重新整理 .net core 实践篇————缓存相关[四十二]
前言
简单整理一下缓存。
正文
缓存是什么?
-
缓存是计算结果的"临时"存储和重复使用
-
缓存本质是用空间换取时间
缓存的场景:
-
计算结果,如:反射对象缓存
-
请求结果,如:DNS 缓存
-
临时共享数据,如:会话存储
-
热点访问内容页,如:商品详情
-
热点变更逻辑数据,如:秒杀的库存数
缓存的策略:
-
越接近最终的数据结构,效果比较好
-
缓存命中率越高越好,命中率低意味着空间的浪费。
缓存的位置:
-
浏览器中
-
反向代理服务器中(nginx)
-
应用进程内存中
-
分布式存储系统中(redis)
缓存实现的要点:
-
存储key生成策略,表示缓存数据的范围、业务含义
-
缓存失效的策略,如:过期时间机制、主动刷新机制
-
缓存的更新策略,表示更新缓存数据的时机
缓存的几个问题:
-
缓存失效,导致数据不一致。是指缓存的数据与我们数据库里面的数据不一致的情况。
-
缓存穿透,查询无数据时,导致缓存不生效,查询都落到了数据库上
-
缓存击穿,缓存失效瞬间,大量请求访问到数据库
-
缓存雪崩,大量缓存在同一时间失效,导致数据库压力大
上面这些哪里看的最多呢?redis的面经的,我现在都没有想明白这些和reids有什么关系,这些本来就是缓存问题,只不过redis当缓存的时候,自然就遇到了缓存的问题了。
下面来简单介绍一下这几个问题。
第一点,缓存失效,就是和我们数据库里面的数据不一致,这个就是代码业务问题了,业务没有做好。
第二个,缓存穿透,因为一些数据不存在,然后缓存中自然是没有的,然后就会一直访问数据库,然后数据库压力就大。
这个很有可能是别人的攻击。那么防护措施可以这么干,当数据库里面没有的时候,可以在缓存中设置key:null,依然加入缓存中取,这样访问的就是缓存了。
第三点,缓存击穿,指的是大量用户访问同一个缓存,当缓存失效的时候,每个请求都会去访问数据库。
那么这个时候,比较简单的方式就是加锁。
// xx查询为空
if(xx==null)
{
lock(obj)
{
// 再查一次
....
//如果没有去数据库里面取数据,加入缓存中
if(xx=null)
{
// 进行数据库查询,加入缓存,给xx赋值
....
}
}
}
这种是大量用户访问同一个缓存的情况,当然也可以设置缓存不过期,但是不能保证缓存不被清理吧。就是说缓存不过期是在理想情况,但是怎么没的,就属于突发情况了。
第四点,缓存雪崩。就是比如说有1w个用户现在来请求了,然后艰难的给他们都加上了缓存,然后就把他们的缓存时间设置为半个小时,然后半个小时后,这一万个请求又来了,但是缓存没了,这时候又要艰难的从数据库里面读取。
那么这种情况怎么解决呢? 最简单的就是不要设置设置固定的缓存失效数字,可以随机一个数字。但是如果用户体过大,同样面临着某一个时间点大量用户失效的情况。那么同样可以,当拿到用户缓存的时候,如果时间快到期了,然后给他续时间。
那么就来举例子。
需要用到的组件如下:
-
responseCache 中间件
-
Miscrosoft.Extensions.Caching.Memory.IMemoryCache MemoryCache
-
Miscrosoft.Extensions.Caching.Distributed.IDistributedCache 分布式cache
-
EasyCaching 开源chache组件
内存缓存和分布式缓存的区别
-
内存缓存可以存储任意的对象
-
分布式缓存的对象需要支持序列化
-
分布式缓存远程请求可能失败(网络问题,或者远程服务缓存进程崩溃等),内存缓存不会(内存缓存没有网络问题)
下面是例子:
需要安装的包:
-
EasyCaching.Redis
-
microsoft.extensions.Caching.StackExchangeRedis
先来介绍一下内存缓存,内存缓存是我们框架自带的。
services.AddMemoryCache();
这样就是就开启了我们的内存缓存。
简答看下AddMemoryCache。
public static IServiceCollection AddMemoryCache(this IServiceCollection services)
{
if (services == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(services));
}
services.AddOptions();
services.TryAdd(ServiceDescriptor.Singleton<IMemoryCache, MemoryCache>());
return services;
}
