MySQL优化
SQL 优化原则
- 尽可能消除全表扫描,除非表数据量是在万条一下
-
增加适当的索引能提高查询的速度,但增加索引需要遵循一定的基本规则:
a. 加在where条件上
b. 加在表之间join的键值上
c. 如果查询范围是少量字段,可以考虑增加覆盖索引(仅走索引)
d. 有多个查询条件时,考虑增加复合索引,并把最常使用的字段放在索引前面
e. 不要将索引加在区别率不高的字段上
f . 字段上增加函数,则字段上的索引用不了,需考虑改变写法 -
去掉不影响查询结果的表
慢查询日志
开启慢查询日志,分日里面执行时间很长语句 , 可以针对性的对常用语句进行建立索引
开启方法my.cnf:
|
1
2
3
|
slow_query_log= on #开启slow_query_log_file = /path/mysql-slow.log # 慢查询文件存放位置long_query_time= 2 #2秒以上的语句被记录 |
慢查询日志并不是只是记录的查出select 语句 ,dml 对数据语句都会记录
SQL 优化测试
创建一个有索引的表
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
create table students (sid int,sname varchar(64),gender int,dept_id int,primary key(sid)); |
创建一个什么索引都没有的表
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
create table students_noindex (sid int,sname varchar(64),gender int,dept_id int); |
利用存储过程, 分别给有索引的表和没有索引的表创建测试数据
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
# 有索引的 表delimiter //CREATE PROCEDURE `proc_students`()BeginDeclare n int default 1;while n<=500000 doInsert into students values(n, concat('zhangsan',n),floor(1+rand()*2),floor(1+rand()*4));Set n=n+1;End while;End;//delimiter ; |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
# 没有索引的 表delimiter //CREATE PROCEDURE `proc_students_noindex`()BeginDeclare n int default 1;while n<=500000 doInsert into students_noindex values(n, concat('zhangsan',n),floor(1+rand()*2),floor(1+rand()*4));Set n=n+1;End while;End;//delimiter ; |
如果 表上所有字段都有索引的情况下,测试对插入性能的影响:
|
1
2
|
create index idx_sname on students(sname);create index idx_gender on students(gender); |
看看两个表students,students_noindex结构

分别在两个表插入数据看时间消耗
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
set autocommit=0;call proc_students();commit;call proc_students_noindex();commit; |
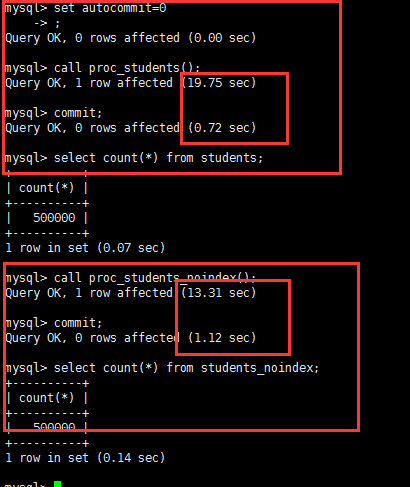
没有索引的表插入数据更快
考虑性能消耗的情况
这是500000万行的记录插入,有索引的插入时间更久 ,没有索引的插入更快
用时整体时间都比没有索引的插入数据慢 , 反应情况来看是索引建的越多对SQL增删改消耗的性能越大 ,因为不仅会修改表数据,还会整理一些索引信息
如果是上亿条的数据记录插入,想想插入时间 , 还有大表数据迁移 在目标表都把索引给删掉,插入数据完成的,在目标表统一建立索引
打开autocommit和关闭autocommit插入数据的区别
|
1
2
3
4
|
truncate table students;truncate table students_noindex;set autocommit=1;call proc_students(); |

插入数据中途可以在打开一个会话窗口看插入了多少数据
select count(*) from students;
自动提交开启插入500000条记录真的要花很长很长时间, 而自动提交关闭 几十秒的时间都把500000行数据插入完了
是因为每条数据插入都会写入磁盘 ,而关闭autocommit 是在插入完数据在统一把500000条记录commit;写入到磁盘
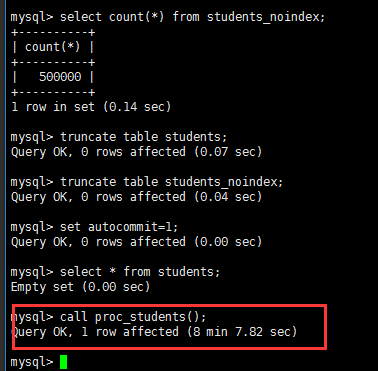
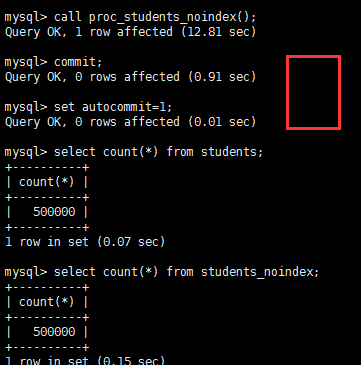
我在把原来没有索引的students_noindex 数据插入回去
测试单表在没有索引下全表扫描和走索引情况下的性能对比:

