chisel安装和使用+联合体union的tagged属性+sv读取文件和显示+sv获取系统时间+vcs编译时改动parameter的值+tree-PLRU和bit-PLRU
chisel安装和使用
sbt:scala build tool,是scala的默认构建工具,配置文件是build.sbt。
mill:一个新的java/scala构建工具,运行较快,与sbt可以共存,配置文件是build.sc。
chisel的安装可以参考这篇文章。安装过程务必联网,而没有联网情况下的安装,按照其它的说明,如移动缓存文件等,并无法正常使用。
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/357342948
https://www.chiselchina.com/tags/Chisel-Bootcamp/
scala这门语言一方面用的人并不多,另一方面敏捷开发本身有点和传统芯片设计有点相悖,加之不同的scala版本库差异很大,学习难度、成本、资料、迁移性、环境搭建等并不顺畅,所以我觉得还是不要学这种东西好些。
如果是出于位宽,连接等基本语法容易错误的问题,那么EDA工具自带了各种APP,可以扫描RTL。
如果是出于架构设计的问题,那么前期把方案完整做好,则后期书写代码是更为清晰。
安装完毕建立工程,以下是测试代码。
in_a宽度是2,in_b的宽度是1。加到的结果的宽度是3。
import chisel3._
import chisel3.Driver
class hello extends Module{
var io = IO(new Bundle() {
var in_a = Input(UInt(2.W))
var in_b = Input(UInt(1.W))
var out = Output(UInt(3.W))
})
io.out := io.in_a + io.in_b
}
object hello extends App{
Driver.emitVerilog(new hello())
}
有如下生成的verilog代码:
in_b的宽度是1,in_a宽度是2,out宽度是3。
module hello(
input clock,
input reset,
input [1:0] io_in_a,
input io_in_b,
output [2:0] io_out
);
wire [1:0] _GEN_0 = {{1'd0}, io_in_b}; // @[hello.scala 10:21]
wire [1:0] _T_1 = io_in_a + _GEN_0; // @[hello.scala 10:21]
assign io_out = {{1'd0}, _T_1}; // @[hello.scala 10:21]
endmodule
demo
// demo
import chisel3._
import chisel3.Driver
class hello extends Module{
var io = IO(new Bundle() {
var in_a = Input(UInt(2.W))
var in_b = Input(UInt(1.W))
var out = Output(UInt(3.W))
})
io.out := io.in_a + io.in_b
}
object hello extends App{
Driver.emitVerilog(new hello())
}
// function call
import chisel3._
import chisel3.Driver
class hello extends Module {
var io = IO(new Bundle() {
var in_a = Input(UInt(2.W))
var in_b = Input(UInt(2.W))
var out = Output(UInt(3.W))
})
private def adder(in_a: UInt, in_b: UInt) = {
in_a + in_b
}
io.out := adder(io.in_a, io.in_b)
}
object hello extends App {
Driver.emitVerilog(new hello())
}
// can't find main function
import chisel3._
import chisel3.Driver
class hello(data_width:Int) extends BlackBox {
val io = IO(new Bundle() {
val clk = Input(Clock())
val reset = Input(Bool())
val addr = Input(UInt(data_width.W))
val rdata = Output(UInt(data_width.W))
})
}
class DUT(data_width:Int) extends Module{
var io = IO(new Bundle(){
val dut_addr = Input(UInt(data_width.W))
val dut_rdata = Output(UInt(data_width.W))
})
val rom = Module(new hello(data_width))
rom.io.clk := clock
rom.io.reset := reset
rom.io.addr :=io.dut_addr
io.dut_rdata := rom.io.rdata
}
object hello1 extends App {
Driver.execute(args, () => new DUT((64)))
}
val 和var
创建变量和常量的语句前面分别带有关键字var和val。通常的做法是尽可能使用val。这是为了防止之后给变量错误地重新赋值,从而使代码难以阅读。
var numberOfKittens = 6
val kittensPerHouse = 101
val alphabet = "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz"
var done = false
numberOfKittens += 1
// kittensPerHouse = kittensPerHouse * 2 // 这一句会出错; 常量kittensPerHouse不可更改
println(alphabet)
done = true
条件语句
if (done) {
println("we are done")
}
else if (numberOfKittens < kittensPerHouse) {
println("more kittens!")