实际上注册了IMemoryCache,为MemoryCache。这个MemoryCache就不看了,就是一些key value 之类缓存的方法。
那么来看一下services.AddResponseCaching();,启动Response cache 服务。
/// <summary>
/// Add response caching services.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="services">The <see cref="IServiceCollection"/> for adding services.</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static IServiceCollection AddResponseCaching(this IServiceCollection services)
{
if (services == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(services));
}
services.TryAddSingleton<ObjectPoolProvider, DefaultObjectPoolProvider>();
return services;
}
这个是我们请求结果的缓存,那么还得写入中间件。
services.AddResponseCaching();
那么简单看一下AddResponseCaching这个中间件。
public static IApplicationBuilder UseResponseCaching(this IApplicationBuilder app)
{
if (app == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(app));
}
return app.UseMiddleware<ResponseCachingMiddleware>();
}
然后就是看下ResponseCachingMiddleware。
public ResponseCachingMiddleware(
RequestDelegate next,
IOptions<ResponseCachingOptions> options,
ILoggerFactory loggerFactory,
ObjectPoolProvider poolProvider)
: this(
next,
options,
loggerFactory,
new ResponseCachingPolicyProvider(),
new MemoryResponseCache(new MemoryCache(new MemoryCacheOptions
{
SizeLimit = options.Value.SizeLimit
})),
new ResponseCachingKeyProvider(poolProvider, options))
{ }
可以看到其使用的cache,是MemoryCache。好的就点到为止吧,后续的可能会写在细节篇中,可能也不会出现在细节篇中,未在计划内。
好吧,然后测试代码:
public class OrderController : Controller
{
[ResponseCache(Duration = 6000)]
public IActionResult Pay()
{
return Content("买买买:"+DateTime.Now);
}
}
看下效果:
第一次请求的时候:
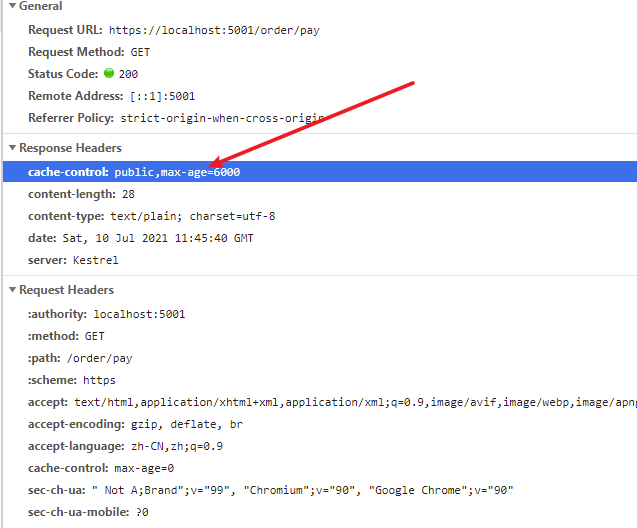
给了这个参数,告诉浏览器,在该段时间内就不要来访问后台了,用缓存就好。
第二次访问:
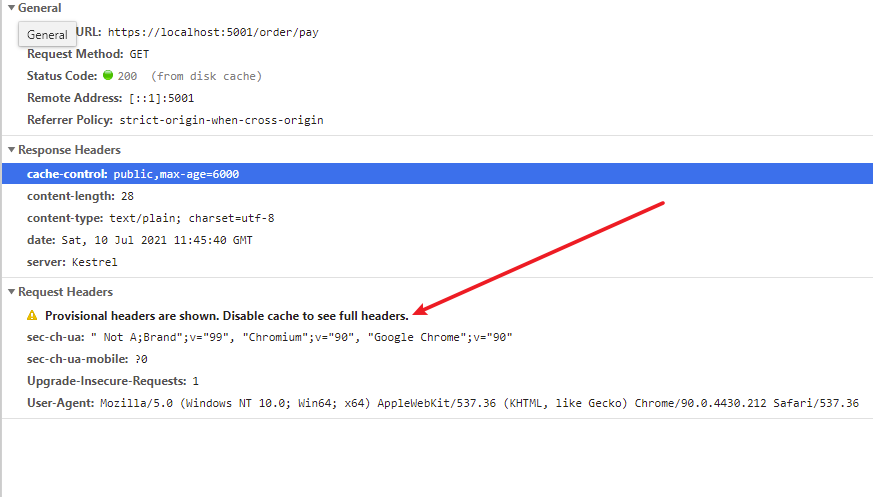
黄色部分的意思该请求没有发出去,用的是缓存。
感觉这样挺好的,那么这个时候就有坑来了。
[ResponseCache(Duration = 6000)]
public IActionResult Pay(string name)
{
return Content("买买买:"+DateTime.Now+name);
}
访问第一次:
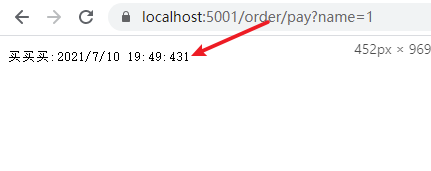
访问第二次:
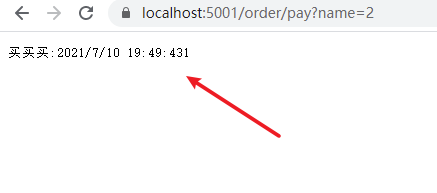
显然第二次是有问题的。
因为name 参数变化了,但是结果相同。
这显然是有问题的,这是客户端缓存吗?不是,浏览器只要是访问链接发生任何变化的时候就会不使用。
