日常记录(63)UVM事件、序列、寄存器
uvm_callback
可以控制组件产生的回调函数
代码:
建立了数据edata类,cb1的回调类,cb2继承于cb1的回调类,comp1注册cb1回调类,然后进行回调执行。
注意在env中,对comp1中添加了cb1和cb2的回调属性。回调进行的时候,add的顺序对回调会有影响,如果先add cb2,则先输出300。
点击查看代码
module uvm_callback_sync;
import uvm_pkg::*;
`include "uvm_macros.svh"
class edata extends uvm_object;
int data;
`uvm_object_utils(edata)
function new(string name = "edata");
super.new(name);
endfunction
endclass
class cb1 extends uvm_callback;
`uvm_object_utils(cb1)
function new(string name = "cb1");
super.new(name);
endfunction
virtual function void do_trans(edata d);
d.data = 200;
`uvm_info("CB", $sformatf("cb1 executed with data %0d", d.data), UVM_LOW)
endfunction
endclass
class cb2 extends cb1;
`uvm_object_utils(cb2)
function new(string name = "cb2");
super.new(name);
endfunction
function void do_trans(edata d);
d.data = 300;
`uvm_info("CB", $sformatf("cb2 executed with data %0d", d.data), UVM_LOW)
endfunction
endclass
class comp1 extends uvm_component;
`uvm_component_utils(comp1)
`uvm_register_cb(comp1, cb1)
function new(string name, uvm_component parent);
super.new(name, parent);
endfunction
function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
endfunction
task run_phase(uvm_phase phase);
edata d = new();
d.data = 100;
`uvm_info("RUN", $sformatf("proceeding data %0d", d.data), UVM_LOW)
`uvm_do_callbacks(comp1, cb1, do_trans(d))
endtask
endclass
class env1 extends uvm_env;
comp1 c1;
cb1 m_cb1;
cb2 m_cb2;
`uvm_component_utils(env1)
function new(string name, uvm_component parent);
super.new(name, parent);
m_cb1 = new("m_cb1");
m_cb2 = new("m_cb2");
endfunction
function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
c1 = comp1::type_id::create("c1", this);
uvm_callbacks #(comp1)::add(c1, m_cb1);
uvm_callbacks #(comp1)::add(c1, m_cb2);
endfunction: build_phase
endclass
class test1 extends uvm_test;
`uvm_component_utils(test1)
env1 env;
function new(string name, uvm_component parent);
super.new(name, parent);
endfunction
function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
env = env1::type_id::create("env", this);
endfunction
task run_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.run_phase(phase);
phase.raise_objection(this);
#1us;
phase.drop_objection(this);
endtask
endclass
initial begin
run_test("test1");
end
endmodule
效果:
点击查看代码
UVM_INFO @ 0: reporter [RNTST] Running test test1...
UVM_INFO taa.sv(48) @ 0: uvm_test_top.env.c1 [RUN] proceeding data 100
UVM_INFO taa.sv(20) @ 0: reporter [CB] cb1 executed with data 200
UVM_INFO taa.sv(31) @ 0: reporter [CB] cb2 executed with data 300
