ARM Trusted Firmware分析——启动、PSCI、OP-TEE接口
关键词:等等。
下图划分成不同EL,分别描述BL1、BL2、BL31、BL32、BL33启动流程,以及PSCI、SP处理流程。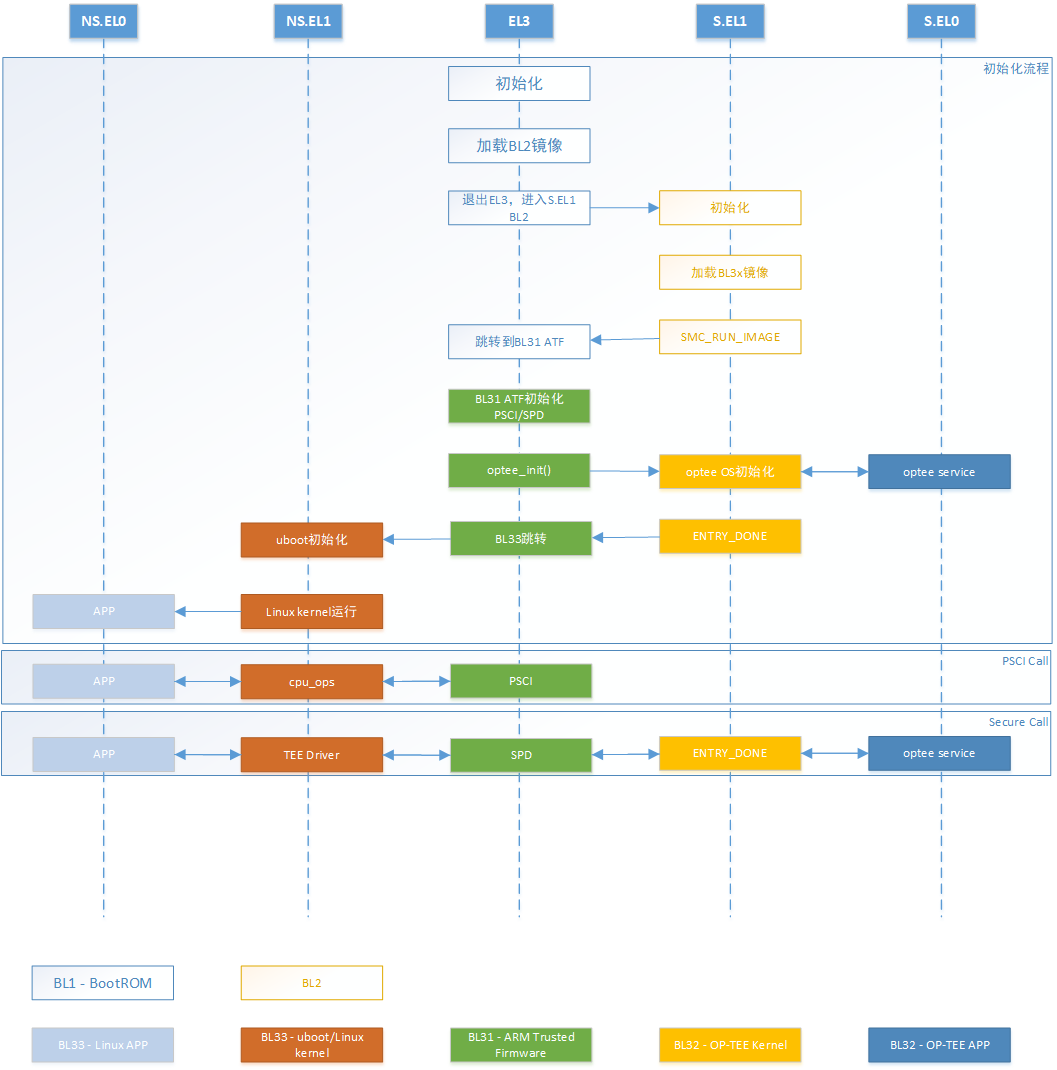
1. 冷启动(Cold boot)流程及阶段划分
ATF冷启动实现分为5个步骤:
- BL1 - AP Trusted ROM,一般为BootRom。
- BL2 - Trusted Boot Firmware,一般为Trusted Bootloader。
- BL31 - EL3 Runtime Firmware,一般为SML,管理SMC执行处理和中断,运行在secure monitor中。
- BL32 - Secure-EL1 Payload,一般为TEE OS Image。
- BL33 - Non-Trusted Firmware,一般为uboot、linux kernel。
ATF输出BL1、BL2、BL31,提供BL32和BL33接口。
启动流程如下:

1.1 BL1
BL1位于ROM中,在EL3下从reset vector处开始运行。
BL1做的工作主要有:
- 决定启动路径:冷启动还是热启动。
- 架构初始化:异常向量、CPU复位处理函数配置、控制寄存器设置(SCRLR_EL3/SCR_EL3/CPTR_EL3/DAIF)
- 平台初始化:使能Trusted Watchdog、初始化控制台、配置硬件一致性互联、配置MMU、初始化相关存储设备。
- 固件更新处理
- BL2镜像加载和执行:
- BL1输出“Booting Trusted Firmware"。
- BL1加载BL2到SRAM;如果SRAM不够或者BL2镜像错误,输出“Failed to load BL2 firmware.”。
- BL1切换到Secure EL1并将执行权交给BL2.
1.2 BL2
BL2位于SRAM中,运行在Secure EL1主要工作有:
- 架构初始化:EL1/EL0使能浮点单元和ASMID。
- 平台初始化:控制台初始化、相关存储设备初始化、MMU、相关设备安全配置、
- SCP_BL2:系统控制核镜像加载,单独核处理系统功耗、时钟、复位等控制。
- 加载BL31镜像:BL2将控制权交给BL1;BL1关闭MMU并关cache;BL1将控制权交给BL31。
- 加载BL32镜像:BL32运行在安全世界,BL2依赖BL31将控制权交给BL32。SPSR通过Secure-EL1 Payload Dispatcher进行初始化。
- 加载BL33镜像:BL2依赖BL31将控制权交给BL33。
1.3 BL31
BL31位于SRAM中,EL3模式。除了做架构初始化和平台初始化外,还做了如下工作:
- PSCI服务初始化,后续提供CPU功耗管理操作。
- BL32镜像运行初始化,处于Secure EL1模式。
- 初始化非安全EL2或EL1,跳转到BL33执行。
- 负责安全非安全世界切换。
- 进行安全服务请求的分发。
2 BL1
BL1镜像的异常向量表初始化了两个:一个是入口bl1_entrypoint,EL1镜像正常执行流程;另一个是SMC调用接口,EL2执行结束会通过SMC返回执行BL31。
vector_base bl1_vector_table
b bl1_entrypoint
b report_exception /* Undef */
b bl1_aarch32_smc_handler /* SMC call */
b report_exception /* Prefetch abort */
b report_exception /* Data abort */
b report_exception /* Reserved */
b report_exception /* IRQ */
b report_exception /* FIQ */
func bl1_aarch32_smc_handler
/* ------------------------------------------------
* SMC in BL1 is handled assuming that the MMU is
* turned off by BL2.
* ------------------------------------------------
*/
/* ----------------------------------------------
* Only RUN_IMAGE SMC is supported.
* ----------------------------------------------
*/
mov r8, #BL1_SMC_RUN_IMAGE--------------------------仅支持BL1_SMC_RUN_IMAGE SMC调用;其他调用触发report_exception。
cmp r8, r0
blne report_exception
/* ------------------------------------------------
* Make sure only Secure world reaches here.
* ------------------------------------------------
*/
ldcopr r8, SCR
tst r8, #SCR_NS_BIT---------------------------------如果处于非安全状态,则触发report_exception。
blne report_exception
/* ---------------------------------------------------------------------
* Pass control to next secure image.
* Here it expects r1 to contain the address of a entry_point_info_t
* structure describing the BL entrypoint.
* ---------------------------------------------------------------------
*/
mov r8, r1------------------------------------------第一个参数r0是功能id,即BL1_SMC_RUN_IMAGE_SMC。第二个参数是entry_point_info_t变量。
mov r0, r1
bl bl1_print_next_bl_ep_info
#if SPIN_ON_BL1_EXIT
bl print_debug_loop_message
debug_loop:
b debug_loop
#endif
mov r0, r8
bl bl1_plat_prepare_exit
stcopr r0, TLBIALL
dsb sy
isb
/*
* Extract PC and SPSR based on struct `entry_point_info_t`
* and load it in LR and SPSR registers respectively.
*/
ldr lr, [r8, #ENTRY_POINT_INFO_PC_OFFSET]
ldr r1, [r8, #(ENTRY_POINT_INFO_PC_OFFSET + 4)]
msr spsr, r1
add r8, r8, #ENTRY_POINT_INFO_ARGS_OFFSET
ldm r8, {r0, r1, r2, r3}----------------------------执行跳转到BL31。
eret
endfunc bl1_aarch32_smc_handler
bl1_entrypoint()进行EL3执行环境初始化,设定向量表,加载bl2镜像并跳转到BL2执行。
func bl1_entrypoint
/* ---------------------------------------------------------------------
* If the reset address is programmable then bl1_entrypoint() is
* executed only on the cold boot path. Therefore, we can skip the warm
* boot mailbox mechanism.