numberOfKittens += 1
}
else {
done = true
}
定义和重载
def times2(x: Int): Int = 2 * x
def distance(x: Int, y: Int, returnPositive: Boolean): Int = {
val xy = x * y
if (returnPositive) xy.abs else -xy.abs
}
def times2(x: String): Int = 2 * x.toInt
times2(5)
times2("7")
列表创建、连接、方法、索引
val x = 7
val y = 14
val list1 = List(1, 2, 3)
val list2 = x :: y :: y :: Nil // 另一种列表的构造方法
val list3 = list1 ++ list2 // 连接两个列表
println(list3)
val m = list2.length
val s = list2.size
val headOfList = list1.head // 取列表的第一个元素
val restOfList = list1.tail // 得到去掉第一个元素的新的列表
val third = list1(2) // 列表的第三个元素(下标从0开始)
for循环索引、遍历
for (i <- 0 to 7) { print(i + " ") }
println()
for (i <- 0 until 7) {
print(i + " ")
}
println()
for (i <- 0 to 10 by 2) {
print(i + " ")
}
println()
val randomList = List(scala.util.Random.nextInt(), scala.util.Random.nextInt(), scala.util.Random.nextInt(), scala.util.Random.nextInt())
var listSum = 0
for (value <- randomList) {
listSum += value
}
println("sum is " + listSum)
module,没有getVerilog
Module是一个Chisel内建的类,所有的硬件模块都必须从它继承。在一个叫做io的常量中声明所有的输入输出端口。这个常量的名称必须叫做io,并且它必须是类IO的对象或实例。这个类要求一个实例化的Bundle:IO(instantiated_bundle)。
:=操作符是一个Chisel操作符,它表示右边的信号驱动左边的信号,它具有方向性。
// Chisel代码:定义一个模块
class Passthrough extends Module {
val io = IO(new Bundle {
val in = Input(UInt(4.W))
val out = Output(UInt(4.W))
})
io.out := io.in
}
getVerilog是在实例中内置的一个函数,应该使用的函数是emitVerilog。
import chisel3._
import chisel3.stage.ChiselStage
class Foo extends Module {
val io = IO(new Bundle {})
printf("I'm a foo")
}
/* For Chisel versions <3.2.0 use the following: */
Driver.emitVerilog(new Foo)
/* For Chisel >=3.2.0 use the following: */
(new ChiselStage).emitVerilog(new Foo)
一个chisel工程还需要main函数。main函数的实现是继承App这个class。如果是没有println,则结果会输出到文件。文件名是Passthrough。
import chisel3._
import chisel3.Driver
class Passthrough extends Module {
val io = IO(new Bundle {
val in = Input(UInt(4.W))
val out = Output(UInt(4.W))
})
io.out := io.in
}
object hello extends App{
println(Driver.emitVerilog(new Passthrough))
}
带参数的class实例化
import chisel3._
import chisel3.Driver.emitVerilog
class PassthroughGenerator(width: Int) extends Module {
val io = IO(new Bundle {
val in = Input(UInt(width.W))
val out = Output(UInt(width.W))
})
io.out := io.in
}
object hello extends App{
println(emitVerilog(new PassthroughGenerator(10)))
}
联合体union的tagged属性
https://www.elecfans.com/d/1922920.html
tagged union包含一个隐式成员,该成员存储tag,也就是标记,它表示这个union最终存储的到底是哪一个成员。
如果从不同的union成员中读取值,仿真器则会报错:
module tagged_union_example;
logic [31:0] x;
typedef union tagged {
int a;
byte b;
bit [15:0] c;
} data;
data d1;
initial begin
d1 = tagged a 32'hffff_ffff; //write to 'a'
//read from 'b'. Since 'a' was written last, cannot access
//'b'. - Error
x = d1.b;
$display("x = %h",x);
end
endmodule
所以,tagged其实是属性检查的作用,在实际的应用中不多。
另外,union的实际用途不明:
在编译和仿真的时候,即便是unpacked union,也会出现数值完全覆盖的情况,
似乎是被当做packed联合体使用了。
应该尽量避免unpacked联合体使用,防止出现意外。
sv读取文件和显示
https://blog.eetop.cn/blog-12852-21369.html
integer file;
string variable;
reg [31:0] value;
file=$fopen("file.txt","r");
while(!$feof(file))
begin
$fscanf(file,"%s %h",variable,value);
h_array[variable] = value;
end
$fclose(file);
sv获取系统时间
以下命令提取不到值:
initial begin
$system("date");
end
用DPI方法可以提取到值,但是是一个格式化的字符串:
#include <time.h>
wallclock() {
time_t t;
t = time(NULL);
return (ctime(&t));
//return time(NULL);
}
import "DPI-C" function string wallclock();
module try;
//int unsigned t;
string t;
initial begin
t = wallclock();
$write("time=%0s\n", t);
end
endmodule
如果需要更详细的自定义的时钟,那么可以先打通C语言的获取,然后再用SV调用。注意调用的格式正确性,而EDA工具有时候并不检查import等形参、返回值的正确性。
https://www.runoob.com/w3cnote/c-time-func-summary.html
vcs编译时改动parameter的值
vcs手册提供两种方案,一种是-pvalue+value_path=value的方法,另一种是-parameters filename的方法。
以第一种方法为例:
module module_name();
parameter a= 3;
initial begin
#10;
$display("%0d", a)
end
endmodule
编译时候添加了如下,则输出的a是1.