UVM_INFO /home/synopsys/vcs-mx/O-2018.09-1/etc/uvm-1.1/base/uvm_objection.svh(1273) @ 1000000: reporter [TEST_DONE] 'run' phase is ready to proceed to the 'extract' phase
uvm_event
可以控制进程之间的同步
https://verificationacademy.com/verification-methodology-reference/uvm/docs_1.2/html/index.html
https://blog.csdn.net/zyj0oo0/article/details/120264318
特点
- 使用uvm_event_poll的方式,获取(在第一次获取时候初始化)
- 能够在trigger后,执行添加的自定义uvm_event_callback回调函数
- 能够在trigger时候传递参数,在wait_trigger_data时候得到参数
- 可以使用get_num_waitters获取等待的进程数量。
总结:回调、传值、获取等待进程数等,方便使用。
- 定义了edata作为基础数据
- 定义了ecb作为event的回调类,其中有pre_trigger和post_trigger两个方法
- 定义了comp1和comp2,进行事件的获取和交互。
其中的comp1获取事件、在run_phase过程中新建基础数据、新建回调类、将事件与回调类绑定,触发过程中顺便发送数据。
其中的comp2获取事件、在run_phase过程中等待时间被触发,获取触发数据。
点击查看代码
module uvm_event_sync;
import uvm_pkg::*;
`include "uvm_macros.svh"
class edata extends uvm_object;
int data;
`uvm_object_utils(edata)
function new(string name = "edata");
super.new(name);
endfunction
endclass
class ecb extends uvm_event_callback;
`uvm_object_utils(ecb)
function new(string name = "ecb");
super.new(name);
endfunction
function bit pre_trigger(uvm_event e, uvm_object data = null);
`uvm_info("EPRETRIG", $sformatf("before trigger event %s", e.get_name()), UVM_LOW)
return 0;
endfunction
function void post_trigger(uvm_event e, uvm_object data = null);
`uvm_info("EPOSTRIG", $sformatf("after trigger event %s", e.get_name()), UVM_LOW)
endfunction
endclass
class comp1 extends uvm_component;
uvm_event e1;
`uvm_component_utils(comp1)
function new(string name, uvm_component parent);
super.new(name, parent);
endfunction
function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
e1 = uvm_event_pool::get_global("e1");
endfunction
task run_phase(uvm_phase phase);
edata d = new();
ecb cb = new();
d.data = 100;
#10ns;
e1.add_callback(cb);
e1.trigger(d);
`uvm_info("ETRIG", $sformatf("trigger sync event at %t ps", $time), UVM_LOW)
endtask
endclass
class comp2 extends uvm_component;
uvm_event e1;
`uvm_component_utils(comp2)
function new(string name, uvm_component parent);
super.new(name, parent);
endfunction
function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
e1 = uvm_event_pool::get_global("e1");
endfunction
task run_phase(uvm_phase phase);
uvm_object tmp;
edata d;
`uvm_info("ESYNC", $sformatf("wait sync event at %t ps", $time), UVM_LOW)
e1.wait_trigger_data(tmp);
void'($cast(d, tmp));
`uvm_info("ESYNC", $sformatf("get data %0d after sync at %t ps", d.data, $time), UVM_LOW)
endtask
endclass
class env1 extends uvm_env;
comp1 c1;
comp2 c2;
`uvm_component_utils(env1)
function new(string name, uvm_component parent);
super.new(name, parent);
endfunction
function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