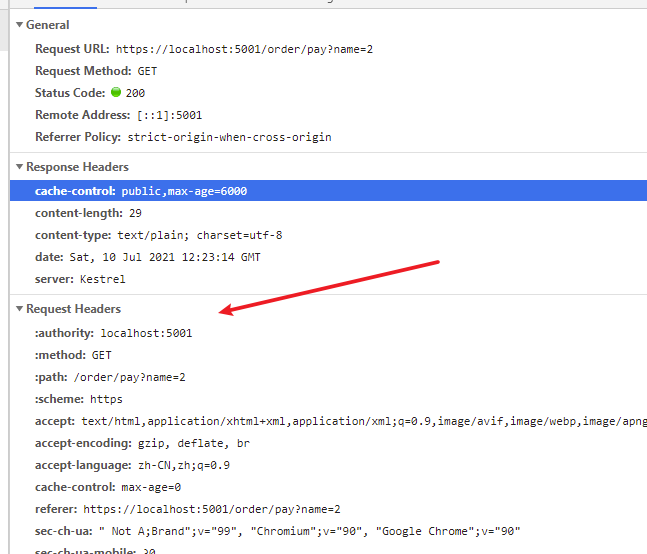
可以看到上面实际上去访问了我们的后台的。
那么应该这样写,表示当name 参数发生变化的时候就不会命中后台的缓存:
public class OrderController : Controller
{
[ResponseCache(Duration = 6000,VaryByQueryKeys =new String[]{ "name"})]
public IActionResult Pay(string name)
{
return Content("买买买:"+DateTime.Now+name);
}
}
为什么这么写呢?这个就要从后台缓存的key开始说起。
看下:ResponseCache 里面的,也就是这个属性类。
public CacheProfile GetCacheProfile(MvcOptions options)
{
CacheProfile selectedProfile = null;
if (CacheProfileName != null)
{
options.CacheProfiles.TryGetValue(CacheProfileName, out selectedProfile);
if (selectedProfile == null)
{
throw new InvalidOperationException(Resources.FormatCacheProfileNotFound(CacheProfileName));
}
}
// If the ResponseCacheAttribute parameters are set,
// then it must override the values from the Cache Profile.
// The below expression first checks if the duration is set by the attribute's parameter.
// If absent, it checks the selected cache profile (Note: There can be no cache profile as well)
// The same is the case for other properties.
_duration = _duration ?? selectedProfile?.Duration;
_noStore = _noStore ?? selectedProfile?.NoStore;
_location = _location ?? selectedProfile?.Location;
VaryByHeader = VaryByHeader ?? selectedProfile?.VaryByHeader;
VaryByQueryKeys = VaryByQueryKeys ?? selectedProfile?.VaryByQueryKeys;
return new CacheProfile
{
Duration = _duration,
Location = _location,
NoStore = _noStore,
VaryByHeader = VaryByHeader,
VaryByQueryKeys = VaryByQueryKeys,
};
}
/// <inheritdoc />
public IFilterMetadata CreateInstance(IServiceProvider serviceProvider)
{
if (serviceProvider == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(serviceProvider));
}
var loggerFactory = serviceProvider.GetRequiredService<ILoggerFactory>();
var optionsAccessor = serviceProvider.GetRequiredService<IOptions<MvcOptions>>();
var cacheProfile = GetCacheProfile(optionsAccessor.Value);
// ResponseCacheFilter cannot take any null values. Hence, if there are any null values,
// the properties convert them to their defaults and are passed on.