* ---------------------------------------------------------------------
*/
el3_entrypoint_common \
_set_endian=1 \----------------------是否设定大小端。
_warm_boot_mailbox=!PROGRAMMABLE_RESET_ADDRESS \-----是否检查当前属于冷启动还是热启动。
_secondary_cold_boot=!COLD_BOOT_SINGLE_CPU \---------确定当前CPU是主CPU还是从CPU。
_init_memory=1 \---------------------是否初始化memory。
_init_c_runtime=1 \----------------------是否初始化C语言执行环境。
_exception_vectors=bl1_exceptions-----------------------异常向量表。
/* ---------------------------------------------
* Architectural init. can be generic e.g.
* enabling stack alignment and platform spec-
* ific e.g. MMU & page table setup as per the
* platform memory map. Perform the latter here
* and the former in bl1_main.
* ---------------------------------------------
*/
bl bl1_early_platform_setup-------------------初始化memory、page table,所需外围设备初始化等。
bl bl1_plat_arch_setup
/* --------------------------------------------------
* Initialize platform and jump to our c-entry point
* for this type of reset.
* --------------------------------------------------
*/
bl bl1_main--------------------------------------------进行必要初始化,加载BL2镜像然后为退出EL3进入S.EL1做好准备。
/* --------------------------------------------------
* Do the transition to next boot image.
* --------------------------------------------------
*/
b el3_exit
endfunc bl1_entrypoint
el3_entrypoint_common()主要完成进入EL3基本设置和向量表注册。
.macro el3_entrypoint_common \
_set_endian, _warm_boot_mailbox, _secondary_cold_boot, \
_init_memory, _init_c_runtime, _exception_vectors
.if \_set_endian-------------------------------------------------------在进行内存读写之前,设置好系统的大小端。
/* -------------------------------------------------------------
* Set the CPU endianness before doing anything that might
* involve memory reads or writes.
* -------------------------------------------------------------
*/
mrs x0, sctlr_el3
bic x0, x0, #SCTLR_EE_BIT
msr sctlr_el3, x0
isb
.endif /* _set_endian */
.if \_warm_boot_mailbox------------------------------------------------根据当前平台的entrypoint判断是冷启动还是热启动。
/* -------------------------------------------------------------
* This code will be executed for both warm and cold resets.
* Now is the time to distinguish between the two.
* Query the platform entrypoint address and if it is not zero
* then it means it is a warm boot so jump to this address.
* -------------------------------------------------------------
*/
bl plat_get_my_entrypoint
cbz x0, do_cold_boot--------------------------------------------如果为0说明是冷启动,执行do_cold_boot();非0则跳转到entrypoint执行。
br x0
do_cold_boot:
.endif /* _warm_boot_mailbox */
/* ---------------------------------------------------------------------
* It is a cold boot.
* Perform any processor specific actions upon reset e.g. cache, TLB
* invalidations etc.
* ---------------------------------------------------------------------
*/
bl reset_handler---------------------------------------------------执行reset_handler()。
el3_arch_init_common \_exception_vectors------------------------------初始化异常向量。
.if \_secondary_cold_boot---------------------------------------------判断当前CPU是主CPU还是从CPU。
/* -------------------------------------------------------------
* Check if this is a primary or secondary CPU cold boot.
* The primary CPU will set up the platform while the
* secondaries are placed in a platform-specific state until the
* primary CPU performs the necessary actions to bring them out
* of that state and allows entry into the OS.
* -------------------------------------------------------------
*/
bl plat_is_my_cpu_primary
cbnz w0, do_primary_cold_boot
/* This is a cold boot on a secondary CPU */
bl plat_secondary_cold_boot_setup
/* plat_secondary_cold_boot_setup() is not supposed to return */
bl el3_panic
do_primary_cold_boot:
.endif /* _secondary_cold_boot */
/* ---------------------------------------------------------------------
* Initialize memory now. Secondary CPU initialization won't get to this
* point.
* ---------------------------------------------------------------------
*/
.if \_init_memory----------------------------------------------------初始化内存。
bl platform_mem_init
.endif /* _init_memory */
/* ---------------------------------------------------------------------
* Init C runtime environment:
* - Zero-initialise the NOBITS sections. There are 2 of them:
* - the .bss section;
* - the coherent memory section (if any).
* - Relocate the data section from ROM to RAM, if required.
* ---------------------------------------------------------------------
*/
.if \_init_c_runtime-------------------------------------------------初始化C执行环境。
#if IMAGE_BL31
/* -------------------------------------------------------------
* Invalidate the RW memory used by the BL31 image. This
* includes the data and NOBITS sections. This is done to
* safeguard against possible corruption of this memory by
* dirty cache lines in a system cache as a result of use by
* an earlier boot loader stage.
* -------------------------------------------------------------
*/
adr x0, __RW_START__
adr x1, __RW_END__
sub x1, x1, x0
bl inv_dcache_range
#endif /* IMAGE_BL31 */
ldr x0, =__BSS_START__
ldr x1, =__BSS_SIZE__
bl zeromem16
#if USE_COHERENT_MEM
ldr x0, =__COHERENT_RAM_START__
ldr x1, =__COHERENT_RAM_UNALIGNED_SIZE__
bl zeromem16
#endif
#if IMAGE_BL1
ldr x0, =__DATA_RAM_START__
ldr x1, =__DATA_ROM_START__
ldr x2, =__DATA_SIZE__
bl memcpy16
#endif
.endif /* _init_c_runtime */
/* ---------------------------------------------------------------------
* Use SP_EL0 for the C runtime stack.
* ---------------------------------------------------------------------
*/
msr spsel, #0
/* ---------------------------------------------------------------------
* Allocate a stack whose memory will be marked as Normal-IS-WBWA when
* the MMU is enabled. There is no risk of reading stale stack memory
* after enabling the MMU as only the primary CPU is running at the
* moment.
* ---------------------------------------------------------------------
*/
bl plat_set_my_stack
.endm
bl1_main()完成架构和平台特有初始化操作,然后加载BL2镜像并跳转执行。
/******************************************************************************* * Function to perform late architectural and platform specific initialization. * It also queries the platform to load and run next BL image. Only called * by the primary cpu after a cold boot. ******************************************************************************/ void bl1_main(void) { unsigned int image_id; /* Announce our arrival */ NOTICE(FIRMWARE_WELCOME_STR); NOTICE("BL1: %s\n", version_string); NOTICE("BL1: %s\n", build_message); INFO("BL1: RAM %p - %p\n", (void *)BL1_RAM_BASE, (void *)BL1_RAM_LIMIT); ... /* Perform remaining generic architectural setup from EL3 */ bl1_arch_setup(); #if TRUSTED_BOARD_BOOT /* Initialize authentication module */ auth_mod_init();----------------------------------------------初始化安全模块和镜像解析模块。 #endif /* TRUSTED_BOARD_BOOT */ /* Perform platform setup in BL1. */ bl1_platform_setup(); /* Get the image id of next image to load and run. */ image_id = bl1_plat_get_next_image_id();----------------------获取下一级启动镜像的ID。 /* * We currently interpret any image id other than * BL2_IMAGE_ID as the start of firmware update. */ if (image_id == BL2_IMAGE_ID) bl1_load_bl2();------------------------------------------将BL2镜像加载到TSRAM中。 else NOTICE("BL1-FWU: *******FWU Process Started*******\n"); bl1_prepare_next_image(image_id);----------------------------获取image_id对应镜像描述信息,并为进入下一级镜像执行准备好上下文。 } /******************************************************************************* * This function locates and loads the BL2 raw binary image in the trusted SRAM. * Called by the primary cpu after a cold boot. * TODO: Add support for alternative image load mechanism e.g using virtio/elf * loader etc. ******************************************************************************/ void bl1_load_bl2(void) { image_desc_t *image_desc; image_info_t *image_info; entry_point_info_t *ep_info; meminfo_t *bl1_tzram_layout; meminfo_t *bl2_tzram_layout; int err; /* Get the image descriptor */ image_desc = bl1_plat_get_image_desc(BL2_IMAGE_ID); assert(image_desc); /* Get the image info */ image_info = &image_desc->image_info; /* Get the entry point info */ ep_info = &image_desc->ep_info; /* Find out how much free trusted ram remains after BL1 load */ bl1_tzram_layout = bl1_plat_sec_mem_layout(); INFO("BL1: Loading BL2\n"); #if LOAD_IMAGE_V2 err = load_auth_image(BL2_IMAGE_ID, image_info); #else /* Load the BL2 image */ err = load_auth_image(bl1_tzram_layout, BL2_IMAGE_ID, image_info->image_base, image_info, ep_info); #endif /* LOAD_IMAGE_V2 */ if (err) { ERROR("Failed to load BL2 firmware.\n"); plat_error_handler(err); } /* * Create a new layout of memory for BL2 as seen by BL1 i.e. * tell it the amount of total and free memory available. * This layout is created at the first free address visible * to BL2. BL2 will read the memory layout before using its * memory for other purposes. */ #if LOAD_IMAGE_V2 bl2_tzram_layout = (meminfo_t *) bl1_tzram_layout->total_base; #else bl2_tzram_layout = (meminfo_t *) bl1_tzram_layout->free_base; #endif /* LOAD_IMAGE_V2 */ bl1_init_bl2_mem_layout(bl1_tzram_layout, bl2_tzram_layout); ep_info->args.arg1 = (uintptr_t)bl2_tzram_layout; NOTICE("BL1: Booting BL2\n"); VERBOSE("BL1: BL2 memory layout address = %p\n", (void *) bl2_tzram_layout); } /******************************************************************************* * This function prepares the context for Secure/Normal world images. * Normal world images are transitioned to EL2(if supported) else EL1. ******************************************************************************/ void bl1_prepare_next_image(unsigned int image_id) { unsigned int security_state; image_desc_t *image_desc; entry_point_info_t *next_bl_ep; #if CTX_INCLUDE_AARCH32_REGS /* * Ensure that the build flag to save AArch32 system registers in CPU * context is not set for AArch64-only platforms. */ if (((read_id_aa64pfr0_el1() >> ID_AA64PFR0_EL1_SHIFT) & ID_AA64PFR0_ELX_MASK) == 0x1) { ERROR("EL1 supports AArch64-only. Please set build flag " "CTX_INCLUDE_AARCH32_REGS = 0"); panic(); } #endif /* Get the image descriptor. */ image_desc = bl1_plat_get_image_desc(image_id);---------------获取镜像描述信息,包括入口地址、名字等等。 assert(image_desc); /* Get the entry point info. */ next_bl_ep = &image_desc->ep_info; /* Get the image security state. */ security_state = GET_SECURITY_STATE(next_bl_ep->h.attr);------镜像是属于安全还是非安全镜像。 /* Setup the Secure/Non-Secure context if not done already. */ if (!cm_get_context(security_state)) cm_set_context(&bl1_cpu_context[security_state], security_state); /* Prepare the SPSR for the next BL image. */ if (security_state == SECURE) {-------------------------------设置镜像运行的SPSR数据。 next_bl_ep->spsr = SPSR_64(MODE_EL1, MODE_SP_ELX, DISABLE_ALL_EXCEPTIONS); } else { /* Use EL2 if supported else use EL1. */ if (read_id_aa64pfr0_el1() & (ID_AA64PFR0_ELX_MASK << ID_AA64PFR0_EL2_SHIFT)) { next_bl_ep->spsr = SPSR_64(MODE_EL2, MODE_SP_ELX, DISABLE_ALL_EXCEPTIONS); } else { next_bl_ep->spsr = SPSR_64(MODE_EL1, MODE_SP_ELX, DISABLE_ALL_EXCEPTIONS); } } /* Allow platform to make change */ bl1_plat_set_ep_info(image_id, next_bl_ep); /* Prepare the context for the next BL image. */ cm_init_my_context(next_bl_ep); cm_prepare_el3_exit(security_state);--------------------------为运行下一个镜像,EL3做好准备。 /* Indicate that image is in execution state. */ image_desc->state = IMAGE_STATE_EXECUTED; print_entry_point_info(next_bl_ep);---------------------------打印下一级进行相关信息。下面即将el3_exit,退出EL3进入新的进项运行。 }
3 BL2
BL2的主要工作就是加载BL3x系列镜像,然后通过SMC进入BL1进而跳转到BL31运行。
bl2_entrypoint()是BL2的入口,前半部分主要进行一系列初始化工作,然后通过bl2_main()加载BL3x镜像到RAM中,最后通过SMC调用执行BL1中指定的smc handler将CPU执行权交给BL31。
func bl2_entrypoint
/*---------------------------------------------
* Save from x1 the extents of the tzram
* available to BL2 for future use.
* x0 is not currently used.
* ---------------------------------------------
*/
mov x20, x1
/* ---------------------------------------------
* Set the exception vector to something sane.
* ---------------------------------------------
*/
adr x0, early_exceptions
msr vbar_el1, x0-------------------------------------设定异常向量。
isb
/* ---------------------------------------------
* Enable the SError interrupt now that the
* exception vectors have been setup.
* ---------------------------------------------
*/
msr daifclr, #DAIF_ABT_BIT
/* ---------------------------------------------
* Enable the instruction cache, stack pointer
* and data access alignment checks
* ---------------------------------------------
*/
mov x1, #(SCTLR_I_BIT | SCTLR_A_BIT | SCTLR_SA_BIT)
mrs x0, sctlr_el1
orr x0, x0, x1
msr sctlr_el1, x0----------------------------------配置cache、内存对齐等属性。
isb
/* ---------------------------------------------
* Invalidate the RW memory used by the BL2
* image. This includes the data and NOBITS
* sections. This is done to safeguard against
* possible corruption of this memory by dirty
* cache lines in a system cache as a result of
* use by an earlier boot loader stage.
* ---------------------------------------------
*/
adr x0, __RW_START__
adr x1, __RW_END__
sub x1, x1, x0
bl inv_dcache_range-------------------------------将BL2的__RW_START__和__RW_END__之间的内存刷回DDR中。
/* ---------------------------------------------
* Zero out NOBITS sections. There are 2 of them:
* - the .bss section;
* - the coherent memory section.
* ---------------------------------------------
*/
ldr x0, =__BSS_START__
ldr x1, =__BSS_SIZE__
bl zeromem16--------------------------------------初始化__BSS_START__开始,大小为__BSS_SIZE__内存为0。
#if USE_COHERENT_MEM
ldr x0, =__COHERENT_RAM_START__
ldr x1, =__COHERENT_RAM_UNALIGNED_SIZE__
bl zeromem16
#endif
/* --------------------------------------------
* Allocate a stack whose memory will be marked
* as Normal-IS-WBWA when the MMU is enabled.
* There is no risk of reading stale stack
* memory after enabling the MMU as only the
* primary cpu is running at the moment.
* --------------------------------------------
*/
bl plat_set_my_stack
/* ---------------------------------------------
* Perform early platform setup & platform
* specific early arch. setup e.g. mmu setup
* ---------------------------------------------
*/
mov x0, x20
bl bl2_early_platform_setup
bl bl2_plat_arch_setup
/* ---------------------------------------------
* Jump to main function.
* ---------------------------------------------
*/
bl bl2_main------------------------------------跳转到BL2主函数执行,该函数加载BL3x镜像,并通过SMC调用BL1指定SMC函数将CPU执行权交给BL31。
/* ---------------------------------------------
* Should never reach this point.
* ---------------------------------------------
*/
no_ret plat_panic_handler
endfunc bl2_entrypoint
bl2_main()主要加载BL3x镜像并验证,然后获取下一个要运行的镜像信息,通过SMC调用让BL1去启动。
/******************************************************************************* * The only thing to do in BL2 is to load further images and pass control to * next BL. The memory occupied by BL2 will be reclaimed by BL3x stages. BL2 * runs entirely in S-EL1. ******************************************************************************/ void bl2_main(void) { entry_point_info_t *next_bl_ep_info; NOTICE("BL2: %s\n", version_string); NOTICE("BL2: %s\n", build_message); /* Perform remaining generic architectural setup in S-EL1 */ bl2_arch_setup(); #if TRUSTED_BOARD_BOOT /* Initialize authentication module */ auth_mod_init(); #endif /* TRUSTED_BOARD_BOOT */ /* Load the subsequent bootloader images. */ next_bl_ep_info = bl2_load_images(); #ifdef AARCH32 /* * For AArch32 state BL1 and BL2 share the MMU setup. * Given that BL2 does not map BL1 regions, MMU needs * to be disabled in order to go back to BL1. */ disable_mmu_icache_secure(); #endif /* AARCH32 */ /* * Run next BL image via an SMC to BL1. Information on how to pass * control to the BL32 (if present) and BL33 software images will * be passed to next BL image as an argument. */ smc(BL1_SMC_RUN_IMAGE, (unsigned long)next_bl_ep_info, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0);----------发起SMC异常启动BL31镜像,交给BL1 bl1_aarch32_smc_handler处理。 }
