借助ftrace生成系统启动进程/线程树
当一个稍微复杂系统启动时,需要研究这过程都创建了哪些进程/线程,用于分析优化启动速度、降低内存开销。
当系统启动后,通过pstree、top等只能获得进程的snapshot。了解ftrace的events之后,可以知道这里面提供了从系统开始创建进程/线程的事件。
下面在cmdline中打开task_newtask/task_rename来记录线程创建轨迹,然后脚本解析呈现全景式的进程树。
1 配置打开ftrace/debugfs
Kernel hacking
->Generic Kernel Debugging Instruments
->Debug Filesystem
->Tracers
->Boot-time Tracing support
task_newtask/task_rename和sched_process_fork/sched_process_exec都可以用于记录进程/线程的创建,下面是对比:
| 特性 | task_newtask | sched_process_fork | sched_process_exec |
|---|---|---|---|
| 触发时机 | 新任务创建时立即触发 | 任务被调度到 CPU 上时触发 | 进程执行新程序时触发 |
| 信息时效性 | 即时 (任务创建时) | 延迟 (任务被调度时) | 延迟 (exec 执行时) |
| 包含信息 | PID, 名称, clone_flags, 父进程 | 父PID, 子PID | 执行文件路径, 命令行参数 |
| 线程/进程区分 | 明确 (通过 clone_flags) | 不明确 | 不明确 |
| 事件密度 | 每个新任务一个事件 | 可能多个事件 (每个调度) | 每个 exec 一个事件 |
| 适用场景 | 精确追踪任务创建 | 分析调度行为 | 追踪程序执行 |
综合来看,还是task_newtask/task_rename更合适。
2 cmdline配置ftrace
通过cmdline可以在系统启动时对ftrace进行配置。
如在Kernel的cmdline增加:
trace_event=task,sched:sched_process_exec
2.1 基本配置语法
1. 启用 ftrace
ftrace=function
- 启用默认的 function tracer
- 可选值:function, function_graph, nop(无操作), blk(块设备跟踪)
2. 设置缓冲区大小
trace_buf_size=16M
- 设置环形缓冲区大小
- 支持单位:K(千字节), M(兆字节), G(千兆字节)
- 默认值:1.4MB/CPU 核心
3. 选择跟踪时钟
trace_clock=global
- 可选值:
- local:本地 CPU 时钟(默认)
- global:全局时钟(同步所有 CPU)
- counter:原子计数器
- uptime:系统启动时间
- perf:性能计数器
2.2 事件跟踪配置
1. 启用特定事件
trace_event=sched:*,irq:irq_handler_entry,irq:irq_handler_exit
- 语法:trace_event=[subsystem]:[event][:filter][,...]
- 支持通配符 * 匹配所有事件
- 多个事件用逗号分隔
2. 事件过滤器
trace_event=sched:sched_switch:prev_comm=="systemd",kmem:kmalloc:bytes_req>1024
- 使用 :filter 语法添加事件过滤器
- 支持比较运算符:==, !=, <, >, <=, >=
- 支持逻辑运算符:&& (AND), || (OR)
3. 启用所有事件
trace_event=*
- 启用所有可用事件(注意:可能产生大量数据)
2.3 Tracer 特定配置
1. function tracer 配置
ftrace_filter=__do_softirq,vfs_*,tcp_* ftrace_notrace=*lock*,*spin*
- ftrace_filter:只跟踪特定函数
- ftrace_notrace:排除特定函数
- 支持通配符 *
2. function_graph tracer 配置
ftrace_graph_filter=SyS_*,do_* ftrace_graph_notrace=*spin*,*lock*
- 配置函数图跟踪器的过滤规则
- 语法与 function tracer 相同
3. 设置函数图深度
ftrace_graph_max_depth=10
- 限制函数图的最大调用深度
- 防止无限递归导致缓冲区溢出
3 处理task_newtask/task_rename,生成进程树全景
解析从/sys/kernel/debug/tracing/trace获取的task_newtask/task_rename日志:
import re from collections import defaultdict # 定义 clone_flags 常量 (来自 Linux 内核 sched.h) CLONE_VM = 0x00000100 CLONE_FS = 0x00000200 CLONE_FILES = 0x00000400 CLONE_SIGHAND = 0x00000800 CLONE_PTRACE = 0x00002000 CLONE_VFORK = 0x00004000 CLONE_PARENT = 0x00008000 CLONE_THREAD = 0x00010000 CLONE_NEWNS = 0x00020000 CLONE_SYSVSEM = 0x00040000 CLONE_SETTLS = 0x00080000 CLONE_PARENT_SETTID = 0x00100000 CLONE_CHILD_CLEARTID = 0x00200000 CLONE_DETACHED = 0x00400000 CLONE_UNTRACED = 0x00800000 CLONE_CHILD_SETTID = 0x01000000 CLONE_NEWCGROUP = 0x02000000 CLONE_NEWUTS = 0x04000000 CLONE_NEWIPC = 0x08000000 CLONE_NEWUSER = 0x10000000 CLONE_NEWPID = 0x20000000 CLONE_NEWNET = 0x40000000 CLONE_IO = 0x80000000 class ProcessTree: def __init__(self, exclude_threads=False, exclude_kthreads=False): self.processes = {} self.children = defaultdict(list) self.root_pid = 0 self.exclude_threads = exclude_threads self.exclude_kthreads = exclude_kthreads # 