return new ResponseCacheFilter(cacheProfile, loggerFactory);
}
可以看到CreateInstance 生成了一个ResponseCacheFilter。
那么来看下这个ResponseCacheFilter:
/// <summary>
/// Creates a new instance of <see cref="ResponseCacheFilter"/>
/// </summary>
/// <param name="cacheProfile">The profile which contains the settings for
/// <see cref="ResponseCacheFilter"/>.</param>
/// <param name="loggerFactory">The <see cref="ILoggerFactory"/>.</param>
public ResponseCacheFilter(CacheProfile cacheProfile, ILoggerFactory loggerFactory)
{
_executor = new ResponseCacheFilterExecutor(cacheProfile);
_logger = loggerFactory.CreateLogger(GetType());
}
/// <inheritdoc />
public void OnActionExecuting(ActionExecutingContext context)
{
if (context == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(context));
}
// If there are more filters which can override the values written by this filter,
// then skip execution of this filter.
var effectivePolicy = context.FindEffectivePolicy<IResponseCacheFilter>();
if (effectivePolicy != null && effectivePolicy != this)
{
_logger.NotMostEffectiveFilter(GetType(), effectivePolicy.GetType(), typeof(IResponseCacheFilter));
return;
}
_executor.Execute(context);
}
那么来看一下ResponseCacheFilterExecutor:
internal class ResponseCacheFilterExecutor
{
private readonly CacheProfile _cacheProfile;
private int? _cacheDuration;
private ResponseCacheLocation? _cacheLocation;
private bool? _cacheNoStore;
private string _cacheVaryByHeader;
private string[] _cacheVaryByQueryKeys;
public ResponseCacheFilterExecutor(CacheProfile cacheProfile)
{
_cacheProfile = cacheProfile ?? throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(cacheProfile));
}
public int Duration
{
get => _cacheDuration ?? _cacheProfile.Duration ?? 0;
set => _cacheDuration = value;
}
public ResponseCacheLocation Location
{
get => _cacheLocation ?? _cacheProfile.Location ?? ResponseCacheLocation.Any;
set => _cacheLocation = value;
}
public bool NoStore
{
get => _cacheNoStore ?? _cacheProfile.NoStore ?? false;
set => _cacheNoStore = value;
}
public string VaryByHeader
{
get => _cacheVaryByHeader ?? _cacheProfile.VaryByHeader;
set => _cacheVaryByHeader = value;
}
public string[] VaryByQueryKeys
{
get => _cacheVaryByQueryKeys ?? _cacheProfile.VaryByQueryKeys;
set => _cacheVaryByQueryKeys = value;
}
public void Execute(FilterContext context)
{
if (context == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(context));
}
if (!NoStore)
{
// Duration MUST be set (either in the cache profile or in this filter) unless NoStore is true.
if (_cacheProfile.Duration == null && _cacheDuration == null)
{
throw new InvalidOperationException(
Resources.FormatResponseCache_SpecifyDuration(nameof(NoStore), nameof(Duration)));
}
}
var headers = context.HttpContext.Response.Headers;
// Clear all headers
headers.Remove(HeaderNames.Vary);
headers.Remove(HeaderNames.CacheControl);
headers.Remove(HeaderNames.Pragma);
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(VaryByHeader))
{
headers[HeaderNames.Vary] = VaryByHeader;
}
if (VaryByQueryKeys != null)
{
var responseCachingFeature = context.HttpContext.Features.Get<IResponseCachingFeature>();
if (responseCachingFeature == null)
{
throw new InvalidOperationException(
Resources.FormatVaryByQueryKeys_Requires_ResponseCachingMiddleware(nameof(VaryByQueryKeys)));
}
responseCachingFeature.VaryByQueryKeys = VaryByQueryKeys;
}
if (NoStore)
{
headers[HeaderNames.CacheControl] = "no-store";
// Cache-control: no-store, no-cache is valid.
if (Location == ResponseCacheLocation.None)
{
headers.AppendCommaSeparatedValues(HeaderNames.CacheControl, "no-cache");
headers[HeaderNames.Pragma] = "no-cache";
}
}
else
{
string cacheControlValue;
switch (Location)
{
case ResponseCacheLocation.Any:
cacheControlValue = "public,";
break;
case ResponseCacheLocation.Client:
cacheControlValue = "private,";
break;
case ResponseCacheLocation.None:
cacheControlValue = "no-cache,";
headers[HeaderNames.Pragma] = "no-cache";
break;
default:
cacheControlValue = null;
break;
}
cacheControlValue = $"{cacheControlValue}max-age={Duration}";
headers[HeaderNames.CacheControl] = cacheControlValue;
}
}
看里面的Execute,这个。
可以看到对于我们的VaryByQueryKeys,其传递给了一个叫做IResponseCachingFeature的子类。
那么什么时候用到了呢?