c1 = comp1::type_id::create("c1", this);
c2 = comp2::type_id::create("c2", this);
endfunction: build_phase
endclass
class test1 extends uvm_test;
`uvm_component_utils(test1)
env1 env;
function new(string name, uvm_component parent);
super.new(name, parent);
endfunction
function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
env = env1::type_id::create("env", this);
endfunction
task run_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.run_phase(phase);
phase.raise_objection(phase);
#1us;
phase.drop_objection(phase);
endtask
endclass
initial begin
run_test("test1");
end
endmodule
运行结果:
结果中,pre_trigger和post_trigger先执行了,然后才是触发获取。
点击查看代码
UVM_INFO @ 0: reporter [RNTST] Running test test1...
UVM_INFO taa.sv(62) @ 0: uvm_test_top.env.c2 [ESYNC] wait sync event at 0 ps
UVM_INFO taa.sv(19) @ 10000: reporter [EPRETRIG] before trigger event e1
UVM_INFO taa.sv(23) @ 10000: reporter [EPOSTRIG] after trigger event e1
UVM_INFO taa.sv(45) @ 10000: uvm_test_top.env.c1 [ETRIG] trigger sync event at 10000 ps
UVM_INFO taa.sv(65) @ 10000: uvm_test_top.env.c2 [ESYNC] get data 100 after sync at 10000 ps
UVM_INFO /home/synopsys/vcs-mx/O-2018.09-1/etc/uvm-1.1/base/uvm_objection.svh(1273) @ 1000000: reporter [TEST_DONE] 'run' phase is ready to proceed to the 'extract' phase
uvm_barrier
可以控制多少个进程等待时候才触发继续执行
uvm_barrier_pool和uvm_event_pool类似,barrier用于等待阈值满足要求后继续执行
代码:
两个comp从池子里获得同一个barrier,然后等,等到整个配置进程数量能够满足启动条件,启动。
点击查看代码
module uvm_barrier_sync;
import uvm_pkg::*;
`include "uvm_macros.svh"
class comp1 extends uvm_component;
uvm_barrier b1;
`uvm_component_utils(comp1)
function new(string name, uvm_component parent);
super.new(name, parent);
endfunction
function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
b1 = uvm_barrier_pool::get_global("b1");
endfunction
task run_phase(uvm_phase phase);
#10ns;
`uvm_info("BSYNC", $sformatf("c1 wait for b1 at %0t ps", $time), UVM_LOW)
b1.wait_for();
`uvm_info("BSYNC", $sformatf("c1 is activated at %0t ps", $time), UVM_LOW)
endtask
endclass
class comp2 extends uvm_component;
uvm_barrier b1;
`uvm_component_utils(comp2)
function new(string name, uvm_component parent);
super.new(name, parent);
endfunction
function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
b1 = uvm_barrier_pool::get_global("b1");
endfunction
task run_phase(uvm_phase phase);
#20ns;
`uvm_info("BSYNC", $sformatf("c2 wait for b1 at %0t ps", $time), UVM_LOW)
b1.wait_for();
`uvm_info("BSYNC", $sformatf("c2 is activated at %0t ps", $time), UVM_LOW)
endtask
endclass
class env1 extends uvm_env;
comp1 c1;
comp2 c2;
uvm_barrier b1;
`uvm_component_utils(env1)