创建默认的进程0,名称为idle self.add_process(0, "idle", None, None) def add_process(self, pid, name, parent_pid, clone_flags): """添加新进程到进程树""" # 检查是否应该排除该进程/线程 if self.should_exclude(pid, name, clone_flags): return False # 如果进程已存在,更新名称(除非是占位符) if pid in self.processes: if self.processes[pid]["name"].startswith("Unknown_"): self.processes[pid]["name"] = name return True # 创建新进程 self.processes[pid] = { "name": name, "parent_pid": parent_pid, "clone_flags": clone_flags } # 如果父进程不存在,创建占位符 if parent_pid is not None and parent_pid not in self.processes: self.add_process(parent_pid, f"Unknown_{parent_pid}", None, None) # 建立父子关系 if parent_pid is not None and parent_pid != pid: # 避免自引用 self.children[parent_pid].append(pid) return True def should_exclude(self, pid, name, clone_flags): """检查是否应该排除该进程/线程""" if pid == self.root_pid: # 永不排除根进程 return False # 排除用户线程 if self.exclude_threads and clone_flags is not None: try: flags = int(clone_flags, 16) # 检查 CLONE_THREAD 标志 (线程共享线程组ID) if flags & CLONE_THREAD: return True except (ValueError, TypeError): pass # 排除内核线程 if self.exclude_kthreads and name.startswith("kworker/"): return True if self.exclude_kthreads and name.startswith("ksoftirqd/"): return True if self.exclude_kthreads and name.startswith("rcu_"): return True if self.exclude_kthreads and name.startswith("migration/"): return True return False def rename_process(self, pid, new_name): """重命名指定PID的进程""" if pid in self.processes: self.processes[pid]["name"] = new_name def resolve_orphans(self): """处理孤儿进程,将它们挂到根节点下""" for pid, proc in list(self.processes.items()): if pid == self.root_pid: continue if proc["parent_pid"] is None or proc["parent_pid"] not in self.processes: # 将孤儿进程挂到根节点下 self.processes[pid]["parent_pid"] = self.root_pid self.children[self.root_pid].append(pid) def build_tree(self): """重建完整的树结构""" # 重建子节点列表 new_children = defaultdict(list) for pid, proc in self.processes.items(): parent_pid = proc["parent_pid"] if parent_pid is not None and parent_pid in self.processes and parent_pid != pid: new_children[parent_pid].append(pid) self.children = new_children def print_tree(self, pid=None, indent=0, output_file=None): """递归打印进程树""" if pid is None: pid = self.root_pid if pid not in self.processes: return proc = self.processes[pid] line = f"{' ' * indent}{pid}:{proc['name']}" print(line) if output_file: output_file.write(line + "\n") # 递归打印子进程,按PID排序 for child_pid in sorted(self.children.get(pid, [])): self.print_tree(child_pid, indent + 4, output_file) def parse_ftrace_events(events, exclude_threads=False, exclude_kthreads=False): """解析ftrace事件并构建进程树""" tree = ProcessTree(exclude_threads=exclude_threads, exclude_kthreads=exclude_kthreads) # 调试信息 debug_info = [] unmatched_lines = [] excluded_processes = [] # 改进的正则表达式模式 - 更通用 newtask_pattern = re.compile( r'^\s*(\S+)-(\d+)\s+.*task_newtask:\s*pid=(\d+)\s+comm=(\S+)\s+clone_flags=(\S+)' ) # 特别注意:task_rename可能有多种格式 rename_pattern = re.compile( r'^\s*(\S+)-(\d+)\s+.*task_rename:\s*pid=(\d+)\s+newcomm=(\S+)' ) # 备选正则表达式 - 处理不同格式 rename_pattern_alt = re.compile( r'^\s*(\S+)-(\d+)\s+.*task_rename:\s*pid=(\d+)\s+.