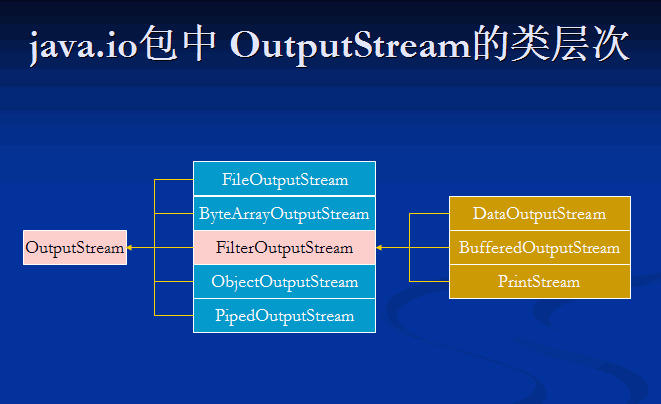
JAVA中IO
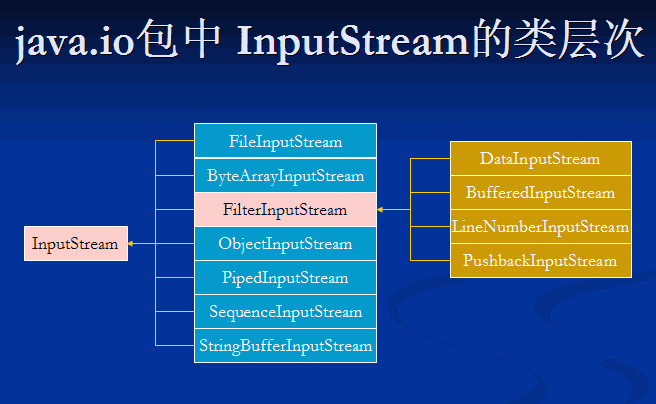
1、FileInputStream读取
read()每次读取一个字节
File file = new File("d:" + File.separator + "demo.txt"); // 要操作的文件 InputStream input = null; // 字节输入流 input = new FileInputStream(file);// 通过子类进行实例化操作 byte b[] = new byte[(int) file.length()];// 开辟空间接收读取的内容 for(int i=0;i<b.length;i++){ b[i] = (byte)input.read() ; // 一个个的读取数据 } System.out.println(new String(b)); // 输出内容,直接转换 input.close(); // 关闭
read(byte[])每次读取x个字节
File file = new File("d:" + File.separator + "demo.txt"); // 要操作的文件 InputStream input = new FileInputStream(file);// 通过子类进行实例化操作 //FileInputStream input = new FileInputStream(file); byte b[] = new byte[100];// 开辟空间接收读取的内容 int len = input.read(b); // 将内容读入到byte数组中 System.out.println(new String(b, 0, len)); // 输出内容 StringBuffer s=new StringBuffer(); while (input.available() > 0) { byte[] a = new byte[2]; while(input.read(a)!= -1) { s.append(a); } System.out.println(s); } System.out.println(s); input.close(); // 关闭
2、FileOutputStream写入
write(byte[])每次写入b字节数据
File file = new File("d:" + File.separator + "demo.txt"); // 要操作的文件 OutputStream out = null; // 声明字节输出流 out = new FileOutputStream(file); // 通过子类实例化 String str = "hello world"; // 要输出的信息 byte b[] = str.getBytes(); // 将String变为byte数组 out.write(b); // 写入数据 out.close(); // 关闭
3、BufferedInputStream与BufferedOutputStream
BufferedInputStream的数据成员buf是一个位数组,默认为2048字节。当读取数据来源时,BufferedInputStream会尽量将buf填满。当使用read()方法时,实际上是先读取buf中的数据,而不是直接对数据来源作读取。当 buf中的数据不足时,BufferedInputStream才会再实现给定的InputStream对象的read()方法,从指定的装置中提取数 据。
BufferedOutputStream的数据成员buf是一个位数组,默认为512字节。当使用write()方法写入数据时,实际上会先将数据写至 buf中,当buf已满时才会实现给定的OutputStream对象的write()方法,将buf数据写至目的地,而不是每次都对目的地作写入的动 作。
byte[] data = new byte[1]; File srcFile = new File(args[0]); File desFile = new File(args[1]); BufferedInputStream bufferedInputStream = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(srcFile)); BufferedOutputStream bufferedOutputStream = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(desFile)); System.out.println("复制文件:"+srcFile.length()+"字节"); while(bufferedInputStream.read(data)!=-1) { bufferedOutputStream.write(data); } //将缓冲区中的数据全部写出 bufferedOutputStream.flush(); //关闭流 bufferedInputStream.close(); bufferedOutputStream.close(); System.out.println("复制完成");
4、ByteArrayOutputStream和ByteArrayInputStream以字节作为对象
String str = "helloworld"; // 定义字符串,全部由小写字母组成 ByteArrayOutputStream bos = null; // 内存输出流 ByteArrayInputStream bis = null; // 内存输入流 bis = new ByteArrayInputStream(str.getBytes()); // 将内容保存在内存之中 bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); // 内存输出流 int temp = 0; while ((temp = bis.read()) != -1) {// 依次读取 char c = (char) temp; // 接收字符 bos.write(Character.toUpperCase(c)); // 输出 } String newStr = bos.toString();// 取出内存输出的内容 System.out.println(newStr);


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号