bl2_mem_params_descs定义了BL2需要加载镜像的信息,通过REGISTER_BL_IMAGE_DESCS()将其和bl_mem_params_desc_ptr关联,并获取需要加载镜像数目bl_mem_params_desc_num。
#define REGISTER_BL_IMAGE_DESCS(_img_desc) \ bl_mem_params_node_t *bl_mem_params_desc_ptr = &_img_desc[0]; \ unsigned int bl_mem_params_desc_num = ARRAY_SIZE(_img_desc); static bl_mem_params_node_t bl2_mem_params_descs[] = { ... #ifdef EL3_PAYLOAD_BASE ... #else /* EL3_PAYLOAD_BASE */ /* Fill BL31 related information */ { .image_id = BL31_IMAGE_ID, SET_STATIC_PARAM_HEAD(ep_info, PARAM_EP, VERSION_2, entry_point_info_t, SECURE | EXECUTABLE | EP_FIRST_EXE), .ep_info.pc = BL31_BASE, .ep_info.spsr = SPSR_64(MODE_EL3, MODE_SP_ELX, DISABLE_ALL_EXCEPTIONS), #if DEBUG .ep_info.args.arg1 = ARM_BL31_PLAT_PARAM_VAL, #endif SET_STATIC_PARAM_HEAD(image_info, PARAM_EP, VERSION_2, image_info_t, IMAGE_ATTRIB_PLAT_SETUP), .image_info.image_base = BL31_BASE, .image_info.image_max_size = BL31_LIMIT - BL31_BASE, # ifdef BL32_BASE .next_handoff_image_id = BL32_IMAGE_ID, # else .next_handoff_image_id = BL33_IMAGE_ID, # endif }, # ifdef BL32_BASE /* Fill BL32 related information */ { .image_id = BL32_IMAGE_ID, SET_STATIC_PARAM_HEAD(ep_info, PARAM_EP, VERSION_2, entry_point_info_t, SECURE | EXECUTABLE), .ep_info.pc = BL32_BASE, SET_STATIC_PARAM_HEAD(image_info, PARAM_EP, VERSION_2, image_info_t, 0), .image_info.image_base = BL32_BASE, .image_info.image_max_size = BL32_LIMIT - BL32_BASE, .next_handoff_image_id = BL33_IMAGE_ID, }, # endif /* BL32_BASE */ /* Fill BL33 related information */ { .image_id = BL33_IMAGE_ID, SET_STATIC_PARAM_HEAD(ep_info, PARAM_EP, VERSION_2, entry_point_info_t, NON_SECURE | EXECUTABLE), # ifdef PRELOADED_BL33_BASE .ep_info.pc = PRELOADED_BL33_BASE, SET_STATIC_PARAM_HEAD(image_info, PARAM_EP, VERSION_2, image_info_t, IMAGE_ATTRIB_SKIP_LOADING), # else .ep_info.pc = PLAT_ARM_NS_IMAGE_OFFSET, SET_STATIC_PARAM_HEAD(image_info, PARAM_EP, VERSION_2, image_info_t, 0), .image_info.image_base = PLAT_ARM_NS_IMAGE_OFFSET, .image_info.image_max_size = ARM_DRAM1_SIZE, # endif /* PRELOADED_BL33_BASE */ .next_handoff_image_id = INVALID_IMAGE_ID, } #endif /* EL3_PAYLOAD_BASE */ }; REGISTER_BL_IMAGE_DESCS(bl2_mem_params_descs) /******************************************************************************* * This function loads SCP_BL2/BL3x images and returns the ep_info for * the next executable image. ******************************************************************************/ entry_point_info_t *bl2_load_images(void) { bl_params_t *bl2_to_next_bl_params; bl_load_info_t *bl2_load_info; const bl_load_info_node_t *bl2_node_info; int plat_setup_done = 0; int err; /* * Get information about the images to load. */ bl2_load_info = plat_get_bl_image_load_info();-----------------获取待加载镜像BL3x或SCP_EL2信息,然后遍历处理。 assert(bl2_load_info); assert(bl2_load_info->head); assert(bl2_load_info->h.type == PARAM_BL_LOAD_INFO); assert(bl2_load_info->h.version >= VERSION_2); bl2_node_info = bl2_load_info->head;---------------------------bl2_node_info指向镜像第一个对象。 while (bl2_node_info) {----------------------------------------循环遍历bl2_mem_params_descs成员并加载处理。 /* * Perform platform setup before loading the image, * if indicated in the image attributes AND if NOT * already done before. */ if (bl2_node_info->image_info->h.attr & IMAGE_ATTRIB_PLAT_SETUP) {----确定加载前是否需要进行特定平台初始化。 if (plat_setup_done) { WARN("BL2: Platform setup already done!!\n"); } else { INFO("BL2: Doing platform setup\n"); bl2_platform_setup(); plat_setup_done = 1; } } if (!(bl2_node_info->image_info->h.attr & IMAGE_ATTRIB_SKIP_LOADING)) {----确定是否需要跳过加载到RAM步骤;如否,则进行验证并加载。 INFO("BL2: Loading image id %d\n", bl2_node_info->image_id); err = load_auth_image(bl2_node_info->image_id, bl2_node_info->image_info);----------------------------------------将镜像加载到RAM,然后进行验证。 if (err) { ERROR("BL2: Failed to load image (%i)\n", err); plat_error_handler(err); } } else { INFO("BL2: Skip loading image id %d\n", bl2_node_info->image_id); } /* Allow platform to handle image information. */ err = bl2_plat_handle_post_image_load(bl2_node_info->image_id);-------------修改特定镜像的加载信息。 if (err) { ERROR("BL2: Failure in post image load handling (%i)\n", err); plat_error_handler(err); } /* Go to next image */ bl2_node_info = bl2_node_info->next_load_info;------------------------------循环加载下一个镜像。 } /* * Get information to pass to the next image. */ bl2_to_next_bl_params = plat_get_next_bl_params();------------------------------获取下一个执行镜像入口信息,属性为EXECUTABLE和EP_FIRST_EXE,也即BL31。 assert(bl2_to_next_bl_params); assert(bl2_to_next_bl_params->head); assert(bl2_to_next_bl_params->h.type == PARAM_BL_PARAMS); assert(bl2_to_next_bl_params->h.version >= VERSION_2); /* Flush the parameters to be passed to next image */ plat_flush_next_bl_params();----------------------------------------------------将bl_mem_params_desc_ptr数据刷到DDR中,后面即将通过SMC跳转到BL1启动BL31,保持数据一致性。 return bl2_to_next_bl_params->head->ep_info; }
4. BL31(EL3 Firmware)
参考文档:《SMC CALLING CONVENTION System Software on ARM® Platforms》
SMCCC定义了每个SMC请求功能的ID以及入参和返回值。
下面逐一介绍运行在EL3固件的运行服务框架的注册、初始化和使用。
SMCCC定义了每个运行服务框架的SMC功能ID、OEN(Owning Entity Numbers)、Fast和Standard调用、SMC32和SMC64调用转换。
需要优先实现的功能有:
- Standard服务调用:
- Secure-EL1 Payload Dispatcher service:如果存在TOS或者S.EL1 Payload,则需要EL3 Secure Monitor负责切换NS.EL1/2和S.EL1。Secure Monitor和S.EL1 Payload之间接口被称为SPD(S.EL1 Payload Dispatcher)。ATF还提供了TSP(Test S.EL1 Payload)和TSPD。
- CPU特有服务:提供CPU特有的的功能服务。
4.1 运行服务注册
DECLARE_RT_SVC()用于注册一个运行服务,指定服务名称、OEN范围、服务类型(SMC_TYPE_FAST/SMC_TYPE_STD)、初始化和调用函数。
通过DECLARE_RT_SVC()注册的每个服务都会在ELF的rt_svc_descs段中存在,__RT_SVC_DESCS_START__和__RT_SVC_DESCS_END__是此段的起始结束地址,并可以通过地址范围计算服务数量RT_SVC_DECS_NUM。
/* * Convenience macro to declare a service descriptor */ #define DECLARE_RT_SVC(_name, _start, _end, _type, _setup, _smch) \ static const rt_svc_desc_t __svc_desc_ ## _name \ __section("rt_svc_descs") __used = { \ .start_oen = _start, \ .end_oen = _end, \ .call_type = _type, \ .name = #_name, \ .init = _setup, \ .handle = _smch } typedef struct rt_svc_desc { uint8_t start_oen;-------------------service内部启动oen uint8_t end_oen;---------------------service内部末尾oen uint8_t call_type;-------------------smc类型,是fast call还是standard call const char *name;--------------------service名称 rt_svc_init_t init;------------------service初始化函数 rt_svc_handle_t handle;--------------对应function id的调用函数 } rt_svc_desc_t;
SMC功能ID范围定义如下:
/******************************************************************************* * Owning entity number definitions inside the function id as per the SMC * calling convention ******************************************************************************/ #define OEN_ARM_START 0 #define OEN_ARM_END 0 #define OEN_CPU_START 1 #define OEN_CPU_END 1 #define OEN_SIP_START 2 #define OEN_SIP_END 2 #define OEN_OEM_START 3 #define OEN_OEM_END 3 #define OEN_STD_START 4 /* Standard Calls */ #define OEN_STD_END 4 #define OEN_TAP_START 48 /* Trusted Applications */ #define OEN_TAP_END 49 #define OEN_TOS_START 50 /* Trusted OS */ #define OEN_TOS_END 63 #define OEN_LIMIT 64
上面的定义根据如下规格:
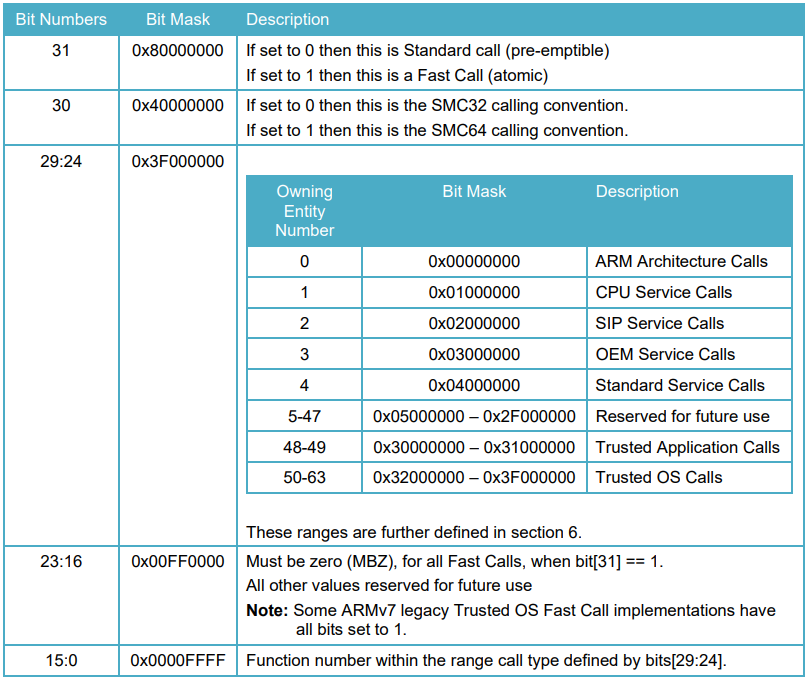
MAX_RT_SVCS为128,是因为OEN有64个,SMC类型有Standard和Fast两种类型,所以一共有128种。rt_svc_descs_indices[]一共有128个。
4.2 ATF初始化
bl31_entrypoint()是冷启动的入口,只会被cpu0执行。