select 查询加上sql_no_cache 查询的时候不使用缓存 ,突出我的实验结果
上面图片很明显是 走索引情况查询速度更快
通过explain 看下
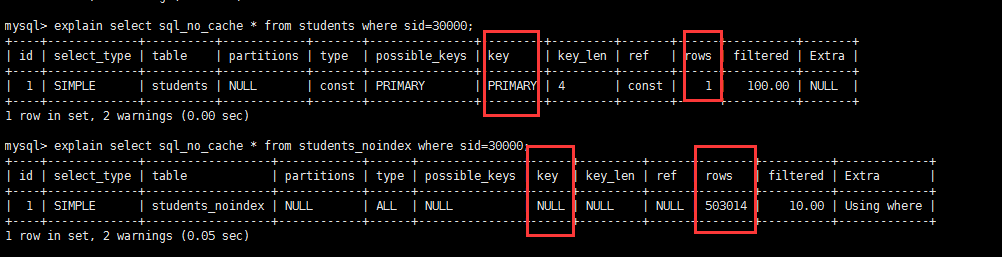
没有索引走的全表扫描
测试通过区别度不高的字段(如gender)上查询和全表查询的性能对比:
|
1
2
|
create temporary table a select * from students where gender=1;create temporary table b select * from students_noindex where gender=1; |
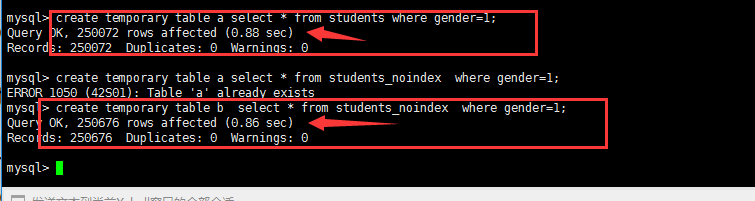
在区别度很低 (gender上有索引)查询和全表查询 性能上差不多
测试通过索引查询表中绝大多数数据和全表查询的性能对比:
|
1
2
|
select SQL_NO_CACHE count(*) from students where sid>1; # 类似全表查询了select SQL_NO_CACHE count(*) from students where sid>10000; # 查询表的大多数数据 |
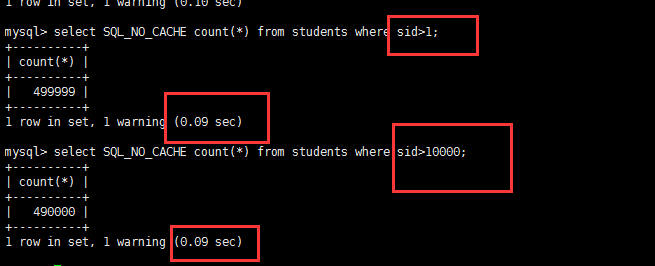
查询时间是一样的 。
使用查询条件更可能小的约束过滤范围
测试表链接关联字段走索引和不走索引的性能对比:
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
create index idx_deptid on students(dept_id);explain select count(*) from students a inner join dept b on a.dept_id=b.id; # dept_id字段有索引explain select count(*) from students_noindex a inner join dept b on a.dept_id=b.id; #students_noindex 的表没有任何索引select SQL_NO_CACHE count(*) from students a inner join dept b on a.dept_id=b.id;select SQL_NO_CACHE count(*) from students_noindex a inner join dept b on a.dept_id=b.id |
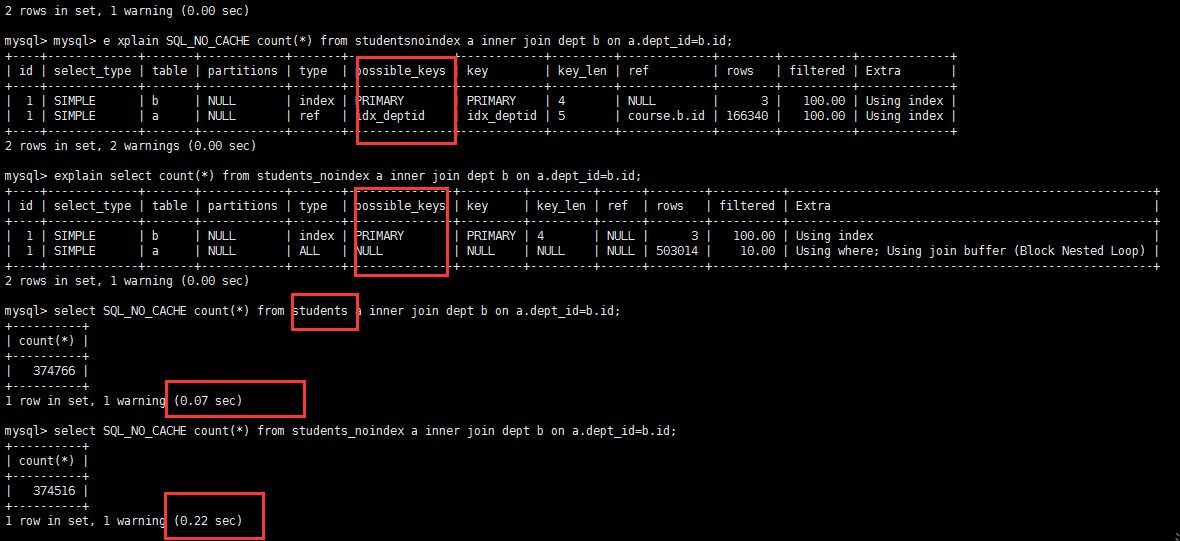
在关联字段上加了索引 查询时间只用了0.07s 用时 比没有走索引的快了很多很多
总结:
优化手段不只一种 ,要根据实际情况,很多情况都是以最低成本去处理, 例如
有可能加索引就能解决, 有可能解决不了,语句的写法的可能有问题(例如语句有函数,表达式),也有可能去改表的结构(例如增加冗余字段),有可能数据库瓶颈问题, 网络情况问题,服务器性能IO 问题,等等。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号