function new(string name, uvm_component parent);
super.new(name, parent);
endfunction
function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
c1 = comp1::type_id::create("c1", this);
c2 = comp2::type_id::create("c2", this);
b1 = uvm_barrier_pool::get_global("b1");
endfunction: build_phase
task run_phase(uvm_phase phase);
b1.set_threshold(3);
`uvm_info("BSYNC", $sformatf("env set b1 threshold %d at %0t ps", b1.get_threshold(), $time), UVM_LOW)
#50ns;
b1.set_threshold(2);
`uvm_info("BSYNC", $sformatf("env set b1 threshold %d at %0t ps", b1.get_threshold(), $time), UVM_LOW)
endtask
endclass
class test1 extends uvm_test;
`uvm_component_utils(test1)
env1 env;
function new(string name, uvm_component parent);
super.new(name, parent);
endfunction
function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
env = env1::type_id::create("env", this);
endfunction
task run_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.run_phase(phase);
phase.raise_objection(this);
#1us;
phase.drop_objection(this);
endtask
endclass
initial begin
run_test("test1");
end
endmodule
效果:
点击查看代码
UVM_INFO @ 0: reporter [RNTST] Running test test1...
UVM_INFO taa.sv(60) @ 0: uvm_test_top.env [BSYNC] env set b1 threshold 3 at 0 ps
UVM_INFO taa.sv(17) @ 10000: uvm_test_top.env.c1 [BSYNC] c1 wait for b1 at 10000 ps
UVM_INFO taa.sv(35) @ 20000: uvm_test_top.env.c2 [BSYNC] c2 wait for b1 at 20000 ps
UVM_INFO taa.sv(63) @ 50000: uvm_test_top.env [BSYNC] env set b1 threshold 2 at 50000 ps
UVM_INFO taa.sv(19) @ 50000: uvm_test_top.env.c1 [BSYNC] c1 is activated at 50000 ps
UVM_INFO taa.sv(37) @ 50000: uvm_test_top.env.c2 [BSYNC] c2 is activated at 50000 ps
UVM_INFO /home/synopsys/vcs-mx/O-2018.09-1/etc/uvm-1.1/base/uvm_objection.svh(1273) @ 1000000: reporter [TEST_DONE] 'run' phase is ready to proceed to the 'extract' phase
start和start_item等
start是seq的操作
操作关系:
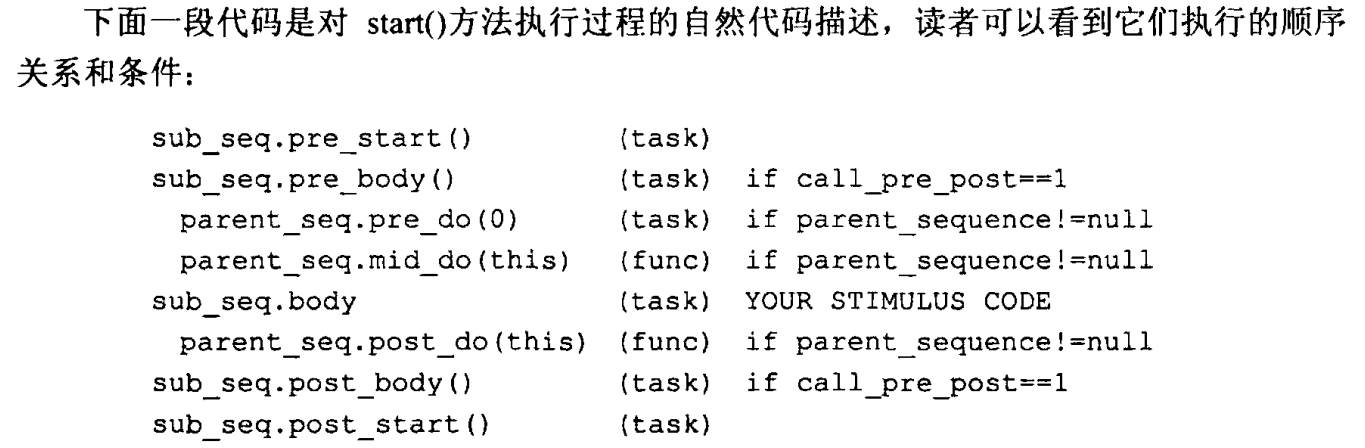
start_item是seq中针对item的操作
操作关系:
其中的uvm_do宏,是生成item,start_item,随机化item、finish_item的合集


uvm_do、uvm_do_with等是宏
用于在seq_item和seq之间进行通用。
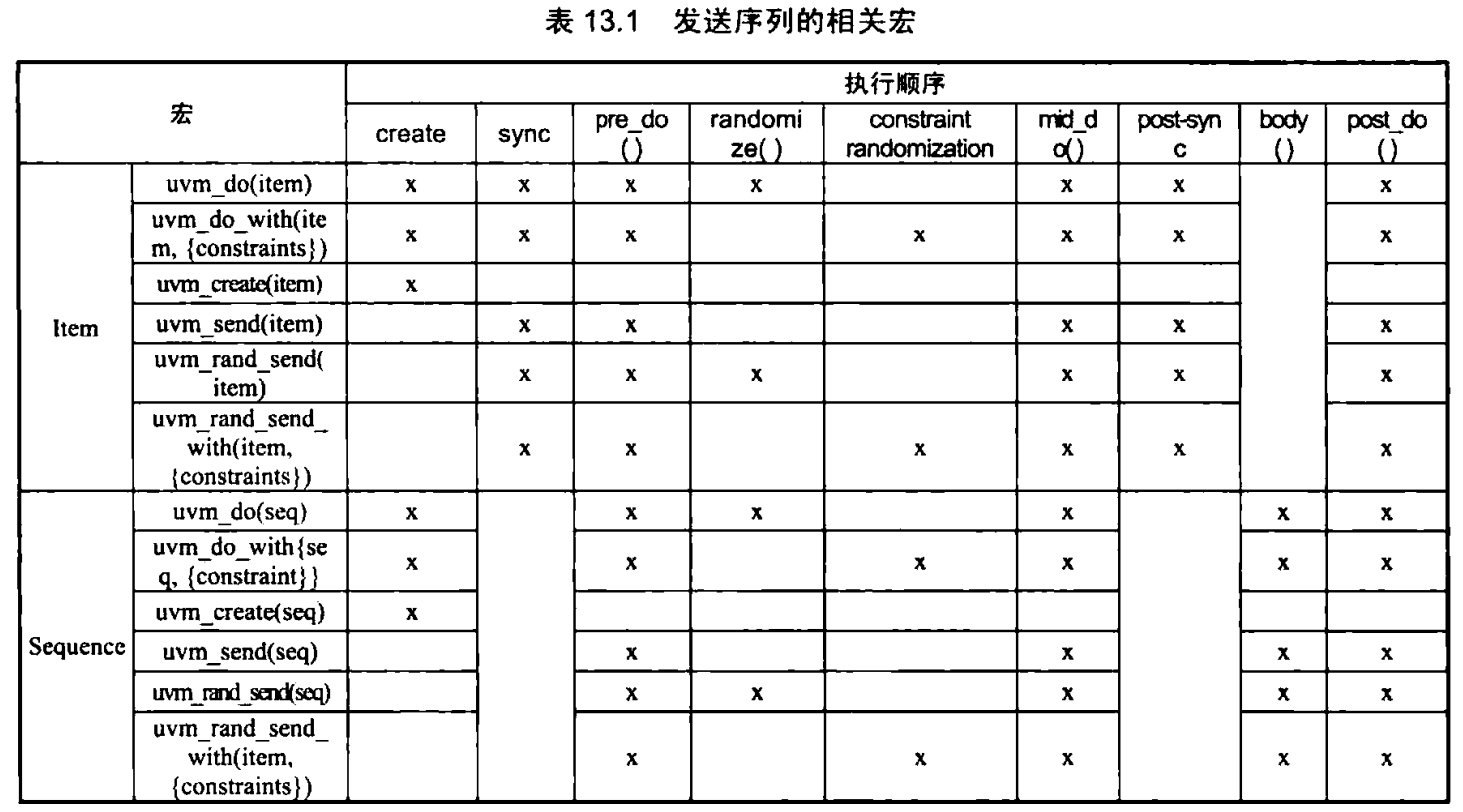
前后门访问
前门访问
uvm_reg的read和write(注明UVM_FRONTDOOR),uvm_reg_sequced的read_reg、write_reg
后门访问
uvm_reg的read和write(注明UVM_BACKDOOR),uvm_reg_sequced的read_reg、write_reg(注明UVM_BACKDOOR),uvm_regd的peek和poke
前面访问通过drv,后门访问没有。调用内部的库。
期望值与镜像值
二者都位于寄存器模型中,期望值是预备要更新到DUT中的值,而镜像值是为了与DUT保持同步的值。镜像值若未得到及时更新,获得的值可能有误。
自动预测的方法是系统自动调用的predict的,而显式预测是通过定义predictor实现的。显式预测捕获物理总线上的数据实现。
前门访问的read和write,通过了总线,显式预测实现同步。
后门访问的read和write,自动预测实现同步。
显式预测由于检测了总线,更准确。
存储器
uvm_mem不存在期望值和镜像值,提供前后门访问
功能覆盖率
- 在read和write的过程(寄存器模型),自动收集。
- 事件外部触发收集(uvm_subscriber)
DPI