-pvalue+module_name.a=1
tree-PLRU和bit-PLRU
tree-PLRU
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pseudo-LRU
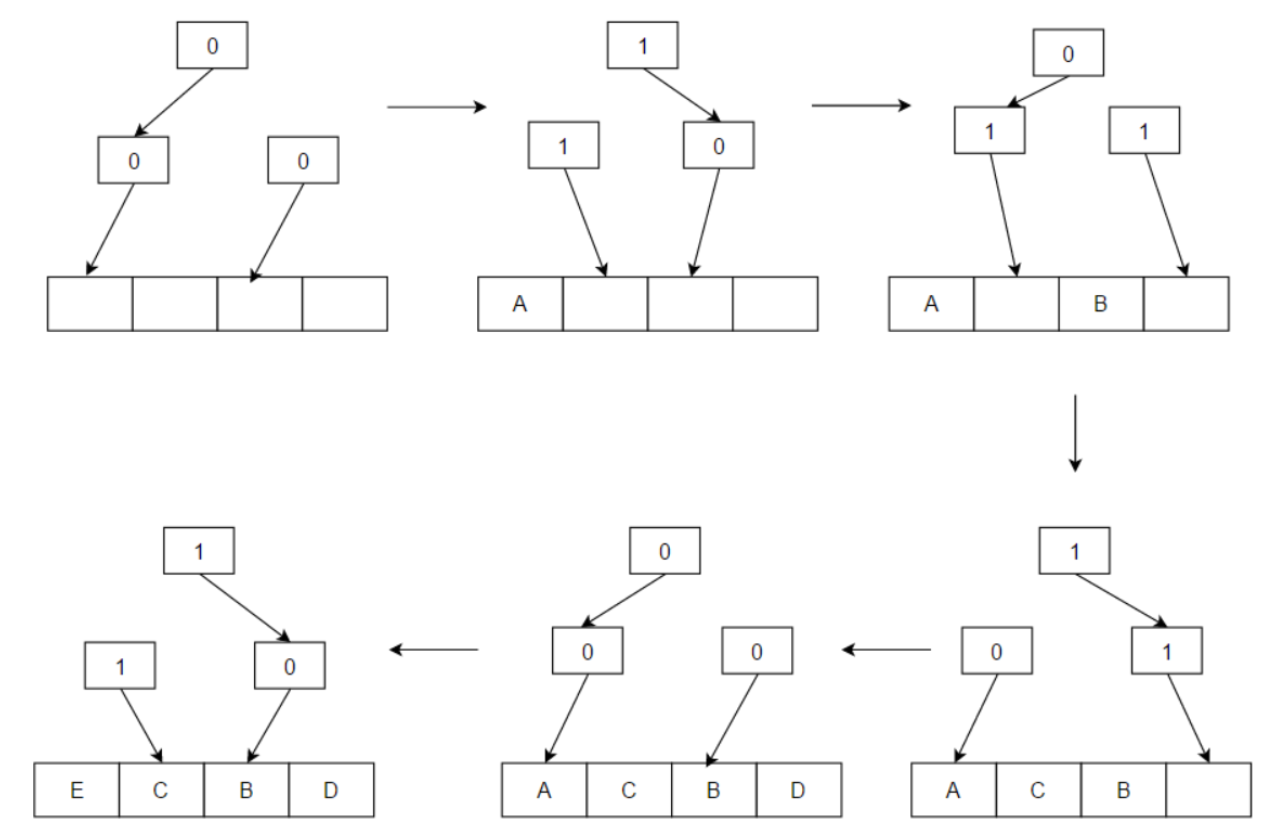
2bit的索引,从00-11一直循环,下一轮访问的被替换。
每次访问过的位置,1变成0,0变成1,将最旧的数据被替换。 如果访问顺序是C, B, D, A, 那么下图中,E替换的位置是B,而不是C。这是因为A和C都在相同的一半,DBD访问后,所有值重新变成0,而最后一次访问A,将算法替换位置定向到C。
填充过程的数值变化:
0指向左边,填充以后变成1指向右边。1指向右边,填充以后变成0指向左边。
访问过程的数值变化:
访问过程的路径如果是和原值相同,则变换数值指向另一方。如果和原值不同,则不变。
bit-PLRU
每个条目上有1bitLRU值,每次访问设置这个值,满了以后变成全0,替换时候选择最左边为0的那个条目替换。
Le vent se lève! . . . il faut tenter de vivre!
Le vent se lève! . . . il faut tenter de vivre!



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号