sched_yield()和nanosleep()对进程调度的影响
关键词:sched_yield()、nanosleep()等等。
sched_yield()主动放弃CPU执行权,nanosleep()是睡眠一段时间后再唤醒。
1. sched_yield()实现
sched_yield()会主动放弃当前CPU给其他进程使用;但是如果当前CPU上无其他进程等待执行,则直接返回继续执行当前进程。
调用sched_yield()之后当前进程会被移动到进程优先级等待队列尾部,让相同或者更高优先级进程运行。
sched_yield()确保当前进程在资源竞争严重时,给其他进程执行机会来提高性能。
SYSCALL_DEFINE0(sched_yield) { struct rq *rq = this_rq_lock(); schedstat_inc(rq->yld_count); current->sched_class->yield_task(rq); __release(rq->lock); spin_release(&rq->lock.dep_map, 1, _THIS_IP_); do_raw_spin_unlock(&rq->lock); sched_preempt_enable_no_resched(); schedule(); return 0; } asmlinkage __visible void __sched schedule(void) { struct task_struct *tsk = current; sched_submit_work(tsk); do { preempt_disable(); __schedule(false); sched_preempt_enable_no_resched(); } while (need_resched()); } static void __sched notrace __schedule(bool preempt) { struct task_struct *prev, *next; unsigned long *switch_count; struct pin_cookie cookie; struct rq *rq; int cpu; ... next = pick_next_task(rq, prev, cookie);---------------------选择优先级最高的进程作为下一个运行进程。 clear_tsk_need_resched(prev); clear_preempt_need_resched(); rq->clock_skip_update = 0; if (likely(prev != next)) {----------------------------------如果sched_yield()后,当前进程prev即为优先级最高的进程,即prev==next。那么则不会进行进程切换操作,直接返回。 rq->nr_switches++; rq->curr = next; ++*switch_count; trace_sched_switch(preempt, prev, next); rq = context_switch(rq, prev, next, cookie); /* unlocks the rq */ } else { lockdep_unpin_lock(&rq->lock, cookie); raw_spin_unlock_irq(&rq->lock); } balance_callback(rq); }
对于CFS调度器类,yield_task()对应yield_task_fair()。
static void yield_task_fair(struct rq *rq) { struct task_struct *curr = rq->curr; struct cfs_rq *cfs_rq = task_cfs_rq(curr); struct sched_entity *se = &curr->se; if (unlikely(rq->nr_running == 1))--------------------如果当前运行队列上仅有一个运行进程,直接返回。 return; clear_buddies(cfs_rq, se); if (curr->policy != SCHED_BATCH) { update_rq_clock(rq); update_curr(cfs_rq); rq_clock_skip_update(rq, true); } set_skip_buddy(se); }
下面是系统无其他进程运行时,可以看出进程独占了CPU很长时间。只是在有其他内核线程运行后,才放弃CPU执行权。
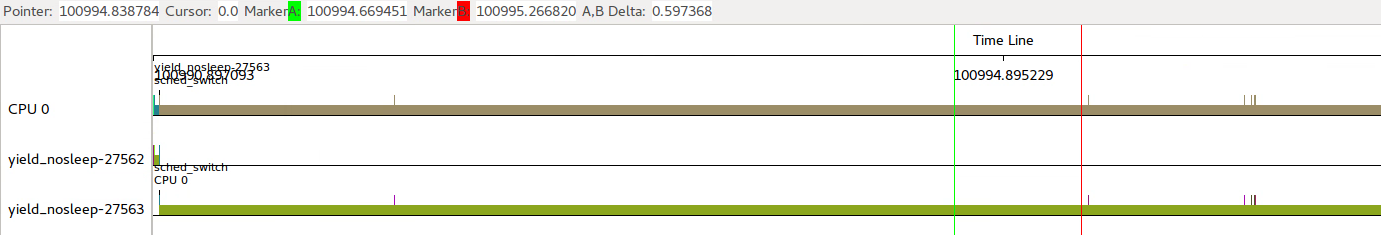
2. nanosleep()和sched_yield()对比
2.1 while(true)尽量独占CPU