func bl31_entrypoint #if !RESET_TO_BL31 /* --------------------------------------------------------------- * Preceding bootloader has populated x0 with a pointer to a * 'bl31_params' structure & x1 with a pointer to platform * specific structure * --------------------------------------------------------------- */ #if HISILICON /* hisilicon use args from uboot, * load_fip.c has set value in address 8 and 16 */ mov x0, 8 mov x1, 16 ldr x20, [x0] ldr x21, [x1] #else mov x20, x0 mov x21, x1 #endif /* --------------------------------------------------------------------- * For !RESET_TO_BL31 systems, only the primary CPU ever reaches * bl31_entrypoint() during the cold boot flow, so the cold/warm boot * and primary/secondary CPU logic should not be executed in this case. * * Also, assume that the previous bootloader has already set up the CPU * endianness and has initialised the memory. * --------------------------------------------------------------------- */ el3_entrypoint_common \ _set_endian=0 \ _warm_boot_mailbox=0 \ _secondary_cold_boot=0 \ _init_memory=0 \ _init_c_runtime=1 \ _exception_vectors=runtime_exceptions----------------------------runtime_exceptions是ATF的异常向量表。 /* --------------------------------------------------------------------- * Relay the previous bootloader's arguments to the platform layer * --------------------------------------------------------------------- */ mov x0, x20 mov x1, x21 #else /* --------------------------------------------------------------------- * For RESET_TO_BL31 systems which have a programmable reset address, * bl31_entrypoint() is executed only on the cold boot path so we can * skip the warm boot mailbox mechanism. * --------------------------------------------------------------------- */ el3_entrypoint_common \ _set_endian=1 \ _warm_boot_mailbox=!PROGRAMMABLE_RESET_ADDRESS \ _secondary_cold_boot=!COLD_BOOT_SINGLE_CPU \ _init_memory=1 \ _init_c_runtime=1 \ _exception_vectors=runtime_exceptions /* --------------------------------------------------------------------- * For RESET_TO_BL31 systems, BL31 is the first bootloader to run so * there's no argument to relay from a previous bootloader. Zero the * arguments passed to the platform layer to reflect that. * --------------------------------------------------------------------- */ mov x0, 0 mov x1, 0 #endif /* RESET_TO_BL31 */ /* --------------------------------------------- * Perform platform specific early arch. setup * --------------------------------------------- */ bl bl31_early_platform_setup-------------------------------------初始化UART,以及获取BL32、BL33的entrypoint。 bl bl31_plat_arch_setup------------------------------------------MMU内存初始化。 /* --------------------------------------------- * Jump to main function. * --------------------------------------------- */ bl bl31_main /* ------------------------------------------------------------- * Clean the .data & .bss sections to main memory. This ensures * that any global data which was initialised by the primary CPU * is visible to secondary CPUs before they enable their data * caches and participate in coherency. * ------------------------------------------------------------- */ adr x0, __DATA_START__ adr x1, __DATA_END__ sub x1, x1, x0 bl clean_dcache_range adr x0, __BSS_START__ adr x1, __BSS_END__ sub x1, x1, x0 bl clean_dcache_range--------------------------------------------刷data和bss段到内存中。 b el3_exit endfunc bl31_entrypoint
BL3异常向量表runtime_exceptions
el3_exit()退出当前ATF执行下一阶段的镜像。
/* ----------------------------------------------------- * This routine assumes that the SP_EL3 is pointing to * a valid context structure from where the gp regs and * other special registers can be retrieved. * ----------------------------------------------------- */ func el3_exit /* ----------------------------------------------------- * Save the current SP_EL0 i.e. the EL3 runtime stack * which will be used for handling the next SMC. Then * switch to SP_EL3 * ----------------------------------------------------- */ mov x17, sp msr spsel, #1 str x17, [sp, #CTX_EL3STATE_OFFSET + CTX_RUNTIME_SP] /* ----------------------------------------------------- * Restore SPSR_EL3, ELR_EL3 and SCR_EL3 prior to ERET * ----------------------------------------------------- */ ldr x18, [sp, #CTX_EL3STATE_OFFSET + CTX_SCR_EL3] ldp x16, x17, [sp, #CTX_EL3STATE_OFFSET + CTX_SPSR_EL3] msr scr_el3, x18 msr spsr_el3, x16 msr elr_el3, x17 /* Restore saved general purpose registers and return */ b restore_gp_registers_eret endfunc el3_exit
bl31_main()是ATF主体,初始化好ATF服务、启动optee os,至此可以提供psci、TOS等服务。然后再为进入BL33做好准备工作。
/******************************************************************************* * BL31 is responsible for setting up the runtime services for the primary cpu * before passing control to the bootloader or an Operating System. This * function calls runtime_svc_init() which initializes all registered runtime * services. The run time services would setup enough context for the core to * swtich to the next exception level. When this function returns, the core will * switch to the programmed exception level via. an ERET. ******************************************************************************/ void bl31_main(void) { NOTICE("BL31: %s\n", version_string); NOTICE("BL31: %s\n", build_message); /* Perform platform setup in BL31 */ bl31_platform_setup();---------------------------------------------------初始化GIC、Timer、Power等工作。 /* Initialise helper libraries */ bl31_lib_init();---------------------------------------------------------初始化BL31中相关全局变量。 /* Initialize the runtime services e.g. psci. */ INFO("BL31: Initializing runtime services\n"); runtime_svc_init();------------------------------------------------------初始化EL3 ATF中注册的服务,编译时放在rt_svc_decs特定段中。 /* * All the cold boot actions on the primary cpu are done. We now need to * decide which is the next image (BL32 or BL33) and how to execute it. * If the SPD runtime service is present, it would want to pass control * to BL32 first in S-EL1. In that case, SPD would have registered a * function to intialize bl32 where it takes responsibility of entering * S-EL1 and returning control back to bl31_main. Once this is done we * can prepare entry into BL33 as normal. */ /* * If SPD had registerd an init hook, invoke it. */ if (bl32_init) { INFO("BL31: Initializing BL32\n"); (*bl32_init)();------------------------------------------------------如果注册了TOS支持,调用对应的init函数初始化TOS。对于optee就是opteed_init()。 } /* * We are ready to enter the next EL. Prepare entry into the image * corresponding to the desired security state after the next ERET. */ bl31_prepare_next_image_entry();-----------------------------------------准备跳转到BL33, /* * Perform any platform specific runtime setup prior to cold boot exit * from BL31 */ bl31_plat_runtime_setup();-----------------------------------------------BL31退出前准备工作。 }
runtime_svc_init()作为BL31初始化一部分,初始化了运行在主CPU上的运行服务框架。这必须在TOS和普通世界软件启动之前执行,因为安全和非安全软件可能需要使用这部分内容。
runtime_svc_init()主要对注册的服务进行有限性验证,调用各自服务的初始化函数init(),以及将不同SMC OEN转换到注册服务ID。
在实际使用中,注册一个服务可能对应一系列SMC调用。
void runtime_svc_init(void) { int rc = 0, index, start_idx, end_idx; /* Assert the number of descriptors detected are less than maximum indices */ assert((RT_SVC_DESCS_END >= RT_SVC_DESCS_START) && (RT_SVC_DECS_NUM < MAX_RT_SVCS)); /* If no runtime services are implemented then simply bail out */ if (RT_SVC_DECS_NUM == 0)-----------------------------------------------对注册到ATF的SMC服务数量进行检查。 return; /* Initialise internal variables to invalid state */ memset(rt_svc_descs_indices, -1, sizeof(rt_svc_descs_indices)); rt_svc_descs = (rt_svc_desc_t *) RT_SVC_DESCS_START; for (index = 0; index < RT_SVC_DECS_NUM; index++) {----------------------遍历rt_svc_descs段, rt_svc_desc_t *service = &rt_svc_descs[index]; rc = validate_rt_svc_desc(service); if (rc) { ERROR("Invalid runtime service descriptor %p\n", (void *) service); panic(); } if (service->init) { rc = service->init();--------------------------------------------执行当前service的init函数。 if (rc) { ERROR("Error initializing runtime service %s\n", service->name); continue; } } start_idx = get_unique_oen(rt_svc_descs[index].start_oen, service->call_type); assert(start_idx < MAX_RT_SVCS); end_idx = get_unique_oen(rt_svc_descs[index].end_oen, service->call_type); assert(end_idx < MAX_RT_SVCS); for (; start_idx <= end_idx; start_idx++)----------------------------根据call_type和oen范围,确定rt_svc_descs_indices对应下标,达到SMC function id到注册service id的转换。 rt_svc_descs_indices[start_idx] = index; } }
