgent
import requests
from lxml import etree
import json
import csv
import time
class XiaoMiSpider(object):
# 初始化方法
def __init__(self):
self.url='https://game.xiaomi.com/api/classify/getCategory?page={}'
self.q=queue.Queue() # 存放所有url地址的队列
self.head=["游戏名字","游戏类型","游戏下载地址"]
# 存放数据的文件对象
self.f=open(file="game.csv",mode="a",encoding="utf-8")
self.writer=csv.DictWriter(self.f,fieldnames=self.head)
self.writer.writeheader()
# 创建锁
self.lock=threading.Lock()
# url 入队列方法
def urlIn(self):
for i in range(0,10):
# 生成url
url=self.url.format(i)
# url入队列
self.q.put(url)
# 获取一个页面的信息
def getUrlInfo(self,url):
# 伪造请求头
ua = UserAgent()
headers = {
"User-Agent": ua.ie
}
resp = requests.get(url=url, headers=headers)
return resp.json()
def parseHtmlAndWrite(self,html):
dataList=[] # 保存结果数据
gameList = html["gameList"]
for game in gameList:
# 保存一个游戏的数据
data = {}
# 游戏名字
gameName = game["gameInfo"]["displayName"]
data.update({"游戏名字": gameName})
# 游戏类型
gameType = game["tag"]
gameT = ""
if len(gameType) > 0:
typeList = {type["name"] for type in gameType}
gameT = "-".join(typeList)
else:
gameT = "未知"
data.update({"游戏类型": gameT})
# app下载地址
gameApk = game["gameInfo"]["gameApk"]
if not gameApk:
gameApk = game["gameInfo"]["gameApkSsl"]
if not gameApk:
gameApk = "敬请期待"
data.update({"游戏下载地址": gameApk})
dataList.append(data)
return dataList
def saveCsv(self,dataList):
self.writer.writerows(dataList)
# 线程任务 请求获取页面-解析数据-保存数据
def myTask(self,threadName):
print(f"{threadName} 线程在执行")
while True:
# 判断队列不为空就继续执行,否则退出
if not self.q.empty():
url=self.q.get() # 从队列中获url信息
# 获取页面
html=self.getUrlInfo(url)
# 解析页面
dataList=self.parseHtmlAndWrite(html)
# 保存数据 因为同时有一个线程进行写操作,所以要加锁
self.lock.acquire() # 获取锁
self.saveCsv(dataList)
self.lock.release() # 释放锁
else:
break
# 函数的执行入口
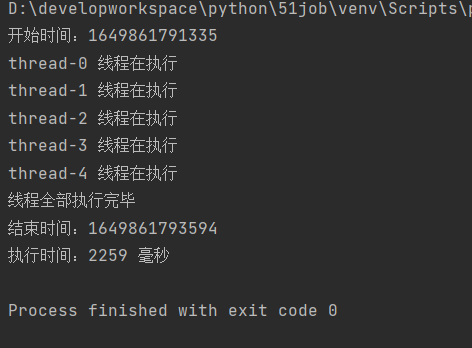
def main(self):
self.urlIn() # 使url进入队列
threadList=[] # 用来保存线程
# 创建线程
for i in range(0,5): # 创建5个线程任务
thread=threading.Thread(target=self.myTask(f"thread-{i}")) # 通过threading创建线程
thread.start() # 启动线程
threadList.append(thread)
for t in threadList:
t.join() # 回收线程
# 关闭文件
self.f.close()
print("线程全部执行完毕")
if __name__=="__main__":
start=int(time.time()*1000)
print("开始时间:%d"%(start))
spider=XiaoMiSpider()
spider.main()
end=int(time.time()*1000)
print("结束时间:%d" % (end))
print("执行时间:%d 毫秒"%(end-start))
其他
向字典中添加元素
dict.update(dict) 把参数字典添加到字典的后面



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号