*newcomm=(\S+)' ) # 另一个备选正则表达式 - 更宽松 rename_pattern_alt2 = re.compile( r'.*task_rename.*pid=(\d+).*newcomm=(\S+)' ) for line_num, line in enumerate(events, 1): line = line.strip() if not line: continue # 解析task_newtask事件 newtask_match = newtask_pattern.match(line) if newtask_match: # 提取父进程信息 parent_name = newtask_match.group(1) parent_pid = int(newtask_match.group(2)) # 提取新进程信息 child_pid = int(newtask_match.group(3)) child_name = newtask_match.group(4) clone_flags = newtask_match.group(5) # 特殊处理swapper进程 if parent_name.startswith("swapper/"): parent_name = "idle" # 确保父进程存在 if parent_pid not in tree.processes: tree.add_process(parent_pid, parent_name, None, None) # 添加新进程 added = tree.add_process(child_pid, child_name, parent_pid, clone_flags) if added: debug_info.append(f"Line {line_num}: ADDED process {child_pid} '{child_name}' with parent {parent_pid} '{parent_name}' flags={clone_flags}") else: excluded_processes.append(f"Line {line_num}: EXCLUDED process {child_pid} '{child_name}' flags={clone_flags}") continue # 尝试多种正则表达式解析task_rename事件 rename_match = None rename_patterns = [rename_pattern, rename_pattern_alt, rename_pattern_alt2] for pattern in rename_patterns: rename_match = pattern.match(line) if rename_match: break if rename_match: # 提取目标进程信息 try: # 不同正则表达式可能有不同分组数 if pattern == rename_pattern_alt2: target_pid = int(rename_match.group(1)) new_name = rename_match.group(2) else: target_pid = int(rename_match.group(3)) new_name = rename_match.group(4) # 更新进程名称 tree.rename_process(target_pid, new_name) debug_info.append(f"Line {line_num}: RENAME - PID:{target_pid} to '{new_name}'") continue except (IndexError, ValueError) as e: debug_info.append(f"Line {line_num}: ERROR parsing rename - {str(e)}") # 如果既不是newtask也不是rename,记录下来 if not newtask_match and not rename_match: unmatched_lines.append(f"Line {line_num}: {line}") # 处理孤儿进程 tree.resolve_orphans() # 构建完整树结构 tree.build_tree() # 写入调试信息 with open('debug.log', 'w') as debug_file: debug_file.write("=== MATCHED AND ADDED EVENTS ===\n") for info in debug_info: debug_file.write(info + "\n") debug_file.write("\n=== EXCLUDED PROCESSES ===\n") for info in excluded_processes: debug_file.write(info + "\n") debug_file.write("\n=== UNMATCHED LINES ===\n") for line in unmatched_lines: debug_file.write(line + "\n") return tree def main(): try: # 从task.log读取数据 with open('task.log', 'r') as f: events = f.readlines() except FileNotFoundError: print("错误:找不到task.log文件") return except Exception as e: print(f"读取文件出错: {e}") return # 配置排除选项 (根据需要修改) exclude_user_threads = False # 排除用户线程 exclude_kernel_threads = False # 排除内核线程 # 解析事件并构建进程树 tree = parse_ftrace_events( events, exclude_threads=exclude_user_threads, exclude_kthreads=exclude_kernel_threads ) try: # 输出分析结果到task_tree.log with open('task_tree.log', 'w') as output_file: tree.print_tree(output_file=output_file) print("进程树已成功写入task_tree.log") print("调试信息已写入debug.log") # 打印排除统计 print(f"\n排除选项: 用户线程={exclude_user_threads}, 内核线程={exclude_kernel_threads}") except Exception as e: print(f"写入输出文件出错: {e}") if __name__ == "__main__": main()
解析结果如下:
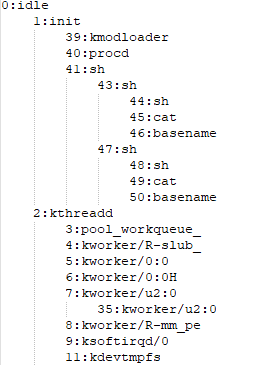