4.3 处理SMC
当EL3 Firmware接收到一个SMC时,SMC功能ID通过W0传递到EL3 Firmware。这是根据寄存位宽和W0进行检查,如果两者不匹配则返回错误。
其中Bit[31]和bits[29:24]共7bit组成一个0~127范围数值,在rt_svc_descs_indices[]所对应具体的软件服务rt_svc_descs[]索引。
进而调用具体软件服务的handle()函数:
uintptr_t handle_runtime_svc(uint32_t smc_fid, void *cookie, void *handle, unsigned int flags) { u_register_t x1, x2, x3, x4; int index, idx; const rt_svc_desc_t *rt_svc_descs; assert(handle); idx = get_unique_oen_from_smc_fid(smc_fid); assert(idx >= 0 && idx < MAX_RT_SVCS); index = rt_svc_descs_indices[idx];---------------------将从x0寄存器中读取的Standard/Fast和OWN组合的idx,找到Runtime Service的index。 if (index < 0 || index >= RT_SVC_DECS_NUM) SMC_RET1(handle, SMC_UNK); rt_svc_descs = (rt_svc_desc_t *) RT_SVC_DESCS_START;---Runtime Service起始地址。 get_smc_params_from_ctx(handle, x1, x2, x3, x4);-------获取x1/x2/x3/x4寄存器。 return rt_svc_descs[index].handle(smc_fid, x1, x2, x3, x4, cookie, handle, flags);--------------------调用具体Runtime Service的handle()函数。 }
5. BL31 PSCI
参考文档:《POWER STATE COORDINATION INTERFACE (PSCI) System Software on ARM® Systems》
PSCI功能作为Standard service一部分,由std_svc_smc_handler()处理。
DECLARE_RT_SVC( std_svc, OEN_STD_START, OEN_STD_END, SMC_TYPE_FAST, std_svc_setup, std_svc_smc_handler-----------------------------对于Fast类型Standard服务调用,主要是进行PSCI处理。 ); uintptr_t std_svc_smc_handler(uint32_t smc_fid, u_register_t x1, u_register_t x2, u_register_t x3, u_register_t x4, void *cookie, void *handle, u_register_t flags) { /* * Dispatch PSCI calls to PSCI SMC handler and return its return * value */ if (is_psci_fid(smc_fid)) { uint64_t ret; ... ret = psci_smc_handler(smc_fid, x1, x2, x3, x4, cookie, handle, flags);---------------------首先判断是否是Fast类型,然后交给psci_smc_handler()进行处理。 ... SMC_RET1(handle, ret); } ... } u_register_t psci_smc_handler(uint32_t smc_fid, u_register_t x1, u_register_t x2, u_register_t x3, u_register_t x4, void *cookie, void *handle, u_register_t flags) { if (is_caller_secure(flags)) return SMC_UNK; /* Check the fid against the capabilities */ if (!(psci_caps & define_psci_cap(smc_fid))) return SMC_UNK; if (((smc_fid >> FUNCID_CC_SHIFT) & FUNCID_CC_MASK) == SMC_32) { ... } else {---------------------------------------------这里以64系统为例。 /* 64-bit PSCI function */ switch (smc_fid) { case PSCI_CPU_SUSPEND_AARCH64: return psci_cpu_suspend(x1, x2, x3); case PSCI_CPU_ON_AARCH64:-----------------------PSCI_CPU_ON_AARCH64为0xc4000003,bit[31]=1:Fast Call、bit[30]=1:SMC64、bits[29:24]=000100:Starndard service、bits[15:0]=0000 0011:内部定义序号。 return psci_cpu_on(x1, x2, x3);
case PSCI_AFFINITY_INFO_AARCH64:
return psci_affinity_info(x1, x2);
case PSCI_MIG_AARCH64:
return psci_migrate(x1);
case PSCI_MIG_INFO_UP_CPU_AARCH64:
return psci_migrate_info_up_cpu();
case PSCI_NODE_HW_STATE_AARCH64:
return psci_node_hw_state(x1, x2);
case PSCI_SYSTEM_SUSPEND_AARCH64:
return psci_system_suspend(x1, x2);
#if ENABLE_PSCI_STAT
case PSCI_STAT_RESIDENCY_AARCH64:
return psci_stat_residency(x1, x2);
case PSCI_STAT_COUNT_AARCH64:
return psci_stat_count(x1, x2);
#endif
default: break; } } WARN("Unimplemented PSCI Call: 0x%x \n", smc_fid); return SMC_UNK; }
5.1 PSCI_VERSION
unsigned int psci_version(void) { return PSCI_MAJOR_VER | PSCI_MINOR_VER; } #define PSCI_MAJOR_VER (1 << 16) #define PSCI_MINOR_VER 0x0
5.2 PSCI_CPU_SUSPEND
int psci_cpu_suspend(unsigned int power_state, uintptr_t entrypoint, u_register_t context_id) { int rc; unsigned int target_pwrlvl, is_power_down_state; entry_point_info_t ep; psci_power_state_t state_info = { {PSCI_LOCAL_STATE_RUN} }; plat_local_state_t cpu_pd_state; /* Validate the power_state parameter */ rc = psci_validate_power_state(power_state, &state_info); if (rc != PSCI_E_SUCCESS) { assert(rc == PSCI_E_INVALID_PARAMS); return rc; } /* * Get the value of the state type bit from the power state parameter. */ is_power_down_state = psci_get_pstate_type(power_state); /* Sanity check the requested suspend levels */ assert(psci_validate_suspend_req(&state_info, is_power_down_state) == PSCI_E_SUCCESS); target_pwrlvl = psci_find_target_suspend_lvl(&state_info); if (target_pwrlvl == PSCI_INVALID_PWR_LVL) { ERROR("Invalid target power level for suspend operation\n"); panic(); } /* Fast path for CPU standby.*/ if (is_cpu_standby_req(is_power_down_state, target_pwrlvl)) { if (!psci_plat_pm_ops->cpu_standby) return PSCI_E_INVALID_PARAMS; /* * Set the state of the CPU power domain to the platform * specific retention state and enter the standby state. */ cpu_pd_state = state_info.pwr_domain_state[PSCI_CPU_PWR_LVL]; psci_set_cpu_local_state(cpu_pd_state); #if ENABLE_PSCI_STAT /* * Capture time-stamp before CPU standby * No cache maintenance is needed as caches * are ON through out the CPU standby operation. */ PMF_CAPTURE_TIMESTAMP(psci_svc, PSCI_STAT_ID_ENTER_LOW_PWR, PMF_NO_CACHE_MAINT); #endif #if ENABLE_RUNTIME_INSTRUMENTATION PMF_CAPTURE_TIMESTAMP(rt_instr_svc, RT_INSTR_ENTER_HW_LOW_PWR, PMF_NO_CACHE_MAINT); #endif psci_plat_pm_ops->cpu_standby(cpu_pd_state); /* Upon exit from standby, set the state back to RUN. */ psci_set_cpu_local_state(PSCI_LOCAL_STATE_RUN); #if ENABLE_RUNTIME_INSTRUMENTATION PMF_CAPTURE_TIMESTAMP(rt_instr_svc, RT_INSTR_EXIT_HW_LOW_PWR, PMF_NO_CACHE_MAINT); #endif #if ENABLE_PSCI_STAT /* Capture time-stamp after CPU standby */ PMF_CAPTURE_TIMESTAMP(psci_svc, PSCI_STAT_ID_EXIT_LOW_PWR, PMF_NO_CACHE_MAINT); /* Update PSCI stats */ psci_stats_update_pwr_up(PSCI_CPU_PWR_LVL, &state_info, PMF_NO_CACHE_MAINT); #endif return PSCI_E_SUCCESS; } /* * If a power down state has been requested, we need to verify entry * point and program entry information. */ if (is_power_down_state) { rc = psci_validate_entry_point(&ep, entrypoint, context_id); if (rc != PSCI_E_SUCCESS) return rc; } /* * Do what is needed to enter the power down state. Upon success, * enter the final wfi which will power down this CPU. This function * might return if the power down was abandoned for any reason, e.g. * arrival of an interrupt */ psci_cpu_suspend_start(&ep, target_pwrlvl, &state_info, is_power_down_state); return PSCI_E_SUCCESS; }
5.3 PSCI_CPU_OFF
int psci_cpu_off(void) { int rc; unsigned int target_pwrlvl = PLAT_MAX_PWR_LVL; /* * Do what is needed to power off this CPU and possible higher power * levels if it able to do so. Upon success, enter the final wfi * which will power down this CPU. */ rc = psci_do_cpu_off(target_pwrlvl); /* * The only error cpu_off can return is E_DENIED. So check if that's * indeed the case. */ assert(rc == PSCI_E_DENIED); return rc; }
5.4 PSCI_CPU_ON
/******************************************************************************* * PSCI frontend api for servicing SMCs. Described in the PSCI spec. ******************************************************************************/ int psci_cpu_on(u_register_t target_cpu, uintptr_t entrypoint, u_register_t context_id) { int rc; entry_point_info_t ep; /* Determine if the cpu exists of not */ rc = psci_validate_mpidr(target_cpu); if (rc != PSCI_E_SUCCESS) return PSCI_E_INVALID_PARAMS; /* Validate the entry point and get the entry_point_info */ rc = psci_validate_entry_point(&ep, entrypoint, context_id); if (rc != PSCI_E_SUCCESS) return rc; /* * To turn this cpu on, specify which power * levels need to be turned on */ return psci_cpu_on_start(target_cpu, &ep); }
