kotlin: 主构造函数和辅助构造函数
一,两者的区别
主构造函数在类名后面使用constructor关键字声明,并且不能做任何操作,
初始化可以在init代码块中进行
在构造函数不具有注释符或者默认的可见性修饰符时,constructor关键字可以省略。
辅助构造函数需要使用constructor关键字声明,
并且直接或者通过别的辅助函数调用主构造函数
二,代码例子
package com.example.okdemo1.activity
import android.os.Bundle
import android.widget.Button
import androidx.activity.enableEdgeToEdge
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity
import com.example.okdemo1.R
class Bottom2Activity : AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
this.enableEdgeToEdge()
setContentView(R.layout.activity_bottom2)
val button1: Button = findViewById(R.id.button1)
button1.setOnClickListener {
// 在这里处理点击事件,主构造函数
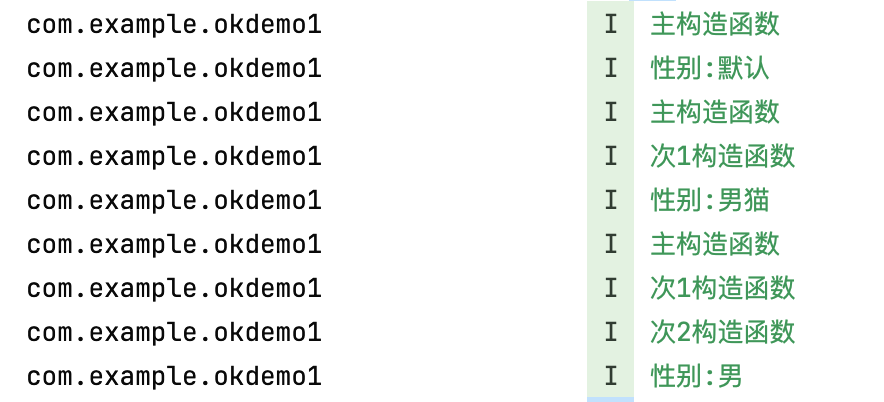
val user1 = User("汤姆",3)
println("性别:"+user1.getSex())
//次1构造函数
val user2 = User("Tom",4,"男猫")
println("性别:"+user2.getSex())
//次2构造函数
val user3 = User("Jerry")
println("性别:"+user3.getSex())
}
}
}
// 主构造函数,直接写在类的定义中,constructor关键字可以省略
class User constructor(name: String, age: Int) {
private var name: String = "";
private var age: Int = 0;
private var sex: String = "默认";
init {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
println("主构造函数")
}
fun getSex():String {
return this.sex
}
//直接调用主构造函数
constructor(name: String, age: Int, sex: String) : this(name, age) {
this.sex = sex;
println("次1构造函数")
}
//间接调用柱构造函数
constructor(name: String) : this(name, 0, "男") {
println("次2构造函数")
}
}三,测试效果



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号