改进:
1. 通过解析sched_process_exec,获取可执行程序的完整路径名。便于知道sh执行的是哪个脚本。
2. 增加统计子进程/线程的功能,方便知道创建了多少进程/进程。
import re from collections import defaultdict # 定义 clone_flags 常量 (来自 Linux 内核 sched.h) CLONE_VM = 0x00000100 CLONE_FS = 0x00000200 CLONE_FILES = 0x00000400 CLONE_SIGHAND = 0x00000800 CLONE_PTRACE = 0x00002000 CLONE_VFORK = 0x00004000 CLONE_PARENT = 0x00008000 CLONE_THREAD = 0x00010000 CLONE_NEWNS = 0x00020000 CLONE_SYSVSEM = 0x00040000 CLONE_SETTLS = 0x00080000 CLONE_PARENT_SETTID = 0x00100000 CLONE_CHILD_CLEARTID = 0x00200000 CLONE_DETACHED = 0x00400000 CLONE_UNTRACED = 0x00800000 CLONE_CHILD_SETTID = 0x01000000 CLONE_NEWCGROUP = 0x02000000 CLONE_NEWUTS = 0x04000000 CLONE_NEWIPC = 0x08000000 CLONE_NEWUSER = 0x10000000 CLONE_NEWPID = 0x20000000 CLONE_NEWNET = 0x40000000 CLONE_IO = 0x80000000 class ProcessTree: def __init__(self, exclude_threads=False, exclude_kthreads=False): self.processes = {} self.children = defaultdict(list) self.root_pid = 0 self.exclude_threads = exclude_threads self.exclude_kthreads = exclude_kthreads self.descendant_counts = {} # 存储每个进程的子孙进程总数量 # 创建默认的进程0,名称为idle self.add_process(0, "idle", None, None) # 记录已经通过exec事件重命名的进程 self.renamed_by_exec = set() def add_process(self, pid, name, parent_pid, clone_flags): """添加新进程到进程树""" # 检查是否应该排除该进程/线程 if self.should_exclude(pid, name, clone_flags): return False # 如果进程已存在,更新名称和父进程(除非是占位符) if pid in self.processes: proc = self.processes[pid] # 更新名称(如果是占位符) if proc["name"].startswith("Unknown_"): proc["name"] = name # 更新父进程(如果当前没有父进程且新事件提供了父进程) if proc["parent_pid"] is None and parent_pid is not None: proc["parent_pid"] = parent_pid return True # 创建新进程 self.processes[pid] = { "name": name, "parent_pid": parent_pid, "clone_flags": clone_flags } # 如果父进程不存在,创建占位符 if parent_pid is not None and parent_pid not in self.processes: self.add_process(parent_pid, f"Unknown_{parent_pid}", None, None) # 建立父子关系 if parent_pid is not None and parent_pid != pid: # 避免自引用 self.children[parent_pid].append(pid) return True def should_exclude(self, pid, name, clone_flags): """检查是否应该排除该进程/线程""" if pid == self.root_pid: # 永不排除根进程 return False # 排除用户线程 if self.exclude_threads and clone_flags is not None: try: flags = int(clone_flags, 16) # 检查 CLONE_THREAD 标志 (线程共享线程组ID) if flags & CLONE_THREAD: return True except (ValueError, TypeError): pass # 排除内核线程 if self.exclude_kthreads and name.startswith("kworker/"): return True if self.exclude_kthreads and name.startswith("ksoftirqd/"): return True if self.exclude_kthreads and name.startswith("rcu_"): return True if self.exclude_kthreads and name.startswith("migration/"): return True return False def rename_process(self, pid, new_name, by_exec=False): """重命名指定PID的进程""" if pid in self.processes: self.processes[pid]["name"] = new_name if by_exec: # 标记为已通过exec事件重命名 self.renamed_by_exec.add(pid) def is_renamed_by_exec(self, pid): """检查进程是否已经通过exec事件重命名""" return pid in self.renamed_by_exec def resolve_orphans(self): """处理孤儿进程,将它们挂到根节点下""" for pid, proc in list(self.processes.items()): if pid == self.root_pid: continue if proc["parent_pid"] is None or proc["parent_pid"] not