5.5 PSCI_AFFINITY_INFO
int psci_affinity_info(u_register_t target_affinity, unsigned int lowest_affinity_level) { unsigned int target_idx; /* We dont support level higher than PSCI_CPU_PWR_LVL */ if (lowest_affinity_level > PSCI_CPU_PWR_LVL) return PSCI_E_INVALID_PARAMS; /* Calculate the cpu index of the target */ target_idx = plat_core_pos_by_mpidr(target_affinity); if (target_idx == -1) return PSCI_E_INVALID_PARAMS; return psci_get_aff_info_state_by_idx(target_idx); }
5.6 PSCI_MIG
int psci_migrate(u_register_t target_cpu) { int rc; u_register_t resident_cpu_mpidr; rc = psci_spd_migrate_info(&resident_cpu_mpidr); if (rc != PSCI_TOS_UP_MIG_CAP) return (rc == PSCI_TOS_NOT_UP_MIG_CAP) ? PSCI_E_DENIED : PSCI_E_NOT_SUPPORTED; /* * Migrate should only be invoked on the CPU where * the Secure OS is resident. */ if (resident_cpu_mpidr != read_mpidr_el1()) return PSCI_E_NOT_PRESENT; /* Check the validity of the specified target cpu */ rc = psci_validate_mpidr(target_cpu); if (rc != PSCI_E_SUCCESS) return PSCI_E_INVALID_PARAMS; assert(psci_spd_pm && psci_spd_pm->svc_migrate); rc = psci_spd_pm->svc_migrate(read_mpidr_el1(), target_cpu); assert(rc == PSCI_E_SUCCESS || rc == PSCI_E_INTERN_FAIL); return rc; }
5.7 PSCI_MIG_INFO_TYPE
int psci_migrate_info_type(void) { u_register_t resident_cpu_mpidr; return psci_spd_migrate_info(&resident_cpu_mpidr); } /******************************************************************************* * This function invokes the migrate info hook in the spd_pm_ops. It performs * the necessary return value validation. If the Secure Payload is UP and * migrate capable, it returns the mpidr of the CPU on which the Secure payload * is resident through the mpidr parameter. Else the value of the parameter on * return is undefined. ******************************************************************************/ int psci_spd_migrate_info(u_register_t *mpidr) { int rc; if (!psci_spd_pm || !psci_spd_pm->svc_migrate_info) return PSCI_E_NOT_SUPPORTED; rc = psci_spd_pm->svc_migrate_info(mpidr); assert(rc == PSCI_TOS_UP_MIG_CAP || rc == PSCI_TOS_NOT_UP_MIG_CAP \ || rc == PSCI_TOS_NOT_PRESENT_MP || rc == PSCI_E_NOT_SUPPORTED); return rc; }
5.8 PSCI_MIG_INFO_UP_CPU
long psci_migrate_info_up_cpu(void) { u_register_t resident_cpu_mpidr; int rc; /* * Return value of this depends upon what * psci_spd_migrate_info() returns. */ rc = psci_spd_migrate_info(&resident_cpu_mpidr); if (rc != PSCI_TOS_NOT_UP_MIG_CAP && rc != PSCI_TOS_UP_MIG_CAP) return PSCI_E_INVALID_PARAMS; return resident_cpu_mpidr; }
5.9 PSCI_SYSTEM_OFF
void psci_system_off(void) { psci_print_power_domain_map(); assert(psci_plat_pm_ops->system_off); /* Notify the Secure Payload Dispatcher */ if (psci_spd_pm && psci_spd_pm->svc_system_off) { psci_spd_pm->svc_system_off(); } /* Call the platform specific hook */ psci_plat_pm_ops->system_off(); /* This function does not return. We should never get here */ }
5.10 PSCI_SYSTEM_RESET
void psci_system_reset(void) { psci_print_power_domain_map(); assert(psci_plat_pm_ops->system_reset); /* Notify the Secure Payload Dispatcher */ if (psci_spd_pm && psci_spd_pm->svc_system_reset) { psci_spd_pm->svc_system_reset(); } /* Call the platform specific hook */ psci_plat_pm_ops->system_reset(); /* This function does not return. We should never get here */ }
5.11 PSCI_FEATURES
int psci_features(unsigned int psci_fid) { unsigned int local_caps = psci_caps; /* Check if it is a 64 bit function */ if (((psci_fid >> FUNCID_CC_SHIFT) & FUNCID_CC_MASK) == SMC_64) local_caps &= PSCI_CAP_64BIT_MASK; /* Check for invalid fid */ if (!(is_std_svc_call(psci_fid) && is_valid_fast_smc(psci_fid) && is_psci_fid(psci_fid))) return PSCI_E_NOT_SUPPORTED; /* Check if the psci fid is supported or not */ if (!(local_caps & define_psci_cap(psci_fid))) return PSCI_E_NOT_SUPPORTED; /* Format the feature flags */ if (psci_fid == PSCI_CPU_SUSPEND_AARCH32 || psci_fid == PSCI_CPU_SUSPEND_AARCH64) { /* * The trusted firmware does not support OS Initiated Mode. */ return (FF_PSTATE << FF_PSTATE_SHIFT) | ((!FF_SUPPORTS_OS_INIT_MODE) << FF_MODE_SUPPORT_SHIFT); } /* Return 0 for all other fid's */ return PSCI_E_SUCCESS; }
5.12 PSCI_SYSTEM_SUSPEND
int psci_system_suspend(uintptr_t entrypoint, u_register_t context_id) { int rc; psci_power_state_t state_info; entry_point_info_t ep; /* Check if the current CPU is the last ON CPU in the system */ if (!psci_is_last_on_cpu()) return PSCI_E_DENIED; /* Validate the entry point and get the entry_point_info */ rc = psci_validate_entry_point(&ep, entrypoint, context_id); if (rc != PSCI_E_SUCCESS) return rc; /* Query the psci_power_state for system suspend */ psci_query_sys_suspend_pwrstate(&state_info); /* Ensure that the psci_power_state makes sense */ assert(psci_find_target_suspend_lvl(&state_info) == PLAT_MAX_PWR_LVL); assert(psci_validate_suspend_req(&state_info, PSTATE_TYPE_POWERDOWN) == PSCI_E_SUCCESS); assert(is_local_state_off(state_info.pwr_domain_state[PLAT_MAX_PWR_LVL])); /* * Do what is needed to enter the system suspend state. This function * might return if the power down was abandoned for any reason, e.g. * arrival of an interrupt */ psci_cpu_suspend_start(&ep, PLAT_MAX_PWR_LVL, &state_info, PSTATE_TYPE_POWERDOWN); return PSCI_E_SUCCESS; }
6. BL31 OPTEE接口
optee注册了Fast和Standard两种调用类型,Fast类型需要使用opteed_setup()进行初始化。两种类型共用opteed_smc_handler()进行smc处理。
/* Define an OPTEED runtime service descriptor for fast SMC calls */ DECLARE_RT_SVC( opteed_fast, OEN_TOS_START, OEN_TOS_END, SMC_TYPE_FAST, opteed_setup, opteed_smc_handler ); /* Define an OPTEED runtime service descriptor for standard SMC calls */ DECLARE_RT_SVC( opteed_std, OEN_TOS_START, OEN_TOS_END, SMC_TYPE_STD, NULL, opteed_smc_handler );
6.1 optee启动
在ATF BL31启动过程中,runtime_svc_init()会调用opteed_setup()来完成optee的启动。
/******************************************************************************* * OPTEE Dispatcher setup. The OPTEED finds out the OPTEE entrypoint and type * (aarch32/aarch64) if not already known and initialises the context for entry * into OPTEE for its initialization. ******************************************************************************/ int32_t opteed_setup(void) { entry_point_info_t *optee_ep_info; uint32_t linear_id; linear_id = plat_my_core_pos(); optee_ep_info = bl31_plat_get_next_image_ep_info(SECURE);-----------------获取BL32即optee os镜像信息。 if (!optee_ep_info) { WARN("No OPTEE provided by BL2 boot loader, Booting device" " without OPTEE initialization. SMC`s destined for OPTEE" " will return SMC_UNK\n"); return 1; } if (!optee_ep_info->pc) return 1; /* * We could inspect the SP image and determine it's execution * state i.e whether AArch32 or AArch64. Assuming it's AArch32 * for the time being. */ opteed_rw = OPTEE_AARCH64; opteed_init_optee_ep_state(optee_ep_info, opteed_rw, optee_ep_info->pc, &opteed_sp_context[linear_id]);------------------------------初始化安全CPU的smc上下文,存放于opteed_sp_context[]中。 /* * All OPTEED initialization done. Now register our init function with * BL31 for deferred invocation */ bl31_register_bl32_init(&opteed_init);-----------------------------------bl32_init指向opteed_init(),在bl31_main()中被调用。 return 0; }
opteed_init()从镜像中获取optee os的入口点,并初始化好ATF和optee切换的上下文,然后进入optee并等待返回结果。