#include <iostream> #include <chrono> #include <thread> #include <atomic> #include <mutex> #include <time.h> std::mutex g_mutex; std::atomic<bool> ready(false); void count1m(int id) { while (true) { } } int main() { std::thread threads; threads = std::thread(count1m, 1); threads.join(); return 0; }
这种情况进程会尽可能独占整个CPU,但是在有竞争进程存在的时候,需要和其他进程均分CPU时间。所以出现下面每工作4ms,然后切换出去4ms时间的情况。
在没有其他进程运行的时候,可以独占CPU时间。
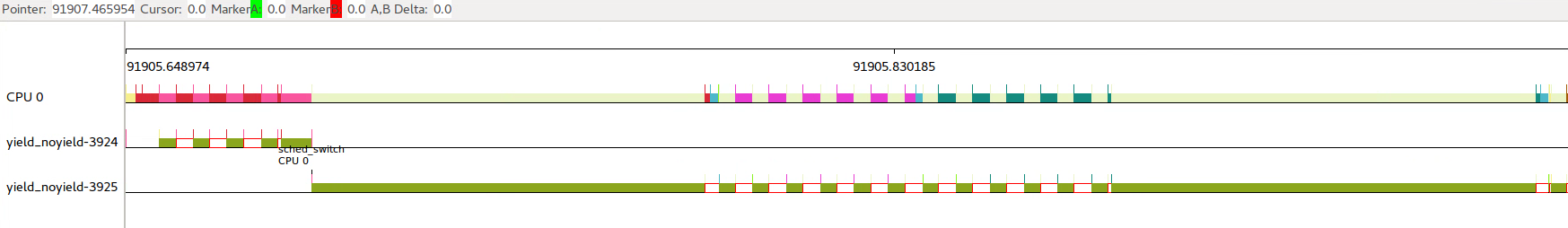
2.2 nanosleep()进程休眠一段时间
#include <iostream> #include <chrono> #include <thread> #include <atomic> #include <mutex> #include <time.h> std::mutex g_mutex; std::atomic<bool> ready(false); void count1m(int id) { struct timespec delay; delay.tv_sec = 0; delay.tv_nsec = 1000000; while (true) { nanosleep(&delay, NULL); } } int main() { std::thread threads; threads = std::thread(count1m, 1); threads.join(); return 0; }
间隔休眠唤醒情况下,即使系统中存在其他进程在运行,当前进程唤醒后仍然可以抢到CPU资源,sched_switch表示放入队列,sched_wakeup表示得到CPU资源,中间可能存在一定延时。
在没有其他进程情况下,能更快得到调度。
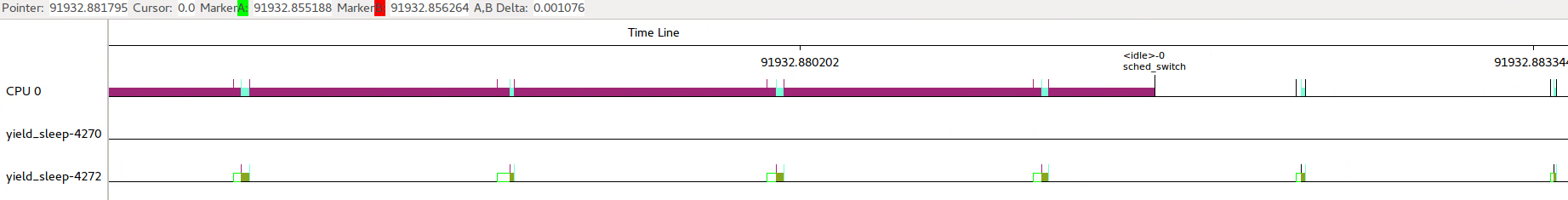
2.3 sched_yield()主动放弃
#include <iostream> #include <chrono> #include <thread> #include <atomic> #include <mutex> #include <time.h> std::mutex g_mutex; std::atomic<bool> ready(false); void count1m(int id) { while (true) { std::this_thread::yield(); } } int main() { std::thread threads; threads = std::thread(count1m, 1); threads.join(); return 0; }
这种情况和第一种区别在于,sched_yield()会主动放弃CPU执行权。第一种情况是根据CFS调度器类来分配时间;这里还结合了进程主动放弃调度的情况。
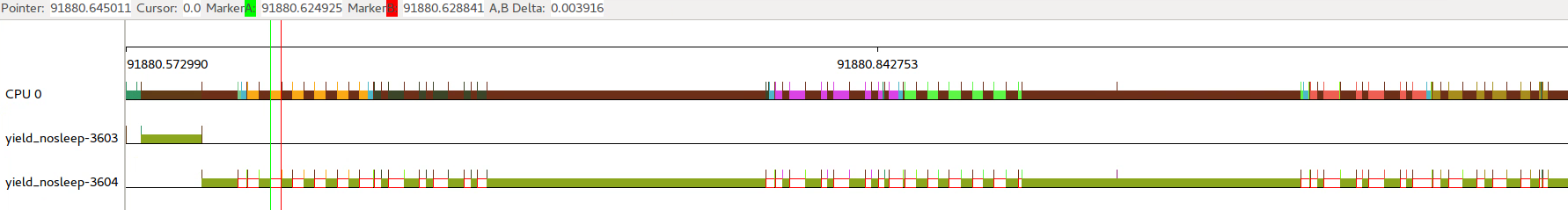
2.4 sched_yield()和nanosleep()混合使用
#include <iostream> #include <chrono> #include <thread> #include <atomic> #include <mutex> #include <time.h> std::mutex g_mutex; std::atomic<bool> ready(false); void count1m(int id) { struct timespec delay; delay.tv_sec = 0; delay.tv_nsec = 1000000; while (true) { std::this_thread::yield(); nanosleep(&delay, NULL); } } int main() { std::thread threads; threads = std::thread(count1m, 1); threads.join(); return 0; }
这种情况下sched_yield()和nanosleep()叠加使用和单独使用nanosleep()效果类似,nanosleep()本省也是主动放弃CPU使用权。
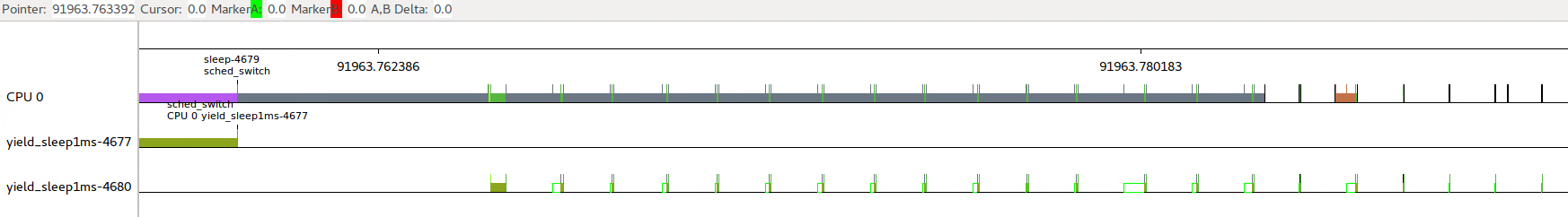
所以综合来看while(1)中使用sched_yield()要比延时的响应更及时,但是也牺牲了CPU占用率。在没有其他进程运行的情况下,sched_yield()就会一个人独占CPU资源。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号