How to Use the EXPLAIN Keyword in MySQL
EXPLAIN in MySQL is a powerful tool used to analyze and understand how MySQL executes a particular query. Here’s what EXPLAIN can do:
Display the query execution plan: EXPLAIN shows how MySQL intends to execute a query, including the order of data retrieval, how data is joined, and how indexes are used.
Identify potential performance bottlenecks: By examining the execution plan, you can pinpoint potential performance issues such as full table scans, file sorting, and unnecessary temporary tables.
Check index usage: EXPLAIN indicates whether indexes are being used in a query and which indexes are being used, which helps in determining if additional or optimized indexes are needed.
Estimate query cost: The EXPLAIN output includes the estimated cost of the query, which can be useful for comparing the performance of different query statements or index strategies.
View table join types: EXPLAIN shows how tables are joined, such as whether nested loops, merge joins, or hash joins are being used.
Determine table read order: EXPLAIN can show the order in which MySQL accesses tables when executing a query.
Understand data filtering in queries: EXPLAIN shows how the WHERE clause and other conditions in a query affect data retrieval.
Diagnose and resolve query performance issues: By analyzing the output of EXPLAIN, you can identify the causes of poor query performance and optimize accordingly.
Using EXPLAIN can help database administrators and developers gain a better understanding of query behavior, which is essential for optimizing database performance.
Here's a simple example to use it
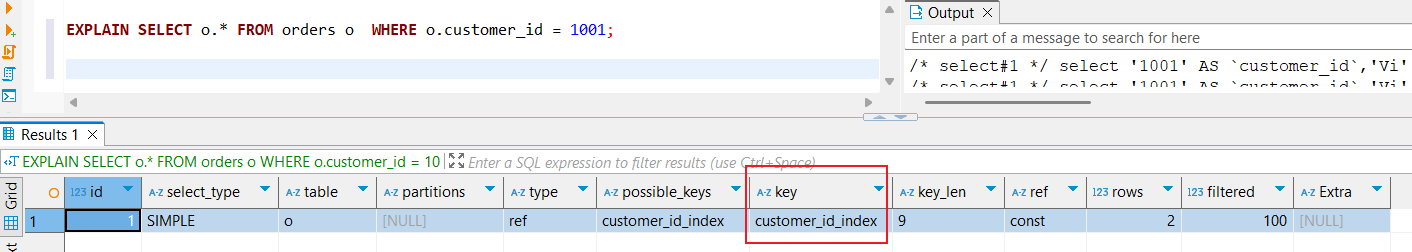
There is a table that names orders.


It has two index columns: order_id, customer_id. I want to know if the customer_id index on this table is used effectively during queries.
Therefore, I can use the EXPLAIN statement to verify if the customer_id index is effective during the query execution.




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号