/******************************************************************************* * This function passes control to the OPTEE image (BL32) for the first time * on the primary cpu after a cold boot. It assumes that a valid secure * context has already been created by opteed_setup() which can be directly * used. It also assumes that a valid non-secure context has been * initialised by PSCI so it does not need to save and restore any * non-secure state. This function performs a synchronous entry into * OPTEE. OPTEE passes control back to this routine through a SMC. ******************************************************************************/ static int32_t opteed_init(void) { uint32_t linear_id = plat_my_core_pos(); optee_context_t *optee_ctx = &opteed_sp_context[linear_id]; entry_point_info_t *optee_entry_point; uint64_t rc; /* * Get information about the OPTEE (BL32) image. Its * absence is a critical failure. */ optee_entry_point = bl31_plat_get_next_image_ep_info(SECURE);-----------------------------获取optee os镜像信息。 assert(optee_entry_point); cm_init_my_context(optee_entry_point);----------------------------------------------------设置当前CPU进入安全状态的上下文。 /* * Arrange for an entry into OPTEE. It will be returned via * OPTEE_ENTRY_DONE case */ rc = opteed_synchronous_sp_entry(optee_ctx);----------------------------------------------启动optee os,并等待OPTEE_ENTRY_DONE返回结果。 assert(rc != 0); return rc; } /******************************************************************************* * This function takes an OPTEE context pointer and: * 1. Applies the S-EL1 system register context from optee_ctx->cpu_ctx. * 2. Saves the current C runtime state (callee saved registers) on the stack * frame and saves a reference to this state. * 3. Calls el3_exit() so that the EL3 system and general purpose registers * from the optee_ctx->cpu_ctx are used to enter the OPTEE image. ******************************************************************************/ uint64_t opteed_synchronous_sp_entry(optee_context_t *optee_ctx) { uint64_t rc; assert(optee_ctx != NULL); assert(optee_ctx->c_rt_ctx == 0); /* Apply the Secure EL1 system register context and switch to it */ assert(cm_get_context(SECURE) == &optee_ctx->cpu_ctx); cm_el1_sysregs_context_restore(SECURE);---------------从optee_ctx->cpu_ctx中恢复S.EL1相关寄存器。 cm_set_next_eret_context(SECURE);---------------------保存从S.EL1返回需要的上下文。 rc = opteed_enter_sp(&optee_ctx->c_rt_ctx);-----------将安全CPU保存的状态恢复到optee_ctx->c_rt_ctx中,并跳转到opteed os执行。 #if DEBUG optee_ctx->c_rt_ctx = 0; #endif return rc; }
func opteed_enter_sp /* Make space for the registers that we're going to save */ mov x3, sp str x3, [x0, #0] sub sp, sp, #OPTEED_C_RT_CTX_SIZE /* Save callee-saved registers on to the stack */ stp x19, x20, [sp, #OPTEED_C_RT_CTX_X19] stp x21, x22, [sp, #OPTEED_C_RT_CTX_X21] stp x23, x24, [sp, #OPTEED_C_RT_CTX_X23] stp x25, x26, [sp, #OPTEED_C_RT_CTX_X25] stp x27, x28, [sp, #OPTEED_C_RT_CTX_X27] stp x29, x30, [sp, #OPTEED_C_RT_CTX_X29] /* --------------------------------------------- * Everything is setup now. el3_exit() will * use the secure context to restore to the * general purpose and EL3 system registers to * ERET into OPTEE. * --------------------------------------------- */ b el3_exit--------------------------------------------------使用配置好的安全上下文,退出EL3进入OPTEE。 endfunc opteed_enter_sp
6.2 optee的SPD
BL31中处理OP-TEE安全请求分发入口函数是opteed_smc_handler()。
uint64_t opteed_smc_handler(uint32_t smc_fid, uint64_t x1, uint64_t x2, uint64_t x3, uint64_t x4, void *cookie, void *handle, uint64_t flags) { cpu_context_t *ns_cpu_context; uint32_t linear_id = plat_my_core_pos(); optee_context_t *optee_ctx = &opteed_sp_context[linear_id];---------------获取当前CPU保存的optee上下文。 uint64_t rc; /* * Determine which security state this SMC originated from */ if (is_caller_non_secure(flags)) { /* * This is a fresh request from the non-secure client. * The parameters are in x1 and x2. Figure out which * registers need to be preserved, save the non-secure * state and send the request to the secure payload. */ assert(handle == cm_get_context(NON_SECURE)); cm_el1_sysregs_context_save(NON_SECURE); /* * We are done stashing the non-secure context. Ask the * OPTEE to do the work now. */ /* * Verify if there is a valid context to use, copy the * operation type and parameters to the secure context * and jump to the fast smc entry point in the secure * payload. Entry into S-EL1 will take place upon exit * from this function. */ assert(&optee_ctx->cpu_ctx == cm_get_context(SECURE)); /* Set appropriate entry for SMC. * We expect OPTEE to manage the PSTATE.I and PSTATE.F * flags as appropriate. */ if (GET_SMC_TYPE(smc_fid) == SMC_TYPE_FAST) { cm_set_elr_el3(SECURE, (uint64_t) &optee_vectors->fast_smc_entry); } else { cm_set_elr_el3(SECURE, (uint64_t) &optee_vectors->std_smc_entry); } cm_el1_sysregs_context_restore(SECURE); cm_set_next_eret_context(SECURE); write_ctx_reg(get_gpregs_ctx(&optee_ctx->cpu_ctx), CTX_GPREG_X4, read_ctx_reg(get_gpregs_ctx(handle), CTX_GPREG_X4)); write_ctx_reg(get_gpregs_ctx(&optee_ctx->cpu_ctx), CTX_GPREG_X5, read_ctx_reg(get_gpregs_ctx(handle), CTX_GPREG_X5)); write_ctx_reg(get_gpregs_ctx(&optee_ctx->cpu_ctx), CTX_GPREG_X6, read_ctx_reg(get_gpregs_ctx(handle), CTX_GPREG_X6)); /* Propagate hypervisor client ID */ write_ctx_reg(get_gpregs_ctx(&optee_ctx->cpu_ctx), CTX_GPREG_X7, read_ctx_reg(get_gpregs_ctx(handle), CTX_GPREG_X7)); SMC_RET4(&optee_ctx->cpu_ctx, smc_fid, x1, x2, x3); } /* * Returning from OPTEE */ switch (smc_fid) { case TEESMC_OPTEED_RETURN_ENTRY_DONE:-------------------------------------optee冷启动初始化完成后返回。 assert(optee_vectors == NULL); optee_vectors = (optee_vectors_t *) x1; if (optee_vectors) { set_optee_pstate(optee_ctx->state, OPTEE_PSTATE_ON); psci_register_spd_pm_hook(&opteed_pm); flags = 0; set_interrupt_rm_flag(flags, NON_SECURE); rc = register_interrupt_type_handler(INTR_TYPE_S_EL1, opteed_sel1_interrupt_handler, flags); if (rc) panic(); } opteed_synchronous_sp_exit(optee_ctx, x1);-----------------------------从optee中返回。 case TEESMC_OPTEED_RETURN_ON_DONE:-----------------------------------------表示optee由cpu_on导致的启动完成,0标识成功,其他失败。 case TEESMC_OPTEED_RETURN_RESUME_DONE:-------------------------------------表示optee从cpu_suspend导致的休眠中唤醒完成;0表示成功,其他失败。 case TEESMC_OPTEED_RETURN_OFF_DONE:----------------------------------------下面分表表示optee对cpu_off/cpu_suspend/system_off/system_reset的响应结果;0表示成功,其他表示失败。其中system_off和system_reset无返回参数。 case TEESMC_OPTEED_RETURN_SUSPEND_DONE: case TEESMC_OPTEED_RETURN_SYSTEM_OFF_DONE: case TEESMC_OPTEED_RETURN_SYSTEM_RESET_DONE: opteed_synchronous_sp_exit(optee_ctx, x1); case TEESMC_OPTEED_RETURN_CALL_DONE:---------------------------------------optee处理完smc之后,需要返回普通世界,x1-x4返回参数。 assert(handle == cm_get_context(SECURE)); cm_el1_sysregs_context_save(SECURE); /* Get a reference to the non-secure context */ ns_cpu_context = cm_get_context(NON_SECURE); assert(ns_cpu_context); /* Restore non-secure state */ cm_el1_sysregs_context_restore(NON_SECURE); cm_set_next_eret_context(NON_SECURE); SMC_RET4(ns_cpu_context, x1, x2, x3, x4); case TEESMC_OPTEED_RETURN_FIQ_DONE:-----------------------------------------optee处理完fiq中断后,需要返回普通世界。 ns_cpu_context = cm_get_context(NON_SECURE); assert(ns_cpu_context); cm_el1_sysregs_context_restore(NON_SECURE); cm_set_next_eret_context(NON_SECURE); SMC_RET0((uint64_t) ns_cpu_context); default: panic(); } } void opteed_synchronous_sp_exit(optee_context_t *optee_ctx, uint64_t ret) { assert(optee_ctx != NULL); /* Save the Secure EL1 system register context */ assert(cm_get_context(SECURE) == &optee_ctx->cpu_ctx); cm_el1_sysregs_context_save(SECURE);------------------------保存S.EL1下optee系统寄存器保存到cpu_context[SECURE]中。 assert(optee_ctx->c_rt_ctx != 0); opteed_exit_sp(optee_ctx->c_rt_ctx, ret);-------------------恢复optee_enter_sp()保存的C运行环境上下文。 /* Should never reach here */ assert(0); }
参考文档
- 《ARM Trusted Firmware Design》:介绍了ATF关键设计思想Cold boot、EL3运行时服务、PSCI、Secure-EL1系统和服务、BL镜像内存划分、FIP、Trusted Firmware内存一致性等等。
- 《学习整理:arm-trusted-firmware》:基本上是对《ARM Trusted Firmware Design》的翻译。
- 《ATF(ARM Trusted firmware)》专题:介绍了ATF启动流程以及各个阶段内容。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号