in self.processes: # 将孤儿进程挂到根节点下 self.processes[pid]["parent_pid"] = self.root_pid self.children[self.root_pid].append(pid) def build_tree(self): """重建完整的树结构""" # 重建子节点列表 new_children = defaultdict(list) for pid, proc in self.processes.items(): parent_pid = proc["parent_pid"] if parent_pid is not None and parent_pid in self.processes and parent_pid != pid: new_children[parent_pid].append(pid) self.children = new_children def compute_descendant_counts(self): """计算每个进程的子孙进程总数量(包括所有后代)""" # 初始化所有进程的子孙数量为0 self.descendant_counts = {pid: 0 for pid in self.processes} # 后序遍历计算子孙数量 def _dfs(pid): total = 0 for child_pid in self.children.get(pid, []): # 递归计算子节点的子孙数量 _dfs(child_pid) # 子孙总数 = 子节点数 + 子节点的子孙总数 total += 1 + self.descendant_counts[child_pid] self.descendant_counts[pid] = total # 从根节点开始计算 _dfs(self.root_pid) def print_tree(self, pid=None, indent=0, output_file=None): """递归打印进程树,显示所有子孙进程的总数量""" if pid is None: pid = self.root_pid if pid not in self.processes: return proc = self.processes[pid] # 获取所有子孙进程的总数量 total_descendants = self.descendant_counts.get(pid, 0) # 在进程名后添加子孙总数 name_display = proc["name"] if total_descendants > 0: name_display += f" ({total_descendants})" line = f"{' ' * indent}{pid}:{name_display}" print(line) if output_file: output_file.write(line + "\n") # 递归打印子进程,按PID排序 for child_pid in sorted(self.children.get(pid, [])): self.print_tree(child_pid, indent + 4, output_file) def parse_ftrace_events(events, exclude_threads=False, exclude_kthreads=False): """解析ftrace事件并构建进程树""" tree = ProcessTree(exclude_threads=exclude_threads, exclude_kthreads=exclude_kthreads) # 调试信息 debug_info = [] unmatched_lines = [] excluded_processes = [] # 改进的正则表达式模式 - 更通用 newtask_pattern = re.compile( r'^\s*(\S+)-(\d+)\s+.*task_newtask:\s*pid=(\d+)\s+comm=(\S+)\s+clone_flags=(\S+)' ) # 特别注意:task_rename可能有多种格式 rename_pattern = re.compile( r'^\s*(\S+)-(\d+)\s+.*task_rename:\s*pid=(\d+)\s+newcomm=(\S+)' ) # 备选正则表达式 - 处理不同格式 rename_pattern_alt = re.compile( r'^\s*(\S+)-(\d+)\s+.*task_rename:\s*pid=(\d+)\s+.*newcomm=(\S+)' ) # 另一个备选正则表达式 - 更宽松 rename_pattern_alt2 = re.compile( r'.*task_rename.*pid=(\d+).*newcomm=(\S+)' ) # sched_process_exec 事件解析 exec_pattern = re.compile( r'.*sched_process_exec:\s*filename=(\S+)\s+pid=(\d+)\s+old_pid=\d+.*' ) for line_num, line in enumerate(events, 1): line = line.strip() if not line: continue # 解析task_newtask事件 newtask_match = newtask_pattern.match(line) if newtask_match: # 提取父进程信息 parent_name = newtask_match.group(1) parent_pid = int(newtask_match.group(2)) # 提取新进程信息 child_pid = int(newtask_match.group(3)) child_name = newtask_match.group(4) clone_flags = newtask_match.group(5) # 特殊处理swapper进程 if parent_name.startswith("swapper/"): parent_name = "idle" # 确保父进程存在 if parent_pid not in tree.processes: tree.add_process(parent_pid, parent_name, None, None) # 添加新进程 added = tree.add_process(child_pid, child_name, parent_pid, clone_flags) if added: debug_info.append(f"Line {line_num}: ADDED process {child_pid} '{child_name}' with parent {parent_pid} '{parent_name}' flags={clone_flags}") else: excluded_processes.append(f"Line {line_num}: EXCLUDED process {child_pid} '{child_name}' flags={clone_flags}") continue # 尝试多种正则表达式解析task_rename事件 rename_match = None rename_patterns = [rename_pattern, rename_pattern_alt, rename_pattern_alt2] for pattern in rename_patterns: rename_match = pattern.match(line) if rename_match: break if rename_match: # 提取目标进程信息 try: # 不同正则表达式可能有不同分组数 if pattern == rename_pattern_alt2: target_pid = int(rename_match.group(1)) new_name = rename_match.group(2) else: target_pid = int(rename_match.group(3)) new_name = rename_match.group(4) # 如果该进程已经通过exec事件重命名,则忽略此重命名事件 if tree.is_renamed_by_exec(target_pid): debug_info.append(f"Line {line_num}: SKIP RENAME (already renamed by exec) for PID:{target_pid}") continue # 更新进程名称 tree.rename_process(target_pid, new_name) debug_info.append(f"Line {line_num}: RENAME - PID:{target_pid} to '{new_name}'") continue except (IndexError, ValueError) as e: debug_info.append(f"Line {line_num}: ERROR parsing rename - {str(e)}") # 解析sched_process_exec事件 exec_match = exec_pattern.match(line) if exec_match: try: filename = exec_match.group(1) pid_val = int(exec_match.group(2)) # 如果进程不存在,先创建它(作为孤儿) if pid_val not in tree.processes: tree.add_process(pid_val, filename, None, None) # 标记为已通过exec事件重命名 tree.rename_process(pid_val, filename, by_exec=True) debug_info.append(f"Line {line_num}: EXEC ADDED process {pid_val} '{filename}' (orphan)") else: # 更新进程名称为执行的文件名,并标记 tree.rename_process(pid_val, filename, by_exec=True) debug_info.append(f"Line {line_num}: EXEC RENAME - PID:{pid_val} to '{filename}'") except (IndexError, ValueError) as e: debug_info.append(f"Line {line_num}: ERROR parsing exec - {str(e)}") continue # 如果所有模式都不匹配,记录下来 if not newtask_match and not rename_match and not exec_match: unmatched_lines.append(f"Line {line_num}: {line}") # 处理孤儿进程 tree.resolve_orphans() # 构建完整树结构 tree.build_tree() # 计算每个进程的子孙进程总数 tree.compute_descendant_counts() # 写入调试信息 with open('debug.log', 'w') as debug_file: debug_file.write("=== MATCHED AND ADDED EVENTS ===\n") for info in debug_info: debug_file.write(info + "\n") debug_file.write("\n=== EXCLUDED PROCESSES ===\n") for info in excluded_processes: debug_file.write(info + "\n") debug_file.write("\n=== UNMATCHED LINES ===\n") for line in unmatched_lines: debug_file.write(line + "\n") return tree def main(): try: # 从task.log读取数据 with open('task.log', 'r') as f: events = f.readlines() except FileNotFoundError: print("错误:找不到task.log文件") return except Exception as e: print(f"读取文件出错: {e}") return # 配置排除选项 (根据需要修改) exclude_user_threads = False # 排除用户线程 exclude_kernel_threads = False # 排除内核线程 # 解析事件并构建进程树 tree = parse_ftrace_events( events, exclude_threads=exclude_user_threads, exclude_kthreads=exclude_kernel_threads ) try: # 输出分析结果到task_tree.log with open('task_tree.log', 'w') as output_file: tree.print_tree(output_file=output_file) print("进程树已成功写入task_tree.log") print("调试信息已写入debug.log") # 打印排除统计 print(f"\n排除选项: 用户线程={exclude_user_threads}, 内核线程={exclude_kernel_threads}") except Exception as e: print(f"写入输出文件出错: {e}") if __name__ == "__main__": main()



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号