为什么要把那么容易的东西绕来绕去,还不给一个时间基准,差点run_phase没调处来?
编译
vcs -sverilog -R -ntb_opts uvm-1.1 -debug_all virtual_core.sv main.c
SV部分
import "DPI-C" context task 导入了两个函数
export "DPI-C" dpi_print = task print将print导出给C用。
点击查看代码
package virtual_core_pkg;
import uvm_pkg::*;
`include "uvm_macros.svh"
typedef class virtual_core;
virtual_core cores[int];
import "DPI-C" context task core0_thread();
import "DPI-C" context task core1_thread();
export "DPI-C" dpi_print = task print ;
task print(input string message, int unsigned id = 0);
cores[id].print(message);
endtask
class virtual_core extends uvm_component;
local int id;
`uvm_component_utils(virtual_core)
function new(string name, uvm_component parent);
super.new(name, parent);
id = cores.size();
cores[id] = this;
endfunction
extern task run_phase(uvm_phase phase);
extern task print(input string message);
endclass
task virtual_core::run_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.run_phase(phase);
#10;
`uvm_info("VIRCORE", $sformatf("@%0t, %m", $time), UVM_LOW);
case(id)
0: core0_thread();
1: core1_thread();
endcase
endtask
task virtual_core::print(input string message);
`uvm_info("CORE", message, UVM_LOW)
endtask
class virtual_core_subsys extends uvm_env;
virtual_core c0;
virtual_core c1;
`uvm_component_utils(virtual_core_subsys)
function new(string name, uvm_component parent);
super.new(name, parent);
endfunction
function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
c0 = virtual_core::type_id::create("c0", this);
c1 = virtual_core::type_id::create("c1", this);
endfunction
task run_phase(uvm_phase phase);
`uvm_info("ENV_INFO", "this is env ", UVM_LOW);
#10
`uvm_info("ENV_INFO", "this is env ", UVM_LOW);
endtask: run_phase
endclass
class test extends uvm_test;
virtual_core_subsys env;
`uvm_component_utils(test)
function new(string name, uvm_component parent);
super.new(name, parent);
endfunction
function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
env = virtual_core_subsys::type_id::create("env", this);
endfunction
task run_phase(uvm_phase phase);
phase.raise_objection(this);
#1000;
phase.drop_objection(this);
endtask
endclass
endpackage: virtual_core_pkg
module virtual_core_tb;
import uvm_pkg::*;
import virtual_core_pkg::*;
initial begin
run_test("test");
end
endmodule
C部分
core0_thread为被调用的,其中的dpi_print是从SV来的
#include "vc_hdrs.h"
void core0_thread() {
dpi_print("core0_thread entered", 0);
}
void core1_thread() {
dpi_print("core1_thread entered", 1);
}
Le vent se lève! . . . il faut tenter de vivre!
Le vent se lève! . . . il faut tenter de vivre!



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号