就在我们中间件的ResponseCachingMiddleware的OnFinalizeCacheHeaders方法中。
/// <summary>
/// Finalize cache headers.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="context"></param>
/// <returns><c>true</c> if a vary by entry needs to be stored in the cache; otherwise <c>false</c>.</returns>
private bool OnFinalizeCacheHeaders(ResponseCachingContext context)
{
if (_policyProvider.IsResponseCacheable(context))
{
var storeVaryByEntry = false;
context.ShouldCacheResponse = true;
// Create the cache entry now
var response = context.HttpContext.Response;
var varyHeaders = new StringValues(response.Headers.GetCommaSeparatedValues(HeaderNames.Vary));
var varyQueryKeys = new StringValues(context.HttpContext.Features.Get<IResponseCachingFeature>()?.VaryByQueryKeys);
context.CachedResponseValidFor = context.ResponseSharedMaxAge ??
context.ResponseMaxAge ??
(context.ResponseExpires - context.ResponseTime.Value) ??
DefaultExpirationTimeSpan;
// Generate a base key if none exist
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(context.BaseKey))
{
context.BaseKey = _keyProvider.CreateBaseKey(context);
}
// Check if any vary rules exist
if (!StringValues.IsNullOrEmpty(varyHeaders) || !StringValues.IsNullOrEmpty(varyQueryKeys))
{
// Normalize order and casing of vary by rules
var normalizedVaryHeaders = GetOrderCasingNormalizedStringValues(varyHeaders);
var normalizedVaryQueryKeys = GetOrderCasingNormalizedStringValues(varyQueryKeys);
// Update vary rules if they are different
if (context.CachedVaryByRules == null ||
!StringValues.Equals(context.CachedVaryByRules.QueryKeys, normalizedVaryQueryKeys) ||
!StringValues.Equals(context.CachedVaryByRules.Headers, normalizedVaryHeaders))
{
context.CachedVaryByRules = new CachedVaryByRules
{
VaryByKeyPrefix = FastGuid.NewGuid().IdString,
Headers = normalizedVaryHeaders,
QueryKeys = normalizedVaryQueryKeys
};
}
// Always overwrite the CachedVaryByRules to update the expiry information
_logger.VaryByRulesUpdated(normalizedVaryHeaders, normalizedVaryQueryKeys);
storeVaryByEntry = true;
context.StorageVaryKey = _keyProvider.CreateStorageVaryByKey(context);
}
// Ensure date header is set
if (!context.ResponseDate.HasValue)
{
context.ResponseDate = context.ResponseTime.Value;
// Setting the date on the raw response headers.
context.HttpContext.Response.Headers[HeaderNames.Date] = HeaderUtilities.FormatDate(context.ResponseDate.Value);
}
// Store the response on the state
context.CachedResponse = new CachedResponse
{
Created = context.ResponseDate.Value,
StatusCode = context.HttpContext.Response.StatusCode,
Headers = new HeaderDictionary()
};
foreach (var header in context.HttpContext.Response.Headers)
{
if (!string.Equals(header.Key, HeaderNames.Age, StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase))
{
context.CachedResponse.Headers[header.Key] = header.Value;
}
}
return storeVaryByEntry;
}
context.ResponseCachingStream.DisableBuffering();
return false;
}
重点关注一下context.StorageVaryKey 是如何生成的,StorageVaryKey就是缓存的key。
if (context.CachedVaryByRules == null ||
!StringValues.Equals(context.CachedVaryByRules.QueryKeys, normalizedVaryQueryKeys) ||
!StringValues.Equals(context.CachedVaryByRules.Headers, normalizedVaryHeaders))
{
context.CachedVaryByRules = new CachedVaryByRules
{
VaryByKeyPrefix = FastGuid.NewGuid().IdString,
Headers = normalizedVaryHeaders,
QueryKeys = normalizedVaryQueryKeys
};
}
context.StorageVaryKey = _keyProvider.CreateStorageVaryByKey(context);
那么可以看下CreateStorageVaryByKey:
// BaseKey<delimiter>H<delimiter>HeaderName=HeaderValue<delimiter>Q<delimiter>QueryName=QueryValue1<subdelimiter>QueryValue2
public string CreateStorageVaryByKey(ResponseCachingContext context)
{
if (context == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(context));
}
var varyByRules = context.CachedVaryByRules;
if (varyByRules == null)
{
throw new InvalidOperationException($"{nameof(CachedVaryByRules)} must not be null on the {nameof(ResponseCachingContext)}");
}
if (StringValues.IsNullOrEmpty(varyByRules.Headers) && StringValues.IsNullOrEmpty(varyByRules.QueryKeys))
{
return varyByRules.VaryByKeyPrefix;
}
var request = context.HttpContext.Request;
var builder = _builderPool.Get();
try
{
// Prepend with the Guid of the CachedVaryByRules
builder.Append(varyByRules.VaryByKeyPrefix);
// Vary by headers
var headersCount = varyByRules?.Headers.Count ?? 0;
if (headersCount > 0)
{
// Append a group separator for the header segment of the cache key
builder.Append(KeyDelimiter)
.Append('H');
var requestHeaders = context.HttpContext.Request.Headers;
for (var i = 0; i < headersCount; i++)
{
var header = varyByRules.Headers[i];
var headerValues = requestHeaders[header];
builder.Append(KeyDelimiter)
.Append(header)
.Append('=');
var headerValuesArray = headerValues.ToArray();
Array.Sort(headerValuesArray, StringComparer.Ordinal);
for (var j = 0; j < headerValuesArray.Length; j++)
{
builder.Append(headerValuesArray[j]);
}
}
}
// Vary by query keys
if (varyByRules?.QueryKeys.Count > 0)
{
// Append a group separator for the query key segment of the cache key
builder.Append(KeyDelimiter)
.Append('Q');
if (varyByRules.QueryKeys.Count == 1 && string.Equals(varyByRules.QueryKeys[0], "*", StringComparison.Ordinal))
{
// Vary by all available query keys
var queryArray = context.HttpContext.Request.Query.ToArray();
// Query keys are aggregated case-insensitively whereas the query values are compared ordinally.
Array.Sort(queryArray, QueryKeyComparer.OrdinalIgnoreCase);
for (var i = 0; i < queryArray.Length; i++)
{
builder.Append(KeyDelimiter)
.AppendUpperInvariant(queryArray[i].Key)
.Append('=');
var queryValueArray = queryArray[i].Value.ToArray();
Array.Sort(queryValueArray, StringComparer.Ordinal);
for (var j = 0; j < queryValueArray.Length; j++)
{
if (j > 0)
{
builder.Append(KeySubDelimiter);
}
builder.Append(queryValueArray[j]);
}
}
}
else
{
for (var i = 0; i < varyByRules.QueryKeys.Count; i++)
{
var queryKey = varyByRules.QueryKeys[i];
var queryKeyValues = context.HttpContext.Request.Query[queryKey];
builder.Append(KeyDelimiter)
.Append(queryKey)
.Append('=');
var queryValueArray = queryKeyValues.ToArray();
Array.Sort(queryValueArray, StringComparer.Ordinal);
for (var j = 0; j < queryValueArray.Length; j++)
{
if (j > 0)
{
builder.Append(KeySubDelimiter);
}
builder.Append(queryValueArray[j]);
}
}
}
}
return builder.ToString();
}
finally
{
_builderPool.Return(builder);
}
}
可以看到如果缓存的key值和我们的VaryByQueryKeys的设置息息相关,只要我们的VaryByQueryKeys设置的key的value发生任何变化,也就是我们的参数的值发生变化,那么生成的缓存key绝对不同,那么就不会命中。
下面就简单介绍一下redis的缓存。
services.AddStackExchangeRedisCache(options =>
{
Configuration.GetSection("redisCache").Bind(options);
});
这样就是redis的缓存。
然后第三方就是easycache 就是:
services.AddEasyCaching(options =>
{
options.UseRedis(Configuration,name:"easycaching");
});
这些都可以直接去看文档,这里觉得没什么要整理的。
结
下一节 apollo 配置中心。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号